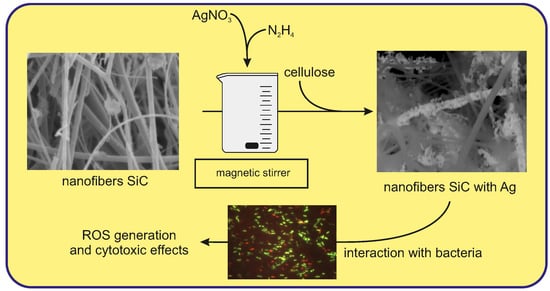
Synthesis of SiC/Ag/Cellulose Nanocomposite and Its Antibacterial Activity by Reactive Oxygen Species Generation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Nanocomposite Characterization
2.2. Respirometric Analysis
2.3. Catalase and Dehydrogenase Activities
2.4. Viability Test
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Synthesis of SiC Nanofibers
3.2. Synthesis of SiC/CE Nanocomposites
3.3. Synthesis of SiC/Ag/CE Nanocomposites
3.4. Synthesis of AgNPs
3.5. Composites Properties
3.6. Microorganisms and Media
3.7. Measurement of CO2 in Cultures with Nanocomposites
3.8. Measurement of Dehydrogenases Activity
3.9. Catalase Activity
3.10. Viability Test
3.11. Protein Measurements
3.12. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaiswal, S.; Duffy, B.; Jaiswal, A.K.; Stobie, N.; McHale, P. Enhancement of the antibacterial properties of silver nanoparticles using β-cyclodextrin as a capping agent. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2010, 36, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Abdolahad, M.; Abdi, Y.; Mohajerzadeh, S. Silver nanoparticles within vertically aligned multi-wall carbon nanotubes with open tips for antibacterial purposes. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, R.; Jin, Y.; Tong, M.; Kim, H. Bactericidal activity of Ag-doped multi-walled carbon nanotubes and the effects of extracellular polymeric substances and natural organic matter. Colloids Surf. B 2013, 104, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhuri, A.R.; Tripathy, S.; Chandra, S.; Roy, S.; Sahu, S.K. A ZnO decorated chitosan–graphene oxide nanocomposite shows significantly enhanced antimicrobial activity with ROS generation. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 49420–49428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huczko, A.; Bystrzejewski, M.; Lange, H.; Fabianowska, A.; Cudziło, S.; Panas, A.; Szala, M. Combustion synthesis as a novel method for production of 1-D SiC nanostructures. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2005, 109, 16244–16251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cudziło, S.; Szala, M.; Huczko, A.; Bystrzejewski, M. Combustion reactions of poly (carbon monofluoride), (CF)n with different reductants and characterization of products. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2007, 32, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barillet, S.; Simon-Deckers, A.; Herlin-Boime, N.; Mayne-L’Hermite, M.; Reynaud, C.; Cassio, D.; Gouget, B.; Carrière, M. Toxicological consequences of TiO2, SiC nanoparticles and multi-walled carbon nanotubes exposure in several mammalian cell types: An in vitro study. J. Nanopart. Res. 2010, 12, 61–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourchez, J.; Forest, V.; Boumahdi, N.; Boudard, D.; Tomatis, M.; Fubini, B.; Herlin-Boime, N.; Leconte, Y.; Guilhot, B.; Cottier, M.; et al. In vitro cellular responses to silicon carbide nanoparticles: impact of physic-chemical features on pro-inflamatory and pro-oxidative effects. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14, 1143–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Szala, M.; Borkowski, A. Toxicity assessment of SiC nanofibers and nanorods against bacteria. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2014, 100, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkowski, A.; Szala, M.; Kowalczyk, P.; Cłapa, T.; Narożna, D.; Selwet, M. Oxidative stress in bacteria (Pseudomonas putida) exposed to nanostructures of silicon carbide. Chemosphere 2015, 135, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Pinault, M.; Pfefferle, L.D.; Elimelech, M.M. Single-walled carbon nanotubes exhibit strong antimicrobial activity. Langmuir 2004, 23, 8670–8673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Toxicity of graphene and graphene oxide nanowalls against bacteria. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sondi, I.; Salopek-Sondi, B. Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: A case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2004, 275, 177–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panáček, A.; Kvítek, L.; Prucek, R.; Kolář, M.; Večeřová, R.; Pizúrová, N.; Sharma, V.K.; Nevěčná, T.; Zbořil, R. Silver Colloid Nanoparticles: Synthesis, Characterization, and Their Antibacterial Activity. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 16248–16253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.S.; Kuk, E.; Yu, K.N.; Kim, J.-H.; Park, S.J.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.K.; Park, Y.H.; Hwang, C.-Y.; et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, V.K.; Yngard, R.A.; Lin, Y. Silver nanoparticles: Green synthesis and their antimicrobial activities. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 145, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petrus, E.M.; Tinakumari, S.; Chai, L.C.; Ubong, A.; Tunung, R.; Elexson, N.; Chai, L.F.; Son, R. A study on the minimum inhibitory concentration and minimum bactericidal concentration of Nano Colloidal Silver on food-borne pathogen. Int. Food. Res. J. 2011, 18, 55–66. [Google Scholar]
- Kittler, S.; Greulich, C.; Diendorf, J.; Köller, M.; Epple, M. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles increases during storage because of slow dissolution under release of silver ions. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4548–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruk, T.; Szczepanowicz, K.; Stefańska, J.; Socha, R.P.; Warszyński, P. Synthesis and antimicrobial activity of monodisperse copper nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B 2015, 128, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Azeredo, H.M.C. Nanocomposites for food packaging applications. Food Res. Int. 2009, 42, 1240–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Moura, M.R.; Mattoso, L.H.C.; Zucolotto, V. Development of cellulose-based bactericidal nanocomposites containing silver nanoparticles and their use as active food packaging. J. Food Eng. 2012, 109, 520–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dallas, P.; Sharma, V.K.; Zboril, R. Silver polymeric nanocomposites as advanced antimicrobial agents: Classification, synthetic paths, applications, and perspectives. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 166, 119–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maneerung, T.; Tokura, S.; Rujiravanit, R. Impregnation of silver nanoparticles into bacterial cellulose for antimicrobial wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2008, 72, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamoorthy, K.; Manivannan, G.; Kim, S.J.; Jeyasubramanian, K.; Premanathan, M. Antibacterial activity of MgO nanoparticles based on lipid peroxidation by oxygen vacancy. J. Nanopart. Res. 2012, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayes, C.M.; Gobin, A.M.; Ausman, K.D.; Mendez, J.; West, J.L.; Colvin, V.L. Nano-C60 cytotoxicity is due to lipid peroxidation. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 7587–7595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Premanathan, M.; Karthikeyan, K.; Jeyasubramanian, K.; Manivannan, G. Selective toxicity of ZnO nanoparticles toward Gram-positive bacteria and cancer cells by apoptosis through lipid peroxidation. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2011, 7, 184–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berridge, M.V.; Herst, P.M.; Tan, A.S. Tetrazolium dyes as tools in cell biology: New insights into their cellular reduction. Biotechnol. Annu. Rev. 2005, 11, 127–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, T.H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: Membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.; Herzberg, M.; Rodrigues, D.F.; Elimelech, M. Antibacterial effects of carbon nanotubes: Size does matter! Langmuir 2008, 24, 6409–6413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borkowski, A.; Owczarek, F.; Szala, M.; Selwet, M. Interaction of Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria with ceramic nanomaterials obtained by combustion synthesis—Adsorption and cytotoxicity studies. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarafdar, J.C. 2,3,5-triphenyltetrazolium chloride (TTC) as electron acceptor of culturable soil bacteria, fungi and actinomycetes. Biol. Fertil. Soils 2003, 38, 186–189. [Google Scholar]
- Luck, H. Catalase. In Methods of Enzymatic Analysis; Bergmeyer, H.U., Ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1963; Section 3; pp. 885–894. [Google Scholar]
- Borkowski, A.; Szala, M.; Cłapa, T. Adsorption studies of the Gram-negative bacteria onto nanostructured silicon carbide. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2015, 175, 1448–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










© 2016 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC-BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Borkowski, A.; Cłapa, T.; Szala, M.; Gąsiński, A.; Selwet, M. Synthesis of SiC/Ag/Cellulose Nanocomposite and Its Antibacterial Activity by Reactive Oxygen Species Generation. Nanomaterials 2016, 6, 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6090171
Borkowski A, Cłapa T, Szala M, Gąsiński A, Selwet M. Synthesis of SiC/Ag/Cellulose Nanocomposite and Its Antibacterial Activity by Reactive Oxygen Species Generation. Nanomaterials. 2016; 6(9):171. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6090171
Chicago/Turabian StyleBorkowski, Andrzej, Tomasz Cłapa, Mateusz Szala, Arkadiusz Gąsiński, and Marek Selwet. 2016. "Synthesis of SiC/Ag/Cellulose Nanocomposite and Its Antibacterial Activity by Reactive Oxygen Species Generation" Nanomaterials 6, no. 9: 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6090171
APA StyleBorkowski, A., Cłapa, T., Szala, M., Gąsiński, A., & Selwet, M. (2016). Synthesis of SiC/Ag/Cellulose Nanocomposite and Its Antibacterial Activity by Reactive Oxygen Species Generation. Nanomaterials, 6(9), 171. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano6090171