A DFT Study of Hydrogen Storage in High-Entropy Alloy TiZrHfScMo
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Computational and Experimental Details
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. The Structural Parameters of the TiZrHfScMo HEA before and after Hydrogenation
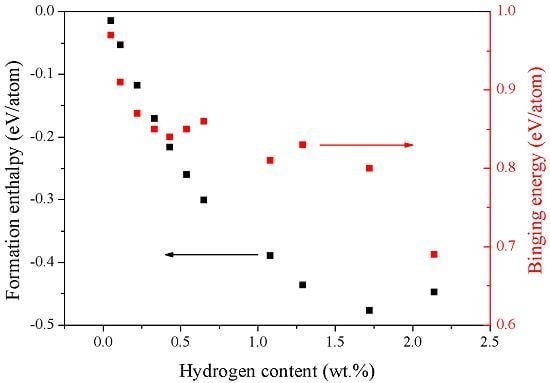
3.2. The Energetic Properties of the TiZrHfScMo HEA and Its Hydrides
3.3. Electronic Structures and Mulliken Population Analysis of TiZrHfScMo-Hx
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abdalla, A.M.; Hossain, S.; Nisfindy, O.B.; Azad, A.T.; Dawood, M.; Azad, A.K. Hydrogen production, storage, transportation and key challenges with applications: A review. Energy Conv. Manag. 2018, 165, 602–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, J.W.; Musyoka, N.M.; Langmi, H.W.; Mathe, M.; Liao, S.J. Current research trends and perspectives on materials-based hydrogen storage solutions: A critical review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2017, 42, 289–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, Z.S.; Zhu, J.C.; Yang, X.W.; Cao, Y.; Lai, Z.H.; Liu, Y. First-principles study of hydrogen storage and diffusion in B2 FeTi alloy. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2014, 81, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Huang, Y.N.; Mao, C.; Peng, P.; Shao, Y.M.; Zhou, D.W. Ab initio calculations on energetics and electronic structures of cubic Mg3MNi2 (M = Al, Ti, Mn) hydrogen storage alloys. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 14477–14483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merlino, A.R.; Luna, C.R.; Juan, A.; Pronsato, M.E. A DFT study of hydrogen storage in Zr(Cr0.5Ni0.5)(2) Laves phase. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2016, 41, 2700–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westlake, D.G. Hydrides of intermetallic compounds: A review of stabilities, stoichiometries and preferred hydrogen sites. J. Less-Common Met. 1983, 91, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunce, I.; Polanski, M.; Bystrzycki, J. Microstructure and hydrogen storage properties of a TiZrNbMoV high entropy alloy synthesized using Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS). Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 9904–9910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.W.; Chen, S.K.; Lin, S.J.; Gan, J.Y.; Chin, T.S.; Shun, T.T.; Tsau, C.H.; Chang, S.Y. Nanostructured high-entropy alloys with multiple principal elements: Novel alloy design concepts and outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Y.J.; Lin, J.P.; Chen, G.L.; Liaw, P.K. Solid-solution phase formation rules for multi-component alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2008, 10, 534–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Wang, Z.J.; Li, Y.Y.; Wu, Q.F.; Li, J.J.; Wang, J.C.; Liu, C.T. Kinetic ways of tailoring phases in high entropy alloys. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 34628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yurchenko, N.; Stepanov, N.; Salishchev, G. Laves-phase formation criterion for high-entropy alloys. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2017, 33, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunce, I.; Polanski, M.; Bystrzycki, J. Structure and hydrogen storage properties of a high entropy ZrTiVCrFeNi alloy synthesized using Laser Engineered Net Shaping (LENS). Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 12180–12189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahlberg, M.; Karlsson, D.; Zlotea, C.; Jansson, U. Superior hydrogen storage in high entropy alloys. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, D.; Ek, G.; Cedervall, J.; Zlotea, C.; Moller, K.T.; Hansen, T.C.; Bednarcik, J.; Paskevicius, M.; Sorby, M.H.; Jensen, T.R.; et al. Structure and Hydrogenation Properties of a HfNbTiVZr High-Entropy Alloy. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 2103–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresse, G.; Hafner, J. Ab initio molecular dynamics for liquid metals. Phys. Rev. B 1993, 47, 558–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficiency of ab-initio total energy calculations for metals and semiconductors using a plane-wave basis set. Comput. Mater. Sci. 1996, 6, 15–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kresse, G.; Furthmüller, J. Efficient iterative schemes for ab initio total-energy calculations using a plane-wave basis set. Phys. Rev. B 1996, 54, 11169–11186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, B.A.; Atkins, D.F. Zirconium-Columbium Diagram. JOM 1955, 7, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, M.C.; Teter, M.P.; Allan, D.C.; Arias, T.A.; Joannopoulos, J.D. Iterative minimization techniques for abinitio total-energy calculations—Molecular-dynamics and conjugate gradients. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1992, 64, 1045–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, Z.S.; Zhu, J.C.; Zhao, R.D. Prediction of structure and elastic properties of AlCrFeNiTi system high entropy alloys. Intermetallics 2017, 86, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakintuna, B.; Lamari-Darkrim, F.; Hirscher, M. Metal hydride materials for solid hydrogen storage: A review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2007, 32, 1121–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, C.A.; Hu, J.P.; Ouyang, C.Y. Hydrogen solution in tetrahedral or octahedral interstitial sites in Al. J. Alloy. Compd. 2011, 509, 9214–9217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesari, S.B.; Pronsato, M.E.; Visintin, A.; Juan, A. Hydrogen Storage in AB(2) Laves Phase (A = Zr, Ti; B = Ni, Mn, Cr, V): Binding Energy and Electronic Structure. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 16832–16836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Zhang, J.; Hu, J.; Zhang, J.; Mao, Y.; Xiao, H.; Zhou, X.; Zu, X. A Novel TiZrHfMoNb High-Entropy Alloy for Solar Thermal Energy Storage. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsumura, T.; Yukawa, H.; Morinaga, M. Alloying effects on the electronic structure of ZrMn2 intermetallic hydride. J. Alloy. Compd. 1998, 279, 192–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slusarski, T.; Brzostowski, B.; Tomecka, D.; Kamieniarz, G. Application of the Package SIESTA to Linear Models of a Molecular Chromium-Based Ring. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2010, 118, 967–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, S.S.; Xiao, X.; Lei, X.; Li, W.H.; Dong, Y.D. Relationship between the widths of supercooled liquid regions and bond parameters of Mg-based bulk metallic glasses. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2003, 321, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadi, M.A.; Christopoulos, S.R.G.; Naqib, S.H.; Chroneos, A.; Fitzpatrick, M.E.; Islam, A. Physical properties and defect processes of M3SnC2 (M = Ti, Zr, Hf) MAX phases: Effect of M-elements. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 748, 804–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zhu, P.X.; Zhu, J.C.; Liu, Y. First-principles study of NiAl alloyed with Co. Comput. Mater. Sci. 2016, 111, 34–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Config. | Lattice Constant (Å) |
|---|---|
| Exp. | 3.444 |
| M | 3.325 |
| M–H0.25 | 3.331 |
| M–H0.5 | 3.337 |
| M–H | 3.350 |
| M–H1.5 | 3.367 |
| M–H2 | 3.383 |
| M–H2.5 | 3.400 |
| M–H3 | 3.420 |
| M–H5 | 3.46 |
| M–H6 | 3.492 |
| M–H8 | 3.526 |
| M–H10 | 3.56 |
| Config. | Formation Enthalpy (eV/Atom) | Binding Energy (eV/Atom) |
|---|---|---|
| M–H0.25 | −0.0147 | 0.97 |
| M–H0.5 | −0.0531 | 0.91 |
| M–H | −0.1174 | 0.87 |
| M–H1.5 | −0.1704 | 0.85 |
| M–H2 | −0.2161 | 0.84 |
| M–H2.5 | −0.2599 | 0.85 |
| M–H3 | −0.3008 | 0.86 |
| M–H5 | −0.3894 | 0.81 |
| M–H6 | −0.4359 | 0.83 |
| M–H8 | −0.477 | 0.8 |
| M–H10 | −0.4478 | 0.69 |
| Config. | H | Ti | Zr | Hf | Sc | Mo |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M–H0.25 | −0.093 | 0.175 | −0.002 | −0.042 | 0.059 | −0.166 |
| M–H0.5 | −0.092 | 0.176 | 0.008 | −0.036 | 0.062 | −0.164 |
| M–H | −0.095 | 0.182 | 0.013 | −0.013 | 0.070 | −0.157 |
| M–H1.5 | −0.103 | 0.193 | 0.026 | 0.010 | 0.077 | −0.151 |
| M–H2 | −0.103 | 0.189 | 0.049 | 0.030 | 0.081 | −0.144 |
| M–H2.5 | −0.106 | 0.185 | 0.053 | 0.060 | 0.086 | −0.119 |
| M–H3 | −0.113 | 0.179 | 0.076 | 0.083 | 0.109 | −0.107 |
| Config. | Ti–H | Zr–H | Hf–H | Sc–H | Mo–H |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M–H0.25 | 0.1520 | 0.0640 | 0.0382 | 0.0888 | 0.0262 |
| M–H0.5 | 0.1159 | 0.0865 | 0.0692 | 0.0875 | 0.0269 |
| M–H | 0.0771 | 0.0711 | 0.0706 | 0.1112 | 0.0357 |
| M–H1.5 | 0.0917 | 0.0716 | 0.0685 | 0.0915 | 0.0477 |
| M–H2 | 0.0793 | 0.0865 | 0.0835 | 0.0768 | 0.0585 |
| M–H2.5 | 0.0683 | 0.0839 | 0.0851 | 0.0784 | 0.0793 |
| M–H3 | 0.0666 | 0.0874 | 0.0853 | 0.0838 | 0.0742 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hu, J.; Shen, H.; Jiang, M.; Gong, H.; Xiao, H.; Liu, Z.; Sun, G.; Zu, X. A DFT Study of Hydrogen Storage in High-Entropy Alloy TiZrHfScMo. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030461
Hu J, Shen H, Jiang M, Gong H, Xiao H, Liu Z, Sun G, Zu X. A DFT Study of Hydrogen Storage in High-Entropy Alloy TiZrHfScMo. Nanomaterials. 2019; 9(3):461. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030461
Chicago/Turabian StyleHu, Jutao, Huahai Shen, Ming Jiang, Hengfeng Gong, Haiyan Xiao, Zijiang Liu, Guangai Sun, and Xiaotao Zu. 2019. "A DFT Study of Hydrogen Storage in High-Entropy Alloy TiZrHfScMo" Nanomaterials 9, no. 3: 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030461
APA StyleHu, J., Shen, H., Jiang, M., Gong, H., Xiao, H., Liu, Z., Sun, G., & Zu, X. (2019). A DFT Study of Hydrogen Storage in High-Entropy Alloy TiZrHfScMo. Nanomaterials, 9(3), 461. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9030461