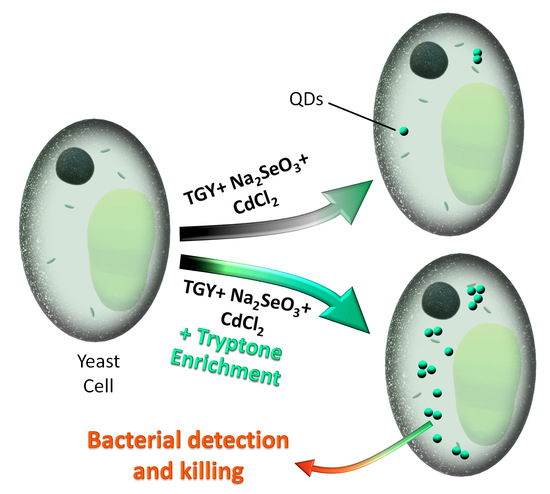
CdSe QD Biosynthesis in Yeast Using Tryptone-Enriched Media and Their Conjugation with a Peptide Hecate for Bacterial Detection and Killing
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Biosynthesis of QDs in Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
2.3. Absorbance and Fluorescence Spectrophotometry
2.4. Fluorescence Microscopy
2.5. Studies on Antioxidant Activity and Glutathione Production
2.6. Extraction of the QDs from Yeast Cells
2.7. Characterization of the Extracted QDs
2.8. Peptide Synthesis
2.9. Conjugation of the QDs with the Peptides
2.10. Application on Bacteria
2.11. Bacterial Cell Viability
2.12. Descriptive Statistics
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Biosynthesis of CdSe QDs Using Tryptone-Supplemented Medium
3.2. Extraction of QDs from Yeast Cells and Their Characterization
3.3. Application of the Extracted QDs in Bacteria
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Resch-Genger, U.; Grabolle, M.; Cavaliere-Jaricot, S.; Nitschke, R.; Nann, T. Quantum dots versus organic dyes as fluorescent labels. Nat. Methods 2008, 5, 763–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.S.; Liu, W.; Liu, F.; Nasr, K.; Misra, P.; Bawendi, M.G.; Frangioni, J.V. Design considerations for tumour-targeted nanoparticles. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2009, 5, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nann, T.; Skinner, W.M. Quantum Dots for Electro-Optic Devices. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5291–5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Michalet, X.; Pinaud, F.F.; Bentolila, L.A.; Tsay, J.M.; Doose, S.; Li, J.J.; Sundaresan, G.; Wu, A.M.; Gambhir, S.S.; Weiss, S. Quantum dots for live cells, in vivo imaging, and diagnostics. Science 2005, 307, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.A.; Peng, X. Formation of High-Quality CdTe, CdSe, and CdS Nanocrystals Using CdO as Precursor. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 183–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, L.; Peng, X. Control of Photoluminescence Properties of CdSe Nanocrystals in Growth. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 2049–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, J.A.; Maddux, B.L.S.; Hutchison, J.E. Toward Greener Nanosynthesis. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 2228–2269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mi, C.C.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhang, J.P.; Huang, H.Q.; Xu, L.R.; Wang, S.; Fang, X.X.; Fang, J.; Mao, C.B.; Xu, S.K. Biosynthesis and characterization of CdS quantum dots in genetically engineered Escherichia coli. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 153, 125–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, T.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Heo, N.S.; Seo, T.S. In Vivo Synthesis of Diverse Metal Nanoparticles by Recombinant Escherichia coli. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 7019–7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominkova, M.; Michalek, P.; Moulick, A.; Nemcova, B.; Zitka, O.; Kopel, P.; Beklova, M.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. Biosynthesis of Quantum Dots (CdTe) and its Effect on Eisenia fetida and Escherichia coli. Chromatographia 2014, 77, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.J.; Zhang, Z.M.; Gong, J. Biological synthesis of semiconductor zinc sulfide nanoparticles by immobilized Rhodobacter sphaeroides. Biotechnol. Lett. 2006, 28, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, P.R.; Holmes, J.D.; Richardson, D.J.; Russell, D.A.; Sodeau, J.R. Photophysical and photochemical characterisation of bacterial semiconductor cadmium sulfide particles. J. Chem. Soc. Faraday Trans. 1998, 94, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmes, J.D.; Smith, P.R.; Evansgowing, R.; Richardson, D.J.; Russell, D.A.; Sodeau, J.R. Energy-dispersive X-ray analysis of the extracellular cadmium sulfide crystallites of Klebsiella aerogenes. Arch. Microbiol. 1995, 163, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Chen, S.Y.; Hu, W.L.; Shi, S.K.; Shen, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.P. In situ synthesis of CdS nanoparticles on bacterial cellulose nanofibers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2009, 76, 509–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kowshik, M.; Deshmukh, N.; Vogel, W.; Urban, J.; Kulkarni, S.K.; Paknikar, K.M. Microbial synthesis of semiconductor CdS nanoparticles, their characterization, and their use in the fabrication of an ideal diode. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2002, 78, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowshik, M.; Vogel, W.; Urban, J.; Kulkarni, S.K.; Paknikar, K.M. Microbial synthesis of semiconductor PbS nanocrystallites. Adv. Mater. 2002, 14, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seshadri, S.; Saranya, K.; Kowshik, M. Green Synthesis of Lead Sulfide Nanoparticles by the Lead Resistant Marine Yeast, Rhodosporidium diobovatum. Biotechnol. Prog. 2011, 27, 1464–1469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, G.S.; Brar, S.K.; Kaur, S.; Verma, M. Green approach for nanoparticle biosynthesis by fungi: Current trends and applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 2012, 32, 49–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Q.; Yi, B.; Zeng, G.M.; Niu, Q.Y.; Yan, M.; Chen, A.W.; Du, J.J.; Huang, J.; Zhang, Q.H. Facile green extracellular biosynthesis of CdS quantum dots by white rot fungus Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Colloid. Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 117, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallardo, C.; Monras, J.P.; Plaza, D.O.; Collao, B.; Saona, L.A.; Duran-Toro, V.; Venegas, F.A.; Soto, C.; Ulloa, G.; Vasquez, C.C.; et al. Low-temperature biosynthesis of fluorescent semiconductor nanoparticles (CdS) by oxidative stress resistant Antarctic bacteria. J. Biotechnol. 2014, 187, 108–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, L.J.; Wan, A.J.; Li, H.L. Synthesis of near-Infrared Quantum Dots in Cultured Cancer Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sturzenbaum, S.R.; Hockner, M.; Panneerselvam, A.; Levitt, J.; Bouillard, J.S.; Taniguchi, S.; Dailey, L.A.; Khanbeigi, R.A.; Rosca, E.V.; Thanou, M.; et al. Biosynthesis of luminescent quantum dots in an earthworm. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trabelsi, H.; Azzouz, I.; Ferchichi, S.; Tebourbi, O.; Sakly, M.; Abdelmelek, H. Nanotoxicological evaluation of oxidative responses in rat nephrocytes induced by cadmium. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 3447–3453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Trabelsi, H.; Azzouz, I.; Sakly, M.; Abdelmelek, H. Subacute toxicity of cadmium on hepatocytes and nephrocytes in the rat could be considered as a green biosynthesis of nanoparticles. Int. J. Nanomed. 2013, 8, 1121–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jamba, L.; Nehru, B.; Bansal, M.P. Effect of selenium supplementation on the influence of cadmium on glutathione and glutathione peroxidase system in mouse liver. J. Trace Elem. Exp. Med. 2000, 13, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulloa, G.; Collao, B.; Araneda, M.; Escobar, B.; Álvarez, S.; Bravo, D.; Pérez-Donoso, J.M. Use of acidophilic bacteria of the genus Acidithiobacillus to biosynthesize CdS fluorescent nanoparticles (quantum dots) with high tolerance to acidic pH. Enzym. Microb. Technol. 2016, 95, 217–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, R.; Liu, J.; Li, M.; Huang, J.; Sun, J.; Qu, H. Epidemiology and antimicrobial resistance among commonly encountered bacteria associated with infections and colonization in intensive care units in a university-affiliated hospital in Shanghai. J. Microbiol. Immunol. Infect. 2014, 47, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- McNeece, G.; Naughton, V.; Woodward, M.J.; Dooley, J.S.G.; Naughton, P.J. Array based detection of antibiotic resistance genes in Gram negative bacteria isolated from retail poultry meat in the UK and Ireland. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 179, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Habiba, K.; Bracho-Rincon, D.P.; Gonzalez-Feliciano, J.A.; Villalobos-Santos, J.C.; Makarov, V.I.; Ortiz, D.; Avalos, J.A.; Gonzalez, C.I.; Weiner, B.R.; Morell, G. Synergistic antibacterial activity of PEGylated silver–graphene quantum dots nanocomposites. Appl. Mater. Today 2015, 1, 80–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulick, A.; Milosavljevic, V.; Vlachova, J.; Podgajny, R.; Hynek, D.; Kopel, P.; Adam, V. Using CdTe/ZnSe core/shell quantum dots to detect DNA and damage to DNA. Int. J. Nanomed. 2017, 12, 1277–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chudobova, D.; Dobes, J.; Nejdl, L.; Maskova, D.; Rodrigo, M.A.M.; Nedecky, B.R.; Krystofova, O.; Kynicky, J.; Konecna, M.; Pohanka, M.; et al. Oxidative Stress in Staphylococcus aureus Treated with Silver(I) Ions Revealed by Spectrometric and Voltammetric Assays. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2013, 8, 4422–4440. [Google Scholar]
- Thaipong, K.; Boonprakob, U.; Crosby, K.; Cisneros-Zevallos, L.; Hawkins Byrne, D. Comparison of ABTS, DPPH, FRAP, and ORAC assays for estimating antioxidant activity from guava fruit extracts. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2006, 19, 669–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kominkova, M.; Michalek, P.; Cihalova, K.; Guran, R.; Cernei, N.; Nejdl, L.; Smerkova, K.; Dostalova, S.; Chudobova, D.; Heger, Z.; et al. Study of linkage between glutathione pathway and the antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli from patients’ swabs. Int J Mol Sci 2015, 16, 7210–7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.C.; Castilho, B.A.; Sattlegger, E. A Rapid Extraction Method for mammalian cell cultures, suitable for quantitative immunoblotting analysis of proteins, including phosphorylated GCN2 and eIF2α. MethodsX 2018, 5, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bzducha-Wróbel, A.; Błażejak, S.; Kawarska, A.; Stasiak-Różańska, L.; Gientka, I.; Majewska, E. Evaluation of the Efficiency of Different Disruption Methods on Yeast Cell Wall Preparation for β-Glucan Isolation. Molecules 2014, 19, 20941–20961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, B.; Wobbe, C.R. Preparation of Protein Extracts from Yeast. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 1993, 23, 13.13.11–13.13.19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Q.; Dong, Y.; Chen, Y.; Lu, C.-H.; Chi, Y.; Yang, H.-H.; Yu, T. Luminescence origin of carbon based dots obtained from citric acid and amino group-containing molecules. Carbon 2017, 118, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Qian, H.; Fang, N.; Ren, J. Study of Fluorescence Quenching and Dialysis Process of CdTe Quantum Dots, Using Ensemble Techniques and Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 11069–11075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulick, A.; Blazkova, I.; Milosavljevic, V.; Fohlerova, Z.; Hubalek, J.; Kopel, P.; Vaculovicova, M.; Adam, V.; Kizek, R. Application of CdTe/ZnSe Quantum Dots in In Vitro Imaging of Chicken Tissue and Embryo. Photochem. Photobiol. 2015, 91, 417–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejdl, L.; Kudr, J.; Moulick, A.; Hegerova, D.; Ruttkay-Nedecky, B.; Gumulec, J.; Cihalova, K.; Smerkova, K.; Dostalova, S.; Krizkova, S.; et al. Platinum nanoparticles induce damage to DNA and inhibit DNA replication. Plos One 2017, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulick, A.; Heger, Z.; Milosavljevic, V.; Richtera, L.; Barroso-Flores, J.; Merlos Rodrigo, M.A.; Buchtelova, H.; Podgajny, R.; Hynek, D.; Kopel, P.; et al. Real-Time Visualization of Cell Membrane Damage Using Gadolinium–Schiff Base Complex-Doped Quantum Dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 35859–35868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, M.-Q.; Chang, E.; Sun, J.; Drezek, R.A. Surface modification and functionalization of semiconductor quantum dots through reactive coating of silanes in toluene. J. Mater. Chem. 2007, 17, 800–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dostalova, S.; Moulick, A.; Milosavljevic, V.; Guran, R.; Kominkova, M.; Cihalova, K.; Heger, Z.; Blazkova, L.; Kopel, P.; Hynek, D.; et al. Antiviral activity of fullerene C60 nanocrystals modified with derivatives of anionic antimicrobial peptide maximin H5. Mon. Für Chem. Chem. Mon. 2016, 147, 905–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinkova, P.; Splichal, Z.; Jimenez, A.M.J.; Haddad, Y.; Mazumdar, A.; Sur, V.P.; Milosavljevic, V.; Kopel, P.; Buchtelova, H.; Guran, R.; et al. Novel vancomycin-peptide conjugate as potent antibacterial agent against vancomycin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Infect Drug Resist 2018, 11, 1807–1817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanches, P.R.S.; Carneiro, B.M.; Batista, M.N.; Braga, A.C.S.; Lorenzon, E.N.; Rahal, P.; Cilli, E.M. A conjugate of the lytic peptide Hecate and gallic acid: Structure, activity against cervical cancer, and toxicity. Amino Acids 2015, 47, 1433–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jelinkova, P.; Vesely, R.; Cihalova, K.; Hegerova, D.; Ananbeh, H.A.A.A.; Richtera, L.; Smerkova, K.; Brtnicky, M.; Kynicky, J.; Moulick, A.; et al. Effect of arsenic (III and V) on oxidative stress parameters in resistant and susceptible Staphylococcus aureus. Environ. Res. 2018, 166, 394–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, M.A.; Imamura, R.; Brown, G.A.; Krishnamurthi, V.R.; Niyonshuti, I.I.; Marcelle, T.; Mathurin, L.E.; Chen, J.; Wang, Y. An experiment-based model quantifying antimicrobial activity of silver nanoparticles on Escherichia coli. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 56173–56182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeStefano Shields, C.E.; Van Meerbeke, S.W.; Housseau, F.; Wang, H.; Huso, D.L.; Casero, R.A., Jr.; O’Hagan, H.M.; Sears, C.L. Reduction of Murine Colon Tumorigenesis Driven by Enterotoxigenic Bacteroides fragilis Using Cefoxitin Treatment. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 214, 122–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kensche, A.; Kirsch, J.; Mintert, S.; Enders, F.; Pötschke, S.; Basche, S.; König, B.; Hannig, C.; Hannig, M. Impact of customary fluoride rinsing solutions on the pellicle’s protective properties and bioadhesion in situ. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannig, C.; Hannig, M.; Rehmer, O.; Braun, G.; Hellwig, E.; Al-Ahmad, A. Fluorescence microscopic visualization and quantification of initial bacterial colonization on enamel in situ. Arch. Oral Biol. 2007, 52, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cui, R.; Zhang, P.; Chen, B.-B.; Tian, Z.-Q.; Li, L.; Hu, B.; Pang, D.-W.; Xie, Z.-X. Mechanism-Oriented Controllability of Intracellular Quantum Dots Formation: The Role of Glutathione Metabolic Pathway. ACS Nano 2013, 7, 2240–2248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.-M.; Su, Y.; Liang, R.-R.; Ai, X.-X.; Qian, J.; Wang, C.; Chen, J.-Q.; Yan, Z.-Y. Crucial factors in biosynthesis of fluorescent CdSe quantum dots in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 79184–79191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrajas, J.R.; Kosmidou, E.; Miranda-Vizuete, A.; Gustafsson, J.-Å; Wright, A.P.H.; Spyrou, G. Identification and Functional Characterization of a Novel Mitochondrial Thioredoxin System in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 6366–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Tarze, A.; Dauplais, M.; Grigoras, I.; Lazard, M.; Ha-Duong, N.-T.; Barbier, F.; Blanquet, S.; Plateau, P. Extracellular Production of Hydrogen Selenide Accounts for Thiol-assisted Toxicity of Selenite against Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 8759–8767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cui, R.; Liu, H.-H.; Xie, H.-Y.; Zhang, Z.-L.; Yang, Y.-R.; Pang, D.-W.; Xie, Z.-X.; Chen, B.-B.; Hu, B.; Shen, P. Living Yeast Cells as a Controllable Biosynthesizer for Fluorescent Quantum Dots. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2009, 19, 2359–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bardajee, G.R.; Hooshyar, Z.; Jafarpour, F. Antibacterial and optical properties of a new water soluble CdSe quantum dots coated by multidentate biopolymer. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2013, 252, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walling, M.A.; Novak, J.A.; Shepard, J.R.E. Quantum dots for live cell and in vivo imaging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 441–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Hu, Y.; Gu, Z.; Liu, L.; Wu, H.-C. Application of Quantum Dots in Biological Imaging. J. Nanomater. 2011, 2011, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avitabile, C.; D’Andrea, L.D.; Romanelli, A. Circular Dichroism studies on the interactions of antimicrobial peptides with bacterial cells. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebenhan, T.; Gheysens, O.; Kruger, H.G.; Zeevaart, J.R.; Sathekge, M.M. Antimicrobial peptides: Their role as infection-selective tracers for molecular imaging. Biomed. Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 867381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sur, V.P.; Kominkova, M.; Buchtova, Z.; Dolezelikova, K.; Zitka, O.; Moulick, A. CdSe QD Biosynthesis in Yeast Using Tryptone-Enriched Media and Their Conjugation with a Peptide Hecate for Bacterial Detection and Killing. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101463
Sur VP, Kominkova M, Buchtova Z, Dolezelikova K, Zitka O, Moulick A. CdSe QD Biosynthesis in Yeast Using Tryptone-Enriched Media and Their Conjugation with a Peptide Hecate for Bacterial Detection and Killing. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(10):1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101463
Chicago/Turabian StyleSur, Vishma Pratap, Marketa Kominkova, Zaneta Buchtova, Kristyna Dolezelikova, Ondrej Zitka, and Amitava Moulick. 2019. "CdSe QD Biosynthesis in Yeast Using Tryptone-Enriched Media and Their Conjugation with a Peptide Hecate for Bacterial Detection and Killing" Nanomaterials 9, no. 10: 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101463
APA StyleSur, V. P., Kominkova, M., Buchtova, Z., Dolezelikova, K., Zitka, O., & Moulick, A. (2019). CdSe QD Biosynthesis in Yeast Using Tryptone-Enriched Media and Their Conjugation with a Peptide Hecate for Bacterial Detection and Killing. Nanomaterials, 9(10), 1463. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101463