A New Hematocrit Measurement Method Using a Chemiluminescence Biosensor and Its Application in a Chemiluminescence Immunoassay Platform for Myocardial Markers Detection with Whole Blood Samples
Abstract
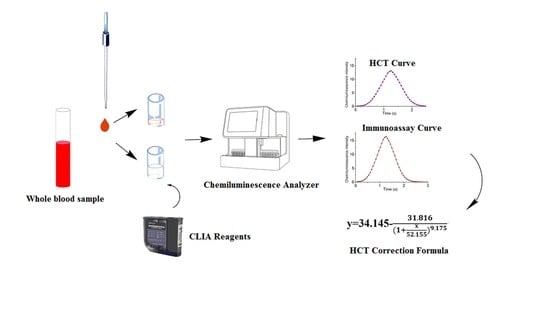
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Getein® CLIA for Myocardial Markers Detections
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. HCT Analysis by Chemiluminescence Biosensor
2.4. HCT Correction Formula for Whole Blood
2.5. Application of HCT Correction for Immunoassay
2.5.1. Repeatability Study
2.5.2. Accuracy Study
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. HCT Measurement
3.2. Effect of HCT on CLIA
3.3. Repeatability Testing
3.4. Accuracy Testing
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kosiborod, M.; Smith, G.L.; Radford, M.J.; Foody, J.M.; Krumholz, H.M. The prognostic importance of anemia in patients with heart failure. Am. J. Med. 2003, 114, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosiborod, M.; Krumholz, H.M.; Jones, P.G.; Pitt, B.; Spertus, J.A. The Relationship Between Anemia, Change in Hematocrit Over Time and Change in Health Status in Patients with Heart Failure After Myocardial Infarction. J. Card. Failure 2008, 14, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dill, D.B.; Costill, D.L. Calculation of percentage changes in volumes of blood, plasma, and red cells in dehydration. J. Appl. Physiol. 1974, 37, 247–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Giorno, R.; Clifford, J.H.; Beverly, S.; Rossing, R.G. Hematology Reference Values Analysis by Different Statistical Technics and Variations with Age and Sex. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1980, 74, 765–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldenfarb, P.B.; Bowyer, F.P.; Hall, E.; Brosious, E. Reproducibility in the Hematology Laboratory: The Microhematocrit Determination. Am. J. Clin. Pathol. 1971, 56, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berry, S.B.; Fernandes, S.C.; Rajaratnam, A.; DeChiara, N.S.; Mace, C.R. Measurement of the hematocrit using paper-based microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3689–3694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudolf, J.; Douglass, J.; Baron, J.; Lewandrowski, K. Evaluation of the i-STAT point-of-care capillary whole blood hematocrit and hemoglobin: Comparison to the Siemens RAPIDLab 1200, Sysmex XE5000, and manual spun hematocrit. Clin. Chim. Acta 2015, 446, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolotiniuk, N.V.; Manecke, G.R.; Pinsky, M.R.; Banks, D. Measures of Blood Hemoglobin and Hematocrit During Cardiac Surgery: Comparison of Three Point-of-Care Devices. J. Cardiothorac. Vasc. Anesth. 2018, 32, 1638–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zwart, A.; van Assendelft, O.W.; Bull, B.S.; England, J.M.; Lewis, S.M.; Zijlstra, W.G. Recommendations for reference method for haemoglobinometry in human blood (ICSH standard 1995) and specifications for international haemiglobinocyanide standard (4th edition). J. Clin. Pathol. 1996, 49, 271–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Su, B.; Kang, J.; Zhou, Z. Evaluation of a novel high sensitivity cardiac troponin I assay with whole blood. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2020, 508, 273–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Lin, Q.; Huang, L.; Zhai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Su, E.; He, N. Ultrasensitive chemiluminescence immunoassay with enhanced precision for the detection of cTnI amplified by acridinium ester-loaded microspheres and internally calibrated by magnetic fluorescent nanoparticles. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 3275–3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Qiu, X.; Su, E.; Huang, L.; Zai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Li, S.; et al. Multiple chemiluminescence immunoassay detection of the concentration ratio of glycosylated hemoglobin A1c to total hemoglobin in whole blood samples. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1192, 339379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.; Su, E.; Huang, L.; Zai, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, S.; Jin, L.; Deng, Y.; He, N. Washing-free chemiluminescence immunoassay for rapid detection of cardiac troponin I in whole blood samples. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thygesen, K.; Alpert, J.S.; Jaffe, A.S.; Chaitman, B.R.; Bax, J.J.; Morrow, D.A.; White, H.D.; Executive Group on behalf of the Joint European Society of Cardiology (ESC)/American College of Cardiology (ACC)/American Heart Association (AHA)/World Heart Federation (WHF) Task Force for the Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction. Fourth Universal Definition of Myocardial Infarction (2018). Circulation 2018, 138, 618–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Choi, K.H.; Lee, J.M.; Kim, H.K.; Hwang, D.; Rhee, T.M.; Kim, J.; Park, T.K.; Yang, J.H.; Song, Y.B.; et al. Prognostic Implications of Door-to-Balloon Time and Onset-to-Door Time on Mortality in Patients With ST-Segment–Elevation Myocardial Infarction Treated with Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019, 8, e012188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Armendáriz, Y.; García, S.; Lopez, R.M.; Pou, L. Hematocrit influences immunoassay performance for the measurement of tacrolimus in whole blood. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 766–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, T.; Homma, M.; Yuzawa, K.; Ohkohchi, N.; Hori, T.; Kaneko, M.; Hasegawa, Y.; Kojima, H.; Nagasawa, T.; Kohda, Y. Effects of Hematocrit Value on Microparticle Enzyme Immunoassay of Tacrolimus Concentration in Therapeutic Drug Monitoring. Ther. Drug Monit. 2005, 27, 94–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbas, S.H.; Ozdem, S.; Caglar, S.; Tuncer, M.; Gurkan, A.; Yucetin, L.; Senol, Y.; Demirbas, A.; Gultekin, M.; Ersoy, F.F.; et al. Effects of some hematological parameters on whole blood tacrolimus concentration measured by two immunoassay-based analytical methods. Clin. Biochem. 2005, 38, 552–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Serio, F.; Caputo, M.; Zaninotto, M.; Ottomano, C.; Plebani, M. Evaluation of analytical performance of the Pathfast cardiac troponin I. Clin. Chem. Lab. Med. 2009, 47, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Enea, N.S.; Zuk, R.; Tan, H.; Wu, A.H.B.; Jaffe, A.S. Performance characteristics of a high-sensitivity cardiac troponin assay using plasma and whole blood samples. Clin. Biochem. 2017, 50, 1249–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struthers, A.D. How to use natriuretic peptide levels for diagnosis and prognosis. Eur. Heart J. 1999, 20, 1374–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunt, P.J.; Richards, A.M.; Nicholls, M.G.; Yandle, T.G.; Doughty, R.N.; Espiner, E.A. Immunoreactive amino-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide (NT-PROBNP): A new marker of cardiac impairment. Clin. Endocrinol. 1997, 47, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talwar, S.; Squire, I.B.; Davies, J.E.; Barnett, D.B.; Ng, L.L. Plasma N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide and the ECG in the assessment of left-ventricular systolic dysfunction in a high risk population. Eur. Heart J. 1999, 20, 1736–1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, C.; Berry, C.; Blue, L.; Morton, J.J.; McMurray, J. N-terminal pro B type natriuretic peptide, but not the new putative cardiac hormone relaxin, predicts prognosis in patients with chronic heart failure. Heart 2003, 89, 879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Li, H.; Saqib, M.; Ge, C.; Zhang, X.; Jin, Y. Enhancing Luminol Electrochemiluminescence by Combined Use of Cobalt-Based Metal Organic Frameworks and Silver Nanoparticles and Its Application in Ultrasensitive Detection of Cardiac Troponin, I. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 3048–3054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.-T.; Zhao, L.-Z.; Fu, Y.-Z.; Liu, X.-M.; Ren, S.-W.; Liu, Y.-M. Tyramide signal amplification and enzyme biocatalytic precipitation on closed bipolar electrode: Toward highly sensitive electrochemiluminescence immunoassay. Sens. Actuators B-Chem. 2021, 331, 129427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Xi, Y.; Zhao, A.; Jiang, J.; Li, B.; Yang, X.; He, J.; Li, F. Cobalt-imidazole metal-organic framework loaded with luminol for paper-based chemiluminescence detection of catechol with use of a smartphone. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 3541–3550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Zhao, A.; Li, Z.; Xi, Y.; Jiang, J.; He, J.; Wang, J.; Cui, H. Multifunctionalized Hydrogel Beads for Label-Free Chemiluminescence Imaging Immunoassay of Acute Myocardial Infarction Biomarkers. Anal. Chem. 2022, 94, 2665–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Lu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Lin, L.; Xu, L. A Novel Acetylcholine Bioensor and Its Electrochemical Behavior. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 736–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, W.; Zhang, C.; Ma, T.; Liu, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, S.; Deng, Y. Advances in aptamer screening and aptasensors’ detection of heavy metal ions. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Chen, Z.; Lv, M.; Xu, J.; Dong, X.; Zhao, J.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; He, N.; Li, Z.; et al. Rapid and label-free classification of pathogens based on light scattering, reduced power spectral features and support vector machine. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 3163–3167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ma, X.; Zhang, X.; Hu, G.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; He, N.; Wu, Y.; Jiang, Z. Novel aerosol detection platform for SARS-CoV-2: Based on specific magnetic nanoparticles adsorption sampling and digital droplet PCR detection. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2023, 34, 107701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ling, Y.; Zhu, Y.; Fan, H.; Zha, H.; Yang, M.; Wu, L.; Chen, H.; Li, W.; Wu, Y.; Chen, H. Rapid Method for Detection of Staphylococcus aureus in Feces. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2019, 15, 1290–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Su, X.; Jin, L.; Wu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; et al. Fast and Accurate Control Strategy for Portable Nucleic Acid Detection (PNAD) System Based on Magnetic Nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2021, 17, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.; Fang, Y.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Ji, M.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, S.; Deng, Y.; Jin, L.; et al. A Detection-Service-Mobile Three-Terminal Software Platform for Point-of-Care Infectious Disease Detection System. Biosensors 2022, 12, 684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Fang, Y.; Liu, H.; Su, X.; Chen, Z.; Li, S.; He, N. A Highly Integrated and Diminutive Fluorescence Detector for Point-of-Care Testing: Dual Negative Feedback Light-Emitting Diode (LED) Drive and Photoelectric Processing Circuits Design and Implementation. Biosensors 2022, 12, 764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, L.; Liu, F.; Ma, P.; Xiao, X. Applications of Gold Nanoparticles in Optical Biosensors. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2014, 10, 2700–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, M.; Liu, X.; Zou, J.; Yang, J.; Ali, Z.; Rehman, H.U.; He, N.; Dai, J.; Tang, Y. On-chip classification of micro-particles using laser light scattering and machine learning. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1885–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Zhao, K.; He, Z.; Luo, X.; Qin, Z.; Tan, Y.; Zheng, X.; Wu, Z.; Deng, Y.; Chen, H.; et al. Development and evaluation of a thermostatic nucleic acid testing device based on magnesium pyrophosphate precipitation for detecting Enterocytozoon hepatopenaei. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 4053–4056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, W.; Ma, C.; Li, Z. Fabrication of an Electrochemical Biosensor Array for Simultaneous Detection of L-Glutamate and Acetylcholine. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 1378–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huang, L.; Zhang, D.; Jiao, L.; Su, E.; He, N. A new quality control method for lateral flow assay. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2018, 29, 1853–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Liu, J.; Liu, X.; Li, G.; Deng, P.; Liang, J. Manganese dioxide Nanorods/electrochemically reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites modified electrodes for cost-effective and ultrasensitive detection of Amaranth. Colloid. Surface B-Biointerface 2018, 172, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.; Su, E.; Liu, Y.; He, N.; Deng, Y.; Jin, L.; Chen, Z.; Li, S. A microfluidic device for accurate detection of hs-cTnI. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1555–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Tian, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; Deng, P.; Chen, D. Electrochemical Sensor for Rapid and Sensitive Detection of Tryptophan by a Cu2O Nanoparticles-Coated Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Yang, G.; Li, T.; Deng, Y.; Chen, Z.; He, N. Selection of a DNA aptamer for the development of fluorescent aptasensor for carbaryl detection. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1957–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Yang, T.; Yang, H.; Li, T.; Nie, L.; Mou, X.; Deng, Y.; He, N.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; et al. A Portable Multi-Channel Turbidity System for Rapid Detection of Pathogens by Loop-Mediated Isothermal Amplification. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Yang, G.; Deng, Y.; Mou, X.; He, N. A simple AuNPs-based colorimetric aptasensor for chlorpyrifos detection. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 1913–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magesa, F.; Wu, Y.; Dong, S.; Tian, Y.; Li, G.; Vianney, J.M.; Buza, J.; Liu, J.; He, Q. Electrochemical Sensing Fabricated with Ta2O5 Nanoparticle-Electrochemically Reduced Graphene Oxide Nanocomposite for the Detection of Oxytetracycline. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Lai, Y.; Yang, G.; Tang, C.; Deng, Y.; Li, S.; Wang, Z. Cd-Aptamer Electrochemical Biosensor Based on AuNPs/CS Modified Glass Carbon Electrode. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 1253–1259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Deng, Y.; Li, T.; Chen, Z.; Chen, H.; Li, S.; Liu, H. Aptamer-Based Electrochemical Biosensor for Mercury Ions Detection Using AuNPs-Modified Glass Carbon Electrode. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2018, 14, 2156–2161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; He, N. Application of adaptive pressure-driven microfluidic chip in thyroid function measurement. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2021, 32, 1747–1750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Dong, H.; Chen, Z.; Lin, L.; Chen, H.; Li, S.; Deng, Y. Magnetic Nanoparticles Enhanced Microarray Detection of Multiple Foodborne Pathogens. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2017, 13, 1333–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.; Li, S.; Xu, L. Preparation and Electrochemical Behavior of L-Glutamate Electrochemical Biosensor. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rothschild, M.-L. The reaction of ferriprotoporphyrin with hydrogen peroxide in alkaline solutions. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1960, 90, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, M.L. The reaction of hemin with H2O2. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 185, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Samples | cTnI | MYO | CK-MB | NT-proBNP | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 | Control | 2.72–3.82% | 2.58–3.87% | 2.95–4.53% | 2.20–3.99% |
| HCT Correction | 1.87–3.13% | 1.81–3.01% | 1.99–3.29% | 1.90–3.07% | |
| Level 2 | Control | 2.44–3.46% | 2.35–3.68% | 2.80–4.19% | 1.85–3.61% |
| HCT Correction | 1.91–2.99% | 1.83–2.98% | 2.06–3.29% | 1.89–2.98% | |
| Level 3 | Control | 2.21–3.13% | 2.13–3.32% | 2.48–3.91% | 2.50–3.14% |
| HCT Correction | 1.85–2.98% | 1.80–2.98% | 2.05–3.32% | 1.88–2.97% | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, H.; Han, H.; Lin, Q.; Huang, L.; Su, X.; Fang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Su, E.; Chen, Z.; Li, S.; et al. A New Hematocrit Measurement Method Using a Chemiluminescence Biosensor and Its Application in a Chemiluminescence Immunoassay Platform for Myocardial Markers Detection with Whole Blood Samples. Biosensors 2023, 13, 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010003
Zhao H, Han H, Lin Q, Huang L, Su X, Fang Y, Zhang Y, Su E, Chen Z, Li S, et al. A New Hematocrit Measurement Method Using a Chemiluminescence Biosensor and Its Application in a Chemiluminescence Immunoassay Platform for Myocardial Markers Detection with Whole Blood Samples. Biosensors. 2023; 13(1):3. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010003
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Huan, Hao Han, Qifeng Lin, Li Huang, Xiangyi Su, Yile Fang, Yuanying Zhang, Enben Su, Zhu Chen, Song Li, and et al. 2023. "A New Hematocrit Measurement Method Using a Chemiluminescence Biosensor and Its Application in a Chemiluminescence Immunoassay Platform for Myocardial Markers Detection with Whole Blood Samples" Biosensors 13, no. 1: 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010003
APA StyleZhao, H., Han, H., Lin, Q., Huang, L., Su, X., Fang, Y., Zhang, Y., Su, E., Chen, Z., Li, S., Deng, Y., & He, N. (2023). A New Hematocrit Measurement Method Using a Chemiluminescence Biosensor and Its Application in a Chemiluminescence Immunoassay Platform for Myocardial Markers Detection with Whole Blood Samples. Biosensors, 13(1), 3. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios13010003