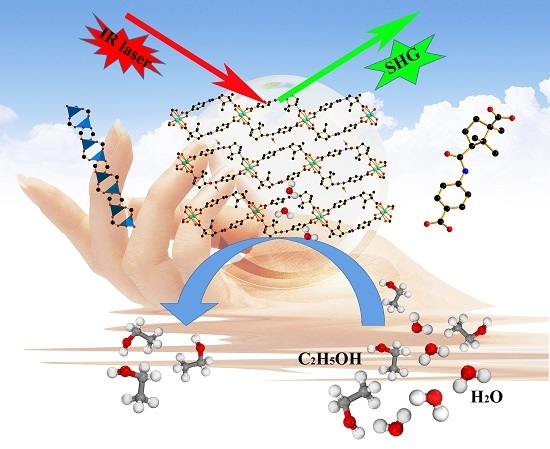
A Homochiral Multifunctional Metal-Organic Framework with Rod-Shaped Secondary Building Units
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Crystal Structure
2.2. Powder X-ray Diffraction Analysis and Thermogravimetric Analysis (TG)
2.3. Circular Dichroism (CD) Spectrum
2.4. Gas and Vapor Sorption Study
2.5. Second-Order NLO Effect
2.6. Photoluminescence
3. Materials and Methods
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhou, H.C.; Long, J.R.; Yaghi, O.M. Introduction to metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 673–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, M.; Srirambalaji, R.; Kim, K. Homochiral metal-organic frameworks for asymmetric heterogeneous catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1196–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suh, M.P.; Park, H.J.; Prasad, T.K.; Lim, D.W. Hydrogen storage in metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 782–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.R.; Sculley, J.; Zhou, H.C. Metal-organic frameworks for separations. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 869–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Yue, Y.; Qian, G.; Chen, B. Luminescent functional metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1126–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Xiong, R.G. Ferroelectric metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 1163–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, P.; Kang, Y.S.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, X.D.; Sun, W.Y. Multifunctional metal-organic frameworks with fluorescent sensing and selective adsorption properties. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 11821–11830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, P.; Vilela, S.M.F.; Tome, J.P.C.; Paz, F.A.A. Multifunctional metal-organic frameworks: From academia to industrial applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 6774–6803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Wen, H.M.; Cui, Y.J.; Zhou, W.; Qian, G.D.; Chen, B.L. Emerging multifunctional metal-organic framework materials. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 8819–8860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.Y.; Chrzanowski, M.; Zhang, Y.M.; Ma, S.Q. Applications of metal-organic frameworks featuring multi-functional sites. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 307, 106–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.H.; Wei, Y.L.; Ji, C.; Ma, M.L.; Zang, S.Q.; Mak, T.C.W. A multifunctional 3D chiral porous ferroelectric metal-organic framework for sensing small organic molecules and dye uptake. Chem. Asian J. 2014, 9, 3094–3098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.B.; Liang, J.; Wang, X.S.; Cao, R. Multifunctional metal-organic framework catalysts: Synergistic catalysis and tandem reactions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 126–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.R.; Li, J.; Du, D.Y.; Qin, J.S.; Li, S.L.; He, W.W.; Su, Z.M.; Lan, Y.Q. A multifunctional microporous anionic metal organic framework for column-chromatographic dye separation and selective detection and adsorption of Cr3+. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 23426–23434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.H.; Xie, Y.; Ci, S.Q.; Jia, J.C.; Cai, P.W.; Yi, L.C.; Wen, Z.H. Multifunctional high-activity and robust electrocatalyst derived from metal-organic frameworks. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 17288–17298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, F.Y.; Li, J.P.; Wu, D.; Sun, Z.M. A series of multifunctional metal-organic frameworks showing excellent luminescent sensing, sensitization, and adsorbent abilities. Chem. Eur. J. 2015, 21, 11475–11482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Jiang, M.; Yan, L.; Peng, R.; Huangfu, M.J.; Guo, X.X.; Li, Y.; Wu, P.Y. Multifunctional luminescent Eu(III)-based metal-organic framework for sensing methanol and detection and adsorption of Fe(III) ions in aqueous solution. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 12660–12668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, L.L.; Zhou, L.; Zhang, B.G.; Meng, X.G.; Qu, H.; Li, D.F. Multifunctional amino-decorated metal-organic frameworks: Nonlinear-optic, ferroelectric, fluorescence sensing and photocatalytic properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 22603–22609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, D.W.; Lee, W.R.; Lim, K.S.; Phang, W.J.; Hong, C.S. Two homochiral bimetallic metal-organic frameworks composed of a paramagnetic metalloligand and chiral camphorates: Multifunctional properties of sorption, magnetism, and enantioselective separation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 6472–6477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.G.; Cao, R.; Wang, X.; Li, H.F.; Yuan, W.B.; Wang, G.J.; Wu, H.H.; Li, J. A multifunctional 3D ferroelectric and NLO-active porous metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 6894–6895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.Q.; Feng, S.S.; Shen, M.L.; Lu, L.P. Construction of multifunctional materials based on Tb3+ and croconic acid, directed by K+ cations: Synthesis, structures, fluorescence, magnetic and ferroelectric behaviors. CrystEngComm 2016, 18, 5344–5352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuéry, P.; Harrowfield, J. Chiral one- to three-dimensional uranyl-organic assemblies from (1R,3S)-(+)-camphoric acid. CrystEngComm 2014, 16, 2996–3004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, K.; Jiang, F.; Qian, J.; Pang, J.; Hu, F.; Bawaked, S.M.; Mokhtar, M.; Al-Thabaiti, S.A.; Hong, M. Bridging different Co4–calix[4]arene building blocks into grids, cages and 2D polymers with chiral camphoric acid. CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 1750–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.-Q.; Li, D.-P.; Zhou, X.-H.; Sui, Y.; Li, Y.-Z.; Zuo, J.-L.; You, X.-Z. Metal-organic coordination polymers generated from chiral camphoric acid and flexible ligands with different spacer lengths: Syntheses, structures, and properties. Cryst. Growth Des. 2009, 9, 4872–4883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.L.; Zhang, J.; Lin, Q.P.; Yin, P.X.; Yao, Y.G. Multifunctional homochiral lanthanide camphorates with mixed achiral terephthalate ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 9257–9264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Yang, Z.; Bai, J.; Zheng, B.; Li, Y.; Li, S. Highly selective CO2 capture of an agw-type metal-organic framework with inserted amides: Experimental and theoretical studies. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moon, D.; Lah, M.S. Face-driven corner-linked octahedral nanocages: M6L8 cages formed by C3-symmetric triangular facial ligands linked via C4-symmetric square tetratopic PdII ions at truncated octahedron corners. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 3530–3531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Hong, S.; Kim, G.H.; Lah, M.S. Porous metal-organic frameworks based on metal-organic polyhedra with nanosized cavities as supramolecular building blocks: Two-fold interpenetrating primitive cubic networks of [Cu6L8]12+ nanocages. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 46, 10208–10213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasegawa, S.; Horike, S.; Matsuda, R.; Furukawa, S.; Mochizuki, K.; Kinoshita, Y.; Kitagawa, S. Three-dimensional porous coordination polymer functionalized with amide groups based on tridentate ligand: Selective sorption and catalysis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 2607–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosi, N.L.; An, J.; Geib, S.J. High and selective CO2 uptake in a cobalt adeninate metal-organic framework exhibiting pyrimidine- and amino-decorated pores. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 38–39. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, C.; Bai, J.; He, C.; Duan, C. New rht-type metal-organic frameworks decorated with acylamide groups for efficient carbon dioxide capture and chemical fixation from raw power plant flue gas. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 31746–31756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pachfule, P.; Garai, B.; Banerjee, R. Functionalization and isoreticulation in a series of metal-organic frameworks derived from pyridinecarboxylates. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 7200–7205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, M.; da Silva, I.; Johnson, M.; Carter, J.H.; Newby, R.; Suyetin, M.; Besley, E.; Manuel, P.; Rudić, S.; Fitch, A.N.; et al. Observation of binding and rotation of methane and hydrogen within a functional metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 9119–9127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoedel, A.; Li, M.; Li, D.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Structures of metal-organic frameworks with rod secondary building units. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 12466–12535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, K.; Zhang, L.N.; Han, L.Q.; Qu, F.Y. Synthesis, characterization and luminescence of a chiral mof based on camphor derivative. Chem. J. Chin. Univ. 2013, 34, 1313–1317. [Google Scholar]
- Borjigin, T.; Sun, F.; Zhang, J.; Cai, K.; Ren, H.; Zhu, G. A microporous metal-organic framework with high stability for gc separation of alcohols from water. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 7613–7615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]









© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, K.; Zhao, N.; Zhang, N.; Sun, F.-X.; Zhao, Q.; Zhu, G.-S. A Homochiral Multifunctional Metal-Organic Framework with Rod-Shaped Secondary Building Units. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7040088
Cai K, Zhao N, Zhang N, Sun F-X, Zhao Q, Zhu G-S. A Homochiral Multifunctional Metal-Organic Framework with Rod-Shaped Secondary Building Units. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(4):88. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7040088
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Kun, Nian Zhao, Ning Zhang, Fu-Xing Sun, Qing Zhao, and Guang-Shan Zhu. 2017. "A Homochiral Multifunctional Metal-Organic Framework with Rod-Shaped Secondary Building Units" Nanomaterials 7, no. 4: 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7040088
APA StyleCai, K., Zhao, N., Zhang, N., Sun, F. -X., Zhao, Q., & Zhu, G. -S. (2017). A Homochiral Multifunctional Metal-Organic Framework with Rod-Shaped Secondary Building Units. Nanomaterials, 7(4), 88. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7040088