Catalytic Performance of Ni/CeO2/X-ZrO2 (X = Ca, Y) Catalysts in the Aqueous-Phase Reforming of Methanol
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Catalysts Preparation
2.2. Catalysts Characterization
2.3. Catalytic Tests
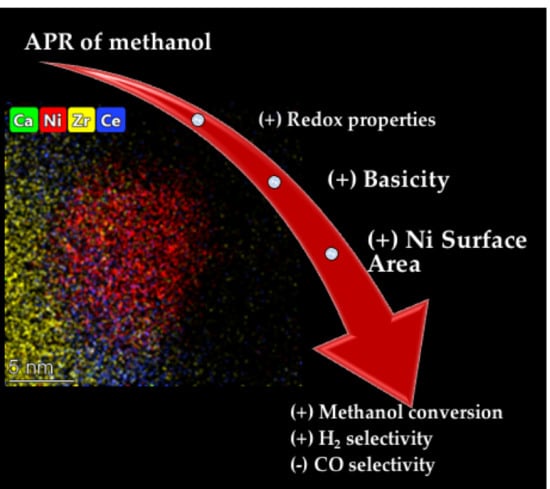
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Catalysts’ Composition and Textural Characterization
3.2. Structural Analysis by X-Ray Diffraction (XRD)
3.3. Hydrogen Chemisorption and Temperature Programmed Reduction (TPR) Studies
3.4. Thermal Programmed Desorption of CO2 Basicity Studies
3.5. Analysis of the Surface by XPS
3.6. Electron Microscopy Study of Ni Catalysts Using HAADF-STEM and EDS-STEM
3.7. Catalytic Activity Tests
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Muradov, N.Z.; Veziroglu, T.N. “Green” path from fossil-based to hydrogen economy: An overview of carbon-neutral technologies. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 6804–6839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krummrich, S.; Llabres, J. Methanol reformer—The next milestone for fuel cell powered submarines. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 5482–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortright, R.D.; Davda, R.R.; Dumesic, J.A. Hydrogen from catalytic reforming of biomass-derived hydrocarbons in liquid water. Nature 2002, 418, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coronado, I.; Stekrova, M.; Reinikainen, M.; Simell, P.; Lefferts, L.; Lehtonen, J. A review of catalytic aqueous-phase reforming of oxygenated hydrocarbons derived from biorefinery water fractions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 11003–11032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davda, R.R.; Shabaker, J.W.; Huber, G.W.; Cortright, R.D.; Dumesic, J.A. A review of catalytic issues and process conditions for renewable hydrogen and alkanes by aqueous-phase reforming of oxygenated hydrocarbons over supported metal catalysts. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2005, 56, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shabaker, J.W.; Huber, G.W.; Dumesic, J.A. Aqueous-phase reforming of oxygenated hydrocarbons over Sn-modified Ni catalysts. J. Catal. 2004, 222, 180–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, G.W.; Shabaker, J.W.; Dumesic, J.A. Raney Ni-Sn catalyst for H-2 production from biomass-derived hydrocarbons. Science 2003, 300, 2075–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Haasterecht, T.; Ludding, C.C.I.; de Jong, K.P.; Bitter, J.H. Stability and activity of carbon nanofiber-supported catalysts in the aqueous phase reforming of ethylene glycol. J. Energy Chem. 2013, 22, 257–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manfro, R.L.; da Costa, A.F.; Ribeiro, N.F.P.; Souza, M.M.V.M. Hydrogen production by aqueous-phase reforming of glycerol over nickel catalysts supported on CeO2. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 330–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roy, B.; Leclerc, C.A. Study of preparation method and oxidization/reduction effect on the performance of nickel-cerium oxide catalysts for aqueous-phase reforming of ethanol. J. Power Sources 2015, 299, 114–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Church, T.L.; Minett, A.I.; Harris, A.T. Effect of CeO2 addition to Al2O3 supports for Pt catalysts on the aqueous-phase reforming of glycerol. ChemSusChem 2013, 6, 1006–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hilaire, S.; Wang, X.; Luo, T.; Gorte, R.J.; Wagner, J. A comparative study of water-gas-shift reaction over ceria-supported metallic catalysts. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2004, 258, 271–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, A.P.; Guo, H.J.; Song, Y.M.; Chen, P.; Lou, H. Recyclable CeO2-ZrO2 and CeO2-TiO2 mixed oxides based Pt catalyst for aqueous-phase reforming of the low-boiling fraction of bio-oil. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 9577–9588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, S.; Park, Y.M.; Saravanan, K.; Han, G.Y.; Kim, B.W.; Lee, J.B.; Bae, J.W. Aqueous phase reforming of ethylene glycol over bimetallic platinum-cobalt on ceria-zirconia mixed oxide. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 9892–9902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larimi, A.S.; Kazemeini, M.; Khorasheh, F. Aqueous phase reforming of glycerol using highly active and stable Pt0.05CeXZr0.95-XO2 ternary solid solution catalysts. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2016, 523, 230–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stekrova, M.; Rinta-Paavola, A.; Karinen, R. Hydrogen production via aqueous-phase reforming of methanol over nickel modified Ce, Zr and La oxide supports. Catal. Today 2018, 304, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Azmat, M.U.; Liu, X.H.; Wang, Y.Q.; Lu, G.Z. Effect of support’s basic properties on hydrogen production in aqueous-phase reforming of glycerol and correlation between WGS and APR. Appl. Energy 2012, 92, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, A.O.; Rodrigues, M.T.; Zimmaro, A.; Borges, L.E.P.; Fraga, M.A. Production of renewable hydrogen from aqueous-phase reforming of glycerol over Pt catalysts supported on different oxides. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 595–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muñoz, M.A.; Calvino, J.J.; Rodríguez-Izquierdo, J.M.; Blanco, G.; Arias, D.C.; Pérez-Omil, J.A.; Hernández-Garrido, J.C.; González-Leal, J.M.; Cauqui, M.A.; Yeste, M.P. Highly stable ceria-zirconia-yttria supported Ni catalysts for syngas production by CO2 reforming of methane. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 426, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercera, P.D.L.; van Ommen, J.G.; Doesburg, E.B.M.; Burggraaf, A.J.; Roes, J.R.H. Stabilized tetragonal zirconium oxide as a support for catalysts Evolution of the texture and structure on calcination in static air. Appl. Catal. 1991, 78, 79–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiménez-González, C.; Boukha, Z.; de Rivas, B.; Delgado, J.J.; Cauqui, M.Á.; González-Velasco, J.R.; Gutiérrez-Ortiz, J.I.; López-Fonseca, R. Structural characterisation of Ni/alumina reforming catalysts activated at high temperatures. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2013, 466, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdz, E.; Lacz, A.; Spalek, Z. Deposition of NiO on 3 mol% yttria-stabilized zirconia and Sr0.96Y0.04TiO3 materials by impregnation method. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 130, 291–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.G.; Wang, H.; Li, K.Z.; Zhu, X.; Du, Y.P. Preparation and characterization of Ce1−xNixO2 as oxygen carrier for selective oxidation methane to syngas in absence of gaseous oxygen. J. Rare Earths 2010, 28, 357–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shan, W.J.; Luo, M.F.; Ying, P.L.; Shen, W.J.; Li, C. Reduction property and catalytic activity of Ce1-xNiXO2 mixed oxide catalysts for CH4 oxidation. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2003, 246, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, C.J.; Li, J.C.; Yao, X.J.; Sun, J.F.; Cao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Gao, F.; Deng, Y.; Dong, L. Mesoporous NiO-CeO2 catalysts for CO oxidation: Nickel content effect and mechanism aspect. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2015, 494, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, H.; Wen, C.J.; Otomo, J.; Eguchi, K.; Takahashi, H. Investigation of the interaction between NiO and yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) in the NiO/YSZ composite by temperature-programmed reduction technique. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2003, 245, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhu, A.M.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Au, C.T.; Yang, X.F.; Shi, C. Catalytic reduction of NO by CO over NiO/CeO2 catalyst in stoichiometric NO/CO and NO/CO/O-2 reaction. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2008, 81, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luisetto, I.; Tuti, S.; Di Bartolomeo, E. Co and Ni supported on CeO2 as selective bimetallic catalyst for dry reforming of methane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 15992–15999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chagas, C.A.; de Souza, E.F.; Manfro, R.L.; Landi, S.M.; Souza, M.M.V.M.; Schmal, M. Copper as promoter of the NiO-CeO2 catalyst in the preferential CO oxidation. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2016, 182, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Ma, J.; Guan, L.; Li, J.; Wei, W.; Sun, Y. Mesoporous CaO–ZrO2 nano-oxides: A novel solid base with high activity and stability. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2009, 117, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radlik, M.; Adamowska-Teyssier, M.; Krztoń, A.; Kozieł, K.; Krajewski, W.; Turek, W.; Da Costa, P. Dry reforming of methane over Ni/Ce0.62Zr0.38O2 catalysts: Effect of Ni loading on the catalytic activity and on H2/CO production. Comptes Rendus Chim. 2015, 18, 1242–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosvenor, A.P.; Biesinger, M.C.; Smart, R.S.; McIntyre, N.S. New interpretations of XPS spectra of nickel metal and oxides. Surf. Sci. 2006, 600, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.; Smart, R.S.C. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic chemical state Quantification of mixed nickel metal, oxide and hydroxide systems. Surf. Interface Anal. 2009, 41, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carley, A.F.; Jackson, S.D.; O’Shea, J.N.; Roberts, M.W. The formation and characterisation of Ni3+—An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic investigation of potassium-doped Ni(110)–O. Surf. Sci. 1999, 440, L868–L874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Löfberg, A.; Guerrero-Caballero, J.; Kane, T.; Rubbens, A.; Jalowiecki-Duhamel, L. Ni/CeO2 based catalysts as oxygen vectors for the chemical looping dry reforming of methane for syngas production. Appl. Catal. B: Environ. 2017, 212, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kugai, J.; Subramani, V.; Song, C.; Engelhard, M.H.; Chin, Y.-H. Effects of nanocrystalline CeO2 supports on the properties and performance of Ni–Rh bimetallic catalyst for oxidative steam reforming of ethanol. J. Catal. 2006, 238, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Xu, X.Y.; Li, M.R.; Zhou, W.; Liu, S.M.; Zhu, Z.H. Coking-resistant Ce0.8Ni0.2O2-delta internal reforming layer for direct methane solid oxide fuel cells. Electrochim. Acta 2018, 282, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Lu, W.; Wang, M.; Xu, X. Characterization and catalytic performances of La doped Pd/CeO2 catalysts for methanol decomposition. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2004, 268, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez-Garcia, S.; Jiang, L.; Tinoco, M.; Hungria, A.B.; Han, J.; Blanco, G.; Calvino, J.J.; Chen, X. Enhanced Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity by Doping Lanthanum in Ceria Nanocubes. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 1891–1901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skårman, B.; Grandjean, D.; Benfield, R.E.; Hinz, A.; Andersson, A.; Reine Wallenberg, L. Carbon monoxide oxidation on nanostructured CuOx/CeO2 composite particles characterized by HREM, XPS, XAS, and high-energy diffraction. J. Catal. 2002, 211, 119–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Requies, J.; Cabrero, M.A.; Barrio, V.L.; Güemez, M.B.; Cambra, J.F.; Arias, P.L.; Pérez-Alonso, F.J.; Ojeda, M.; Peña, M.A.; Fierro, J.L.G. Partial oxidation of methane to syngas over Ni/MgO and Ni/La2O3 catalysts. Appl. Catal. A: Gen. 2005, 289, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Francisco, M.S.P.; Mastelaro, V.R.; Nascente, P.A.P.; Florentino, A.O. Activity and characterization by XPS, HR-TEM, Raman spectroscopy, and bet surface area of CuO/CeO2-TiO2 catalysts. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 10515–10522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Catalysts | Composition from ICP (% w/w) | SBET (m2·g−1) | Pore Volume (cm3·g−1) | Average Pore Radius (nm) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Ce | Ca | Y | Zr | ||||
| NiZr | 7.0 | - | - | - | 60.0 | 30 | 0.178 | 9.4 |
| NiCeZr | 5.9 | 12.6 | - | - | 48.4 | 30 | 0.141 | 7.7 |
| Ni4CSZ | 5.0 | - | 1.20 | - | 60.0 | 48 | 0.214 | 5.7 |
| NiCe4CSZ | 5.9 | 13.0 | 1.80 | - | 47.6 | 47 | 0.123 | 3.9 |
| Ni8YSZ | 5.6 | - | - | 4.30 | 56.4 | 53 | 0.192 | 5.7 |
| NiCe8YSZ | 5.5 | 12.7 | - | 3.62 | 46.1 | 42 | 0.123 | 3.9 |
| Ni14CSZ | 6.9 | - | 4.90 | - | 53.0 | 54 | 0.220 | 4.8 |
| NiCe14CSZ | 5.5 | 13.5 | 4.00 | - | 43.3 | 67 | 0.133 | 2.8 |
| Catalysts | Metal Surface 1 (m2·g−1) | Ni Particle Size 1 (nm) | Crystallite Size (nm) 2 | H2 Uptake 3 (mmol·g−1) | Reduction Degree 3 (%) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | NiO | CeO2 | |||||
| NiZr | 1.7 | 27.0 ± 1.0 | 24 | 22 | - | 1.16 | 97 |
| NiCeZr | 1.7 | 24.5 ± 2.0 | 10 | 17 | 22 | 1.53 | 105 |
| Ni4CSZ | 2.2 | 15.6 ± 0.5 | 17 | 15 | - | 0.94 | 110 |
| NiCe4CSZ | 2.1 | 19.3 ± 1.2 | 11 | 17 | 13 | 1.63 | 110 |
| Ni8YSZ | 1.2 | 32.5 ± 3.3 | 19 | 21 | - | 0.93 | 97 |
| NiCe8YSZ | 1.3 | 24.0 ± 1.6 | 16 | 18 | 15 | 1.28 | 92 |
| Ni14CSZ | 1.2 | 38.0 ± 1.4 | 21 | 18 | - | 1.24 | 105 |
| NiCe14CSZ | 1.4 | 25.7 ± 1.2 | 16 | 15 | 10 | 1.69 | 118 |
| Samples | Weak (90–180 °C) (µmol·g−1) | Intermediate (180–400 °C) (µmol·g−1) | Strong (>400 °C) (µmol·g−1) | Total (µmol·g−1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiZr | 7.4 | 3.3 | 2.9 | 13.7 |
| Ni4CSZ | 21.1 | 1.5 | 3.1 | 25.6 |
| Ni8YSZ | 18.1 | 7.9 | - | 26.0 |
| Ni14CSZ | 29.0 | 7.4 | - | 36.5 |
| NiCeZr | 7.3 | 3.9 | 2.6 | 13.8 |
| NiCe4CSZ | 10.1 | 6.9 | 4.7 | 21.8 |
| NiCe8YSZ | 12.5 | 14.6 | 9.9 | 37.0 |
| NiCe14CSZ | 17.4 | 15.8 | 6.9 | 40.1 |
| Samples | Ni 2p | Ce 3d | O 1s | Ce3+ (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiZr | 852.7, -, 855.4 | - | 529.5, 531.2 | - |
| Ni4CSZ | 852.9, -, 855.3 | - | 529.7, 531.7 | - |
| Ni8YSZ | 852.8, -, 855.6 | - | 529.7, 531.7 | - |
| Ni14CSZ | 852.7, -, 855.3 | - | 529.8, 531.4 | - |
| NiCeZr | 852.2, 853.5, 855.4 | 885.0, 898.3 | 529.6, 531.3 | 9 |
| NiCe4CSZ | 851.9, 853.2, 855.2 | 884.7, 898.2 | 529.4, 531.0 | 19 |
| NiCe8YSZ | 851.9, 853.2, 855.1 | 885.2, 898.2 | 529.7, 531.7 | 34 |
| NiCe14CSZ | 852.1, 853.4, 855.5 | 884.7, 898.3 | 529.4, 531.1 | 18 |
| Sample | Particle Size from H2 Chemisorption (nm) | Crystallite Size from XRD (nm) | (nm) | (nm) | D (%) 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiZr | 27 | 24 | 14 | 27 | 5.2 |
| Ni4CSZ | 16 | 17 | 14 | 20 | 6.4 |
| Ni8YSZ | 32 | 19 | 9 | 23 | 5.4 |
| Ni14CSZ | 38 | 21 | 13 | 20 | 6.4 |
| NiCe4CSZ | 26 | 16 | 14 | 21 | 5.9 |
| Sample | Conversion (%) | Selectivity (%) | Products Ratio | H2 Yield (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| H2 | CO2 | CO | CH4 | H2/CO2 | CO2/CO | |||
| NiZr | 48 | 72.9 | 20.2 | 4.6 | 2.2 | 3.6 | 4.4 | 40 |
| Ni4CSZ | 75 | 73.9 | 23.9 | 0.2 | 2.1 | 3.1 | 119.5 | 64 |
| Ni8YSZ | 46 | 75.5 | 21.5 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 3.5 | 14.3 | 36 |
| Ni14CSZ | 63 | 73.8 | 23.7 | 0.5 | 2.1 | 3.1 | 47.4 | 46 |
| NiCeZr | 40 | 76.8 | 20.5 | 1.8 | 0.9 | 3.7 | 11.4 | 34 |
| NiCe4CSZ | 68 | 73.8 | 23.4 | 0.6 | 2.2 | 3.2 | 39.0 | 57 |
| NiCe8YSZ | 54 | 74.1 | 21.3 | 2.2 | 2.5 | 3.5 | 9.7 | 40 |
| NiCe14CSZ | 44 | 75.7 | 21.6 | 1.9 | 0.9 | 3.5 | 11.4 | 33 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goma, D.; Delgado, J.J.; Lefferts, L.; Faria, J.; Calvino, J.J.; Cauqui, M.Á. Catalytic Performance of Ni/CeO2/X-ZrO2 (X = Ca, Y) Catalysts in the Aqueous-Phase Reforming of Methanol. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111582
Goma D, Delgado JJ, Lefferts L, Faria J, Calvino JJ, Cauqui MÁ. Catalytic Performance of Ni/CeO2/X-ZrO2 (X = Ca, Y) Catalysts in the Aqueous-Phase Reforming of Methanol. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(11):1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111582
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoma, Daniel, Juan José Delgado, Leon Lefferts, Jimmy Faria, José Juan Calvino, and Miguel Ángel Cauqui. 2019. "Catalytic Performance of Ni/CeO2/X-ZrO2 (X = Ca, Y) Catalysts in the Aqueous-Phase Reforming of Methanol" Nanomaterials 9, no. 11: 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111582
APA StyleGoma, D., Delgado, J. J., Lefferts, L., Faria, J., Calvino, J. J., & Cauqui, M. Á. (2019). Catalytic Performance of Ni/CeO2/X-ZrO2 (X = Ca, Y) Catalysts in the Aqueous-Phase Reforming of Methanol. Nanomaterials, 9(11), 1582. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111582