Antimicrobial Properties of Silver Cations Substituted to Faujasite Mineral
Abstract
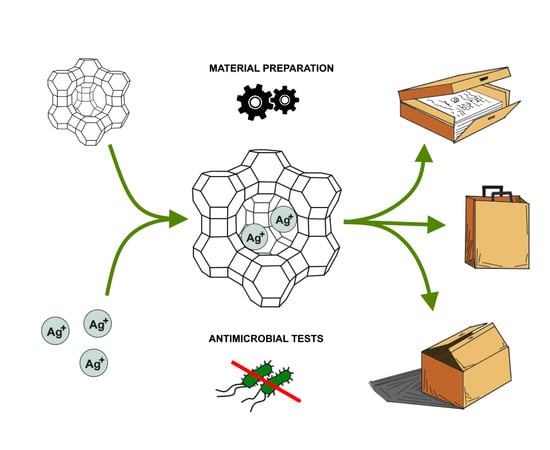
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Zeolite Preparation
2.2. Paper Preparation
2.3. Reference Materials Preparation
2.4. Antimicrobial Tests
3. Results
3.1. Bacterial Strains
3.2. Fungal Strains
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Russell, A.D.; Hugo, W. Antimicrobial activity and action of silver. Prog. Med. Chem. 1994, 31, 351–370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Damn, C.; Neumann, M.; Munstedt, H. Properties of nanosilver coatings on polymethyl methacrylate. Soft Mater. 2006, 3, 71–88. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, K.Y.; Hoon Byeon, J.; Park, J.H.; Hwang, J. Susceptibility constants of Escherichia coli and Bacillus subtilis to silver and copper nanoparticles. Sci. Total Environ. 2007, 373, 572–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venous, A. Antimicrobial-impregnated central venous. N. Engl. J. Med. 1999, 340, 1761–1762. [Google Scholar]
- Böswald, M.; Mende, K.; Bernschneider, W.; Bonakdar, S.; Ruder, H.; Kissler, H.; Sieber, E.; Guggenbichler, J.P. Biocompatibility testing of a new silver-impregnated catheterin vivo. Infection 1999, 27, S38–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Jing, L.; Valladares, A.; Mehta, S.L.; Wang, Z.; Andy Li, P.; Bang, J.J. Silver nanoparticle exposure induced mitochondrial stress, caspase-3 activation and cell death: Amelioration by sodium selenite. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2015, 11, 860–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bressan, E.; Ferroni, L.; Gardin, C.; Rigo, C.; Stocchero, M.; Vindigni, V.; Cairns, W.; Zavan, B. Silver nanoparticles and mitochondrial interaction. Int. J. Dent. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toole, G.O.; Kaplan, H.B.; Kolter, R. Biofilm formation as microbial development. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 2000, 54, 49–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clement, J.L.; Jarrett, P.S. Antibacterial silver. Met. Based Drugs 1994, 1, 467–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Socrates, G. Organic silicone compounds. In Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies Tables and Charts; Socrates, G., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2001; pp. 239–246. ISBN 3527306730. [Google Scholar]
- Walder, B.; Pittet, D.; Tramer, M. Prevention of bloodstream infections with central venous catheters treated with anti-infective agents depends on catheter type and insertion time: Evidence from a meta-analysis. Infect. Control Hosp. Epidemiol. 2002, 23, 748–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schierholz, J.M.; Lucas, L.J.; Rump, A.; Pulverer, G. Efficacy of silver-coated medical devices. J. Hosp. Infect. 1998, 40, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdock, R.C.; Braydich-Stolle, L.; Schrand, A.M.; Schlager, J.J.; Hussain, S.M. Characterization of nanomaterial dispersion in solution prior to in vitro exposure using dynamic light scattering technique. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 101, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Warheit, D.B. How meaningful are the results of nanotoxicity studies in the absence of adequate material characterization? Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 101, 183–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajipour, M.J.; Fromm, K.M.; Akbar Ashkarran, A.; Jimenez de Aberasturi, D.; de Larramendi, I.R.; Rojo, T.; Serpooshan, V.; Parak, W.J.; Mahmoudi, M. Antibacterial properties of nanoparticles. Trends Biotechnol. 2012, 30, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehy, K.; Casey, A.; Murphy, A.; Chambers, G. Antimicrobial properties of nano-silver: A cautionary approach to ionic interference. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 443, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Puppala, H.L.; Colvin, V.L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Negligible particle-specific antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles. Am. Chem. Soc. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4271–4275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, M.; Mukherjee, A.; Chandrasekaran, N. Genotoxicity of silver nanoparticles in Allium cepa. Sci. Total Environ. 2009, 407, 5243–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuura, T.; Abe, Y.; Sato, Y.; Okamoto, K.; Ueshige, M.; Akagawa, Y. Prolonged antimicrobial effect of tissue conditioners containing silver-zeolite. J. Dent. 1997, 25, 373–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaali, P.; Strömberg, E.; Aune, R.E.; Czél, G.; Momcilovic, D.; Karlsson, S. Antimicrobial properties of Ag+ loaded zeolite polyester polyurethane and silicone rubber and long-term properties after exposure to in vitro ageing. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2010, 95, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, K.; Tsuruda, K.; Morishita, M.; Uchida, M. Antibacterial effect of silver-zeolite on oral bacteria under anaerobic conditions. Dent. Mater. 2000, 16, 452–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Seff, K. Silver clusters and chemistry in Zeolites. Chem. Rev. 1994, 94, 857–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Łojewska, J.; Jedrzejczyk, R.J.; Łojewski, T.; Thomas, J.L.; Pawcenis, D.; Milczarek, J.; Gil, B.; Kołodziej, A.; Turnau, K. Modified Nanocomposite Material, Method for Its Production and Its Application. U.S. Patent Application 15/309,474 PCT number: PCT/IB2015/053408, 9 May 2015. [Google Scholar]
- TAPPI standard practice for conditioning paper and paper products for testing. 2002, 93, 5–7.
- Welschmeyer, N.A.; Kuo, J. Analysis of Adenosine Triphosphate (ATP) as a Rapid, Quantitative Compliance Test for Ships’ Ballast Water; Moss Landing Marine Laboratories: Moss Landing, CA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Ataullakhanov, F.I.; Vitvitsky, V.M. What determines the intracellular ATP concentration. Biosci. Rep. 2002, 22, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siebel, E.; Wang, Y.; Egli, T.; Hammes, F. Correlations between total cell concentration, total adenosine tri-phosphate concentration and heterotrophic plate counts during microbial monitoring of drinking water. Drink. Water Eng. Sci. Discuss. 2008, 1, 71–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaginuma, H.; Kawai, S.; Tabata, K.V.; Tomiyama, K.; Kakizuka, A.; Komatsuzaki, T.; Noji, H.; Imamura, H. Diversity in ATP concentrations in a single bacterial cell population revealed by quantitative single-cell imaging. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 6522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bergey, D.H. Bergey’s Manual of Systematic Bacteriology—The Proteobacteria Part A—Introductory Essays; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2005; Volume 2, pp. 1–304. [Google Scholar]
- Morozzi, G.; Cenci, G.; Scardazza, F.; Pitzurra, M. Cadmium uptake by growing cells of gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. Microbios 1986, 48, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nies, D.H. Microbial heavy-metal resistance. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1999, 51, 730–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruins, M.R.; Kapil, S.; Oehme, F.W. Microbial resistance to metals in the environment. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2000, 45, 198–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuertz, S.; Mergeay, M.; van Elsas, J.D.; Trevors, J.T.; Wellington, E.M.H. The Impact of Heavy Metals on Soil Microbial Communities and Their Activities; van Elsas, J.D., Trevors, J.T., Wellington, E.M.H., Eds.; Marcel Dekker Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1997; pp. 607–642. [Google Scholar]
- Cervantes, C.; Gutierrez-Corona, F. Copper resistance mechanisms in bacteria and fungi. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 1994, 14, 121–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nies, D.H. Efflux-mediated heavy metal resistance in prokaryotes. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2003, 27, 313–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Maury, L.; Garcia-Dominguez, M.; Florencio, F.J.; Reyes, J.C. A two-component signal transduction system involved in nickel sensing in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. PCC 6803. Mol. Microbiol. 2002, 43, 247–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, S. Genes for all metals—A bacterial view of the periodic table, the 1996 Thom award lecture. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1998, 20, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadd, G.M. Metals, minerals and microbes: Geomicrobiology and bioremediation. Microbiology 2010, 156, 609–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, J.R.; Bailey, E.H.; William Purvis, O. Bioaccumulation of metals by lichens: Uptake of aqueous uranium by Peltigera membranacea as a function of time and pH. Am. Mineral. 1998, 83, 1494–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tobin, J.M.; White, C.; Gadd, G.M. Metal accumulation by fungi: Applications in environmental biotechnology. J. Ind. Microbiol. 1994, 13, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, O.; Deng, K.K.; Kim, N.J.; Ross, L.; Surampalli, R.Y.; Hu, Z. The inhibitory effects of silver nanoparticles, silver ions, and silver chloride colloids on microbial growth. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3066–3074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-Castañón, G.A.; Niño-Martínez, N.; Martínez-Gutierrez, F.; Martínez-Mendoza, J.R.; Ruiz, F. Synthesis and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles with different sizes. J. Nanopart. Res. 2008, 10, 1343–1348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rai, M.; Yadav, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles as a new generation of antimicrobials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2009, 27, 76–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veerasamy, R.; Xin, T.Z.; Gunasagaran, S.; Xiang, T.F.W.; Yang, E.F.C.; Jeyakumar, N.; Dhanaraj, S.A. Biosynthesis of silver nanoparticles using mangosteen leaf extract and evaluation of their antimicrobial activities. J. Saudi Chem. Soc. 2011, 15, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Z.M.; Ma, J.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Differential effect of common ligands and molecular oxygen on antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles versus silver ions. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 9003–9008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogar, A.; Tylko, G.; Turnau, K. Antifungal properties of silver nanoparticles against indoor mould growth. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 521–522, 305–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahverdi, A.R.; Fakhimi, A.; Shahverdi, H.R.; Minaian, S. Synthesis and effect of silver nanoparticles on the antibacterial activity of different antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 168–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabikhan, A.; Kandasamy, K.; Raj, A.; Alikunhi, N.M. Synthesis of antimicrobial silver nanoparticles by callus and leaf extracts from saltmarsh plant, Sesuvium portulacastrum L. Colloids Surfaces B Biointerfaces 2010, 79, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhong, S.; Zhang, M.; Lin, Y. Antibacterial activity of silver-loaded zeolite A prepared by a fast microwave-loading method. J. Mater. Sci. 2009, 44, 457–462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwakye-Awuah, B.; Williams, C.; Kenward, M.A.; Radecka, I. Antimicrobial action and efficiency of silver-loaded zeolite X. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2008, 104, 1516–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirci, S.; Ustaoğlu, Z.; Yılmazer, G.A.; Sahin, F.; Baç, N. Antimicrobial properties of zeolite-X and zeolite-A Ion-Exchanged with silver, copper, and zinc against a broad range of microorganisms. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2014, 172, 1652–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Sample Name | Studied Component | Description | Silver Content, wt % |
|---|---|---|---|
| P | pure cellulose | Whatman filter paper No. 1 | 0 |
| PZ0 | sodium form of faujasite, FAU | pure faujasite suspended in paper | 0 |
| PAg+ | silver cations, Ag+ | silver nitrate dissolved in paper | 0.5 ± 0.1 |
| PAg0 | silver nanoparticles, Ag0 | silver nitrate sonicated and suspended in paper | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| PZAg+ | silver cation-exchanged faujasite and silver oxide nanoparticles, AgFAU, Ag2O | the exchanged faujasite suspended in paper | 1.5 ± 0.1 |
| PZAg+_EDTA | silver cation-exchanged faujasite, AgFAU | the exchanged faujasite washed with Na2EDTA and then suspended in paper | 1.1 ± 0.1 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jędrzejczyk, R.J.; Turnau, K.; Jodłowski, P.J.; Chlebda, D.K.; Łojewski, T.; Łojewska, J. Antimicrobial Properties of Silver Cations Substituted to Faujasite Mineral. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090240
Jędrzejczyk RJ, Turnau K, Jodłowski PJ, Chlebda DK, Łojewski T, Łojewska J. Antimicrobial Properties of Silver Cations Substituted to Faujasite Mineral. Nanomaterials. 2017; 7(9):240. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090240
Chicago/Turabian StyleJędrzejczyk, Roman J., Katarzyna Turnau, Przemysław J. Jodłowski, Damian K. Chlebda, Tomasz Łojewski, and Joanna Łojewska. 2017. "Antimicrobial Properties of Silver Cations Substituted to Faujasite Mineral" Nanomaterials 7, no. 9: 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090240
APA StyleJędrzejczyk, R. J., Turnau, K., Jodłowski, P. J., Chlebda, D. K., Łojewski, T., & Łojewska, J. (2017). Antimicrobial Properties of Silver Cations Substituted to Faujasite Mineral. Nanomaterials, 7(9), 240. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano7090240