Antibacterial and Barrier Properties of Gelatin Coated by Electrospun Polycaprolactone Ultrathin Fibers Containing Black Pepper Oleoresin of Interest in Active Food Biopackaging Applications
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
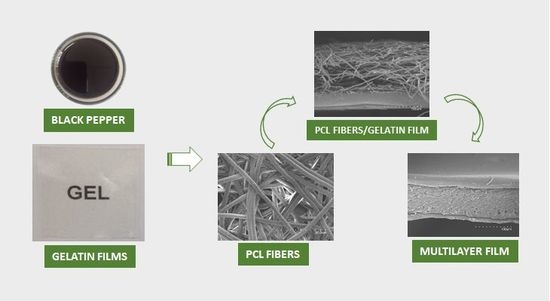
2.2. Elaboration of the Gelatin Films by Solution Casting
2.3. Preparation of the Water Barrier and Active Solution
2.4. Preparation of the Electrospun Coatings
2.5. Characterization of the Materials
2.5.1. Film Thickness
2.5.2. Morphology
2.5.3. Transparency
2.5.4. Thermogravimetric Analysis (TGA)
2.5.5. Water Vapor Permeance (WVP)
2.5.6. Water Contact Angle
2.5.7. Oxygen Permeance
2.5.8. Mechanical Test
2.5.9. Antimicrobial Activity
2.5.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology
3.2. Thermogravimetric Analysis
3.3. Water Vapor Permeance and Oxygen Permeance
3.4. Water Contact Angle
3.5. Mechanical Test
3.6. Antimicrobial Activity
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Atarés, L.; Chiralt, A. Essential oils as additives in biodegradable films and coatings for active food packaging. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 48, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nur Azira, T.; Che Man, T.; Raja Mohd Hafidz, R.; Aina, M.; Amin, I. Use of principal component analysis for differentiation of gelatine sources based on polypeptide molecular weights. Food Chem. 2014, 151, 286–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clarke, D.; Molinaro, S.; Tyuftin, A.; Bolton, D.; Fanning, S.; Kerry, J.P. Incorporation of commercially-derived antimicrobials into gelatin-based films and assessment of their antimicrobial activity and impact on physical film properties. Food Control 2016, 64, 202–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhreddin Hosseini, S.; Rezaei, M.; Zandi, M.; Farahmandghavi, F. Development of bioactive fish gelatin/chitosan nanoparticles composite films with antimicrobial properties. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 1266–1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavoosi, G.; Rahmatollahi, A.; Mahdi Dadfar, S.M.; Purfard, A.M. Effects of essential oil on the water binding capacity, physico-mechanical properties, antioxidant and antibacterial activity of gelatin films. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 57, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, B.; Marques, A.; Pires, C.; Ramos, C.; Batista, I.; Saraiva, J.A.; Nunes, M.L. Characterization of fish protein films incorporated with essential oils of clove, garlic and origanum: Physical, antioxidant and antibacterial properties. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 59, 533–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Shi, L.; Zhang, X.; Liu, K.; Ullah, I.; Cheng, P. Electrospinning of polycaprolactone nanofibers using H2O as benign additive in polycaprolactone/glacial acetic acid solution. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2018, 135, 45578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, M.J.; Lopez-Rubio, A.; Lagaron, J.M. High barrier polyhydroxyalcanoate food packaging film by means of nanostructured electrospun interlayers of zein. Food Hydrocoll. 2013, 32, 106–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Chen, W.; Sun, B.; Li, H.; Wu, T.; Ke, Q.; Huang, C.; EI-Hamshary, H.; Al-Deyab, S.; Mo, X. A comparison of nanoscale and multiscale PCL/gelatin scaffolds prepared by disc-electrospinning. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 146, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coimbra, P.; Santos, P.; Alves, P.; Miguel, S.; Carvalho, M.; de Sá, K.; Correia, I.; Ferreira, P. Coaxial electrospun PCL/Gelatin-MA fibers as scaffolds for vascular tissue engineering. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 159, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramírez-Agudelo, R.; Scheuermann, K.; Gala-García, A.; Monteiro, A.P.; Pinzón-García, A.D.; Cortés, M.E.; Sinisterra, R.D. Hybrid nanofibers based on poly-caprolactone/gelatin/hydroxyapatite nanoparticles-loaded Doxycycline: Effective anti-tumoral and antibacterial activity. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 83, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, R.; Geng, H.; Gong, M.; Ye, J.; Wu, C.; Hu, X.; Zhang, L. Long-acting and broad-spectrum antimicrobial electrospun poly (ε-caprolactone)/gelatin micro/nanofibers for wound dressing. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2018, 509, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Basar, A.; Castro, S.; Torres-Giner, S.; Lagaron, J.M.; Turkoglu Sasmazel, H. Novel poly(ε-caprolactone)/gelatin wound dressings prepared by emulsion electrospinning with controlled release capacity of Ketoprofen antiinflammatory drug. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 81, 459–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aydogdu, A.; Sumnu, G.; Sahin, S. A novel electrospun hydroxypropyl methylcellulose/polyethylene oxide blend nanofibers: Morphology and physicochemical properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 181, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Masiá, R.; Lagaron, J.M.; López-Rubio, A. Development and Optimization of Novel Encapsulation Structures of Interest in Functional Foods through Electrospraying. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2014, 7, 3236–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerqueira, M.A.; Fabra, M.J.; Castro-Mayorga, J.L.; Bourbon, A.I.; Pastrana, L.M.; Vicente, A.A.; Lagaron, J.M. Use of Electrospinning to Develop Antimicrobial Biodegradable Multilayer Systems: Encapsulation of Cinnamaldehyde and Their Physicochemical Characterization. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2016, 9, 1874–1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro-Mayorga, J.L.; Fabra, M.J.; Cabedo, L.; Lagaron, J.M. On the Use of the Electrospinning Coating Technique to Produce Antimicrobial Polyhydroxyalkanoate Materials Containing In Situ-Stabilized Silver Nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cherpinski, A.; Torres-Giner, S.; Cabedo, L.; Mendez, J.A.; Lagaron, J.M. Multilayer structures based on annealed electrospun biopolymer coatings of interest in water and aroma barrier fiber-based food packaging applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2017, 135, 45501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherpinski, A.; Torres-Giner, S.; Vartiainen, J.; Peresin, M.S.; Lahtinen, P.; Lagaron, J.M. Improving the water resistance of nanocellulose-based films with polyhydroxyalkanoates processed by the electrospinning coating technique. Cellulose 2018, 25, 1291–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Pascal Kamdem, D. Development and characterization of biodegradable chitosan films containing two essential oils. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2015, 74, 289–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ribeiro-Santos, R.; Andrade, M.; Ramos de Melo, N.; dos Santos, F.R.; de Araújo Neves, I.; de Carvalho, M.G.; Sanches-Silva, A. Biological activities and major components determination in essential oils intended for a biodegradable food packaging. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 97, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martucci, J.; Gende, L.; Neira, L.; Ruseckaite, R. Oregano and lavender essential oils as antioxidant and antimicrobial additives of biogenic gelatin films. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2015, 71, 205–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tongnuanchan, P.; Benjakul, S.; Prodpran, T.; Pisuchpen, S.; Osako, K. Mechanical, thermal and heat sealing properties of fish skin gelatin film containing palm oil and basil essential oil with different surfactants. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 56, 93–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acosta, S.; Chiralt, A.; Santamarina, P.; Rosello, J.; Gonzalez-Martínez, C.; Chafer, M. Antifungal films based on starch-gelatin blend, containing essential oils. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanga, W.; Wanga, K.; Xiaoa, J.; Liua, Y.; Zhaoa, Y.; Liua, A. Performance of high amylose starch-composited gelatin filmsinfluenced by gelatinization and concentration. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 94, 258–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM. Standards designations: E96-95. In Annual Book of ASTM Standards; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2011; pp. 406–413. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM. Standard test methods for tensil properties of plastics D638. In Annual Book of ASTM Standards; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010; pp. 46–58. [Google Scholar]
- Aytac, Z.; Ipek, S.; Durgun, E.; Tekinay, T.; Uyar, T. Antibacterial electrospun zein nanofibrous web encapsulating thymol/cyclodextrin-inclusion complex for food packaging. Food Chem. 2017, 233, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, P.; Zhu, D.H.; Wu, H.; Zong, M.H.; Jing, Y.R.; Han, S.Y. Encapsulation of cinnamon essential oil in electrospun nanofibrous film for active food packaging. Food Control 2016, 59, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabra, M.J.; López-Rubio, A.; Cabedo, L.; Lagaron, J.M. Tailoring barrier properties of thermoplastic corn starch-based films (TPCS) by means of a multilayer design. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2016, 483, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahraee, S.; Milani, J.M.; Ghanbarzadeh, B.; Hamishehkar, H. Effect of corn oil on physical, thermal, and antifungal properties of gelatin-based nanocomposite films containing nano chitin. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 76, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeki, B. Chapter 1—Physical Properties of Food Materials. In Food Process Engineering and Technology, 2nd ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2013; pp. 1–27. ISBN 978-0-12-415923-5. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmadzadeh, S.; Nasirpour, A.; Keramat, J.; Desobry, S. Chapter 4—Powerful Solution to Mitigate the Temperature Variation Effect: Development of Novel Superinsulating Materials. In Food Packaging and Preservation; A volume in Handbook of Food Bioengineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherland, 2018; pp. 137–176. ISBN 978-0-12-811516-9. [Google Scholar]
- Carr, J.M.; Mackey, M.; Flandin, L.; Hiltner, A.; Baer, E. Structure and transport properties of polyethylene terephthalate and poly (vinylidene fluoride-co-tetrafluoroethylene) multilayer films. Polymer 2013, 54, 1679–1690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Toro, R.; Contreras, J.; Talens, P.; Chiralt, A. Physical and structural properties and thermal behaviour of starch-poly(e-caprolactone) blend films for food packaging. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2015, 5, 10–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Testin, R.; Vergano, P.; Park, H.; Weller, C. Fatty Acid Distribution and Its Effect on Oxygen Permeability in Laminated Edible Films. J. Food Sci. 1996, 61, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshar, S.; Baniasadi, H. Investigation the effect of graphene oxide and gelatin/starch weight ratio on the properties of starch/gelatin/GO nanocomposite films: The RSM study. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 1019–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez Córdoba, L.J.; Sobral, P.J. Physical and antioxidant properties of films based on gelatin, gelatin chitosan or gelatin-sodium caseinate blends loaded with nanoemulsified active compounds. J. Food Eng. 2017, 213, 47–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueroa-Lopez, K.J.; Andrade-Mahecha, M.M.; Torres-Varga, O.L. Development of Antimicrobial Biocomposite Films to Preserve the Quality of Bread. Molecules 2018, 23, 212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davachi, S.M.; Heidari, B.S.; Hejazi, I.; Seyfi, J.; Oliaei, E.; Farzanehb, A.; Rashedi, H. Interface modified polylactic acid/starch/poly e-caprolactone antibacterial nanocomposite blends for medical applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 155, 336–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Navarro-Baena, I.; Sessini, V.; Dominici, F.; Torre, L.; Kenny, J.M.; Peponi, L. Design of biodegradable blends based on PLA and PCL: From morphological, thermal and mechanical studies to shape memory behavior. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 132, 97–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debiagi, F.; Kobayashi, R.K.; Nakazato, G.; Panagio, L.A.; Mali, S. Biodegradable active packaging based on cassava bagasse, polyvinylalcohol and essential oils. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 52, 664–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pankey, G.A.; Sabath, L.D. Clinical relevance of bacteriostatic versus bactericidal mechanisms of action in the treatment of Gram-Positive Bacterial infections. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2004, 38, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felgentrager, A.; Maisch, T.; Spath, A.; Schroder, J.A.; Baumler, W. Singlet oxygen generation in porphyrin-doped polymeric surface coating enables antimicrobial effects on Staphylococcus aureus. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2014, 16, 20598–20607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dutta, S.; Bhattacharjee, P. Enzyme-assisted supercritical carbon dioxide extraction of black pepper oleoresin for enhanced yield of piperine-rich extract. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2015, 120, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perakis, C.; Louli, V.; Magoulas, K. Supercritical fluid extraction of black pepper oil. J. Food Eng. 2005, 71, 386–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Sample Code | Composition |
|---|---|
| GEL | Gelatin film |
| PCL | Polycaprolactone fibers mats after curing |
| PCL-GEL-PCL (PCL+OR)-GEL-(PCL+OR) | Multilayer system Active multilayer system containing 7 wt % of black pepper oleoresin (OR) |
| Sample Code | Thickness (µm) | WVP × 10−10 (Kg·m−2·s−1·Pa−1) | OP × 10−15 (m3·m−2·s−1·Pa−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GEL | 60 ± 0.05 | 2290 ± 0.2 a | 13.8 ± 1.7 a |
| PCL | 17 ± 0.09 | 2.3 ± 0.5 b | - |
| PCL-GEL-PCL | 76 ± 0.3 | 3.3 ± 0.3 b | 8.2 ± 1.1 a |
| (PCL+OR)-GEL-(PCL+OR) | 79 ± 0.2 | 9.4 ± 0.7 b | - |
| Sample Code | θ (°) |
|---|---|
| GEL | 50.3 ± 6.4 c |
| PCL | 74.3 ± 3.2 b |
| PCL-GEL-PCL | 83.9 ± 1.8 a |
| (PCL+OR)-GEL-(PCL+OR) | 85.6 ± 2.4 a |
| Sample Code | (MPa) | (MPa) | (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| GEL | 1392 ± 220 a | 42 ± 4.3 a | 5.83 ± 1.69 b |
| PCL-GEL-PCL | 883 ± 131 b | 31.2 ± 2.2 b | 15.5 ± 0.2 a |
| (PCL+OR)-GEL-(PCL+OR) | 745 ± 197 b | 29.7 ± 8.4 b | 17.4 ± 3.95 a |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Figueroa-Lopez, K.J.; Castro-Mayorga, J.L.; Andrade-Mahecha, M.M.; Cabedo, L.; Lagaron, J.M. Antibacterial and Barrier Properties of Gelatin Coated by Electrospun Polycaprolactone Ultrathin Fibers Containing Black Pepper Oleoresin of Interest in Active Food Biopackaging Applications. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040199
Figueroa-Lopez KJ, Castro-Mayorga JL, Andrade-Mahecha MM, Cabedo L, Lagaron JM. Antibacterial and Barrier Properties of Gelatin Coated by Electrospun Polycaprolactone Ultrathin Fibers Containing Black Pepper Oleoresin of Interest in Active Food Biopackaging Applications. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(4):199. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040199
Chicago/Turabian StyleFigueroa-Lopez, Kelly Johana, Jinneth Lorena Castro-Mayorga, Margarita María Andrade-Mahecha, Luis Cabedo, and Jose Maria Lagaron. 2018. "Antibacterial and Barrier Properties of Gelatin Coated by Electrospun Polycaprolactone Ultrathin Fibers Containing Black Pepper Oleoresin of Interest in Active Food Biopackaging Applications" Nanomaterials 8, no. 4: 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040199
APA StyleFigueroa-Lopez, K. J., Castro-Mayorga, J. L., Andrade-Mahecha, M. M., Cabedo, L., & Lagaron, J. M. (2018). Antibacterial and Barrier Properties of Gelatin Coated by Electrospun Polycaprolactone Ultrathin Fibers Containing Black Pepper Oleoresin of Interest in Active Food Biopackaging Applications. Nanomaterials, 8(4), 199. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8040199