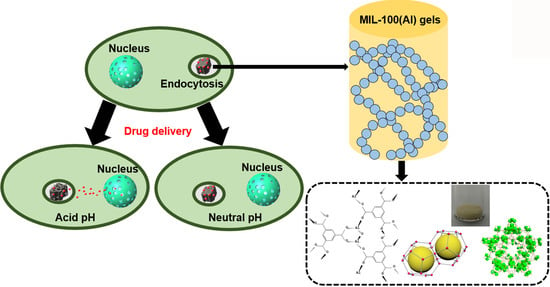
MIL-100(Al) Gels as an Excellent Platform Loaded with Doxorubicin Hydrochloride for pH-Triggered Drug Release and Anticancer Effect
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Synthesis of MIL-100(Al) Gels
2.3. Incorporation of DOX
2.4. Drug Release
2.5. Cell Cytotoxicity of DOX-Loaded MOGs
2.6. Flow Cytometry
2.7. Fluorescence Microscopy Images
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Morphology and Structure Characterization of MIL-100(Al) Gels
3.2. Drug Loading and Release Behaviors
3.3. Cell Cytotoxicity of DOX-Loaded MOGs
3.4. Flow Cytometry
3.5. Fluorescence Microscopy Images
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jain, R.K.; Stylianopoulos, T. Delivering nanomedicine to solid tumors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2010, 7, 653–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Davis, M.E.; Chen, Z.; Shin, D.M. Nanoparticle therapeutics: An emerging treatment modality for cancer. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 771–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maeda, H.; Nakamura, H.; Fang, J. The EPR effect for macromolecular drug delivery to solid tumors: Improvement of tumor uptake, lowering of systemic toxicity, and distinct tumor imaging in vivo. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Ai, K.; Liu, J.; Sun, G.Y.; Yin, Q.; Lu, L.H. Multifunctional envelope-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles for pH-responsive drug delivery and magnetic resonance imaging. Biomaterials 2015, 60, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chowdhuri, A.R.; Singh, T.; Ghosh, S.K.; Sahu, S.K. Carbon dots embedded magnetic nanoparticles @chitosan @metal organic framework as a nanoprobe for pH sensitive targeted anticancer drug delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 16573–16583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.Y.; Teng, Z.; Yao, H.; Wang, S.J.; Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y.L.; Liu, W.F.; Tian, W.; Zheng, L.J.; Lu, N.; et al. A multifunctional PB@mSiO2−PEG/DOX nanoplatform for combined photothermal−chemotherapy of tumor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 17038–17046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalvandi, J.; White, M.; Gao, Y.; Truong, Y.B.; Padhye, R.; Kyratzis, I.L. Polyvinyl alcohol composite nanofibres containing conjugated levofloxacin-chitosan for controlled drug release. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 73, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, D.D.; Zhou, J.J.; Chen, R.H.; Shi, R.H.; Zhao, G.Z.; Xia, G.L.; Li, R.; Liu, Z.B.; Tian, J.; Wang, H.J.; et al. Controllable synthesis of dual-MOFs nanostructures for pH-responsive artemisinin delivery, magnetic resonance and optical dual-model imaging-guided chemo/photothermal combinational cancer therapy. Biomaterials 2016, 100, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, D.; Timmons, D.J.; Yuan, D.; Zhou, H.C. Tuning the Topology and Functionality of Metal−Organic Frameworks by Ligand Design. Acc. Chem. Res. 2011, 44, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corma, A.; Garcia, H.; Llabres, F.X.; Xamena, I. Engineering Metal Organic Frameworks for Heterogeneous Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4606–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keskin, S.; Kizilel, S. Biomedical Applications of Metal Organic Frameworks. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 1799–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Chen, X.H.; Hou, G.H.; Guan, R.F.; Shao, R.; Xie, M.H. A multiresponsive metal–organic framework: Direct chemiluminescence, photoluminescence, and dual tunable sensing applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, R.; Kim, K.H.; Paul, A.K.; Deep, A. Recent advances in the photovoltaic applications of coordination polymers and metal organic frameworks. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 3991–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Guo, K.; Wu, C.; Shu, L.; Guo, S.; Hou, J.; Zhao, N.; Wei, L.; Man, X.; Zhang, L. Controlled and Targeted Drug Delivery by a UV-responsive Liposome for Overcoming Chemo-resistance in Non-Hodgkin Lymphoma. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 2015, 86, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, F.; Ji, X.; Li, Y.; Shi, J. A pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles-based multi-drug delivery system for overcoming multi-drug resistance. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 7711–7720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunzio, M.R.; Agostoni, V.; Cohen, B.; Gref, R.; Douhal, A. A “Ship in a Bottle” Strategy to Load a Hydrophilic Anticancer Drug in Porous Metal Organic Framework Nanoparticles: Efficient Encapsulation, Matrix Stabilizationand Photodelivery. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, K.K.; Li, L.; Yu, X.L.; Liu, L.; Meng, Q.T.; Wang, F.; Zhang, R. Functionalization of mixed ligand metal-organic frame-works as the transport vehicles for drugs. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 486, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasconcelos, I.B.; Silva, T.G.; Militao, G.C.; Soares, T.A.; Rodrigues, N.M.; Rodrigues, M.O.; Freire, N.B.; Junior, S.A. Cytotoxicity and slow release of the anti-cancer drug doxorubicin from ZIF-8. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 9437–9442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, S.; Mondal, R. Metal-Organic-Particle-Supported Metallogel Formation Using a Nonconventional Chelating Pyridine-Pyrazole-Based Bis-Amide Ligand. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 5537–5541. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Su, C.Y. Metal-organic gels: From discrete to coordination polymers. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2013, 257, 1373–1408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, B.; Zhang, Q.; Huang, C.; Li, Y. Luminescent Zn(II)–terpyridine metal organic gel for visual recognition of anions. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 2857–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiyappa, H.B.; Saha, S.; Wadge, P.; Banerjee, R.S. Fe(III) phytatemetallogel as a prototype anhydrous, intermediate temperature proton conductor. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, M.; Mi, K.; Zhang, J.H.; Liu, H.L.; Yu, T.T.; Yuan, A.; Kong, Q.; Xiong, S. MOF-derived bi-metal embedded N-doped carbon polyhedral nanocages with enhanced lithium storage. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.S.; Yu, Q.; Li, J. Synthetic Methodology for the Fabrication of Porous Porphyrin Materials with Metal-Organic-Polymer Aerogels. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 5287–5296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Xiang, S.L.; Cao, S.Q.; Zhang, J.Y.; Ouyang, G.F.; Chen, L.P.; Su, C.Y. A synthetic route to ultralight hierarchically micro/mesoporousAl(III)-carboxylate metal-organic aerogels. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1774–1782. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmood, A.; Xia, W.; Mahmood, N.; Wang, Q.F.; Zou, R.Q. Hierarchical heteroaggregation of binary metal-organic gels with tunable porosity and mixed valence metal sites for removal of dyes in water. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sutar, P.; Maji, T.K. Coordination polymer gels: Soft metal–organic supramolecular materials and versatile applications. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 8055–8074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.R.; He, L.; Zhang, J.; Wang, X.; Su, C.Y. Evolution of spherical assemblies to fibrous networked Pd(II) metallo gels from a pyridine-based tripodal ligand and their catalytic property. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 557–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, W.; Zhang, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, Y.; Lin, J.; Zou, R. Facile and economical synthesis of metal–organicframework MIL-100(Al) gels for high efficiency removalof microcystin-LR. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 11007–11013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkringer, C.; Popov, D.; Loiseau, T.; Ferey, G.; Burghammer, M.; Riekel, C.; Haouas, M.; Taulelle, F. Synthesis, Single-Crystal X-ray Microdiffraction, and NMR Characterizations of the Giant Pore Metal-Organic Framework Aluminum Trimesate MIL-100. Chem. Mater. 2009, 21, 5695–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjmez, G.P.; Cabello, C.P.; Opanasenko, M.; Horacek, M.; Cejka, J. Superior Activity of Isomorphously Substituted MOFs with MIL-100 (M = Al, Cr, Fe, In, Sc, V) Structure in the Prins Reaction: Impact of Metal Type. ChemPlusChem 2017, 82, 152–159. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, S.Y.; Ang, C.Y.; Mahmood, A.; Qu, Q.; Li, P.; Zou, R.; Zhao, Y.L. Doxorubicin-Loaded Metal-Organic Gels for pH and Glutathione Dual-Responsive Release. ChemNanoMat 2016, 2, 504–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayal, S.; Ramanujan, R.V. Doxorubicin loaded PVA coated iron oxide nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2010, 30, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Grailer, J.J.; Rowland, I.J.; Javadi, A.; Hurley, S.A.; Matson, V.Z. Multifunctional Stable and pH-Responsive Polymer Vesicles Formed by Heterofunctional Triblock Copolymer for Targeted Anticancer Drug Delivery and Ultrasensitive MR Imaging. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6805–6817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Zong, E.; Fu, H.; Zheng, S.; Xu, Z.; Zhu, D. Adsorption of aromatic compounds on porous covalent triazine-based framework. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2012, 372, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, X.; Hao, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, P.C.; Zou, G.; Liang, X.J. Multifunctional Hybrid Silica Nanoparticles for Controlled Doxorubicin Loading and Release with Thermal and pH Dual Response. J. Mater. Chem. B 2013, 1, 1109–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, Y.; Wang, C.; Ke, F.; Zang, J.; Zhu, J. MIL-100(Al) Gels as an Excellent Platform Loaded with Doxorubicin Hydrochloride for pH-Triggered Drug Release and Anticancer Effect. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8060446
Feng Y, Wang C, Ke F, Zang J, Zhu J. MIL-100(Al) Gels as an Excellent Platform Loaded with Doxorubicin Hydrochloride for pH-Triggered Drug Release and Anticancer Effect. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(6):446. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8060446
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Yuge, Chengliang Wang, Fei Ke, Jianye Zang, and Junfa Zhu. 2018. "MIL-100(Al) Gels as an Excellent Platform Loaded with Doxorubicin Hydrochloride for pH-Triggered Drug Release and Anticancer Effect" Nanomaterials 8, no. 6: 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8060446
APA StyleFeng, Y., Wang, C., Ke, F., Zang, J., & Zhu, J. (2018). MIL-100(Al) Gels as an Excellent Platform Loaded with Doxorubicin Hydrochloride for pH-Triggered Drug Release and Anticancer Effect. Nanomaterials, 8(6), 446. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8060446