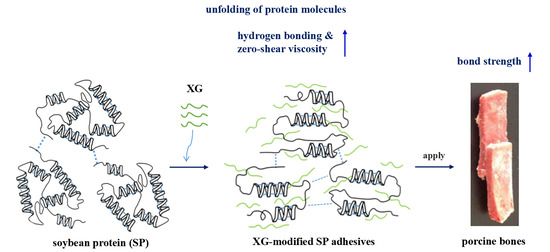
Characterization of Soybean Protein Adhesives Modified by Xanthan Gum
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Soybean Proteins
2.3. Preparation of XG-Modified SP (SP-XG) Adhesives
2.4. Characterizations of SP-XG Adhesives
2.4.1. Raman Spectroscopic Measurement
2.4.2. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.4.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) Analysis
2.5. Adhesion Properties of SP-XG Adhesives
2.5.1. Rheological Properties
2.5.2. Measurement of Tensile Shear Strength Using an In Vitro Adhesives Bonding Model
2.6. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Adhesion Properties of SP-XG Adhesives
3.1.1. Effect of XG on Tensile Shear Strength of SP Adhesives
3.1.2. Effect of XG on Zero-Shear Viscosity of SP Adhesives
3.2. Characterizations of SP-XG Adhesives
3.2.1. Raman Spectroscopic Analysis
3.2.2. FTIR Spectroscopy
3.2.3. X-ray Diffraction (XRD) of SP-XG
3.3. Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) Analysis of SP-XG Adhesives
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Machado, V.G.; Hirata, T.A.M.; Menegalli, F.C. Agglomeration of soy protein isolate in a pulsed fluidized bed: Experimental study and process optimization. Powder Technol. 2014, 254, 248–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Yu, M.; Wang, L. Preparation and characterization of antioxidant soy protein isolate films incorporating licorice residue extract. Food Hydrocolloids 2018, 75, 187–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Chen, N.; Bian, L.; Fan, M. Development and mechanism characterization of high performance soy-based bio-adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2012, 34, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayyıldız, S.N.; Ayyıldız, A. Cyanoacrylic tissue glues: Biochemical properties and their usage in urology. Turk. J. Urol. 2017, 43, 14–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wu, M.; Liu, H.M. Emulsifying and physicochemical properties of soy hull hemicelluloses-soy protein isolate conjugates. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 163, 181–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peles, Z.; Zilberman, M. Novel soy protein wound dressings with controlled antibiotic release: Mechanical and physical properties. Acta Biomater. 2012, 8, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, K.B.; Chung, E.J.; Shah, R.N. Investigation of soy protein hydrogels for biomedical applications: Materials characterization, drug release, and biocompatibility. J. Biomater. Appl. 2014, 28, 1085–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chien, K.B.; Aguado, B.A.; Bryce, P.J.; Shah, R.N. In vivo acute and humoral response to three-dimensional porous soy protein scaffolds. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8983–8990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merolli, A.; Nicolais, L.; Ambrosio, L.; Santin, M. A degradable soybean-based biomaterial used effectively as a bone filler in vivo in a rabbit. Biomed. Mater. 2010, 5, 015008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, G.A.; Vaz, C.M.; Coutinho, O.P.; Cunha, A.M.; Reis, R.L. In vitro degradation and cytocompatibility evaluation of novel soy and sodium caseinate-based membrane biomaterials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2003, 14, 1055–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santin, M.; Morris, C.; Standen, G.; Nicolais, L.; Ambrosio, L. A new class of bioactive and biodegradable soybean-based bone fillers. Biomacromolecules 2007, 8, 2706–2711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouten, P.J.; Zonjee, M.; Bender, J.; Yauw, S.T.; van Goor, H.; van Hest, J.C.; Hoogenboom, R. The chemistry of tissue adhesive materials. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 1375–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benthien, J.P.; Russlies, M.; Behrens, P. Investigating the effects of bone cement, cyanoacrylate glue and marine mussel adhesive protein from Mytilus edulis on human osteoblasts and fibroblasts in vitro. Ann. Anat. 2004, 186, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, T.A.; Giulivi, A.; Griffith, M.; Hincke, M. Fibrin glues in combination with mesenchymal stem cells to develop a tissue-engineered cartilage substitute. Tissue Eng. Part A 2011, 17, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Annabi, N.; Yue, K.; Tamayol, A.; Khademhosseini, A. Elastic sealants for surgical applications. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2015, 95, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sekine, T.; Nakamura, T.; Shimizu, Y.; Ueda, H.; Matsumoto, K.; Takimoto, Y.; Kiyotani, T. A new type of surgical adhesive made from porcine collagen and polyglutamic acid. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2001, 54, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balakrishnan, B.; Soman, D.; Payanam, U.; Laurent, A.; Labarre, D.; Jayakrishnan, A. A novel injectable tissue adhesive based on oxidized dextran and chitosan. Acta Biomater. 2017, 53, 343–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waite, J.H.; Tanzer, M.L. Polyphenolic substance of Mytilus edulis: Novel adhesive containing L-dopa and hydroxyproline. Science 1981, 212, 1038–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverma, H.G.; Roberto, F.F. Understanding marine mussel adhesion. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 4039–4046. [Google Scholar]
- Ninan, L.; Monahan, J.; Stroshine, R.L.; Wilker, J.J.; Shi, R. Adhesive strength of marine mussel extracts on porcine skin. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 4091–4099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ninan, L.; Stroshine, R.L.; Wilker, J.J.; Shi, R. Adhesive strength and curing rate of marine mussel protein extracts on porcine small intestinal submucosa. Acta Biomater. 2007, 3, 687–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nordqvist, P.; Khabbaz, F.; Malmström, E. Comparing bond strength and water resistance of alkali-modified soy protein isolate and wheat gluten adhesives. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2010, 30, 72–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Li, K. Chemical modification of soy protein for wood adhesives. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 23, 739–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; An, L.-P.; Zhang, X.T.; Liu, H. Physicochemical properties of soy protein adhesives modified by tartaric acid acylating agent. Soybean Sci. 2016, 95, 818–823. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, Y.; Cui, S.W.; Wang, Q. Gelling property of soy protein–gum mixtures. Food Hydrocolloids 2003, 17, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, Z.; Mo, J.; Yi, L.; Tang, X.; Shen, X. Effects of guar gum on adhesion properties of soybean protein isolate onto porcine bones. Int. J. Adhes. Adhes. 2017, 75, 124–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hazirah, M.N.; Isa, M.I.N.; Sarbon, N.M. Effect of xanthan gum on the physical and mechanical properties of gelatin-carboxymethyl cellulose film blends. Food Packag. Shelf Life 2016, 9, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bemiller, J.N.; Bemiller, J.N. Carbohydrate Chemistry for Food Scientists; AACC International: St. Paul, MN, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Carp, D.J.; Bartholomai, G.B.; Relkin, P.; Pilosof, A.M.R. Effects of denaturation on soy protein–xanthan interactions: Comparison of a whipping–rheological and a bubbling method. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2001, 21, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, D.M.; Zhou, C.X.; Zhang, M.X.; Hong, P.Z. Effect of xanthan gum on emulsion stability on tilapia and soybean protein mixture. Food Ferment. Ind. 2016, 42, 114–119. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, S.M.; Chang, S.J.; Wang, H.Y.; Tang, S.C.; Yang, S.W. Evaluation of the ability of xanthan gum/gellan gum/hyaluronan hydrogel membranes to prevent the adhesion of postrepaired tendons. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 114, 230–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, M.; Tiwary, A.K.; Kaur, G. Investigations on interpolymer complexes of cationic guar gum and xanthan gum for formulation of bioadhesive films. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2010, 5, 79–87. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Taskiajdukovic, K.; Djordjevic, V.; Vidic, M.; Vujakovic, M. Subunit composition of seed storage proteins in high-protein soybean genotypes. Pesqui. Agropecu. Bras. 2010, 45, 721–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Alm, B.; Azevedo, A.; Marques, M.J.; Menossi, M.; Cunha, R.L. Interactions between soy protein isolate and xanthan in heat-induced gels: The effect of salt addition. Food Hydrocolloids 2006, 20, 1178–1189. [Google Scholar]
- Rudolph, N.M.; Agudelo, A.C.; Granada, J.C.; Park, H.E.; Osswald, T.A. WLF model for the pressure dependence of zero shear viscosity of polycarbonate. Rheol. Acta 2016, 55, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Internation, A.S.T.M. Standard Test Method for Apparent Shear Strength of Single-Lap-Joint Adhesively Bonded Metal Specimens by Tension Loading (Metal-to-Metal); Astm International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, Y.Y.; Li, D.; Wang, L.J.; Bi, C.H.; Adhikari, B. Effect of gums on the rheological characteristics and microstructure of acid-induced SPI-gum mixed gels. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 108, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, X.J.; Turgeon, S.L. Study of the shear effects on the mixture of whey protein/polysaccharides-2: Application of flow models in the study of the shear effects on wpi/polysaccharide system. Food Hydrocolloids 2007, 21, 1014–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Chen, H.J.; Lü, Y.; Liu, Y.X.; Tang, X.Z.; Shen, X.C. Effects of sodium carboxymethyl cellulose on adhesion properties of soybean protein isolate onto porcine bones. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2016, 49, 1550–1558. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, Z.; Liu, J.; Jin, L.; Zhang, Q. Extraction and application of Perna viridis foot protein as bioadhesive. J. Biomed. Eng. 2010, 27, 1266–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Liu, C.; Lu, X.; Yin, M. Co-polypeptides of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine and L-lysine to mimic marine adhesive protein. Biomaterials 2007, 28, 3456–3468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Fantner, G.; Adams, J.; Hansma, P.; Waite, J. The role of calcium and magnesium in the concrete tubes of the sandcastle worm. J. Exp. Biol. 2007, 210, 1481–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Maurer, P.; Bekes, K.; Gernhardt, C.R. Comparison of the bond strength of selected adhesive dental systems to cortical bone under in vitro conditions. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 33, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weber, S.C.; Chapman, M.W. Adhesives in orthopaedic surgery. A review of the literature and in vitro bonding strengths of bone-bonding agents. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1984, 191, 249–261. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, J.T.; Yang, X.Q.; Huang, L.X. Changes of viscosity during preparation of soy protein isolate adhesives and their adhesive properties. China Oils Fats 2005, 30, 68–70. [Google Scholar]
- Brewster, V.L.; Ashton, L.; Goodacre, R. Monitoring the glycosylation status of proteins using Raman spectroscopy. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 6074–6081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, N.; Li-Chan, E. Elucidation of interactions of lysozyme with whey proteins by Raman spectroscopy. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 31, 439–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dickinson, E.; Euston, S.R. Stability of food emulsions containing both protein and polysaccharide. Food Polym. Gels Colloids 1991, 23, 132–146. [Google Scholar]
- Mc, V.D.L.; Rutten, A.A.; Frens, G. How to develop globular proteins into adhesives. J. Biotechnol. 2000, 79, 211–221. [Google Scholar]
- Abrusán, G.; Marsh, J.A. Alpha helices are more robust to mutations than beta strands. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2016, 12, e1005242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z. Urea-modified soy globulin proteins (7S and 11S): Effect of wettability and secondary structure on adhesion. J. Am. Oil Chem. Soc. 2007, 84, 853–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li-Chan, E.C.Y. The applications of Raman spectroscopy in food science. Trends. Food Sci. Technol. 1996, 7, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, O.H.; Kumar, R.N.; Rozman, H.D.; Mam, N. Grafting of sodium carboxymethylcellulose (CMC) with glycidyl methacrylate and development of UV curable coatings from CMC-g-GMA induced by cationic photoinitiators. Carbohydr. Polym. 2005, 59, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byler, D.M.; Susi, H. Examination of the secondary structure of proteins by deconvolved FTIR spectra. Biopolymers 1986, 25, 469–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D.; Ivanov, I.B.; Campbell, B. Coalescence stability of emulsions containing globular milk proteins. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 123, 259–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barth, A. Infrared spectroscopy of proteins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA) Bioenerget. 2007, 1767, 1073–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhu, W.; Xue, H.; Chen, Z.; Chen, Y.; Wang, X. Physical and structural properties of peanut protein isolate-gum arabic films prepared by various glycation time. Food Hydrocolloids 2015, 43, 322–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toda, H.; Kijima, T. Relation between crystallinity and adhesive property for hemicelluloses from various pulps. Jpn. Tappi J. 2010, 15, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, L.V.D.; Rosenberg, Y.; Van Boekel, M.A.; Rosenberg, M.; Van de Velde, F. Microstructural features of composite whey protein/polysaccharide gels characterized at different length scales. Food Hydrocolloids 2009, 23, 1288–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Putta, A.; Mottishaw, J.D.; Wang, Z.; Sun, H. Rational design of lamellar π–π stacked organic crystalline materials with short interplanar distance. Cryst. Growth Des. 2014, 14, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, S.; Zhu, L.; Fan, J. Microstructural features of composite whey protein/polysaccharide gels characterized at different length scales. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 93, 561–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| XG Concentration (%) | α-Helix | β-Sheet | β-Turn | Random Coil | I760/I1003 | I850/I830 | Nburied | Nexposed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 24.17 ± 0.62 a | 27.68 ± 1.07 a | 16.63 ± 0.93 | 31.52 ± 1.31 | 0.37 ± 0.03 | 1.09 ± 0.02 a | 0.21 ± 0.02 a | 0.79 ± 0.02 a |
| 0.25 | 21.21 ± 1.4 b | 29.47 ± 1.04 a | 17.26 ± 0.85 | 32.06 ± 0.95 | 0.34 ± 0.02 | 0.96 ± 0.11 a | 0.39 ± 0.15 a | 0.61 ± 0.15 a |
| 0.5 | 18.49 ± 2.05 bc | 32.68 ± 1.18 b | 18.27 ± 1.01 | 30.56 ± 2.07 | 0.36 ± 0.03 | 0.8 ± 0.06 b | 0.6 ± 0.07 b | 0.4 ± 0.07 b |
| 1 | 18.66 ± 0.69 c | 33.99 ± 0.46 b | 16.28 ± 1.27 | 31.06 ± 1.47 | 0.35 ± 0.02 | 0.84 ± 0.03 b | 0.54 ± 0.04 b | 0.46 ± 0.04 b |
| XG Concentration (%) | 1666/2930 cm−1 | 1651/2930 cm−1 | 1635/2930 cm−1 | 1621/2930 cm−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 2.257 ± 0.093 a | 2.499 ± 0.088 a | 2.372 ± 0.083 a | 1.212 ± 0.079 a |
| 0.25 | 2.455 ± 0.081 b | 2.402 ± 0.072 a | 2.411 ± 0.118 a | 1.264 ± 0.072 a |
| 0.5 | 2.497 ± 0.107 b | 2.303 ± 0.075 b | 2.572 ± 0.092 b | 1.381 ± 0.066 b |
| 1 | 2.488 ± 0.096 b | 2.241 ± 0.121 b | 2.690 ± 0.132 b | 1.424 ± 0.097 b |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Feng, C.; Wang, F.; Xu, Z.; Sui, H.; Fang, Y.; Tang, X.; Shen, X. Characterization of Soybean Protein Adhesives Modified by Xanthan Gum. Coatings 2018, 8, 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8100342
Feng C, Wang F, Xu Z, Sui H, Fang Y, Tang X, Shen X. Characterization of Soybean Protein Adhesives Modified by Xanthan Gum. Coatings. 2018; 8(10):342. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8100342
Chicago/Turabian StyleFeng, Chen, Fang Wang, Zheng Xu, Huilin Sui, Yong Fang, Xiaozhi Tang, and Xinchun Shen. 2018. "Characterization of Soybean Protein Adhesives Modified by Xanthan Gum" Coatings 8, no. 10: 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8100342
APA StyleFeng, C., Wang, F., Xu, Z., Sui, H., Fang, Y., Tang, X., & Shen, X. (2018). Characterization of Soybean Protein Adhesives Modified by Xanthan Gum. Coatings, 8(10), 342. https://doi.org/10.3390/coatings8100342