Application of Aluminum Hydroxide for Improvement of Label-Free SERS Detection of Some Cephalosporin Antibiotics in Urine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of SERS Substrate
2.3. Preparation of Aluminum Hydroxide Gel (AHG)
2.4. Urine Collection and Sample Pretreatment
2.5. SERS Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. SERS Signal of Pure Urine
3.1.1. Influence of pH
3.1.2. Influence of Dilution
3.1.3. Treatment by AHG
3.2. Stability of AHG during the Storage and Batch-to-Batch Reproducibility
3.3. Influence of the Pretreatment on Analyte Concentration
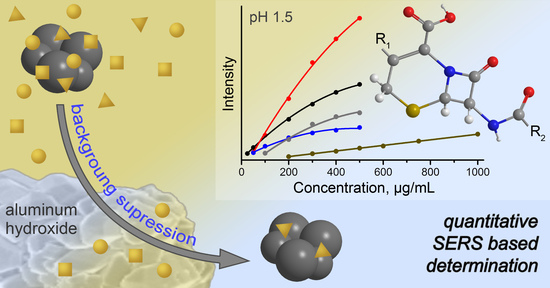
3.4. SERS Analysis of Spiked Urine and Analytical Performance
3.4.1. Analysis Protocol
3.4.2. Calibration Curves and Influence of Sample Pretreatment
3.4.3. Limits of Quantification and Signal Deviation
3.4.4. Limitations and Possible Modifications of the Protocol
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jaworska, A.; Fornasaro, S.; Sergo, V.; Bonifacio, A. Potential of surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy (SERS) in therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM). A critical review. Biosensors 2016, 6, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.A.; Norris, R.; Paterson, D.L.; Martin, J.H. Therapeutic drug monitoring of antimicrobials. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2011, 73, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Drayer, D.E. Pharmacologically active drug metabolites: Therapeutic and toxic activities, plasma and urine data in man, accumulation in renal failure. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 1976, 1, 426–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evenepoel, P. Acute toxic renal failure. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2004, 18, 37–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Yan, B.; Chen, L. SERS tags: Novel optical nanoprobes for bioanalysis. Chem. Rev. 2013, 113, 1391–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, X.S.; Jahn, I.J.; Weber, K.; Cialla-May, D.; Popp, J. Label-free SERS in biological and biomedical applications: Recent progress, current challenges and opportunities. Spectrochim. Acta A 2018, 197, 56–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Z.; Chen, L.; Lv, H.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, B. Magnetic imprinted surface enhanced Raman scattering (MI-SERS) based ultrasensitive detection of ciprofloxacin from a mixed sample. Anal. Method 2014, 6, 1627–1632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markina, N.E.; Volkova, E.K.; Zakharevich, A.M.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; Markin, A.V. SERS detection of ceftriaxone and sulfadimethoxine using copper nanoparticles temporally protected by porous calcium carbonate. Microchim. Acta 2018, 185, 481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markina, N.E.; Zakharevich, A.M.; Markin, A.V. Improvement of creatinine SERS detection using molecularly imprinted silica gel. Proc. SPIE 2019, 11065, 110651M. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidi, I.J.; Jahn, M.; Pletz, M.W.; Weber, K.; Cialla-May, D.; Popp, J. Toward levofloxacin monitoring in human urine samples by employing the LoC-SERS technique. J. Phys. Chem. C 2016, 120, 20613–20623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Han, S.; Li, X. Detection of tobacco-related biomarkers in urine samples by surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy coupled with thin-layer chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2013, 405, 6815–6822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markina, N.E.; Goryacheva, I.Y.; Markin, A.V. Sample pretreatment and SERS-based detection of ceftriaxone in urine. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 2221–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huttner, A.; Harbarth, S.; Hope, W.W.; Lipman, J.; Roberts, J.A. Therapeutic drug monitoring of the β-lactam antibiotics: What is the evidence and which patients should we be using it for? J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2015, 70, 3178–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leopold, N.; Lendl, B. A new method for fast preparation of highly surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) active silver colloids at room temperature by reduction of silver nitrate with hydroxylamine hydrochloride. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 5723–5727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yurova, N.S.; Markina, N.E.; Pozharov, M.V.; Zakharevich, A.M.; Rusanova, T.Y.; Markin, A.V. SERS-active sorbent based on aluminum oxide loaded with silver nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A 2016, 495, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rose, C.; Parker, A.; Jefferson, B.; Cartmell, E. The characterization of feces and urine: A review of the literature to inform advanced treatment technology. Crit. Rev. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 45, 1827–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsich, L.; Bonifacio, A.; Mandal, S.; Krol, S.; Beleites, C.; Sergo, V. Poly-l-lysine-coated silver nanoparticles as positively charged substrates for surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Langmuir 2012, 28, 13166–13171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vikram, K.; Mishra, S.; Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, R.K. Low temperature Raman and DFT study of creatinine. J. Mol. Struct. 2012, 1012, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paragi, G.; Kovács, L.; Kupihár, Z.; Szolomájer, J.; Penke, B.; Guerra, C.F.; Bickelhaupt, F.M. Neutral and positively charged new purine tetramer structures: A computational study of xanthine and uric acid derivatives. New J. Chem. 2011, 35, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masilamani, V.; AlSalhi, M.S.; Vijmasi, T.; Govindarajan, K.; Rai, R.R.; Atif, M.; Prasad, S.; Aldwayyan, A. Fluorescence spectra of blood and urine for cervical cancer detection. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 098001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leiner, M.J.P.; Hubmann, M.R.; Wolfbeis, O.S. The total fluorescence of human urine. Anal. Chim. Acta 1987, 198, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arbeloa, F.L.; Ojeda, P.R.; Arbeloa, I.L. Flourescence self-quenching of the molecular forms of Rhodamine B in aqueous and ethanolic solutions. J. Lumin. 1989, 44, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.J.; Chen, P.Y.; Nien, P.C.; Lin, C.Y.; Vittal, R.; Ling, T.R.; Ho, K.C. Preparation of a novel molecularly imprinted polymer by the sol–gel process for sensing creatinine. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 711, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Czerwinski, A.W.; Pederson, J.A.; Barry, J.P. Cefazolin plasma concentrations and urinary excretion in patients with renal impairment. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1974, 14, 560–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosmidis, J.; Stathakis, C.; Anyfantis, A.; Daikos, G.K. Cefuroxime in renal insufficiency: Therapeutic results in various infections and pharmacokinetics including the effects of dialysis. Proc. R. Soc. Med. 1977, 70, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, R.R.; Peddie, B.; Blake, E. Serum and urine concentrations of cefoperazone in severe chronic renal failure. Drugs 1981, 22, 46–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, I.H.; Chen, S.; Parsonnet, M.; Hackman, M.R.; Brooks, M.A.; Onikoff, J.; Kaplan, S.A. Pharmacokinetics of ceftriaxone in humans. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 1981, 20, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ohkawa, M.; Okasho, A.; Motoi, I.; Tokunaga, S.; Shoda, R.; Kawaguchi, S.; Sawaki, M.; Shimamura, M.; Hirano, S.; Kuroda, K.; et al. Elimination kinetics of cefotaxime and desacetyl cefotaxime in patients with renal insufficiency and during hemodialysis. Chemotherapy 1983, 29, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Emmons, E.D.; Fountain, A.W.; Guicheteau, J.A.; Moskovits, M.; Christesen, S.D. Critical role of adsorption equilibria on the determination of surface-enhanced Raman enhancement. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 584–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Analyte | λ, nm | Calibration Equation | Cinitial, μg/mL | Cfinal, μg/mL | Content, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CZL | 273 | y = 0.019x + 0.004 R2 = 0.998 | 100 | 20 | 20 |
| 200 | 32 | 16 | |||
| CPR | 227 | y = 0.033x + 0.015 R2 = 0.999 | 100 | 19 | 19 |
| 200 | 35 | 18 | |||
| CTX | 232 | y = 0.028x − 0.087 R2 = 0.999 | 100 | 17 | 17 |
| 200 | 26 | 13 | |||
| CTR | 239 | y = 0.043x + 0.040 R2 = 0.999 | 100 | 1.7 | 1.7 |
| 200 | 3.4 | 1.7 | |||
| CRX | 280 | y = 0.031x + 0.088 R2 = 0.994 | 100 | 16 | 16 |
| 200 | 31 | 16 |
| Analyte | Volume, μL | Range, μg/mL | LOQ, μg/mL | LOQwater, * μg/mL |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CZL | 100 | 25–500 | 19 | 1.7 |
| CPR | 100 | 50–500 | 45 | 4.1 |
| CTX | 100 | 50–500 | 34 | 2.0 |
| CTR | 175 | 100–500 | 92 | 1.0 |
| CRX | 175 | 200–1000 | 280 | 13 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Markina, N.E.; Markin, A.V. Application of Aluminum Hydroxide for Improvement of Label-Free SERS Detection of Some Cephalosporin Antibiotics in Urine. Biosensors 2019, 9, 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030091
Markina NE, Markin AV. Application of Aluminum Hydroxide for Improvement of Label-Free SERS Detection of Some Cephalosporin Antibiotics in Urine. Biosensors. 2019; 9(3):91. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030091
Chicago/Turabian StyleMarkina, Natalia E., and Alexey V. Markin. 2019. "Application of Aluminum Hydroxide for Improvement of Label-Free SERS Detection of Some Cephalosporin Antibiotics in Urine" Biosensors 9, no. 3: 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030091
APA StyleMarkina, N. E., & Markin, A. V. (2019). Application of Aluminum Hydroxide for Improvement of Label-Free SERS Detection of Some Cephalosporin Antibiotics in Urine. Biosensors, 9(3), 91. https://doi.org/10.3390/bios9030091