Electrically Guided DNA Immobilization and Multiplexed DNA Detection with Nanoporous Gold Electrodes
Abstract
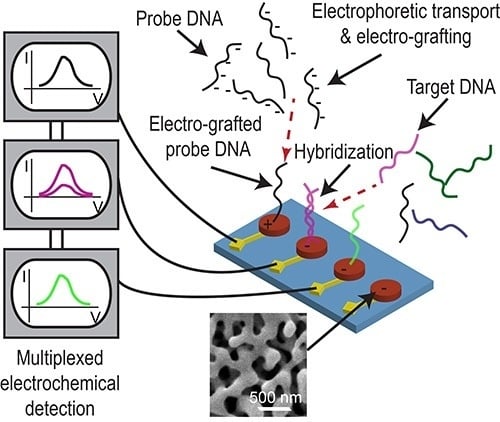
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals and Reagents
2.2. Electrode Fabrication
2.3. Electrode Characterization
2.4. Electro-Grafting Protocol in Macro-Scale Electrochemical Cell
2.5. Hybridization Protocol for Microfluidic Electrochemical Cell
2.6. Electro-Grafting Protocol for Multiplexed Detection
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Electrode Properties
3.2. Influence of Electrode Morphology on Electro-Grafting
3.3. Hybridization Efficiency for Microelectrodes
3.4. Multiplexed Detection of Cancer Markers
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Overview of the Integrated Device and Macro-Scale Electrochemical Cell

Appendix A.2. Fabrication of Nanoporous Gold Electrodes

Appendix A.3. Fabrication of Microfluidic Channels

Appendix A.4. Preparation of DNA Sensor
- Probe ssDNA: 5ThioMC6-D/CGT GTT ATA AAA TGT AAT TTG GAA TT;
- Target DNA: AAT TCC AAA TTA CAT TTT ATA ACA CG
- BRCA1 probe: 5ThioMC6-D/GATTTTCTTCCTTTTGTTC
- BRCA2 probe: 5ThioMC6-D/TACGGCCCTGAAGTACA
- p53 probe: 5ThioMC6-D/TCCTCCGGTTCATGCCA
- BRCA1 target: GAACAAAAGGAAGAAAATC
- BRCA2 target: TGTACTTCAGGGCCGTA
- p53 target: TGGCATGAACCGGAGGA
Appendix B
Appendix B.1. Electrochemical Methods and Square Wave Voltammetry (SWV) Raw Data




Appendix B.2. Mercaptohexanol (MCH) Incubation Optimization for Different np-Au Morphologies


References
- Cederquist, K.B.; Kelley, S.O. Nanostructured biomolecular detectors: Pushing performance at the nanoscale. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2012, 16, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Li, P.C.H. Microfluidic DNA microarray analysis: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2011, 687, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldhirsch, A.; Wood, W.C.; Coates, A.S.; Gelber, R.D.; Thurlimann, B.; Senn, H.J.; Panel, M. Strategies for subtypes-dealing with the diversity of breast cancer: Highlights of the St Gallen International Expert Consensus on the Primary Therapy of Early Breast Cancer 2011. Ann. Oncol. 2011, 22, 1736–1747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sassolas, A.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D.; Blum, L.J. DNA biosensors and microarrays. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 109–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheek, B.J.; Steel, A.B.; Torres, M.P.; Yu, Y.Y.; Yang, H.J. Chemiluminescence detection for hybridization assays on the flow-thru chip, a three-dimensional microchannel biochip. Anal. Chem. 2001, 73, 5777–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lord, H.; Kelley, S.O. Nanomaterials for ultrasensitive electrochemical nucleic acids biosensing. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 3127–3134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, S.; Rao, T.P.; Rao, K.S.; Rani, S.U.; Naidu, G.R.K.; Lee, H.Y.; Kawai, T. A review of DNA functionalized/grafted carbon nanotubes and their characterization. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2007, 122, 672–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparac, R.; Taft, B.J.; Lapierre-Devlin, M.A.; Lazareck, A.D.; Xu, J.M.; Kelley, S.O. Ultrasensitive electrocatalytic DNA detection at two- and three-dimensional nanoelectrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126, 12270–12271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bin, X.M.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Nanostructuring of Sensors Determines the Efficiency of Biomolecular Capture. Anal. Chem. 2010, 82, 5928–5931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleymani, L.; Fang, Z.C.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. Programming the detection limits of biosensors through controlled nanostructuring. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 4, 844–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Kim, H.C.; Chung, T.D. Electrochemical analysis based on nanoporous structures. Analyst 2012, 137, 3891–3903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.; Park, S.; Chung, T.D.; Kim, H.C. Integration of a nanoporous platinum thin film into a microfluidic system for non-enzymatic electrochemical glucose sensing. Anal. Sci. 2007, 23, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, J.; Ivanov, I.; Montermini, L.; Rak, J.; Sargent, E.H.; Kelley, S.O. An electrochemical clamp assay for direct, rapid analysis of circulating nucleic acids in serum. Nat. Chem. 2015, 7, 569–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, J.; Kelley, S.O. Tuning the Bacterial Detection Sensitivity of Nanostructured Microelectrodes. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 7333–7338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daggumati, P.; Appelt, S.; Matharu, Z.; Marco, M.L.; Seker, E. Sequence-Specific Electrical Purification of Nucleic Acids with Nanoporous Gold Electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 7711–7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daggumati, P.; Matharu, Z.; Seker, E. Effect of Nanoporous Gold Thin Film Morphology on Electrochemical DNA Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8149–8156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daggumati, P.; Matharu, Z.; Wang, L.; Seker, E. Biofouling-Resilient Nanoporous Gold Electrodes for DNA Sensing. Anal. Chem. 2015, 87, 8618–8622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matharu, Z.; Daggumati, P.; Wang, L.; Dorofeeva, T.S.; Li, Z.D.; Seker, E. Nanoporous-Gold-Based Electrode Morphology Libraries for Investigating Structure-Property Relationships in Nucleic Acid Based Electrochemical Biosensors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 12959–12966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanaviciene, A.; Ramanavicius, A. Pulsed amperometric detection of DNA with an ssDNA/polypyrrole-modified electrode. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 379, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hong, J.; Edel, J.B.; de Mello, A.J. Micro- and nanofluidic systems for high-throughput biological screening. Drug Discov. Today 2009, 14, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edman, C.F.; Raymond, D.E.; Wu, D.J.; Tu, E.G.; Sosnowski, R.G.; Butler, W.F.; Nerenberg, M.; Heller, M.J. Electric field directed nucleic acid hybridization on microchips. Nucl. Acids Res. 1997, 25, 4907–4914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fixe, F.; Branz, H.M.; Louro, N.; Chu, V.; Prazeres, D.M.F.; Conde, J.P. Electric-field assisted immobilization and hybridization of DNA oligomers on thin-film microchips. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2061–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gultepe, E.; Nagesha, D.; Sridhar, S.; Amiji, M. Nanoporous inorganic membranes or coatings for sustained drug delivery in implantable devices. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 305–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howorka, S.; Siwy, Z. Nanopore analytics: Sensing of single molecules. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2360–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, P. Soft matter in hard confinement: phase transition thermodynamics, structure, texture, diffusion and flow in nanoporous media. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2015, 27, 103102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finch, A.; Metcalfe, K.; Lui, J.; Springate, C.; Demsky, R.; Armel, S.; Rosen, B.; Murphy, J.; Elit, L.; Sun, P.; et al. Breast and ovarian cancer risk perception after prophylactic salpingo-oophorectomy due to an inherited mutation in the BRCA1 or BRCA2 gene. Clin. Genet. 2009, 75, 220–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levine, A.J. p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 1997, 88, 323–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Seker, E. Configurable microfluidic platform for investigating therapeutic delivery from biomedical device coatings. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 3331–3337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erlebacher, J.; Aziz, M.J.; Karma, A.; Dimitrov, N.; Sieradzki, K. Evolution of nanoporosity in dealloying. Nature 2001, 410, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.D.; Hu, D.; Zhao, Z.T.; Zhou, M.Y.; Liu, R.; Lo, J.F. Balancing oxygen diffusion and convection in spiral microfluidics to mimic radial biological gradients. Biomed. Microdevices 2015, 17, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matharu, Z.; Bandodkar, A.J.; Gupta, V.; Malhotra, B.D. Fundamentals and application of ordered molecular assemblies to affinity biosensing. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 1363–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scanlon, M.D.; Salaj-Kosla, U.; Belochapkine, S.; MacAodha, D.; Leech, D.; Ding, Y.; Magner, E. Characterization of nanoporous gold electrodes for bioelectrochemical applications. Langmuir 2011, 28, 2251–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heinze, J. Ultramicroelectrodes in electrochemistry. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1993, 32, 1268–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerman, K.; Ozkan, D.; Kara, P.; Meric, B.; Gooding, J.J.; Ozsoz, M. Voltammetric determination of DNA hybridization using methylene blue and self-assembled alkanethiol monolayer on gold electrodes. Anal. Chim. Acta 2002, 462, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collinson, M.M. Nanoporous gold electrodes and their applications in analytical chemistry. ISRN Anal. Chem. 2013, 2013, 692484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seker, E.; Gaskins, J.; Bart-Smith, H.; Zhu, J.; Reed, M.; Zangari, G.; Kelly, R.; Begley, M. The effects of annealing prior to dealloying on the mechanical properties of nanoporous gold microbeams. Acta Mater. 2007, 56, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtulus, O.; Daggumati, P.; Seker, E. Molecular release from patterned nanoporous gold thin films. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 7062–7071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, I.Y.; Melosh, N.A. Directed hybridization and melting of DNA linkers using counterion-screened electric fields. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 3521–3526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peterson, A.W.; Heaton, R.J.; Georgiadis, R.M. The effect of surface probe density on DNA hybridization. Nucl. Acids Res. 2001, 29, 5163–5168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, F.; Lai, R.Y.; Heeger, A.J.; Plaxco, K.W.; Sumner, J.J. Effect of molecular crowding on the response of an electrochemical DNA sensor. Langmuir 2007, 23, 6827–6834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soleymani, L.; Li, F. Mechanistic challenges and advantages of biosensor miniaturization into the nanoscale. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmueser, I.; Walton, A.J.; Terry, J.G.; Woodvine, H.L.; Freeman, N.J.; Mount, A.R. A systematic study of the influence of nanoelectrode dimensions on electrode performance and the implications for electroanalysis and sensing. Faraday Discuss. 2013, 164, 295–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schwarzenbach, H. Circulating nucleic acids as biomarkers in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. 2013, 15, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steel, A.B.; Levicky, R.L.; Herne, T.M.; Tarlov, M.J. Immobilization of nucleic acids at solid surfaces: Effect of oligonucleotide length on layer assembly. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 975–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Veselinovic, J.; Li, Z.; Daggumati, P.; Seker, E. Electrically Guided DNA Immobilization and Multiplexed DNA Detection with Nanoporous Gold Electrodes. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050351
Veselinovic J, Li Z, Daggumati P, Seker E. Electrically Guided DNA Immobilization and Multiplexed DNA Detection with Nanoporous Gold Electrodes. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(5):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050351
Chicago/Turabian StyleVeselinovic, Jovana, Zidong Li, Pallavi Daggumati, and Erkin Seker. 2018. "Electrically Guided DNA Immobilization and Multiplexed DNA Detection with Nanoporous Gold Electrodes" Nanomaterials 8, no. 5: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050351
APA StyleVeselinovic, J., Li, Z., Daggumati, P., & Seker, E. (2018). Electrically Guided DNA Immobilization and Multiplexed DNA Detection with Nanoporous Gold Electrodes. Nanomaterials, 8(5), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050351