Fabrication Flexible and Luminescent Nanofibrillated Cellulose Films with Modified SrAl2O4: Eu, Dy Phosphors via Nanoscale Silica and Aminosilane
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
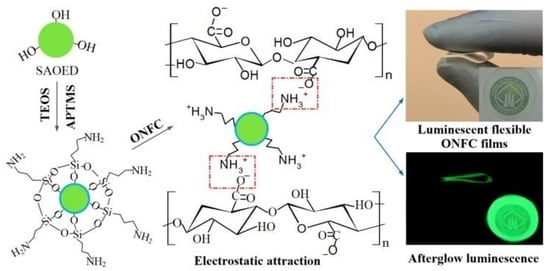
2.2. Surface Modification of SAOED Phosphors
2.3. Fabrication of Luminescent ONFC Composite Films
2.4. Characterization
3. Results and discussions
3.1. Surface Modification of SAOED Phosphors
3.2. Preparation of Suspension and Luminescent Composite Films
3.3. Characterization of Luminescent Films with Modified Phosphors
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kasuga, T.; Isobe, N.; Yagyu, H.; Koga, H.; Nogi, M. Clearly transparent nanopaper from highlyconcentrated cellulose nanofiber dispersion using dilution and sonication. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, Y.; Liu, H.; Gao, R.; Xiao, S.; Zhang, M.; Yin, Y.; Wang, S.; Li, J.; Yang, D. Coherent interface assembled Ag2O anchored nanofibrillated cellulose porous aerogels for radioactive iodine capture. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 29179–29185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benhamou, K.; Dufresne, A.; Magnin, A.; Mortha, G.; Kaddami, H. Control of size and viscoelastic properties of nanofibrillated cellulose from palm tree by varying the TEMPO-mediated oxidation time. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 99, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Fan, D.; Han, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, S. Length-controlled cellulose nanofibrils produced using enzyme pretreatment and grinding. Cellulose 2017, 24, 5431–5442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virtanen, S.; Vuoti, S.; Heikkinen, H.; Lahtinen, P. High strength modified nanofibrillated cellulose-polyvinyl alcohol films. Cellulose 2014, 21, 3561–3571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Chen, Z.; Lyu, S.; Fu, F.; Wang, S. Highly flexible cross-linked cellulose nanofibril sponge-like aerogels with improved mechanical property and enhanced flame retardancy. Carbohydr. Polym. 2018, 179, 333–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uetani, K.; Okada, T.; Oyama, H.T. Thermally conductive and optically transparent flexible films with surface-exposed nanocellulose skeletons. J. Mater. Chem. C 2016, 4, 9697–9703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.; Chang, H.; Fu, F.; Hu, L.; Huang, J.; Wang, S. Cellulose-coupled graphene/ polypyrrole composite electrodes containing conducting networks built by carbon fibers as wearable supercapacitors with excellent foldability and tailorability. J. Power Sources 2016, 327, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, W.; Ran, M.; Lu, H.; Yang, Y. Recent advances of rare-earth ion doped luminescent nanomaterials in perovskite solar cells. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kontturi, E.; Laaksonen, P.; Linder, M.B.; Gröschel, A.H.; Rojas, O.J.; Ikkala, O. Advanced materials through assembly of nanocelluloses. Adv. Mater. 2018, 1703779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M.; Zhao, J.; Feng, X.; Cao, Y.; Cao, S.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, X.; Sun, L.; Shi, L.; Fang, J. Fast fabrication of transparent and multi-luminescent TEMPO-oxidized nanofibrillated cellulose nanopaper functionalized with lanthanide complexes. J. Mater. Chem. C 2015, 3, 2511–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.; Peng, J.; Zhang, L.; Pang, D. Strongly fluorescent hydrogels with quantum dots embedded in cellulose matrices. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 7771–7776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, C.; Li, J. Embedding ZnO nanorods into porous cellulose aerogels via a facile one-step low-temperature hydrothermal method. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 620–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toivonen, M.S.; Onelli, O.D.; Jacucci, G.; Lovikka, V.; Rojas, O.J.; Ikkala, O.; Vignolini, S. Anomalous-diffusion-assisted brightness in white cellulose nanofibril membranes. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagata, E.; Ara, T.; Nakano, H. Mechanochromic luminescence of 1-alkanoylaminopyrenes adsorbed onto cellulose papers. Dyes Pigments 2017, 141, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Wei, Z.; Feng, X.; Miao, M.; Sun, L.; Cao, S.; Shi, L.; Fang, J. Luminescent and transparent nanopaper based on rare-earth up-converting nanoparticle grafted nanofibrillated cellulose derived from garlic skin. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 14945–14951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Pan, L.; Piao, X.; Sun, Z. Long afterglow SrAl2O4:Eu, Dy phosphors for CdS quantum dot-sensitized solar cells with enhanced photovoltaic performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 6388–6392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, F.; Wei, S.; Gao, J.; Huang, Z.; Ding, X.; Tang, C. Fabrication of BN nanosheets-coated SrAl2O4:Eu2+ as a new water-resistant phosphor by a one-pot method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2008, 108, 440–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, T.; Liu, H.; Yang, H.; Yan, C. Synthesis of SrAl2O4:Eu, Dy phosphor nanometer powders by sol–gel processes and its optical properties. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2004, 85, 68–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Ye, S.; Wang, D.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H. Surface modification of SrAl2O4: Eu2+, Dy3+ and Sr4Al14O25:Eu2+, Dy3+ long lasting phosphors and their application in water-borne paint. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 2, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, H.; Chang, C.; Zhang, L. Properties and applications of biodegradable transparent and photoluminescent cellulose films prepared via a green process. Green Chem. 2009, 11, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Ge, M. Effect of red emitting fluorescent pigment on fluorescent color of SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphors. J. Rare Earths 2017, 35, 247–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Hirata, G.A.; Farías, M.H.; Castillón, F.F. Synthesis and characterization of (3-Aminopropyl) trimethoxy-silane (APTMS) functionalized Gd2O3:Eu3+ red phosphor with enhanced quantum yield. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 065601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Zhang, S.; Yang, J. Highly water-resistant and organic miscible inorganic/polymer composite luminescent material. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 1172–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Wang, Y.; Ding, D.; Zhang, X.; Yang, W. Water resistance of rare earth fluorescent bamboo plastic composites modified with hydrogen silicone oil. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 2015, 31, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Qu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chu, H. Effect of the composition of lanthanide complexes on their luminescence enhancement by Ag@SiO2 core-shell nanoparticles. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qi, T.; Xia, H.; Zhang, Z.; Kong, S.; Peng, W.; Zhao, Q.; Huang, Z. Improved water resistance of SrAl2O4: Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphor directly achieved in a water-containing medium. Solid State Sci. 2017, 65, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Ge, M.; Fu, S.; Lin, T. Superhydrophobic and luminescent cotton fabrics prepared by dip-coating of APTMS modified SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Dy3+ particles in the presence of SU8 and fluorinated alkyl silane. J. Rare Earths 2016, 34, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Ma, H.; Li, Y. Preparation and characterization of cellulose-strontium aluminate composite films. J. Cellul. Sci. Technol. 2011, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Y.; Moser, C.; Lindström, M.E.; Henriksson, G.; Li, J. Cellulose nanofibers from softwood, hardwood, and tunicate: Preparation-structure-film performance interrelation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 13508–13519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soni, B.; Schilling, M.W.; Mahmoud, B. Transparent bionanocomposite films based on chitosan and TEMPO-oxidized cellulose nanofibers with enhanced mechanical and barrier properties. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 151, 779–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junka, K.; Guo, J.; Filpponen, I.; Laine, J.; Rojas, O.J. Modification of cellulose nanofibrils with luminescent carbon dots. Biomacromolecules 2014, 15, 876–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, J.; Carrasco-Hernandez, S.; Barud, H.S.; Oliveira, R.L.; Carvalho, R.A.; Amaral, A.C.; Tercjak, A. Transparent nanostructured cellulose acetate films based on the self assembly of PEO-b-PPO-b-PEO block copolymer. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 165, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Z.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, A.; Lyu, W.; Wang, Y.; Geng, H.; Wang, J.; Qin, M. Fabrication of cellulose self-assemblies and high-strength ordered cellulose films. Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 117, 414–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyu, X. Silica encapsulation study on SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphors. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2005, 93, 526–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamaura, M.; Camilo, R.L.; Sampaio, L.C.; Macêdo, M.A.; Nakamura, M.; Toma, H.E. Preparation and characterization of (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane-coated magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2004, 279, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Sun, R.; Du, H. Improved moisture resistance of SrSO4: Sm3+ phosphors coated with SiO2. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 4569–4573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, S.Y.; Karacaoglu, E.; Karasu, B. Effect of Al/Sr ratio on the luminescence properties of SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphors. Ceram. Int. 2012, 38, 3701–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mothudi, B.M.; Ntwaeaborwa, O.M.; Kumar, A.; Sohn, K.; Swart, H.C. Phosphorescent and thermoluminescent properties of SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphors prepared by solid state reaction method. Physica B 2012, 407, 1679–1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sideridou, I.D.; Karabela, M.M. Effect of the amount of 3-methacyloxypropyl-trimethoxysilane coupling agent on physical properties of dental resin nanocomposites. Dent. Mater. 2009, 25, 1315–1324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.; Wang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Hu, Z.; Liu, C. Modification on luminescent properties of SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Dy3+ phosphor by Yb3+ ions doping. J. Lumin. 2008, 128, 1180–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clabau, F.; Rocquefelte, X.; Jobic, S.; Deniard, P.; Whangbo, M.H.; Garcia, A.; Mercier, T.L. Mechanism of phosphorescence appropriate for the long-lasting phosphors Eu2+-doped SrAl2O4 with codopants Dy3+ and B3+. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 3904–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adegoke, O.; Seo, M.W.; Kato, T.; Kawahito, S.; Park, E.Y. An ultrasensitive SiO2-encapsulated alloyed CdZnSeS quantum dot-molecular beacon nanobiosensor for norovirus. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 86, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, W.; Wang, M.; Sun, Y.; Huang, W.; Cui, Y.; Xu, C. Color-tuned FRET polystyrene microspheres by single wavelength excitation. Opt. Mater. 2008, 30, 1803–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Han, G.; Zhang, L.; Yang, B. Gel combustion synthesis and luminescence properties of nanoparticles of monoclinic SrAl2O4:Eu2+, Dy3+. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2009, 113, 255–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, L.; Lyu, S.; Chen, Z.; Wang, S. Fabrication Flexible and Luminescent Nanofibrillated Cellulose Films with Modified SrAl2O4: Eu, Dy Phosphors via Nanoscale Silica and Aminosilane. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050352
Zhang L, Lyu S, Chen Z, Wang S. Fabrication Flexible and Luminescent Nanofibrillated Cellulose Films with Modified SrAl2O4: Eu, Dy Phosphors via Nanoscale Silica and Aminosilane. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(5):352. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050352
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Longfei, Shaoyi Lyu, Zhilin Chen, and Siqun Wang. 2018. "Fabrication Flexible and Luminescent Nanofibrillated Cellulose Films with Modified SrAl2O4: Eu, Dy Phosphors via Nanoscale Silica and Aminosilane" Nanomaterials 8, no. 5: 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050352
APA StyleZhang, L., Lyu, S., Chen, Z., & Wang, S. (2018). Fabrication Flexible and Luminescent Nanofibrillated Cellulose Films with Modified SrAl2O4: Eu, Dy Phosphors via Nanoscale Silica and Aminosilane. Nanomaterials, 8(5), 352. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050352