The Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Anaerobic Bacteria in Major Liver Resection
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Clinical Characteristics
2.2. Clinical Comparison of Anaerobic Infections
2.3. Microbiological Results
2.4. Risk Factor Analysis for Anaerobic Infection
2.5. Treatment of Anaerobic Infections
3. Discussion
Strengths and Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Data Acquisition
4.2. Clinical Definitions
4.3. Isolation and Identification of Strains
4.4. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ASA | American Society of Anesthesiologist |
| CRLM | Colorectal Liver Metastasis |
| BMI | Body Mass Index |
| CI | Confidence Interval |
| FET | Fisher´s Exact Test |
| iCCA | intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma |
| GBCA | Gallbladder Carcinoma |
| HCC | Hepatocellular Carcinoma |
| MALDI-TOF | Matrix-Assisted Laser Desorption/Ionization-Time Of Flight |
| MELD | Model of End-Stage Liver Disease |
| MWU | Mann-Whitney U-Test |
| NET | Neuroendocrine Tumor |
| NGS | Next-Generation Sequencing |
| phCCA | perihilar Cholangiocarcinoma |
| PHLF | Post-Hepatectomy Liver Failure |
| SD | Standard Deviation |
| SSI | Surgical Site Infection |
| Χ2 | Chi-Square test |
References
- Moreno Elola-Olaso, A.; Davenport, D.L.; Hundley, J.C.; Daily, M.F.; Gedaly, R. Predictors of surgical site infection after liver resection: A multicentre analysis using National Surgical Quality Improvement Program data. HPB (Oxford) 2012, 14, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yamashita, Y.-I.; Hamatsu, T.; Rikimaru, T.; Tanaka, S.; Shirabe, K.; Shimada, M.; Sugimachi, K. Bile leakage after hepatic resection. Ann. Surg. 2001, 233, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spetzler, V.N.; Schepers, M.; Pinnschmidt, H.O.; Fischer, L.; Nashan, B.; Li, J. The incidence and severity of post-hepatectomy bile leaks is affected by surgical indications, preoperative chemotherapy, and surgical procedures. Hepatobiliary Surg. Nutr. 2019, 8, 101–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Würstle, S.; Göß, A.; Spinner, C.D.; Huber, W.; Algül, H.; Schlag, C. A retrospective clinical and microbial analysis of 32 patients with bilomas. BMC Gastroenterol. 2019, 19, 50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugawara, G.; Ebata, T.; Yokoyama, Y.; Igami, T.; Takahashi, Y.; Takara, D.; Nagino, M. The effect of preoperative biliary drainage on infectious complications after hepatobiliary resection with cholangiojejunostomy. Surgery 2013, 153, 200–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, Y.M.; Rao, X. Clinical and Microbiological Characteristics of Patients with Complicated Intra-abdominal Infections in Intensive Care Unit. Curr. Med. Sci. 2020, 40, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, P.S.; Schønheyder, H.C. Pyogenic hepatic abscess. A 10-year population-based retrospective study. APMIS 1998, 106, 396–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.J.; Pitt, H.A.; Lipsett, P.A.; Osterman, F.A., Jr.; Lillemoe, K.D.; Cameron, J.L.; Zuidema, G.D. Pyogenic hepatic abscess. Changing trends over 42 years. Ann. Surg. 1996, 223, 600–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, X.F.; Li, N.; Chen, X.F.; Zhang, L.; Yan, M. Incidence and Risk Factors for Liver Abscess After Thermal Ablation of Liver Neoplasm. Hepat. Mon. 2016, 16, e34588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Giorgio, A.; Merola, M.G.; Montesarchio, L.; Merola, F.; Gatti, P.; Coppola, C.; Calisti, G. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis: Analysis of complications in a single centre over 20 years. Br. J. Radiol. 2017, 90, 20160804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyrhovden, R.; Øvrebø, K.K.; Nordahl, M.V.; Nygaard, R.M.; Ulvestad, E.; Kommedal, Ø. Bacteria and fungi in acute cholecystitis. A prospective study comparing next generation sequencing to culture. J. Infect. 2020, 80, 16–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schneider, J.; Hapfelmeier, A.; Fremd, J.; Schenk, P.; Obermeier, A.; Burgkart, R.; Weber, A. Biliary endoprosthesis: A prospective analysis of bacterial colonization and risk factors for sludge formation. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e110112. [Google Scholar]
- Gomi, H.; Solomkin, J.S.; Schlossberg, D.; Okamoto, K.; Takada, T.; Strasberg, S.M.; Ukai, T.; Endo, I.; Iwashita, Y.; Hibi, T.; et al. Tokyo Guidelines 2018: Antimicrobial therapy for acute cholangitis and cholecystitis. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2018, 25, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Capobianco, I.; Rolinger, J.; Nadalin, S. Resection for Klatskin tumors: Technical complexities and results. Transl. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 3, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Moustafa, M.; Linecker, M.; Lurje, G.; Capobianco, I.; Baumgart, J.; Nadalin, S. ALPPS for Locally Advanced Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma: Did Aggressive Surgery Lead to the Oncological Benefit? An International Multi-center Study. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 1372–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strasberg, S.M.; Belghiti, J.; Clavien, P.A.; Gadzijev, E.; Garden, J.O.; Lau, W.Y.; Strong, R.W. The Brisbane 2000 Terminology of Liver Anatomy and Resections. HPB 2000, 2, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bressan, A.K.; Isherwood, S.; Bathe, O.F.; Dixon, E.; Sutherland, F.R.; Ball, C.G. Preoperative Single-Dose Methylprednisolone Prevents Surgical Site Infections After Major Liver Resection: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Surg. 2020. Publish Ahead of Print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welch, B.T.; Schmitz, J.J.; Atwell, T.D.; McGauvran, A.M.; Kurup, A.N.; Callstrom, M.R.; Schmit, G.D. Evaluation of infectious complications following percutaneous liver ablation in patients with bilioenteric anastomoses. Abdom. Radiol. 2017, 42, 1579–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, R.; Rempp, H.; Schmidt, D.; Pereira, P.L.; Claussen, C.D.; Clasen, S. Prolonged antibiotic prophylaxis in patients with bilioenteric anastomosis undergoing percutaneous radiofrequency ablation. J. Vasc. Interv. Radiol. 2012, 23, 545–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kokudo, T.; Uldry, E.; Demartines, N.; Halkic, N. Risk factors for incisional and organ space surgical site infections after liver resection are different. World J. Surg. 2015, 39, 1185–1192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, A.; Ricci, A.D.; Frega, G.; Palloni, A.; De Lorenzo, S.; Abbati, F.; Brandi, G. How to Choose Between Percutaneous Transhepatic and Endoscopic Biliary Drainage in Malignant Obstructive Jaundice: An Updated Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. In Vivo 2020, 34, 1701–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrero, A.; Lo Tesoriere, R.; Viganò, L.; Caggiano, L.; Sgotto, E.; Capussotti, L. Preoperative biliary drainage increases infectious complications after hepatectomy for proximal bile duct tumor obstruction. World J. Surg. 2009, 33, 318–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hochwald, S.N.; Burke, E.C.; Jarnagin, W.R.; Fong, Y.; Blumgart, L.H. Association of preoperative biliary stenting with increased postoperative infectious complications in proximal cholangiocarcinoma. Arch. Surg. 1999, 134, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Shinkawa, H.; Tanaka, S.; Takemura, S.; Amano, R.; Kimura, K.; Nishioka, T.; Ito, T.; Miyazaki, T.; Ishihara, A.; Kubo, S. Giving short-term prophylactic antibiotics in patients undergoing open and laparoscopic hepatic resection. Ann. Gastroenterol. Surg. 2019, 3, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sudo, T.; Murakami, Y.; Uemura, K.; Hayashidani, Y.; Hashimoto, Y.; Ohge, H.; Sueda, T. Specific Antibiotic Prophylaxis Based on Bile Cultures Is Required to Prevent Postoperative Infectious Complications in Pancreatoduodenectomy Patients Who Have Undergone Preoperative Biliary Drainage. World J. Surg. 2007, 31, 2230–2235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Okamura, K.; Tanaka, K.; Miura, T.; Nakanishi, Y.; Noji, T.; Nakamura, T. Randomized controlled trial of perioperative antimicrobial therapy based on the results of preoperative bile cultures in patients undergoing biliary reconstruction. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Sci. 2017, 24, 382–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Said, A.; Safdar, N.; Lucey, M.R.; Knechtle, S.J.; D’Alessandro, A.; Musat, A.; Pirsch, J.; Kalayoglu, M.; Maki, D.G. Infected bilomas in liver transplant recipients, incidence, risk factors and implications for prevention. Am. J. Transplant. 2004, 4, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tachopoulou, O.A.; Vogt, D.P.; Henderson, J.M.; Baker, M.; Keys, T.F. Hepatic abscess after liver transplantation: 1990–2000. Transplantation 2003, 75, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Copeland-Halperin, L.R.; Kaminsky, A.J.; Bluefeld, N.; Miraliakbari, R. Sample procurement for cultures of infected wounds: A systematic review. J. Wound Care 2016, 25, S4–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aggarwal, V.K.; Higuera, C.; Deirmengian, G.; Parvizi, J.; Austin, M.S. Swab cultures are not as effective as tissue cultures for diagnosis of periprosthetic joint infection. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2013, 471, 3196–3203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Begley, M.; Gahan, C.G.; Hill, C. The interaction between bacteria and bile. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2005, 29, 625–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Strohäker, J.; Wiegand, L.; Beltzer, C.; Königsrainer, A.; Ladurner, R.; Meier, A. Clinical Presentation and Incidence of Anaerobic Bacteria in Surgically Treated Biliary Tract Infections and Cholecystitis. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thabit, A.K. Antibiotics in the Biliary Tract: A Review of the Pharmacokinetics and Clinical Outcomes of Antibiotics Penetrating the Bile and Gallbladder Wall. Pharmacotherapy 2020, 40, 672–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takesue, Y.; Kusachi, S.; Mikamo, H.; Sato, J.; Watanabe, A.; Kiyota, H.; Yanagihara, K. Antimicrobial susceptibility of common pathogens isolated from postoperative intra-abdominal infections in Japan. J. Infect. Chemother. 2018, 24, 330–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Brown, K.A.; Khanafer, N.; Daneman, N.; Fisman, D.N. Meta-analysis of antibiotics and the risk of community-associated Clostridium difficile infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 2326–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Buhl, M.; Willmann, M.; Liese, J.; Autenrieth, I.B.; Marschal, M. Prevotella colorans sp. nov., isolated from a human wound. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 2016, 66, 3005–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Surgical Details and Outcome | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, Gender | Diagnosis | Procedure | Location of Specimen | Anaerobe | Preoperative Stent | Complications | Length of Stay | Outcome |
| 34 f | iCCA | Right Trisectionectomy * + Resection of Extrahepatic bile duct and bilioenteric anastomosis | Bile duct 1st Procedure | Prevotella buccae Prevotella melaninogenica | Yes | 11d | alive | |
| 72 m | HCC | Right Trisectionectomy + Resection of Extrahepatic bile duct and bilioenteric anastomosis | Bile duct 1st Procedure | Anaerobe not otherwise specified | Yes | death from septic shock due to post-hepatectomy liver failure | 29d | dead |
| 44 w | Embryonal Sarcoma of the Liver | Right Trisectionectomy + Segmental Colectomy | Anastomotic leak Revision | Bacteroides vulgatus | No | death from multi-organ failure with bile leak and peritonitis & post-hepatectomy liver failure | 35d | dead |
| 38 m | Echinococcus alveolaris | Right Trisectionectomy + Resection of Extrahepatic bile duct and bilioenteric anastomosis | Bile duct 1st Procedure | Bifidobacterium animalis | Yes | 28d | alive | |
| 71 m | phCCA | Left Hepatectomy + Resection of Extrahepatic bile duct and bilioenteric anastomosis | Bile duct 1st Procedure | Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron | Yes | 13d | alive | |
| 78 f | phCCA | Left Hepatectomy + Resection of Extrahepatic bile duct and bilioenteric anastomosis | Bile duct 1st Procedure | Prevotella buccae | Yes | 20d | alive | |
| 40 m | Echinococcus granulosus | Right Hepatectomy | Abscess perihepatic and subcutaneous Revision | Finegoldia magna | No | perihepatic abscess, wound dehiscence | 29d | alive |
| 80 m | Klatskin-mimicking Lesion | Right Trisectionectomy + Resection of Extrahepatic bile duct and bilioenteric anastomosis | Bilioma CT-Drain | Prevotella melaninogenica | Yes | infected bilioma | 35d | alive |
| 68 f | GBCA | Right Trisectionectomy + Resection of Extrahepatic bile duct and bilioenteric anastomosis | Bile duct 1st Procedure | Bilophila wadsworthia Veillonella parvula | Yes | revision laparotomy for postoperative bleeding | 31d | alive |
| 54 f | Recurrent Cholangitis | Right Hepatectomy + Resection of Extrahepatic bile duct and bilioenteric anastomosis | Bile duct 1st Procedure | Bacteroides fragilis | No | 8d | alive | |
| 58 f | iCCA | Right Trisectionectomy + Resection of Extrahepatic bile duct and bilioenteric anastomosis | Deep subcutaneous abscess | Prevotella buccae | No | revision laparotomy for postoperative bleeding | 25d | alive |
| 60 f | NET-Metastasis | Right Trisectionectomy + Resection of Extrahepatic bile duct and bilioenteric anastomosis | Deep subcutaneous abscess | Finegoldia magna | No | revision laparotomy for postoperative ileus | 36d | alive |
| 60 f | CRLM | Left Hepatectomy | Bilioma Revision | Finegoldia magna | No | revision laparotomy for postoperative bile leak | 21d | alive |
| Anaerobic Group vs. Control Group | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Anaerobes (n = 13) | No Anaerobes (n = 232) | p | |
| Gender m (Percentage) | 5 (38%) | 131 (56%) | 0.204 |
| Median age in years | 60 (± 15) | 64 (± 13) | 0.373 |
| Body mass index (BMI) in kg/m2 | 25.2 (± 4.7) | 24.6 (± 4.6) | 0.415 |
| Diabetes | 3 (23%) | 35 (15%) | 0.439 |
| Diagnosis Malignant Recurrent infections | 9 (69%) 1 (8%) | 204 (88%) 35 (15%) | 0.052 0.429 |
| Preoperative biliary stent | 7 (54%) | 85 (27%) | 0.000 |
| Procedure Right Hepatectomy Right Trisectionectomy Left Hepatectomy Left Trisectionectomy Central Resection | 2 (15%) 8 (62%) 3 (23%) 0 0 | 91 (39%) 75 (32%) 33 (14%) 25 (11%) 5 (2%) | 0.114 |
| Median operating time in minutes Median length of stay in days | 292 (± 73) 28 (± 9) | 247 (± 100) 13 (± 13) | 0.035 0.002 |
| Resection of extrahepatic bile duct | 9 (69%) | 75 (32%) | 0.006 |
| Bile leak | 7 (54%) | 41 (18%) | 0.001 |
| Elevated risk for PHLF | 10 (78%) | 147 (63%) | 0.390 |
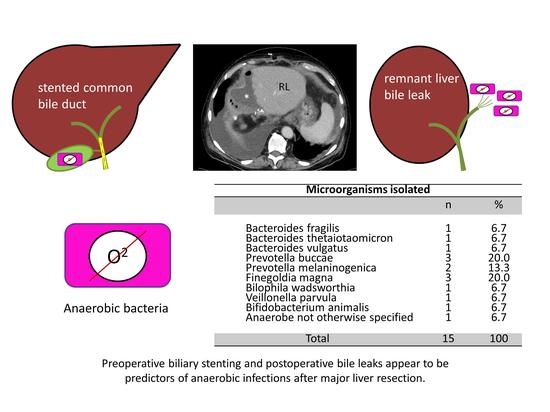
| Microorganisms Isolated | ||
|---|---|---|
| n | % | |
| Bacteroides fragilis Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron Bacteroides vulgatus Prevotella buccae Prevotella melaninogenica Finegoldia magna Bilophila wadsworthia Veillonella parvula Bifidobacterium animalis Anaerobe not otherwise specified | 1 1 1 3 2 3 1 1 1 1 | 6.7 6.7 6.7 20.0 13.3 20.0 6.7 6.7 6.7 6.7 |
| Total | 15 | 100 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Strohäker, J.; Bareiß, S.; Nadalin, S.; Königsrainer, A.; Ladurner, R.; Meier, A. The Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Anaerobic Bacteria in Major Liver Resection. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020139
Strohäker J, Bareiß S, Nadalin S, Königsrainer A, Ladurner R, Meier A. The Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Anaerobic Bacteria in Major Liver Resection. Antibiotics. 2021; 10(2):139. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020139
Chicago/Turabian StyleStrohäker, Jens, Sophia Bareiß, Silvio Nadalin, Alfred Königsrainer, Ruth Ladurner, and Anke Meier. 2021. "The Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Anaerobic Bacteria in Major Liver Resection" Antibiotics 10, no. 2: 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020139
APA StyleStrohäker, J., Bareiß, S., Nadalin, S., Königsrainer, A., Ladurner, R., & Meier, A. (2021). The Prevalence and Clinical Significance of Anaerobic Bacteria in Major Liver Resection. Antibiotics, 10(2), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/antibiotics10020139