Synergistical Use of Electrostatic and Hydrophobic Interactions for the Synthesis of a New Class of Multifunctional Nanohybrids: Plasmonic Magneto-Liposomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Preparation of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
2.3. Liposomal Dispersion Synthesis
2.4. PEGylated Gold Colloid Synthesis
2.5. Plasmonic Liposomes Synthesis
2.6. Methods
2.6.1. UV-Vis Absorption Measurements
2.6.2. Transmission Electron Microscopy (TEM) and Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) Measurements
2.6.3. X-ray Diffraction Measurements
2.6.4. Photon Correlation Spectroscopy Measurements
2.6.5. (Surface-Enhanced) Raman Spectroscopy (SERS) Measurements
2.6.6. Magnetic Measurements
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. SPIONs
3.2. PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles
3.3. Magneto-Liposomes
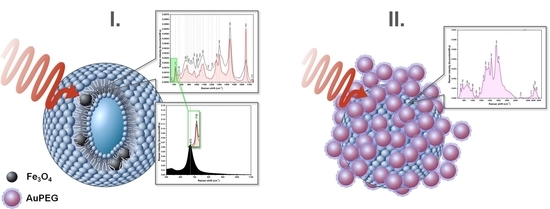
3.4. Multifunctional Plasmonic Magneto-Liposomes
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Etheridge, M.L.; Campbell, S.A.; Erdman, A.G.; Haynes, C.L.; Wolf, S.M.; McCullough, J. The big picture on nanomedicine: The state of investigational and approved nanomedicine products. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2013, 9, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahoo, S.K.; Parveen, S.; Panda, J.J. The present and future of nanotechnology in human health care. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2007, 3, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamboni, W.C.; Torchilin, V.; Patri, A.K.; Hrkach, J.; Stern, S.; Lee, R.; Nel, A.; Panaro, N.J.; Grodzinski, P. Best Practices in Cancer Nanotechnology: Perspective from NCI Nanotechnology Alliance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2012, 18, 3229–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozzuto, G.; Molinari, A. Liposomes as nanomedical devices. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 975–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, J.; Nakamura, H.; Maeda, H. The EPR effect: Unique features of tumor blood vessels for drug delivery, factors involved, and limitations and augmentation of the effect. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2011, 63, 136–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Jain, P.K.; El-Sayed, I.H.; El-Sayed, M.A. Plasmonic photothermal therapy (PPTT) using gold nanoparticles. Lasers Med. Sci. 2008, 23, 217–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-X.J. Superparamagnetic iron oxide based MRI contrast agents: Current status of clinical application. Quant. Imaging Med. Surg. 2011, 1, 35–40. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, H.I.; Yeh, M.K. Clinical development of liposome-based drugs: Formulation, characterization, and therapeutic efficacy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 49–60. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, M.-C.; Astruc, D. Gold Nanoparticles: Assembly, Supramolecular Chemistry, Quantum-Size-Related Properties, and Applications toward Biology, Catalysis, and Nanotechnology. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 293–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schasfoort, R.B.M. Handbook of Surface Plasmon Resonance, 2nd ed.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: Croydon, UK, 2017; pp. 31–46. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, W.Q.; Gao, Z. Plasmonic nanoparticles in biomedicine. Nano Today 2016, 11, 168–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brust, M.; Walker, M.; Bethell, D.; Schiffrin, D.J.; Whyman, R. Synthesis of thiol-derivatised gold nanoparticles in a two-phase Liquid-Liquid system. J. Chem. Soc. Chem. Commun. 1994, 7, 801–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zayats, A.V.; Smolyaninov, I.I.; Maradudin, A.A. Nano-optics of surface plasmon polaritons. Phys. Rep. 2005, 408, 131–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, Y.-C.; Creran, B.; Rotello, V. Gold Nanoparticles: Preparation, Properties, and Applications in Bionanotechnology. Nanoscale 2011, 4, 1871–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, S.; Baillargeat, D.; Ho, H.-P.; Yong, K.-T. Nanomaterials enhanced surface plasmon resonance for biological and chemical sensing applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 3426–3452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khlebtsov, N.; Bogatyrev, V.; Dykman, L.; Khlebtsov, B.; Staroverov, S.; Shirokov, A.; Matora, L.; Khanadeev, V.; Pylaev, T.; Tsyganova, N.; et al. Analytical and Theranostic Applications of Gold Nanoparticles and Multifunctional Nanocomposites. Theranostics 2013, 3, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; El-Sayed, M.A. Gold nanoparticles: Optical properties and implementations in cancer diagnosis and photothermal therapy. J. Adv. Res. 2010, 1, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giljohann, D.A.; Seferos, D.S.; Daniel, W.L.; Massich, M.D.; Patel, P.C.; Mirkin, C.A. Gold nanoparticles for biology and medicine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2010, 49, 3280–3294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.T.; Saha, K.; Kim, C.; Rotello, V.M. The Role of Surface Functionality in Determining Nanoparticle Cytotoxicity. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 681–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, B.; Kim, C.; Rotello, V.M. Gold nanoparticle platforms as drug and biomacromolecule delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2010, 148, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hervault, A.; Thanh, N.T. Magnetic nanoparticle-based therapeutic agents for thermo-chemotherapy treatment of cancer. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11553–11573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Kim, J.W.; Cheon, J. Magnetic nanoparticles for multi-imaging and drug delivery. Mol. Cells 2013, 35, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Jin, C.; Jiang, Y.; Li, J.; Di, Y.; Ni, Q.; Fu, D. Liposome based delivery systems in pancreatic cancer treatment: From bench to bedside. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2011, 37, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balazs, D.A.; Godbey, W. Liposomes for Use in Gene Delivery. J. Drug Deliv. 2011, 2011, 326497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbarzadeh, A.; Rezaei-Sadabady, R.; Davaran, S.; Joo, S.W.; Zarghami, N.; Hanifehpour, Y.; Samiei, M.; Kouhi, M.; Nejati-Koshki, K. Liposome: Classification, preparation, and applications. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Çağdaş, M.; Sezer, A.D.; Bucak, S. Liposomes as Potential Drug Carrier Systems for Drug Delivery. In Application of Nanotechnology in Drug Delivery; Sezer, A.D., Ed.; InTech: Rijeka, Croatia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Zylberberg, C.; Matosevic, S. Pharmaceutical liposomal drug delivery: A review of new delivery systems and a look at the regulatory landscape. Drug Deliv. 2016, 23, 3319–3329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allen, T.M.; Cullis, P.R. Liposomal drug delivery systems: From concept to clinical applications. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 36–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sercombe, L.; Veerati, T.; Moheimani, F.; Wu, S.Y.; Sood, A.K.; Hua, S. Advances and Challenges of Liposome Assisted Drug Delivery. Front. Pharmacol. 2015, 6, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arouri, A.; Hansen, A.H.; Rasmussen, T.E.; Mouritsen, O.G. Lipases, liposomes and lipid-prodrugs. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 18, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacovita, C.; Stiufiuc, R.; Radu, T.; Florea, A.; Stiufiuc, G.; Dutu, A.; Mican, S.; Tetean, R.; Lucaciu, C.M. Polyethylene Glycol-Mediated Synthesis of Cubic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with High Heating Power. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiufiuc, R.; Iacovita, C.; Lucaciu, C.M.; Stiufiuc, G.; Dutu, A.G.; Braescu, C.; Leopold, N. SERS-active silver colloids prepared by reduction of silver nitrate with short-chain polyethylene glycol. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2013, 8, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiufiuc, R.; Iacovita, C.; Nicoara, R.; Stiufiuc, G.; Florea, A.; Achim, M.; Lucaciu, C.M. One-Step Synthesis of PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles with Tunable Surface Charge. J. Nanomater. 2013, 2013, 146031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitica, S.; Moldovan, A.I.; Toma, V.; Moldovan, C.S.; Berindan-Neagoe, I.; Stiufiuc, G.; Lucaciu, C.M.; Stiufiuc, R. PEGylated Gold Nanoparticles with Interesting Plasmonic Properties Synthesized Using an Original, Rapid, and Easy-to-Implement Procedure. J. Nanomater. 2018, 2018, 5954028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stiufiuc, G.; Toma, V.; Moldovan, A.I.; Stiufiuc, R.; Lucaciu, C.M. One pot microwave assisted synthesis of cyclodextrins capped spherical gold nanoparticles. Dig. J. Nanomater. Biostruct. 2017, 12, 1089–1095. [Google Scholar]
- Benedec, D.; Oniga, I.; Cuibus, F.; Sevastre, B.; Stiufiuc, G.; Duma, M.; Hanganu, D.; Iacovita, C.; Stiufiuc, R.; Lucaciu, C.M. Origanum vulgare mediated green synthesis of biocompatible gold nanoparticles simultaneously possessing plasmonic, antioxidant and antimicrobial properties. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 1041–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Stiufiuc, R.; Iacovita, C.; Stiufiuc, G.; Florea, A.; Achim, M.; Lucaciu, C.M. A new class of pegylated plasmonic liposomes: Synthesis and characterization. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 437, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radu, T.; Iacovita, C.; Benea, D.; Turcu, R. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopic Characterization of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 405, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Dutz, S.; Häfeli, U.O.; Mahmoudi, M. Magnetic fluid hyperthermia: Focus on superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 166, 8–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosensweig, R.E. Heating magnetic fluid with alternating magnetic field. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2002, 252, 370–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzales-Weimuller, M.; Zeisberger, M.; Krishnan, K.M. Size-dependant heating rates of iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic fluid hyperthermia. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2009, 321, 1947–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haiss, W.; Thanh, N.T.K.; Aveyard, J.; Fernig, D.G. Determination of Size and Concentration of Gold Nanoparticles from UV−Vis Spectra. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 4215–4221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czamara, K.; Majzner, K.; Pacia, M.Z.; Kaczor, A.; Barańska, M.; Kochan, K. Raman spectroscopy of lipids: A review. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2015, 46, 4–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Movasaghi, Z.; Rehman, S.; Rehman, I.U. Raman Spectroscopy of Biological Tissues. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2007, 42, 493–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chourpa, I.; Douziech-Eyrolles, L.; Ngaboni-Okassa, L.; Fouquenet, J.-F.; Cohen-Jonathan, S.; Soucé, M.; Marchais, H.; Dubois, P. Molecular composition of iron oxide nanoparticles, precursors for magnetic drug targeting, as characterized by confocal Raman microspectroscopy. Analyst 2005, 130, 1395–1403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Faria, D.L.A.; Venâncio Silva, S.; de Oliveira, M.T. Raman microspectroscopy of some iron oxides and oxyhydroxides. J. Raman Spectrosc. 1998, 28, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]









© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Știufiuc, G.F.; Nițică, Ș.; Toma, V.; Iacoviță, C.; Zahn, D.; Tetean, R.; Burzo, E.; Lucaciu, C.M.; Știufiuc, R.I. Synergistical Use of Electrostatic and Hydrophobic Interactions for the Synthesis of a New Class of Multifunctional Nanohybrids: Plasmonic Magneto-Liposomes. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111623
Știufiuc GF, Nițică Ș, Toma V, Iacoviță C, Zahn D, Tetean R, Burzo E, Lucaciu CM, Știufiuc RI. Synergistical Use of Electrostatic and Hydrophobic Interactions for the Synthesis of a New Class of Multifunctional Nanohybrids: Plasmonic Magneto-Liposomes. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(11):1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111623
Chicago/Turabian StyleȘtiufiuc, Gabriela Fabiola, Ștefan Nițică, Valentin Toma, Cristian Iacoviță, Dietrich Zahn, Romulus Tetean, Emil Burzo, Constantin Mihai Lucaciu, and Rareș Ionuț Știufiuc. 2019. "Synergistical Use of Electrostatic and Hydrophobic Interactions for the Synthesis of a New Class of Multifunctional Nanohybrids: Plasmonic Magneto-Liposomes" Nanomaterials 9, no. 11: 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111623
APA StyleȘtiufiuc, G. F., Nițică, Ș., Toma, V., Iacoviță, C., Zahn, D., Tetean, R., Burzo, E., Lucaciu, C. M., & Știufiuc, R. I. (2019). Synergistical Use of Electrostatic and Hydrophobic Interactions for the Synthesis of a New Class of Multifunctional Nanohybrids: Plasmonic Magneto-Liposomes. Nanomaterials, 9(11), 1623. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9111623