From Ion Current to Electroosmotic Flow Rectification in Asymmetric Nanopore Membranes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Preparation of Asymmetric Nanopore Membranes
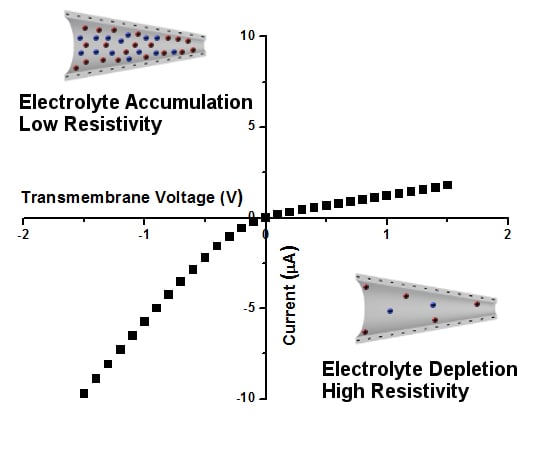
3. Ion Current Rectification in Asymmetric Pores
4. Electroosmotic Flow Rectification in Asymmetric Pores
5. Alternating Current Electroosmotic Flow Pump
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sparreboom, W.; van den Berg, A.; Eijkel, J.C.T. Principles and applications of nanofluidic transport. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daiguji, H.; Yang, P.; Majumdar, A. Ion transport in nanofluidic channels. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daiguji, H. Ion transport in nanofluidic channels. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 901–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napoli, M.; Eijkel, J.C.T.; Pennathur, S. Nanofluidic technology for biomolecule applications: A critical review. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 957–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgreen, D.; Nakache, F.R. Electrokinetic flow in ultrafine capillary slits. J. Phys. Chem. 1964, 68, 1084–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, C.L.; Whitehead, R. Electrokinetic flow in a narrow cylindrical capillary. J. Phys. Chem. 1965, 69, 4017–4024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plecis, A.; Schoch, R.B.; Renaud, P. Ionic transport phenomena in nanofluidics: Experimental and theoretical study of the exclusion-enrichment effect on a chip. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1147–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jin, X.; Aluru, N.R. Gated transport in nanofluidic devices. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2011, 11, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, X. Ion separation in nanofluidics. Electrophoresis 2008, 29, 3737–3743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haywood, D.G.; Saha-Shah, A.; Baker, L.A.; Jacobson, S.C. Fundamental studies of nanofluidics: Nanopores, nanochannels, and nanopipets. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 172–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovarik, M.L.; Jacobson, S.C. Nanofluidics in lab-on-a-chip devices. Anal. Chem. 2009, 81, 7133–7140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segerink, L.I.; Eijkel, J.C.T. Nanofluidics in point of care applications. Lab. Chip 2014, 14, 3201–3205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwy, Z.S. Ion-current rectification in nanopores and nanotubes with broken symmetry. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2006, 16, 735–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.J.; Edwards, M.A.; Luo, L.; Perera, R.T.; Wu, X.; Martin, C.R.; White, H.S. Voltage-rectified current and fluid flow in conical nanopores. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 2605–2613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, C.; Bard, A.J.; Feldberg, S.W. Current rectification at quartz nanopipet electrodes. Anal. Chem. 1997, 69, 4627–4633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siwy, Z.; Heins, E.; Harrell, C.C.; Kohli, P.; Martin, C.R. Conical-nanotube ion-current rectifiers: The role of surface charge. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 10850–10851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cervera, J.; Schiedt, B.; Neumann, R.; Mafe, S.; Ramirez, P. Ionic conduction, rectification, and selectivity in single conical nanopores. J. Chem. Phys. 2006, 124, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, H.S.; Bund, A. Ion current rectification at nanopores in glass membranes. Langmuir 2008, 24, 2212–2218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sa, N.; Lan, W.J.; Shi, W.; Baker, L.A. Rectification of ion current in nanopipettes by external substrates. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 11272–11282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlushkou, D.; Perry, J.M.; Jacobson, S.C.; Tallarek, U. Propagating concentration polarization and ionic current rectification in a nanochannel-nanofunnel device. Anal. Chem. 2012, 84, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daiguji, H.; Oka, Y.; Shirono, K. Nanofluidic diode and bipolar transistor. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2274–2280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlassiouk, I.; Siwy, Z.S. Nanofluidic diode. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 552–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnik, R.; Duan, C.; Castelino, K.; Daiguji, H.; Majumdar, A. Rectification of ionic current in a nanofluidic diode. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, R. Diodes. In Solid–State Devices and Applications; Newnes: Oxford, UK; Boston, MA, USA, 1971; pp. 12–27. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.S. P–N junction diodes. In Semiconductor Physical Electronics; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 1993; pp. 287–326. [Google Scholar]
- Miller, S.A.; Young, V.Y.; Martin, C.R. Electroosmotic flow in template-prepared carbon nanotube membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 12335–12342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Probstein, R.F. Solutions of electrolytes. In Physicochemical Hydrodynamics; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1994; pp. 165–210. [Google Scholar]
- Slater, G.W.; Tessier, F.; Kopecka, K. The electroosmotic flow (eof). In Microengineering in Biotechnology; Hughes, M.P., Hoettges, K.F., Eds.; Humana Press: Totawa, NJ, USA, 2010; pp. 121–134. [Google Scholar]
- Kovarik, M.L.; Jacobson, S.C. Attoliter-scale dispensing in nanofluidic channels. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparreboom, W.; van den Berg, A.; Eijkel, J.C.T. Transport in nanofluidic systems: A review of theory and applications. J. Phys. 2010, 12, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, P.; Mukaibo, H.; Horne, L.P.; Bishop, G.W.; Martin, C.R. Electroosmotic flow rectification in pyramidal-pore mica membranes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 2118–2119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bishop, G.W.; Lopez, M.M.; Rajasekaran, P.R.; Wu, X.; Martin, C.R. Electroosmotic flow rectification in membranes with asymmetrically shaped pores: Effects of current and pore density. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 16633–16638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Rajasekaran, P.R.; Martin, C.R. An alternating current electroosmotic pump based on conical nanopore membranes. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 4637–4643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kneller, A.R.; Haywood, D.G.; Jacobson, S.C. AC electroosmotic pumping in nanofluidic funnels. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 6390–6394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aksimentiev, A.; Schulten, K. Imaging α-hemolysin with molecular dynamics: Ionic conductance, osmotic permeability, and the electrostatic potential map. Biophys. J. 2005, 88, 3745–3761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonome, E.L.; Cecconi, F.; Chinappi, M. Electroosmotic flow through an alpha-hemolysin nanopore. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2017, 21, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukhet, M.; Piguet, F.; Ouldali, H.; Pastoriza-Gallego, M.; Pelta, J.; Oukhaled, A. Probing driving forces in aerolysin and alpha-hemolysin biological nanopores: Electrophoresis versus electroosmosis. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 18352–18359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, G.; Willems, K.; Soskine, M.; Wloka, C.; Maglia, G. Electro-osmotic capture and ionic discrimination of peptide and protein biomarkers with frac nanopores. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, W.; Tian, Y.; Jiang, L. Asymmetric ion transport through ion-channel-mimetic solid-state nanopores. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2834–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigworth, F.J. Voltage gating of ion channels. Q. Rev. Biophys. 1994, 27, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karim, S.; Ensinger, W.; Mujahid, S.A.; Maaz, K.; Khan, E.U. Effect of etching conditions on pore shape in etched ion-track polycarbonate membranes. Radiat. Meas. 2009, 44, 779–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, N.; Yu, S.; Harrell, C.C.; Martin, C.R. Conical nanopore membranes. Preparation and transport properties. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 2025–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukaibo, H.; Horne, L.P.; Park, D.; Martin, C.R. Controlling the length of conical pores etched in ion-tracked poly(ethylene terephthalate) membranes. Small 2009, 5, 2474–2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwy, Z.; Dobrev, D.; Neumann, R.; Trautmann, C.; Voss, K. Electro-responsive asymmetric nanopores in polyimide with stable ion-current signal. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2003, 76, 781–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Galusha, J.; Shiozawa, P.G.; Wang, G.; Bergren, A.J.; Jones, R.M.; White, R.J.; Ervin, E.N.; Cauley, C.C.; White, H.S. Bench-top method for fabricating glass-sealed nanodisk electrodes, glass nanopore electrodes, and glass nanopore membranes of controlled size. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4778–4787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Apel, P.Y.; Blonskaya, I.V.; Orelovitch, O.L.; Ramirez, P.; Sartowska, B.A. Effect of nanopore geometry on ion current rectification. Nanotechnol. 2011, 22, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovarik, M.L.; Zhou, K.; Jacobson, S.C. Effect of conical nanopore diameter on ion current rectification. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 113, 15960–15966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubeil, C.; Bund, A. The role of nanopore geometry for the rectification of ionic currents. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 7866–7873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietschmann, J.F.; Wolfram, M.T.; Burger, M.; Trautmann, C.; Nguyen, G.; Pevarnik, M.; Bayer, V.; Siwy, Z. Rectification properties of conically shaped nanopores: Consequences of miniaturization. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 16917–16926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramirez, P.; Apel, P.Y.; Cervera, J.; Mafe, S. Pore structure and function of synthetic nanopores with fixed charges: Tip shape and rectification properties. Nanotechnol. 2008, 19, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Kvetny, M.; Feng, J.; Wang, D.; Wu, B.; Brown, W.; Wang, G. Surface charge density determination of single conical nanopores based on normalized ion current rectification. Langmuir 2012, 28, 1588–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behrens, S.H.; Grier, D.G. The charge of glass and silica surfaces. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 6716–6721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumal, R.R.; Karam, T.E.; Haber, L.H. Determination of the surface charge density of colloidal gold nanoparticles using second harmonic generation. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 16200–16207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rojas, O.J. Adsorption of polyelectrolytes on mica. In Encyclopedia of Surface and Colloid Science, 3rd ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, US, 2015; pp. 245–261. [Google Scholar]
- Dejardin, P.; Vasina, E.N.; Berezkin, V.V.; Sobolev, V.D.; Volkov, V.I. Streaming potential in cylindrical pores of poly(ethylene terephthalate) track-etched membranes: Variation of apparent zeta potential with pore radius. Langmuir 2005, 21, 4680–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Xie, Y.; Yan, Y.; Ke, J.; Wang, G. Surface charge density of the track-etched nanopores in polyethylene terephthalate foils. Biomicrofluidics 2009, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwy, Z.S.; Martin, C.R. Tuning ion current rectification in synthetic nanotubes. In Controlled Nanoscale Motion: Nobel Symposium 131; Linke, H., Månsson, A., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2007; pp. 349–365. [Google Scholar]
- Keesom, W.H.; Zelenka, R.L.; Radke, C.J. A zeta-potential model for ionic surfactant adsorption on an ionogenic hydrophobic surface. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1988, 125, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, B.E.; Spohr, R. Production and use of nuclear tracks - imprinting structure on solids. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1983, 55, 907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apel, P.Y.; Korchev, Y.E.; Siwy, Z.; Spohr, R.; Yoshida, M. Diode-like single-ion track membrane prepared by electro-stopping. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Interact. Mater. Atoms 2001, 184, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrell, C.C.; Siwy, Z.S.; Martin, C.R. Conical nanopore membranes: Controlling the nanopore shape. Small 2006, 2, 194–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwy, Z.S.; Howorka, S. Engineered voltage-responsive nanopores. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 1115–1132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.J.; Guo, L.J. Nanofluidic diodes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 923–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siwy, Z.; Fulinski, A. A nanodevice for rectification and pumping ions. Am. J. Phys. 2004, 72, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockris, J.O’.M.; Reddy, A.K.N.; Gamboa-Aldeco, M. Modern Electrochemistry 2A: Fundamentals of Electrodics, 2nd ed.; Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2000; pp. 771–782. [Google Scholar]
- Gouy, M. Sur la constitution de la charge électrique à la surface d’un électrolyte. J. Phys. Theor. Appl. 1910, 9, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, D.L. A contribution to the theory of electrocapillarity. Lond. Edinb. Dublin Philos. Mag. J. Sci. 1913, 25, 475–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debye, P.; Falkenhagen, H. Original announcements. The dispersion of conductance and dielectricity constants in strong electrolytes. Phys. Z. 1928, 29, 121–132. [Google Scholar]
- Nishizawa, M.; Menon, V.P.; Martin, C.R. Metal nanotubule membranes with electrochemically switchable ion-transport selectivity. Science 1995, 268, 700–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, P.; Martin, C.R. Voltage charging enhances ionic conductivity in gold nanotube membranes. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 8266–8272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lal, S.; Christia, G.D. Potentiometric studies with an ion permselective membrane. Anal. Chem. 1971, 43, 410–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bard, A.J.; Faulkner, L.R. Electrochemical Methods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 65–72. [Google Scholar]
- Kosinska, I.D.; Goychuk, I.; Kostur, M.; Schmid, G.; Hanggi, P. Rectification in synthetic conical nanopores: A one-dimensional poisson-nernst-planck model. Phys. Rev. E 2008, 77, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- White, R.J.; Zhang, B.; Daniel, S.; Tang, J.M.; Ervin, E.N.; Cremer, P.S.; White, H.S. Ionic conductivity of the aqueous layer separating a lipid bilayer membrane and a glass support. Langmuir 2006, 22, 10777–10783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Guo, W.; Xie, Y.B.; Wang, X.W.; Xue, J.M.; Wang, Y.G. Nanofluidic diode generated by pH gradient inside track-etched conical nanopore. Radiat. Meas. 2009, 44, 1119–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biggs, S.; Mulvaney, P.; Zukoski, C.F.; Grieser, F. Study of anion adsorption at the gold-aqueous solution interface by atomic-force microscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1994, 116, 9150–9157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, T.A.; Friend, C.M.; Kaxiras, E. Nature of Cl bonding on the Au (111) surface: Evidence of a mainly covalent interaction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 3720–3721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Cheng, C.; Wang, S.; Liu, S. Electroosmotic pumps and their applications in microfluidic systems. Microfluid. Nanofluid. 2009, 6, 145–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlandsson, P.G.; Robinson, N.D. Electrolysis-reducing electrodes for electrokinetic devices. Electrophoresis 2011, 32, 784–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.W.; Yao, S.; Posner, J.D.; Myers, A.M.; Santiago, J.G. Toward orientation-independent design for gas recombination in closed-loop electroosmotic pumps. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 128, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momotenko, D.; Girault, H.H. Scan-rate-dependent ion current rectification and rectification inversion in charged conical nanopores. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 14496–14499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Umehara, S.; Pourmand, N.; Webb, C.D.; Davis, R.W.; Yasuda, K.; Karhanek, M. Current rectification with poly-l-lysine-coated quartz nanopipettes. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2486–2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrette, J.P.; Zhang, B. Scan-rate-dependent current rectification of cone-shaped silica nanopores in quartz nanopipettes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 17088–17091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woermann, D. Electrochemical transport properties of a cone-shaped nanopore: High and low electrical conductivity states depending on the sign of an applied electrical potential difference. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2003, 5, 1853–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]













| Material | Surface Charge (mC·m−2) | Typical Base Diameter (µm) | Typical Tip Diameter (nm) | Electrolyte Solutions Used | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Glass or Quartz | −0.5 [52] | 25–100 | 20–150 | 0.1 mM–0.1 M KCl | [14,15,45] |
| Gold | −2 [53] | 0.6 | 10 | 0.1 M KCl or KF | [16] |
| Mica | −340 [54] | 0.1–0.5 | 10–50 | 10 mM Na2HPO4 | [31,32] |
| polyethylene terephthalate (PET) | −12 [55,56] | 0.1–0.6 | 2–30 | 0.001–1 M KCl | [17,33,47,57] |
| Polycarbonate | −2 [58] | 0.1–3.5 | 50–100 | / | [41,42] |
| Tip Radius (nm) | Percent of Ions in the Double Layer | t+ |
|---|---|---|
| 5 | 94 | 0.97 |
| 10 | 72 | 0.85 |
| 20 | 46 | 0.72 |
| 50 | 22 | 0.59 |
| 100 | 12 | 0.54 |
| Tip lmaj (nm) | Base lmaj (nm) | veof (mm s−1) | reof | ric | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base to Tip | Tip to Base | ||||
| 17 | 122 | 3.8 | 0.37 | 10.3 | 5.3 |
| 35 | 244 | 1.7 | 0.35 | 4.9 | 2.7 |
| 52 | 366 | 0.55 | 0.32 | 1.7 | 1.3 |
| 70 | 488 | 0.32 | 0.23 | 1.4 | 1.2 |
| 11 | 11 | 12 | 12 | 1.0 | 1.0 |
| Japp a (A cm−2) | reof 106 Pores cm−2 Membrane | reof 107 Pores cm−2 Membrane |
|---|---|---|
| 0.22 | - | 1.8 ± 0.9 |
| 0.44 | - | 1.3 ± 0.4 |
| 1.11 | 4.5 ± 0.8 | 2.8 ± 0.7 |
| 2.21 | 5.8 ± 0.9 | 4.7 ± 0.9 |
| 3.32 | 9 ± 1 | 6 ± 1 |
| 4.43 | 12 ± 1 | 6 ± 1 |
| 5.54 | 12 ± 1 | - |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Experton, J.; Wu, X.; Martin, C.R. From Ion Current to Electroosmotic Flow Rectification in Asymmetric Nanopore Membranes. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120445
Experton J, Wu X, Martin CR. From Ion Current to Electroosmotic Flow Rectification in Asymmetric Nanopore Membranes. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(12):445. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120445
Chicago/Turabian StyleExperton, Juliette, Xiaojian Wu, and Charles R. Martin. 2017. "From Ion Current to Electroosmotic Flow Rectification in Asymmetric Nanopore Membranes" Nanomaterials 7, no. 12: 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120445
APA StyleExperton, J., Wu, X., & Martin, C. R. (2017). From Ion Current to Electroosmotic Flow Rectification in Asymmetric Nanopore Membranes. Nanomaterials, 7(12), 445. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7120445