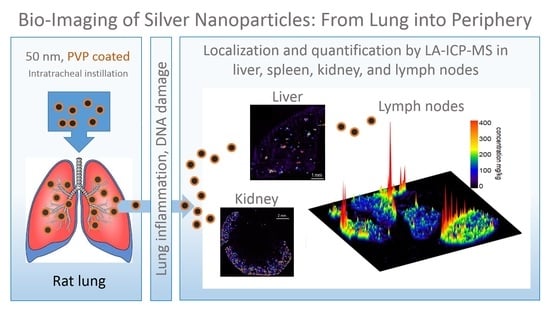
Silver Nanoparticles in the Lung: Toxic Effects and Focal Accumulation of Silver in Remote Organs
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Dose-Finding Studies with Silver Nanoparticles
In Vitro Experiments
2.2. In Vivo Experiments
2.3. Lung Toxicity of Ag50-PVP Nanoparticles
2.3.1. Analyses of the Broncho-Alveolar Lavage Fluid
2.3.2. γH2AX Immunocytochemistry and Cell Proliferation
2.4. Peripheral Localization of Ag50-PVP
2.4.1. General Organ Distribution of Silver
2.4.2. Laser Ablation Inductively-Coupled Mass Spectrometry of Liver Sections
2.4.3. Laser-Ablation Inductively-Coupled Mass Spectrometry of Spleen Sections
2.4.4. Laser-Ablation Inductively-Coupled Mass Spectrometry of Kidney Sections
2.4.5. Laser-Ablation Inductively-Coupled Mass Spectrometry of Mediastinal Lymph Node Sections
2.4.6. Detection of Ag-NP with Enhanced Dark Field Microscopy
2.4.7. Autometallographic Detection of Silver
3. Discussion
3.1. Discrepancy between In Vitro and In Vivo Testing
3.2. Toxic Effects of Ag50-PVP In Vivo and Selection of Appropriate Doses for Bio-Imaging Experiments
3.3. Silver Distribution in the Body upon Instillation of Ag50-PVP into the Lung
3.3.1. General Aspects
3.3.2. Organ Distribution of Silver
3.3.3. Estimation of the Silver Burden in Single Cells
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Particle Characterization
4.2. In Vitro Experiments
4.3. Preparation of Particle Suspension for Instillation Experiments in Rats
4.4. Animal Experiments and Organ Preparation
4.5. BALF Analysis
4.6. Immunocytochemistry, Fluorescence Microscopy and Hyperspectral Imaging
4.7. Quantitative Bio-Imaging of 107Ag with LA-ICP-MS
4.7.1. Chemicals
4.7.2. Matrix-Matched Standards and Standard Curve Generation
4.7.3. LA-ICP-MS Analysis of Tissue Sections
4.8. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Estimation of the Ag Content of a Single Cell under Ideal Conditions
- It is assumed that each signal is retrieved from a tissue volume of 17,500 µm3 (50 × 50 × 7 µm3); within this volume, there is only one Ag-containing cell sectioned, and no dissolved or particular Ag contributes to the background.
- It is further assumed that the calibration from AgNO3 concentration (Ag mass per mass tissue) is valid and the concentrations determined with the matrix-matched standard method for 7 µm-thick sections are correct.
- It is further assumed that the loss of section mass upon drying is of no relevance for the calibration, because these conditions are equally valid also for the sectioned matrix-matched standard material.
- Then, a typical Ag signal measured in the lymph node’s medulla (see Figure 8c) is = 200 µg/g.
- Assuming a density of 1 g/mL, the mass of the ablated area per laser shot (before drying) is: 50 µm × 50 µm × 7 µm/thickness = 17,500 µm3 = 17.5 ng.
- For the measured peak value of 200 µg Ag/g, the Ag mass contained in the ablated mass is calculated as: 200 µg/1,000,000 µg = X/0.0175 µg. Thus, X = 0.0000035 µg = 3.5 pg.
- Given that a cell has a thickness of 14 µm (typical for, e.g., a macrophage), the above value doubles to 7 pg for a single sectioned DFM-positive cell.
- According to this calculation, the peak value found in an LN (4000 µg/g (see Figure 8c) would correspond to a cell burden of 140 pg.
References
- Reidy, B.; Haase, A.; Luch, A.; Dawson, K.; Lynch, I. Mechanisms of Silver Nanoparticle Release, Transformation and Toxicity: A Critical Review of Current Knowledge and Recommendations for Future Studies and Applications. Materials 2013, 6, 2295–2350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weldon, B.A.; M Faustman, E.; Oberdörster, G.; Workman, T.; Griffith, W.C.; Kneuer, C.; Yu, I.J. Occupational exposure limit for silver nanoparticles: Considerations on the derivation of a general health-based value. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 945–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wijnhoven, S.W.P.; Peijnenburg, W.J.G.M.; Herberts, C.A.; Hagens, W.I.; Oomen, A.G.; Heugens, E.H.W.; Roszek, B.; Bisschops, J.; Gosens, I.; Van De Meent, D.; et al. Nano-silver—A review of available data and knowledge gaps in human and environmental risk assessment. Nanotoxicology 2009, 3, 109–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stensberg, M.C.; Wei, Q.; McLamore, E.S.; Porterfield, D.M.; Wei, A.; Sepúlveda, M.S. Toxicological studies on silver nanoparticles: Challenges and opportunities in assessment, monitoring and imaging. Nanomedicine 2011, 6, 879–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lankveld, D.P.K.; Oomen, A.G.; Krystek, P.; Neigh, A.; Troost-de Jong, A.; Noorlander, C.W.; Van Eijkeren, J.C.H.; Geertsma, R.E.; De Jong, W.H. The kinetics of the tissue distribution of silver nanoparticles of different sizes. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8350–8361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, M.F.; Wang, J.; Patterson, T.A.; Saini, U.T.; Robinson, B.L.; Newport, G.D.; Murdock, R.C.; Schlager, J.J.; Hussain, S.M.; Ali, S.F. Expression of genes related to oxidative stress in the mouse brain after exposure to silver-25 nanoparticles. Toxicol. Lett. 2009, 187, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fewtrell, L.; Majuru, B.; Hunter, P.R. A re-assessment of the safety of silver in household water treatment: Rapid systematic review of mammalian in vivo genotoxicity studies. Environ. Health Glob. Access Sci. Source 2017, 16, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.-S.; Duffin, R.; Thielbeer, F.; Bradley, M.; Megson, I.L.; MacNee, W.; Poland, C.A.; Tran, C.L.; Donaldson, K. Zeta Potential and Solubility to Toxic Ions as Mechanisms of Lung Inflammation Caused by Metal/Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Toxicol. Sci. 2012, 126, 469–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seiffert, J.; Buckley, A.; Leo, B.; Martin, N.G.; Zhu, J.; Dai, R.; Hussain, F.; Guo, C.; Warren, J.; Hodgson, A.; et al. Pulmonary effects of inhalation of spark-generated silver nanoparticles in Brown-Norway and Sprague-Dawley rats. Respir. Res. 2016, 17, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sung, J.H.; Ji, J.H.; Park, J.D.; Yoon, J.U.; Kim, D.S.; Jeon, K.S.; Song, M.Y.; Jeong, J.; Han, B.S.; Han, J.H.; et al. Subchronic inhalation toxicity of silver nanoparticles. Toxicol. Sci. 2009, 108, 452–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, H.; Zhang, J.; Boudreau, M.; Meng, J.; Yin, J.; Liu, J.; Xu, H. Intravenous administration of silver nanoparticles causes organ toxicity through intracellular ROS-related loss of inter-endothelial junction. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2016, 13, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glover, R.D.; Miller, J.M.; Hutchison, J.E. Generation of metal nanoparticles from silver and copper objects: Nanoparticle dynamics on surfaces and potential sources of nanoparticles in the environment. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 8950–8957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, Z.; Liu, F.D.; Kane, A.B.; Hurt, R.H. Chemical transformations of nanosilver in biological environments. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 9887–9899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Kuang, H.; Zhang, W.; Aguilar, Z.P.; Wei, H.; Xu, H. Comparisons of the biodistribution and toxicological examinations after repeated intravenous administration of silver and gold nanoparticles in mice. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 3303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Yao, Y.; Sullivan, N.; Chen, Y. Modeling the primary size effects of citrate-coated silver nanoparticles on their ion release kinetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 4422–4428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, D.L.; Yu, I.J.; Genter, M.B. Use of Autometallography in Studies of Nanosilver Distribution and Toxicity. Int. J. Toxicol. 2016, 35, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loeschner, K.; Hadrup, N.; Qvortrup, K.; Larsen, A.; Gao, X.; Vogel, U.; Mortensen, A.; Lam, H.R.; Larsen, E.H. Distribution of silver in rats following 28 days of repeated oral exposure to silver nanoparticles or silver acetate. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Su, C.-K.; Liu, H.-T.; Hsia, S.-C.; Sun, Y.-C. Quantitatively profiling the dissolution and redistribution of silver nanoparticles in living rats using a knotted reactor-based differentiation scheme. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 8267–8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, J.; Li, F.; Zhou, H.; Bai, Y.; Liu, S.; Jiang, Y.; Jiang, G.; Yan, B. Oral Exposure to Silver Nanoparticles or Silver Ions May Aggravate Fatty Liver Disease in Overweight Mice. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2017, 51, 9334–9343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kittler, S.; Greulich, C.; Diendorf, J.; Köller, M.; Epple, M. Toxicity of Silver Nanoparticles Increases during Storage Because of Slow Dissolution under Release of Silver Ions. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4548–4554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gliga, A.R.; Skoglund, S.; Wallinder, I.O.; Fadeel, B.; Karlsson, H.L. Size-dependent cytotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in human lung cells: The role of cellular uptake, agglomeration and Ag release. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hsiao, I.-L.; Hsieh, Y.-K.; Wang, C.-F.; Chen, I.-C.; Huang, Y.-J. Trojan-horse mechanism in the cellular uptake of silver nanoparticles verified by direct intra- and extracellular silver speciation analysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 3813–3821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.; Choi, J.E.; Choi, J.; Chung, K.-H.; Park, K.; Yi, J.; Ryu, D.-Y. Oxidative stress-dependent toxicity of silver nanoparticles in human hepatoma cells. Toxicol. In Vitro 2009, 23, 1076–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pratsinis, A.; Hervella, P.; Leroux, J.-C.; Pratsinis, S.E.; Sotiriou, G.A. Toxicity of silver nanoparticles in macrophages. Small Weinh. Bergstr. Ger. 2013, 9, 2576–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drescher, D.; Giesen, C.; Traub, H.; Panne, U.; Kneipp, J.; Jakubowski, N. Quantitative imaging of gold and silver nanoparticles in single eukaryotic cells by laser ablation ICP-MS. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 9684–9688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaske, F.; Reifschneider, O.; Gosheger, G.; Wehe, C.A.; Sperling, M.; Karst, U.; Hauschild, G.; Höll, S. Elemental bioimaging of nanosilver-coated prostheses using X-ray fluorescence spectroscopy and laser ablation-inductively coupled plasma-mass spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2014, 86, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alessandrini, F.; Vennemann, A.; Gschwendtner, S.; Neumann, A.; Rothballer, M.; Seher, T.; Wimmer, M.; Kublik, S.; Traidl-Hoffmann, C.; Schloter, M.; et al. Pro-Inflammatory versus Immunomodulatory Effects of Silver Nanoparticles in the Lung: The Critical Role of Dose, Size and Surface Modification. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valdiglesias, V.; Giunta, S.; Fenech, M.; Neri, M.; Bonassi, S. γH2AX as a marker of DNA double strand breaks and genomic instability in human population studies. Mutat. Res. 2013, 753, 24–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, R.J.B.; Rivera, Z.H.; van Bemmel, G.; Marvin, H.J.P.; Weigel, S.; Bouwmeester, H. Development and validation of single particle ICP-MS for sizing and quantitative determination of nano-silver in chicken meat. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 3875–3885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiemann, M.; Vennemann, A.; Sauer, U.G.; Wiench, K.; Ma-Hock, L.; Landsiedel, R. An in vitro alveolar macrophage assay for predicting the short-term inhalation toxicity of nanomaterials. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panas, A.; Marquardt, C.; Nalcaci, O.; Bockhorn, H.; Baumann, W.; Paur, H.-R.; Mülhopt, S.; Diabaté, S.; Weiss, C. Screening of different metal oxide nanoparticles reveals selective toxicity and inflammatory potential of silica nanoparticles in lung epithelial cells and macrophages. Nanotoxicology 2012, 7, 259–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vennemann, A.; Alessandrini, F.; Wiemann, M. Differential Effects of Surface-Functionalized Zirconium Oxide Nanoparticles on Alveolar Macrophages, Rat Lung, and a Mouse Allergy Model. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kroll, A.; Dierker, C.; Rommel, C.; Hahn, D.; Wohlleben, W.; Schulze-Isfort, C.; Göbbert, C.; Voetz, M.; Hardinghaus, F.; Schnekenburger, J. Cytotoxicity screening of 23 engineered nanomaterials using a test matrix of ten cell lines and three different assays. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2011, 8, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, K.M.; Gokulan, K.; Cerniglia, C.E.; Khare, S. Size and dose dependent effects of silver nanoparticle exposure on intestinal permeability in an in vitro model of the human gut epithelium. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 14, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Takabayashi, F.; Ibuki, Y. Coexposure to silver nanoparticles and ultraviolet A synergistically enhances the phosphorylation of histone H2AX. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2016, 162, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.E.; Kim, S.; Ahn, J.H.; Youn, P.; Kang, J.S.; Park, K.; Yi, J.; Ryu, D.-Y. Induction of oxidative stress and apoptosis by silver nanoparticles in the liver of adult zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2010, 100, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahamed, M.; Karns, M.; Goodson, M.; Rowe, J.; Hussain, S.M.; Schlager, J.J.; Hong, Y. DNA damage response to different surface chemistry of silver nanoparticles in mammalian cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2008, 233, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nymark, P.; Catalán, J.; Suhonen, S.; Järventaus, H.; Birkedal, R.; Clausen, P.A.; Jensen, K.A.; Vippola, M.; Savolainen, K.; Norppa, H. Genotoxicity of polyvinylpyrrolidone-coated silver nanoparticles in BEAS 2B cells. Toxicology 2013, 313, 38–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karlsson, H.L.; Gliga, A.R.; Calléja, F.M.G.R.; Gonçalves, C.S.A.G.; Wallinder, I.O.; Vrieling, H.; Fadeel, B.; Hendriks, G. Mechanism-based genotoxicity screening of metal oxide nanoparticles using the ToxTracker panel of reporter cell lines. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2014, 11, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyoda, T.; Akagi, J.-I.; Cho, Y.-M.; Mizuta, Y.; Onami, S.; Suzuki, I.; Ogawa, K. Detection of γ-H2AX, a Biomarker for DNA Double-strand Breaks, in Urinary Bladders of N-Butyl-N-(4-Hydroxybutyl)-Nitrosamine-Treated Rats. J. Toxicol. Pathol. 2013, 26, 215–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rittinghausen, S.; Bellmann, B.; Creutzenberg, O.; Ernst, H.; Kolling, A.; Mangelsdorf, I.; Kellner, R.; Beneke, S.; Ziemann, C. Evaluation of immunohistochemical markers to detect the genotoxic mode of action of fine and ultrafine dusts in rat lungs. Toxicology 2013, 303, 177–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asare, N.; Duale, N.; Slagsvold, H.H.; Lindeman, B.; Olsen, A.K.; Gromadzka-Ostrowska, J.; Meczynska-Wielgosz, S.; Kruszewski, M.; Brunborg, G.; Instanes, C. Genotoxicity and gene expression modulation of silver and titanium dioxide nanoparticles in mice. Nanotoxicology 2016, 10, 312–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.; Dan, M.; Yang, Y.; Lyu, J.; Shao, A.; Cheng, X.; Chen, L.; Xu, L. Acute toxicity and genotoxicity of silver nanoparticle in rats. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0185554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarhan, O.M.M.; Hussein, R.M. Effects of intraperitoneally injected silver nanoparticles on histological structures and blood parameters in the albino rat. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 1505–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Recordati, C.; De Maglie, M.; Bianchessi, S.; Argentiere, S.; Cella, C.; Mattiello, S.; Cubadda, F.; Aureli, F.; D’Amato, M.; Raggi, A.; et al. Tissue distribution and acute toxicity of silver after single intravenous administration in mice: Nano-specific and size-dependent effects. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2015, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Jong, W.H.; Van Der Ven, L.T.M.; Sleijffers, A.; Park, M.V.D.Z.; Jansen, E.H.J.M.; Van Loveren, H.; Vandebriel, R.J. Systemic and immunotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in an intravenous 28 days repeated dose toxicity study in rats. Biomaterials 2013, 34, 8333–8343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leclerc, S.; Wilkinson, K.J. Bioaccumulation of Nanosilver by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii-nanoparticle or the free ion? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 358–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McRae, R.; Bagchi, P.; Sumalekshmy, S.; Fahrni, C.J. In Situ Imaging of Metals in Cells and Tissues. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 4780–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Plüddemann, A. Tissue macrophages: Heterogeneity and functions. BMC Biol. 2017, 15, 53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.; Ashitate, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.H.; Matsui, A.; Insin, N.; Bawendi, M.G.; Semmler-Behnke, M.; Frangioni, J.V.; Tsuda, A. Rapid translocation of nanoparticles from the lung airspaces to the body. Nat. Biotechnol. 2010, 28, 1300–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Den Haan, J.M.M.; Martinez-Pomares, L. Macrophage heterogeneity in lymphoid tissues. Semin. Immunopathol. 2013, 35, 541–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harmsen, A.G.; Muggenburg, B.A.; Snipes, M.B.; Bice, D.E. The role of macrophages in particle translocation from lungs to lymph nodes. Science 1985, 230, 1277–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pauluhn, J. Subchronic 13-week inhalation exposure of rats to multiwalled carbon nanotubes: Toxic effects are determined by density of agglomerate structures, not fibrillar structures. Toxicol. Sci. 2010, 113, 226–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tojo, A.; Kinugasa, S. Mechanisms of glomerular albumin filtration and tubular reabsorption. Int. J. Nephrol. 2012, 2012, 481520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sardari, R.R.R.; Zarchi, S.R.; Talebi, A.; Nasri, S.; Imani, S.; Khoradmehr, A.; Sheshde, S.A.R. Toxicological effects of silver nanoparticles in rats. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2012, 6, 5587–5593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izak-Nau, E.; Voetz, M. As produced: Intrinsic physico-chemical properties and appropriate characterization tools. In Safety of Nanomaterials along Their Lifecycle. Release, Exposure and Human Hazards; Wohlleben, W., Kuhlbusch, T.A.J., Schnekenburger, J., Lehr, C.-M., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA; London, UK; Taylor & Francis Group: New York, NY, USA, 2015; pp. 3–24. ISBN 978-1-4665-6786-3. [Google Scholar]
- Hellack, B.; Hülser, T.; Izak, E.; Kuhlbusch, T.A.J.; Meyer, F.; Spree, M.; Voetz, M.; Wiggers, H.; Wohlleben, W. Deliverable 1.3.1 Charakterisierungsbericht zu Allen Materialien/Characterization Report for All nanoGEM Materials. Available online: http://www.nanogem.de/cms/nanogem/upload/Veroeffentlichungen/nanoGEM_Del1.3.1_Characterization_Materials_2013_04_24.pdf (accessed on 25 October 2017).
- Wang, X.; Ji, Z.; Chang, C.H.; Zhang, H.; Wang, M.; Liao, Y.-P.; Lin, S.; Meng, H.; Li, R.; Sun, B.; et al. Use of Coated Silver Nanoparticles to Understand the Relationship of Particle Dissolution and Bioavailability to Cell and Lung Toxicological Potential. Small 2014, 10, 385–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.M.; Anderson, D.S.; Franzi, L.M.; Peake, J.L.; Edwards, P.C.; Van Winkle, L.S.; Pinkerton, K.E. Pulmonary Effects of Silver Nanoparticle Size, Coating, and Dose over Time upon Intratracheal Instillation. Toxicol. Sci. 2015, 144, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rehn, B.; Seiler, F.; Rehn, S.; Bruch, J.; Maier, M. Investigations on the inflammatory and genotoxic lung effects of two types of titanium dioxide: Untreated and surface treated. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 189, 84–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danscher, G. Autometallography. A new technique for light and electron microscopic visualization of metals in biological tissues (gold, silver, metal sulphides and metal selenides). Histochemistry 1984, 81, 331–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]












| Particle size (nm) | Ag50-PVP (F12-K, Serum-Free) | Ag50-PVP (DMEM/FCS) | Ag200-PVP (F12-K, Serum-Free) | Ag200-PVP (DMEM/FCS) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean 1 | 107.5 ± 0.8 | 105.6 ± 1.3 | 175.9 ± 0.7 | 167.2 ± 0.9 |
| Mode 1 | 96.5 ± 5.0 | 100.9 ± 2.6 | 135.4 ± 18.6 | 154.3 ± 4.9 |
| Ag Concentration Measured by ICP-MS (mg/kg) | Intensity Measured by LA-ICP-MS (Counts per Second) |
|---|---|
| 6.1 × 10−3 | 661 |
| 12.5 × 10−3 | 883 |
| 93.5 × 10−3 | 1300 |
| 25.4 × 10−2 | 2610 |
| 42.9 × 10−2 | 2950 |
| 89.5 × 10−2 | 5950 |
| 18.70 | 130 × 103 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wiemann, M.; Vennemann, A.; Blaske, F.; Sperling, M.; Karst, U. Silver Nanoparticles in the Lung: Toxic Effects and Focal Accumulation of Silver in Remote Organs. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120441
Wiemann M, Vennemann A, Blaske F, Sperling M, Karst U. Silver Nanoparticles in the Lung: Toxic Effects and Focal Accumulation of Silver in Remote Organs. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(12):441. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120441
Chicago/Turabian StyleWiemann, Martin, Antje Vennemann, Franziska Blaske, Michael Sperling, and Uwe Karst. 2017. "Silver Nanoparticles in the Lung: Toxic Effects and Focal Accumulation of Silver in Remote Organs" Nanomaterials 7, no. 12: 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120441
APA StyleWiemann, M., Vennemann, A., Blaske, F., Sperling, M., & Karst, U. (2017). Silver Nanoparticles in the Lung: Toxic Effects and Focal Accumulation of Silver in Remote Organs. Nanomaterials, 7(12), 441. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120441