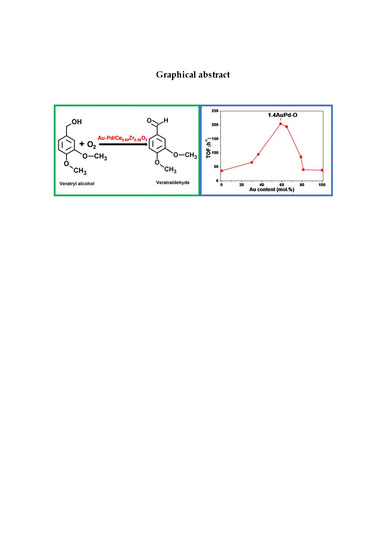
Selective Oxidation of Veratryl Alcohol over Au-Pd/Ce0.62Zr0.38O2 Catalysts Synthesized by Sol-Immobilization: Effect of Au:Pd Molar Ratio
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Catalyst Preparation
2.2. Catalyst Characterization
2.3. Catalytic Activity for Veratryl Alcohol Oxidation
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Textural and Structural Properties
3.2. STEM Results
3.3. XPS Results
3.4. TPR Results
3.5. Catalytic Activity for Veratryl Alcohol Oxidation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Holladay, J.E.; White, J.F.; Bozell, J.J.; Johnson, D. Top Value-Added Chemicals from Biomass Volume II—Results of Screening for Potential Candidates from Biorefinery Lignin; Pacific Northwest National Lab. (PNNL): Richland, WA, USA, 2007; Volume II, p. 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhao, X.; Wang, A.; Huber, G.W.; Zhang, T. Catalytic transformation of lignin for the production of chemicals and fuels. Chem. Rev. 2015, 115, 11559–11624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collinson, S.R.; Thielemans, W. The catalytic oxidation of biomass to new materials focusing on starch, cellulose and lignin. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2010, 254, 1854–1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lange, H.; Decina, S.; Crestini, C. Oxidative upgrade of lignin–Recent routes reviewed. Eur. Polym. J. 2013, 49, 1151–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Behling, R.; Valange, S.; Chatel, G. Heterogeneous catalytic oxidation for lignin valorization into valuable chemicals: What results? what limitations? what trends? Green Chem. 2016, 18, 1839–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, Q.; Lee, Y.Y. Oxidative cracking of precipitated hardwood lignin by hydrogen peroxide. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2000, 1–9, 153–162. [Google Scholar]
- Deng, W.; Zhang, H.; Wu, X.; Li, R.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, Y. Oxidative conversion of lignin and lignin model compounds catalyzed by CeO2-supported Pd nanoparticles. Green Chem. 2015, 17, 5009–5018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawange, M.; Galkin, M.V.; Samec, J.S.M. Selective aerobic benzylic alcohol oxidation of lignin model compounds: Route to aryl ketones. ChemCatChem. 2015, 7, 401–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mate, V.R.; Jha, A.; Joshi, U.D.; Patil, K.R.; Shirai, M.; Rode, C.V. Effect of preparation parameters on characterization and activity of Co3O4 catalyst in liquid phase oxidation of lignin model substrates. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2014, 487, 130–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badamali, S.K.; Luque, R.; Clark, J.H.; Breeden, S.W. Unprecedented oxidative properties of mesoporous silica materials: Towards microwave-assisted oxidation of lignin model compounds. Catal. Commun. 2013, 31, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hara, M.; Nakajima, K.; Kamata, K. Recent progress in the development of solid catalysts for biomass conversion into high value-added chemicals. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2015, 16, 34903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zakzeski, J.; Dbczak, A.; Bruijnincx, P.C.A.; Weckhuysen, B.M. Catalytic oxidation of aromatic oxygenates by the heterogeneous catalyst Co-ZIF-9. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2011, 394, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melián-Rodríguez, M.; Saravanamurugan, S.; Kegnæs, S.; Riisager, A. Aerobic oxidation of veratryl alcohol to veratraldehyde with heterogeneous ruthenium catalysts. Top. Catal. 2015, 58, 1036–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villa, A.; Wang, D.; Su, D.S.; Prati, L. New challenges in gold catalysis: Bimetallic systems. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2015, 5, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sankar, M.; Dimitratos, N.; Miedziak, P.J.; Wells, P.P.; Kiely, C.J.; Hutchings, G.J. Designing bimetallic catalysts for a green and sustainable future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 8099–8139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olmos, C.M.; Chinchilla, L.E.; Rodrigues, E.G.; Delgado, J.J.; Hungría, A.B.; Blanco, G.; Pereira, M.F.R.; Órfão, J.J.M.; Calvino, J.J.; Chen, X. Synergistic effect of bimetallic Au-Pd supported on ceria-zirconia mixed oxide catalysts for selective oxidation of glycerol. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2016, 197, 222–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Xie, Y.; Sun, Z.; Tao, R.; Huang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Z. In-situ loading ultrafine AuPd particles on ceria: Highly active catalyst for solvent-free selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol. Langmuir 2011, 27, 1152–1157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abad, A.; Concepción, P.; Corma, A.; García, H. A collaborative effect between gold and a support induces the selective oxidation of alcohols. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2005, 44, 4066–4069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vlaic, G.; Di Monte, R.; Fornasiero, P.; Fonda, E.; Kašpar, J.; Graziani, M. Redox property–local structure relationships in the Rh-loaded CeO2–ZrO2 mixed oxides. J. Catal. 1999, 182, 378–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katabathini, N.; Ali, T.T. Catalytic oxidative cracking of propane over nanosized gold supported Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 catalysts. Catal. Lett. 2013, 143, 1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olmos, C.M.; Chinchilla, L.E.; Villa, A.; Delgado, J.J.; Pan, H.; Hungría, A.B.; Blanco, G.; Calvino, J.J.; Prati, L.; Chen, X. Influence of pretreatment atmospheres on the performance of bimetallic Au-Pd supported on ceria-zirconia mixed oxide catalysts for benzyl alcohol oxidation. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2016, 525, 145–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Haro, M.; Delgado, J.J.; Cies, J.M.; Del Rio, E.; Bernal, S.; Burch, R.; Cauqui, M.A.; Trasobares, S.; Pérez-Omil, J.A.; Bayle-Guillemaud, P.; et al. Bridging the gap between CO adsorption studies on gold model surfaces and supported nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 1981–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cíes, J.M.; Del Río, E.; López-Haro, M.; Delgado, J.J.; Blanco, G.; Collins, S.; Calvino, J.J.; Bernal, S. Fully reversible metal deactivation effects in gold/ceria-zirconia catalysts: Role of the redox state of the support. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 9744–9748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villa, A.; Janjic, N.; Spontoni, P.; Wang, D.; Su, D.S.; Prati, L. Au–Pd/AC as catalysts for alcohol oxidation: Effect of reaction parameters on catalytic activity and selectivity. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2009, 364, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Olmos, C.M.; Chinchilla, L.E.; Delgado, J.J.; Hungría, A.B.; Blanco, G.; Calvino, J.J.; Chen, X. CO oxidation over bimetallic Au-Pd supported on ceria-zirconia catalysts: Effects of oxidation temperature and Au:Pd molar ratio. Catal. Lett. 2016, 146, 144–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchilla, L.E.; Olmos, C.M.; Villa, A.; Carlsson, A.; Prati, L.; Chen, X.; Blanco, G.; Calvino, J.J.; Hungría, A.B. Ru-modified Au catalysts supported on ceria–zirconia for the selective oxidation of glycerol. Catal. Today 2015, 253, 178–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, J.H.; Althahban, S.; Nowicka, E.; Freakley, S.J.; Morgan, D.J.; Shah, P.M.; Golunski, S.; Kiely, C.J.; Hutchings, G.J. Synergy and anti-synergy between palladium and gold in nanoparticles dispersed on a reducible support. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 6623–6633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pritchard, J.; Kesavan, L.; Piccinini, M.; He, Q.; Tiruvalam, R.; Dimitratos, N.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.A.; Carley, A.F.; Edwards, J.K.; Kiely, C.J.; et al. Direct synthesis of hydrogen peroxide and benzyl alcohol oxidation using Au-Pd catalysts prepared by sol immobilization. Langmuir 2010, 26, 16568–16577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marx, S.; Baiker, A. Beneficial interaction of gold and palladium in bimetallic catalysts for the selective oxidation of benzyl alcohol. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 6191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, H.; Liu, C.-J.; Zeng, Z.; Zhang, H.; Zhou, C.; Jia, X.; Yang, Y. Formation of monometallic Au and Pd and bimetallic Au–Pd nanoparticles confined in mesopores via Ar glow-discharge plasma reduction and their catalytic applications in aerobic oxidation of benzyl alcohol. J. Catal. 2012, 289, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collins, S.E.; Cies, J.M.; del Rio, E.; Lopez-Haro, M.; Trasobares, S.; Calvino, J.J.; Pintado, J.M.; Bernal, S. Hydrogen interaction with a ceria−zirconia supported gold catalyst. Influence of CO Co-adsorption and pretreatment conditions. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 14371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Ran, R.; Wu, X.; Zhao, B.; Wan, J.; Weng, D. Comparative study of ageing condition effects on Pd/Ce0.5Zr0.5O2 and Pd/Al2O3 catalysts: Catalytic activity, palladium nanoparticle structure and Pd-support interaction. Appl. Catal. A Gen. 2013, 457, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, R.; Lingaiah, N.; Sreedhar, B.; Suryanarayana, I.; Sai Prasad, P.S.; Obuchi, A. Highly stable Pd/CeO2 catalyst for hydrodechlorination of chlorobenzene. Appl. Catal. B Environ. 2003, 46, 587–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinchilla, L.E.; Olmos, C.; Kurttepeli, M.; Bals, S.; Van Tendeloo, G.; Villa, A.; Prati, L.; Blanco, G.; Calvino, J.J.; Chen, X.; et al. Combined macroscopic, nanoscopic, and atomic-scale characterization of gold–ruthenium bimetallic catalysts for octanol oxidation. Part. Part. Syst. Charact. 2016, 33, 419–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Catalyst | Au Loading (wt %) | Pd Loading (wt %) | Theoretical Au:Pd Molar Ratio | Actual Au:Pd Molar Ratio b | Au Content (mol%) | SBET (m2 g−1) | Average Particle Size (nm) c | Metal Dispersion (%) c | Conversion (%) d | TOF (h−1) e | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical | Actual a | Theoretical | Actual a | |||||||||
| 0.86%AuCZ | 1.0 | 0.86 | - | - | - | - | 100 | 67 | 6.0 ± 0.2 | 20 | 8.0 | 36 |
| 0.4AuPd-O | 0.50 | 0.37 | 0.5 | 0.47 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 29.8 | 63 | 5.2 ± 0.2 | 21 | 32.4 | 66 |
| 0.6AuPd-O | 0.6 | 0.36 | 0.4 | 0.34 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 36.4 | 66 | 3.6 ± 0.1 | 27 | 50.3 | 95 |
| 1.4AuPd-O | 0.73 | 0.55 | 0.27 | 0.21 | 1.5 | 1.4 | 58.0 | 66 | 3.5 ± 0.1 | 29 | 72.3 | 204 |
| 1.8AuPd-O | 0.8 | 0.54 | 0.2 | 0.16 | 2.2 | 1.8 | 64.6 | 66 | 5.3 ± 0.2 | 21 | 58.4 | 194 |
| 3.7AuPd-O | 0.9 | 0.69 | 0.1 | 0.10 | 4.9 | 3.7 | 78.9 | 65 | 5.9 ± 0.2 | 18 | 24.5 | 86 |
| 4.3AuPd-O | 0.92 | 0.64 | 0.08 | 0.08 | 6.2 | 4.3 | 81.2 | 66 | 4.5 ± 0.2 | 25 | 20.1 | 40 |
| 0.82%PdCZ | - | - | 1.0 | 0.82 | - | - | 0 | 66 | 2.7 ± 0.1 | 37 | 15.3 | 38 |
| Catalyst | Number of Particles in Each Composition Category | Mean Particle Size (nm) a | Au Content in Bimetallic Particles (%) c | Interval of Au Content in the Bimetallic Particles (%) | Au Content in All Particles (%) d | Au:Pd Molar Ratio d | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au | Pd | Au-Pd | Au | Pd b | Au-Pd | |||||
| 0.6AuPd-O | 16 | - | 45 | 4.5 | - | 4.8 | 69 | 10–91 | 79 | 3.8 |
| 1.4AuPd-O | 43 | - | 13 | 3.9 | - | 2.7 | 73 | 22–88 | 98 | 57 |
| 1.8AuPd-O | 22 | - | 40 | 5.9 | - | 6.5 | 89 | 64–97 | 93 | 12.8 |
| 3.7AuPd-O | 25 | - | 40 | 6.1 | - | 5.8 | 90 | 72–97 | 95 | 18 |
| 4.3AuPd-O | 44 | - | 20 | 5.2 | - | 4.7 | 91 | 81–96 | 98 | 48 |
| Catalyst | Ce3+ (%) | Au 4f7/2 | Pd 3d5/2 | Molar ratios | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Au0 (%) | Binding Energy of Au0 (eV) | Pd0 (%) | Binding Energy of Pd0 (eV) | Pdδ+ (%) | Binding Energy of Pdδ+ (eV) | Au:Zr | Pd:Zr | Au:Pd | Au Content (mol%) | ||
| 0.86%AuCZ | 25 | 100 | 84.2 | - | - | - | - | 0.06 | - | - | |
| 0.4AuPd-O | 10 | 100 | 84.3 | 39 | 336.6 | 61 | 338.5 | 0.04 | 0.15 | 0.30 | 23 |
| 0.6AuPd-O | 26 | 100 | 84.2 | 50 | 336.6 | 50 | 338.4 | 0.06 | 0.06 | 0.80 | 44 |
| 1.4AuPd-O | 21 | 100 | 84.2 | 55 | 336.0 | 45 | 338.1 | 0.08 | 0.06 | 1.49 | 60 |
| 1.8AuPd-O | 10 | 100 | 84.2 | 41 | 337.2 | 59 | 338.7 | 0.04 | 0.07 | 0.70 | 41 |
| 3.7AuPd-O | 13 | 100 | 84.3 | 48 | 337.0 | 52 | 338.7 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 1.41 | 59 |
| 4.3AuPd-O | 30 | 100 | 84.2 | 56 | 335.8 | 44 | 337.9 | 0.08 | 0.04 | 2.20 | 69 |
| 0.82%PdCZ | 14 | - | - | 82 | 335.9 | 18 | 338.1 | - | 0.42 | - | |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olmos, C.M.; Chinchilla, L.E.; Cappella, A.M.; Villa, A.; Delgado, J.J.; Hungría, A.B.; Blanco, G.; Calvino, J.J.; Prati, L.; Chen, X. Selective Oxidation of Veratryl Alcohol over Au-Pd/Ce0.62Zr0.38O2 Catalysts Synthesized by Sol-Immobilization: Effect of Au:Pd Molar Ratio. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090669
Olmos CM, Chinchilla LE, Cappella AM, Villa A, Delgado JJ, Hungría AB, Blanco G, Calvino JJ, Prati L, Chen X. Selective Oxidation of Veratryl Alcohol over Au-Pd/Ce0.62Zr0.38O2 Catalysts Synthesized by Sol-Immobilization: Effect of Au:Pd Molar Ratio. Nanomaterials. 2018; 8(9):669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090669
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlmos, Carol M., Lidia E. Chinchilla, Andrea M. Cappella, Alberto Villa, Juan J. Delgado, Ana B. Hungría, Ginesa Blanco, Jose J. Calvino, Laura Prati, and Xiaowei Chen. 2018. "Selective Oxidation of Veratryl Alcohol over Au-Pd/Ce0.62Zr0.38O2 Catalysts Synthesized by Sol-Immobilization: Effect of Au:Pd Molar Ratio" Nanomaterials 8, no. 9: 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090669
APA StyleOlmos, C. M., Chinchilla, L. E., Cappella, A. M., Villa, A., Delgado, J. J., Hungría, A. B., Blanco, G., Calvino, J. J., Prati, L., & Chen, X. (2018). Selective Oxidation of Veratryl Alcohol over Au-Pd/Ce0.62Zr0.38O2 Catalysts Synthesized by Sol-Immobilization: Effect of Au:Pd Molar Ratio. Nanomaterials, 8(9), 669. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8090669