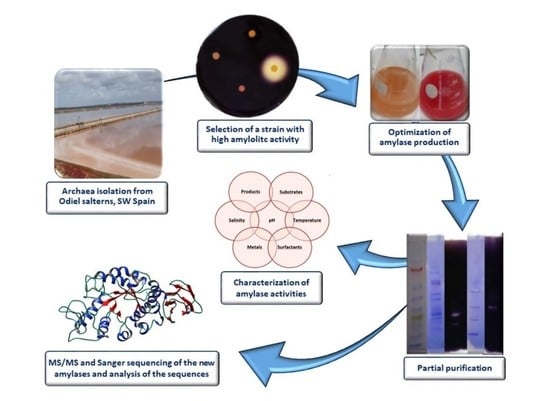
Biochemical Characterization of the Amylase Activity from the New Haloarchaeal Strain Haloarcula sp. HS Isolated in the Odiel Marshlands
Abstract
:Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Screening and Selection of Amylase Producing Haloarchaea
2.2. Identification of the Selected Microorganism
2.3. Culture Conditions for Enzyme Production
2.4. Partial Purification of Cell-Associated and Extracellular Amylases
2.5. Amylase Activity Assay
2.6. Native Electrophoresis and Zymogram
2.7. Effect of NaCl, Temperature, pH, Metals, and Detergents on the Amylase Activities of the New Isolated Strain Haloarcula sp. HS
2.8. Proteomic Analysis
2.9. Identification of Amylase Coding Genes Based on Protein Sequences
2.10. Starch Hydrolysis from Bakery Waste
3. Results
3.1. Selection of Amylase-Producing Haloarchaea Isolated from Odiel Salterns Ponds
3.2. Optimization of a Two-Stage Culture Strategy to Induce the Production of Amylase
3.3. Extracellular and Cell-Associated Amylase Activities in Haloarcula sp. HS
3.4. Characterization of Extracellular and Cell-Associated Amylase Activities
3.5. Effects of Metals and Surfactants on the Amylase Enzymatic Activities
3.6. Identification of Amylases in Cellular and Extracellular Concentrated Extracts of Haloarcula sp. HS by a Proteomic Approach
3.7. Hydrolysis of Bakery Waste
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kanekar, P.P.; Kelkar, A.S.; Dhakephalkar, P.K. Halophiles—Taxonomy, Diversity, Physiology and Applications. In Microorganisms in Environmental Management; Metzler, J.B., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 9789400722, pp. 1–34. [Google Scholar]
- Ventosa, A.; Márquez, M.C.; Sánchez-Porro, C.; De La Haba, R.R. Taxonomy of Halophilic Archaea and Bacteria. In Advances in Understanding the Biology of Halophilic Microorganisms; Vreeland, R.H., Ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 59–80. [Google Scholar]
- Oren, A. Life at high salt concentrations, intracellular KCl concentrations, and acidic proteomes. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mevarech, M.; Frolow, F.; Gloss, L.M. Halophilic enzymes: Proteins with a grain of salt. Biophys. Chem. 2000, 86, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, D.; Satyanarayana, T. Bacterial and Archaeal α-Amylases: Diversity and Amelioration of the Desirable Characteristics for Industrial Applications. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cabrera, M. Ángeles; Blamey, J.M. Biotechnological applications of archaeal enzymes from extreme environments. Biol. Res. 2018, 51, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vaidya, S.; Srivastava, P.; Rathore, P.; Pandey, A. Amylases: A prospective enzyme in the field of biotechnology. J. Appl. Biosci. 2015, 41, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Sangwan, P.; Singh, D.; Gill, P.K. Global scenario of industrial enzyme market. In Industrial Enzymes: Trends, Scope and Relevance; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2014; pp. 176–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.; Gigras, P.; Mohapatra, H.; Goswami, V.K.; Chauhan, B. Microbial α-amylases: A biotechnological perspective. Process. Biochem. 2003, 38, 1599–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, P. Enzymatic processing in the food industry. In Reference Module in Food Science; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Gopinath, S.C.B.; Anbu, P.; Arshad, M.K.M.; Lakshmipriya, T.; Voon, C.H.; Hashim, U.; Chinni, S.V. Biotechnological processes in microbial amylase production. BioMed Res. Int. 2017, 2017, 272193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mobini-Dehkordi, M.; Javan, F.A. Application of alpha-amylase in biotechnology. J. Biol. Today World 2012, 1, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kumar, V.; Longhurst, P. Recycling of food waste into chemical building blocks. Curr. Opin. Green Sustain. Chem. 2018, 13, 118–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- van der Maarel, M.J.; van der Veen, B.; Uitdehaag, J.C.; Leemhuis, H.; Dijkhuizen, L. Properties and applications of starch-converting enzymes of the α-amylase family. J. Biotechnol. 2002, 94, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Taniguchi, H.; Honnda, Y. Amylases. In Encyclopedia of Microbiology; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2009; pp. 159–173. [Google Scholar]
- John, J. Amylases-bioprocess and potential applications: A review. Int. J. Bioinform. Biol. Sci. 2017, 5, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Villegas, P.; Vigara, J.; León, R. Characterization of the microbial population inhabiting a solar saltern pond of the odiel marshlands (SW Spain). Mar. Drugs 2018, 16, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gómez-Villegas, P.; Vigara, J.; Vila, M.; Varela, J.; Barreira, L.; Léon, R. Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Bioactive Potential of Two New Haloarchaeal Strains Isolated from Odiel Salterns (Southwest Spain). Biology 2020, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altschul, S.F.; Gish, W.; Miller, W.; Myers, E.W.; Lipman, D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990, 215, 403–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-Dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1976, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelley, L.A.; Mezulis, S.; Yates, C.M.; Wass, M.N.; Sternberg, M.J.E. The Phyre2 web portal for protein modeling, prediction and analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2015, 10, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Petersen, B.; Petersen, T.N.; Andersen, P.; Nielsen, M.; Lundegaard, C. A generic method for assignment of reliability scores applied to solvent accessibility predictions. BMC Struct. Biol. 2009, 9, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pettersen, E.F.; Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Couch, G.S.; Greenblatt, D.M.; Meng, E.C.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF Chimera—A visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1605–1612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein Identification and Analysis Tools on the ExPASy Server. In The Proteomics Protocols Handbook; Walker, J.M., Ed.; Humana Press: New York, NY, USA, 2005; pp. 571–607. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Stecher, G.; Li, M.; Knyaz, C.; Tamura, K. MEGA X: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis across computing platforms. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2018, 35, 1547–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Pomares, F.; Bautista, V.; Ferrer, J.; Pire, C.; Marhuenda-Egea, F.C.; Bonete, M.-J.; Marhuenda-Egea, F. α-Amylase activity from the halophilic archaeon Haloferax mediterranei. Extremophiles 2003, 7, 299–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutcheon, G.W.; Vasisht, N.; Bolhuis, A. Characterisation of a highly stable α-amylase from the halophilic archaeon Haloarcula hispanica. Extremophiles 2005, 9, 487–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, D.; Satyanarayana, T. Biochemical and molecular characterization of recombinant acidic and thermostable raw-starch hydrolysing α-amylase from an extreme thermophile Geobacillus thermoleovorans. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2013, 85–86, 229–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, T.-C.; Mijts, B.N.; Swaminathan, K.; Patel, B.K.; Divne, C. Crystal Structure of the Polyextremophilic α-Amylase AmyB from Halothermothrix orenii: Details of a Productive Enzyme–Substrate Complex and an N Domain with a Role in Binding Raw Starch. J. Mol. Biol. 2008, 378, 852–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, D.K.; Vasudeva, G.; Sidhu, C.; Pinnaka, A.K.; Prasad, S.E.; Thakur, K.G. Biochemical and Taxonomic Characterization of Novel Haloarchaeal Strains and Purification of the Recombinant Halotolerant α-Amylase Discovered in the Isolate. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boel, E.; Brady, L.; Brzozowski, A.M.; Derewenda, Z.; Dodson, G.G.; Jensen, V.J.; Petersen, S.B.; Swift, H.; Thim, L.; Woldike, H.F. Calcium binding in alpha.-amylases: An X-ray diffraction study at 2.1-.ANG. Resolution of two enzymes from Aspergillus. Biochemistry 1990, 29, 6244–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svensson, B. Protein engineering in the α-amylase family: Catalytic mechanism, substrate specificity, and stability. Plant Mol. Biol. 1994, 25, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strokopytov, B.; Penninga, D.; Rozeboom, H.J.; Kalk, K.H.; Dijkhuizen, L.; Dijkstra, B.W. X-ray Structure of Cyclodextrin Glycosyltransferase Complexed with Acarbose. Implications for the Catalytic Mechanism of Glycosidases. Biochemistry 1995, 34, 2234–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Machovič, M.; Janeček, Š. The invariant residues in the α-amylase family: Just the catalytic triad. Biol. Sect. Cell. Mol. Biol. 2003, 58, 1127–1132. [Google Scholar]
- Zona, R.; Chang-Pi-Hin, F.; O’Donohue, M.J.; Janeček, Š. Bioinformatics of the glycoside hydrolase family 57 and identification of catalytic residues in amylopullulanase from Thermococcus hydrothermalis. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 271, 2863–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roth, C.; Moroz, O.V.; Turkenburg, J.P.; Blagova, E.; Waterman, J.; Ariza, A.; Ming, L.; Tianqi, S.; Andersen, C.; Davies, G.J.; et al. Structural and Functional Characterization of Three Novel Fungal Amylases with Enhanced Stability and pH Tolerance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oda, Y.; Park, B.-S.; Moon, K.-H.; Tonomura, K. Recycling of bakery wastes using an amylolytic lactic acid bacterium. Bioresour. Technol. 1997, 60, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiotelli, E.; Pilosio, G.; Le Meste, M. Effect of sodium chloride on the gelatinization of starch: A multimeasurement study. Biopolymers 2001, 63, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santorelli, M.; Maurelli, L.; Pocsfalvi, G.; Fiume, I.; Squillaci, G.; La Cara, F.; Del Monaco, G.; Morana, A. Isolation and characterisation of a novel alpha-amylase from the extreme haloarchaeon Haloterrigena turkmenica. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 92, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertoldo, C.; Antranikian, G. Starch-hydrolyzing enzymes from thermophilic archaea and bacteria. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2002, 6, 151–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidu, M.A.; Saranraj, P. Bacterial amylase: A review. Int. J. Pharm. Biol. Arch. 2013, 4, 274–287. [Google Scholar]
- Saranraj, P.; Stella, D. Fungal amylase-a review. Int. J. Microbiol. Res. 2013, 4, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.; Wu, G. Analysis on evolutionary relationship of amylases from archaea, bacteria and eukaryota. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fukushima, T.; Mizuki, T.; Echigo, A.; Inoue, A.; Usami, R. Organic solvent tolerance of halophilic α-amylase from a Haloarchaeon, Haloarcula sp. strain S-1. Extremophiles 2004, 9, 85–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, T.; Kanai, H.; Hayashi, T.; Akiba, T.; Akaboshi, R.; Horikoshi, K. Haloalkaliphilic maltotriose-forming alpha-amylase from the archaebacterium Natronococcus sp. strain Ah-36. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 3439–3444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moshfegh, M.; Shahverdi, A.R.; Zarrini, G.; Faramarzi, M.A. Biochemical characterization of an extracellular polyextremophilic α-amylase from the halophilic archaeon Halorubrum xinjiangense. Extremophiles 2013, 17, 677–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bajpai, B.; Chaudhary, M. Production and Characterization of α-Amylase from an Extremely Halophilic Archaeon, Haloferax sp. HA10. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 2015, 53, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgaonkar, B.B.; Sawant, D.T.; Harinarayanan, S.; Bragança, J.M. Alpha-amylase Production by Extremely Halophilic ArchaeonHalococcusStrain GUVSC8. Starch Stärke 2018, 71, 1800018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onodera, M.; Yatsunami, R.; Tsukimura, W.; Fukui, T.; Nakasone, K.; Takashina, T.; Nakamura, S. Gene Analysis, Expression, and Characterization of an Intracellular α-Amylase from the Extremely Halophilic Archaeon Haloarcula japonica. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2013, 77, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Erdagi, A.N.; Attar, A.; Basaran-Elalmis, Y.; Yücel, S.; Birbir, M. Production of α-Amylase from Haloarcula hispanica 2TK2 Strain: Optimization of the Parameters That Effecting Activity. Adv. Sci. Lett. 2013, 19, 3551–3555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Porro, C.; Martin, S.; Mellado, E.; Ventosa, A. Diversity of moderately halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolytic enzymes. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2003, 94, 295–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lichi, T.; Ring, G.; Eichler, J. Membrane binding of SRP pathway components in the halophilic archaea Haloferax volcanii. JBIC J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2004, 271, 1382–1390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shafiei, M.; Ziaee, A.-A.; Amoozegar, M.A. Purification and biochemical characterization of a novel SDS and surfactant stable, raw starch digesting, and halophilic α-amylase from a moderately halophilic bacterium, Nesterenkonia sp. strain F. Process. Biochem. 2010, 45, 694–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarian, F.D.; Janeček, Š.; Pijning, T.; Nurachman, Z.; Radjasa, O.K.; Dijkhuizen, L.; Natalia, D.; Van Der Maarel, M.J.E.C. A new group of glycoside hydrolase family 13 α-amylases with an aberrant catalytic triad. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, srep44230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Linden, A.; Mayans, O.; Meyer-Klaucke, W.; Antranikian, G.; Wilmanns, M. Differential Regulation of a Hyperthermophilic α-Amylase with a Novel (Ca,Zn) Two-metal Center by Zinc. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 9875–9884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sivakumar, N.; Li, N.; Tang, J.W.; Patel, B.K.; Swaminathan, K. Crystal structure of AmyA lacks acidic surface and provide insights into protein stability at poly-extreme condition. FEBS Lett. 2006, 580, 2646–2652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janeček, Š.; Lévêque, E.; Belarbi, A.; Haye, B. Close evolutionary relatedness of α-amylases from archaea and plants. J. Mol. Evol. 1999, 48, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zorgani, M.A.; Patron, K.; Desvaux, M. New insight in the structural features of haloadaptation in α-amylases from halophilic Archaea following homology modeling strategy: Folded and stable conformation maintained through low hydrophobicity and highly negative charged surface. J. Comput. Mol. Des. 2014, 28, 721–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janeček, Š. α-amylases from Archaea: Sequences, structures and evolution. Biotechnol. Extrem. 2016, 1, 505–524. [Google Scholar]
- Ştefan Andrei, A.; Banciu, H.L.; Oren, A. Living with salt: Metabolic and phylogenetic diversity of archaea inhabiting saline ecosystems. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2012, 330, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Fallal, A.; Abou, M.; El-Sayed, A.; Omar, A.E.-S.A.N. Starch and microbial α-amylases: From concepts to biotechnological applications. Carbohydr. Compr. Stud. Glycobiol. Glycotechnol. 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]








| Primers | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| AMY_HS1 | ACCGGCAGTAAGCAGGCGTCTC | GGCGGCGTCCCAGCGAATACC |
| GGCTCGTCGGGCTGAAGGACC | CCCTCTCGCTCGTAGACGTACAGGTC | |
| AMY_HS2 | CGTCGGCGAATCGGTCGAACT | GTCGCGTTTCCGGTTCCACTGTC |
| GGAACGCGACAGTGGAACCGGA | CGAAGTGCAGAACGACCACGAGCG | |
| AMY_HS3 | GGAGACGGCCCGGTCGAACA | CGCGTCGAAGGGCGATTC |
| GCCGGCGATAGCGACGAAT | TCGTACGGGATTCGGAGGAGG |
| Dextrins (%) | Maltose (%) | Glucose (%) | Starch (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cell-associated amylase | ND | 86.1 ± 3.6 | 6.6 ± 0.8 | 7.3 ± 2.9 |
| Extracellular amylase | 18.5 ± 1.1 | 79.7 ± 1.3 | ND | 1.7 ± 0.2 |
| Commercial α-amylase | 20.8 ± 3.1 | 73.8 ± 3.4 | ND | 5.4 ± 0.3 |
| Name | N | MW (kDa) | IP | Z | GRAVY | Aliph. Index |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AMY_HS1 | 393 | 43.70 | 4.27 | −35.577 | −0.518 | 72.72 |
| AMY_HS2 | 639 | 70.16 | 4.43 | −66.227 | −0.382 | 73.43 |
| AMY_HS3 | 549 | 60.02 | 4.37 | −59.604 | −0.463 | 71.89 |
| Microorganism | Enzyme | NaCl (M) | pH | Tª (°C) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Haloarcula sp. HS | Cellular α-amylase | 2.6 | 7 | 50 | This study |
| H. japonica | Intracellular α-amylase | 2.6 | 6.5 | 45 | [49] |
| Haloarcula sp. HS | Extracellular α-amylase | 5 | 5 | 60 | This study |
| Halococcus GUVSC8 | Extracellular α-amylase | 2 | 6 | 45 | [48] |
| Haloarcula sp. S-1 | Extracellular α-amylase | 4.3 | 7 | 50 | [44] |
| H. hispanica B3 | Extracellular α-amylase | 4–5 | 6.5 | 50 | [27] |
| H. hispanica 2TK2 | Extracellular α-amylase | 5 | 6.9 | 52 | [50] |
| H. xinjiangense | Extracellular α-amylase | 4 | 8.5 | 70 | [46] |
| Haloferax sp. HA10 | Extracellular α-amylase | 1 | 6 | 55 | [47] |
| H. mediterranei | Extracellular α-amylase | 3 | 7–8 | 50–60 | [26] |
| H.turkmenica | Extracellular α-amylase | 2 | 8.5 | 55 | [39] |
| N.amylolyticus | Extracellular α-amylase | 2.5 | 8.7 | 55 | [45] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gómez-Villegas, P.; Vigara, J.; Romero, L.; Gotor, C.; Raposo, S.; Gonçalves, B.; Léon, R. Biochemical Characterization of the Amylase Activity from the New Haloarchaeal Strain Haloarcula sp. HS Isolated in the Odiel Marshlands. Biology 2021, 10, 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10040337
Gómez-Villegas P, Vigara J, Romero L, Gotor C, Raposo S, Gonçalves B, Léon R. Biochemical Characterization of the Amylase Activity from the New Haloarchaeal Strain Haloarcula sp. HS Isolated in the Odiel Marshlands. Biology. 2021; 10(4):337. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10040337
Chicago/Turabian StyleGómez-Villegas, Patricia, Javier Vigara, Luis Romero, Cecilia Gotor, Sara Raposo, Brígida Gonçalves, and Rosa Léon. 2021. "Biochemical Characterization of the Amylase Activity from the New Haloarchaeal Strain Haloarcula sp. HS Isolated in the Odiel Marshlands" Biology 10, no. 4: 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10040337
APA StyleGómez-Villegas, P., Vigara, J., Romero, L., Gotor, C., Raposo, S., Gonçalves, B., & Léon, R. (2021). Biochemical Characterization of the Amylase Activity from the New Haloarchaeal Strain Haloarcula sp. HS Isolated in the Odiel Marshlands. Biology, 10(4), 337. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology10040337