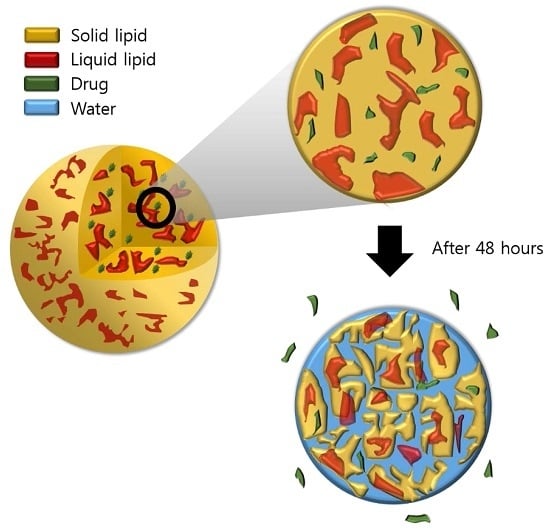
The Improvement of Skin Whitening of Phenylethyl Resorcinol by Nanostructured Lipid Carriers
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Screening of PR in Solid and Liquid Lipids
2.2. Measurements of Particle Size and Polydispersity Index (PDI)
2.3. Determination of EE and LC
2.4. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) Analysis
2.5. Fourier-Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Analysis
2.6. Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC) Analysis
2.7. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.8. Stability Test
2.9. In Vitro Release Study
2.10. Cytotoxicity Study
2.11. Cellular Uptake Study
2.12. Cellular Tyrosinase Inhibition Study
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Cell Cultures
3.3. Screening of Solid and Liquid Lipids
3.4. Preparation of PR-NLCs
3.5. Measurements of Particle Size and PDI
3.6. Determination of EE and LC
3.7. HPLC Analysis
3.8. TEM Analysis
3.9. FT-IR Analysis
3.10. DSC Analysis
3.11. XRD Analysis
3.12. Stability Test
3.13. In Vitro Release Study
3.14. Cytotoxicity Study
3.15. Cellular Uptake Study
3.16. Cellular Tyrosinase Inhibition Assay
3.17. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Schmaus, G.; Vielhaber, G.; Jacobs, K.; Franke, H. 4-(1-Phenylethyl) 1, 3-benzenediol: A new highly potent lightening agent. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2006, 57, 197–198. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chang, T.S. An updated review of tyrosinase inhibitors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 2440–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, H.; Liu, G.; Huang, Y.; Li, Y.; Xia, Q. Development of a nanostructured lipid carrier formulation for increasing photo-stability and water solubility of Phenylethyl Resorcinol. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 288, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Mäder, K.; Gohla, S. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery–a review of the state of the art. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2000, 50, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.H.; Radtke, M.; Wissing, S.A. Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) and nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) in cosmetic and dermatological preparations. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2002, 54, S131–S155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehnert, W.; Mäder, K. Solid lipid nanoparticles: production, characterization and applications. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2001, 47, 165–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'driscoll, C.M.; Griffin, B.T. Biopharmaceutical challenges associated with drugs with low aqueous solubility-the potential impact of lipid-based formulations. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 617–624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, C.Y.; Li, N.; Wang, M.; Zhang, X.N.; Pan, W.S.; Peng, J.J.; Pan, Y.S.; Tang, X. Preparation and characterization of vinpocetine loaded nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC) for improved oral bioavailability. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 394, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.Y.; Fang, C.L.; Liu, C.H.; Su, Y.H. Lipid nanoparticles as vehicles for topical psoralen delivery: Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) versus nanostructured lipid carriers (NLC). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2008, 70, 633–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pastor-Nieto, M.A.; Sánchez-Pedreño, P.; Martínez-Menchón, T.; Melgar-Molero, V.; Alcántara-Nicolás, F.; Cruz-Murie, P. Allergic contact dermatitis caused by phenylethyl resorcinol, a skin-lightening agent contained in a sunscreen. Contact Dermatitis 2016, 75, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baek, J.S.; Pham, C.V.; Myung, C.S.; Cho, C.W. Tadalafil-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers using permeation enhancers. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.; Singh, M.; Tripathi, C.B.; Arya, M.; Saraf, S.A. Development and evaluation of ultra-small nanostructured lipid carriers: novel topical delivery system for athlete’s foot. Drug. Deliv. Transl. Res. 2016, 6, 38–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil-Gadhe, A.; Pokharkar, V. Montelukast-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: part I oral bioavailability improvement. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 88, 160–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vitorino, C.; Carvalho, F.A.; Almeida, A.J.; Sousa, J.J.; Pais, A.A. The size of solid lipid nanoparticles: An interpretation from experimental design. Colloids Surf. B: Biointerfaces 2011, 84, 117–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Shen, J.; Zhang, D.; Duan, C.; Liu, G.; Zheng, D.; Tian, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Q. In vitro and in vivo evaluation of oridonin-loaded long circulating nanostructured lipid carriers. Int. J. Biol. Macromole. 2012, 50, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Randhawa, J.K. Preparation and characterization of Paliperidone loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 102, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadiq, A.A.; Rassol, A.A. Formulation and evaluation of silibinin loaded solid lipid nanoparticles for peroral use targeting lower part of gastrointestinal tract. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 6, 55–67. [Google Scholar]
- Sangsen, Y.; Wiwattanawongsa, K.; Likhitwitayawuid, K.; Sritularak, B.; Wiwattanapatapee, R. Modification of oral absorption of oxyresveratrol using lipid based nanoparticles. Colloids Surfaces. B Biointerfaces 2015, 131, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, W.M.; Rajinikanth, P.S.; Mallikarjun, C.; Kang, Y.B. Formulation and delivery of itraconazole to the brain using a nanolipid carrier system. Int. J. Nanomed. 2014, 9, 2117–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.H.; Ramasamy, T.; Truong, D.H.; Choi, H.G.; Yong, C.S.; Kim, J.O. Preparation and characterization of fenofibrate-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers for oral bioavailability enhancement. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2014, 15, 1509–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shete, H.; Patravale, V. Long chain lipid based tamoxifen NLC. Part I: Preformulation studies, formulation development and physicochemical characterization. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhao, Y.; He, M.; Zhang, X.; Niu, M.; Feng, N. Nanostructured lipid carriers versus microemulsions for delivery of the poorly water-soluble drug luteolin. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 476, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.D.; Na, K.; Choi, H.K. Preparation and characterization of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) made of cacao butter and curdlan. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2005, 24, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Date, P.V.; Samad, A.; Devarajan, P.V. Freeze thaw: A simple approach for prediction of optimal cryoprotectant for freeze drying. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2010, 11, 304–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siri, M.; Grasselli, M.; Alonso, S.D.V. Albumin-based nanoparticle trehalose lyophilisation stress-down to preserve structure/function and enhanced binding. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2016, 126, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wosicka-Frąckowiak, H.; Cal, K.; Stefanowska, J.; Główka, E.; Nowacka, M.; Struck-Lewicka, W.; Govedarica, W.; Pasikowska, M.; Dębowska, R.; Jesionowski, T.; et al. Roxithromycin-loaded lipid nanoparticles for follicular targeting. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 495, 807–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, H.S.; Rasedee, A.; How, C.W.; Abdul, A.B.; Zeenathul, N.A.; Othman, H.H.; Saeed, M.I.; Yeap, S.K. Zerumbone-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers: Preparation, characterization, and antileukemic effect. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 2769–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doktorovova, S.; Souto, E.B.; Silva, A.M. Nanotoxicology applied to solid lipid nanoparticles and nanostructured lipid carriers–a systematic review of in vitro data. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabata, Y.; Ikada, Y. Phagocytosis of polymer microspheres by macrophages. In New Polymer Materials; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 107–141. [Google Scholar]
- How, C.W.; Rasedee, A.; Manickam, S.; Rosli, R. Tamoxifen-loaded nanostructured lipid carrier as a drug delivery system: Characterization, stability assessment and cytotoxicity. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2013, 112, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyadarkunte, A.Y.; Patole, M.S.; Pokharkar, V.B. Cellular interactions and photoprotective effects of idebenone-loaded nanostructured lipid carriers stabilized using PEG-free surfactant. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 479, 77–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hillaireau, H.; Couvreur, P. Nanocarriers’ entry into the cell: Relevance to drug delivery. Cell. Mol. Life. Sci. 2009, 66, 2873–2896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Li, X.; Yu, S.; Yang, X.; Kong, J.; Pan, W. Enhanced cellular uptake and anti-proliferating effect of chitosan hydrochlorides modified genistein loaded NLC on human lens epithelial cells. Int. J. Pharm. 2014, 471, 118–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, G.; Todd, C.; Cresswell, J.E.; Thody, A.J. Alpha-melanocyte stimulating hormone and its analogue Nle4DPhe7 alpha-MSH affect morphology, tyrosinase activity and melanogenesis in cultured human melanocytes. J. Cell. Sci. 1994, 1071, 205–211. [Google Scholar]
- Han, E.B.; Chang, B.Y.; Kim, D.S.; Cho, H.K.; Kim, S.Y. Melanogenesis inhibitory effect of aerial part of Pueraria thunbergiana in vitro and in vivo. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2015, 307, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, G.H.; Lee, B.J.; Cho, C.W. Mechanisms of drug release from advanced drug formulations such as polymeric-based drug-delivery systems and lipid nanoparticles. J. Pharm. Investig. 2017, 47, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkateswarlu, V.; Manjunath, K. Preparation, characterization and in vitro release kinetics of clozapine solid lipid nanoparticles. J. Control. Release 2004, 95, 627–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, K.; Padhye, S.; Nagarsenker, M. Duloxetine HCl lipid nanoparticles: Preparation, characterization, and dosage form design. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2012, 13, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosny, K.M.; Banjar, Z.M.; Hariri, A.H.; Hassan, A.H. Solid lipid nanoparticles loaded with iron to overcome barriers for treatment of iron deficiency anemia. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2015, 9, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]














| Formulation | Particle Size (nm) | PDI | EE (%) | LC (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank-NLCs | 55.6 ± 1.2 | 0.25 ± 0.01 | - | - |
| PR-NLCs | 57.9 ± 1.3 | 0.24 ± 0.01 | 93.1 ± 4.2 | 8.5 ± 0.4 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, B.-S.; Na, Y.-G.; Choi, J.-H.; Kim, I.; Lee, E.; Kim, S.-Y.; Lee, J.-Y.; Cho, C.-W. The Improvement of Skin Whitening of Phenylethyl Resorcinol by Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090241
Kim B-S, Na Y-G, Choi J-H, Kim I, Lee E, Kim S-Y, Lee J-Y, Cho C-W. The Improvement of Skin Whitening of Phenylethyl Resorcinol by Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(9):241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090241
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Bo-Sik, Young-Guk Na, Jae-Hwan Choi, Inhye Kim, Eunji Lee, Sung-Yeon Kim, Jae-Young Lee, and Cheong-Weon Cho. 2017. "The Improvement of Skin Whitening of Phenylethyl Resorcinol by Nanostructured Lipid Carriers" Nanomaterials 7, no. 9: 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090241
APA StyleKim, B. -S., Na, Y. -G., Choi, J. -H., Kim, I., Lee, E., Kim, S. -Y., Lee, J. -Y., & Cho, C. -W. (2017). The Improvement of Skin Whitening of Phenylethyl Resorcinol by Nanostructured Lipid Carriers. Nanomaterials, 7(9), 241. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090241