Discrimination of Adzuki Bean (Vigna angularis) Geographical Origin by Targeted and Non-Targeted Metabolite Profiling with Gas Chromatography Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
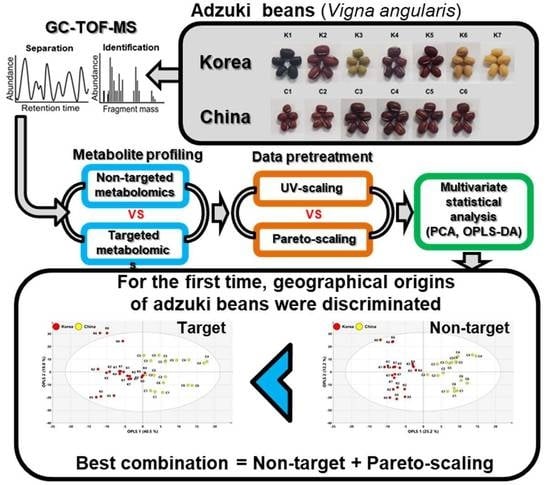
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Comparison of Targeted and Non-Targeted Metabolite Profiling Using GC–TOFMS
2.2. Geographical Discrimination of Adzuki Beans Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis with UV-Scaling
2.3. Geographical Discrimination of Adzuki Beans Using Multivariate Statistical Analysis with Pareto-Scaling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Samples and Chemicals
4.2. Extraction and Analysis of Hydrophilic Compounds
4.3. Non-Targeted Metabolite Profiling Data Processing
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Xu, N.; Cheng, X.-Z.; Wang, S.-H.; Wang, L.-X.; Zhao, D. Establishment of an adzuki bean (Vigna angularis) core collection based on geographical distribution and phenotypic data in China. Acta Agron. Sin. 2008, 34, 1366–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lestari, P.; Kang, Y.J.; Han, K.-S.; Gwag, J.-G.; Moon, J.-K.; Kim, Y.H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Lee, S.-H. Genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism discovery and validation in adzuki bean. Mol. Breed. 2014, 33, 497–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murata, K. Breeding of adzuki bean [Vigna angularis] cultivar “Erimo-shozu” and clutivars with large seeds or resistance to soil-born diseases in Hokkaido [Japan]: The adzuki bean breeder group of Tokachi Agricultural Experiment Station. Breed. Res. 1999, 1, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomooka, N.; Vaughan, D.; Moss, H.; Maxted, N. The Asian Vigna: Genus Vigna Subgenus Ceratotropis Genetic Resources; Springer Science & Business Media: Berlin, Germany, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Kramer, C.; Soltani, N.; Robinson, D.E.; Swanton, C.J.; Sikkema, P.H. Control of volunteer adzuki bean in soybean. Agric. Sci. 2012, 3, 501–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahama, U.; Yamauchi, R.; Hirota, S. Isolation and characterization of a cyanidin-catechin pigment from adzuki bean (Vigna angularis). Food Chem. 2013, 141, 282–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luykx, D.M.; Van Ruth, S.M. An overview of analytical methods for determining the geographical origin of food products. Food Chem. 2008, 107, 897–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, B.; Barlet, N.; Loiseau, G.; Montet, D. Review of the current methods of analytical traceability allowing determination of the origin of foodstuffs. Food Control 2007, 18, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korea Statistical Information Service. Available online: http://kosis.kr/statHtml/statHtml.do?orgId=101&tblId=DT_1ET0025&conn_path=I2 (accessed on 27 February 2020).
- Korea Agricultural Trade Information. Available online: http://www.kati.net/statistics/regionalPerformanceByProduct.do (accessed on 27 February 2020).
- Chung, I.-M.; Kim, J.-K.; Lee, J.-K.; Kim, S.-H. Discrimination of geographical origin of rice (Oryza sativa L.) by multielement analysis using inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy and multivariate analysis. J. Cereal Sci. 2015, 65, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu-xiao, Z.; Vaughan, D.; Tomooka, N.; Kaga, A.; Xin-wang, W.; Jian-ping, G.; Shu-min, W. Preliminary study on geographical distribution and evolutionary relationships between cultivated and wild adzuki bean (Vigna angularis var. angularis and var. nipponensis) by AFLP analysis. Plant Genet. Resour. 2003, 1, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isemura, T.; Noda, C.; Mori, S.; Yamashita, M.; Nakanishi, H.; Inoue, M.; Kamijima, O. Genetic variation and geographical distribution of Azuki bean (Vigna angularis) landraces based on the electrophoregram of seed storage proteins. Breed. Sci. 2001, 51, 225–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mo, C.; Lim, J.; Kwon, S.W.; Lim, D.K.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, G.; Kang, J.; Kwon, K.-D.; Cho, B.-K. Hyperspectral imaging and partial least square discriminant analysis for geographical origin discrimination of white rice. J. Biosyst. Eng. 2017, 42, 293–300. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.E.; Lee, B.J.; Chung, J.O.; Hwang, J.A.; Lee, S.J.; Lee, C.H.; Hong, Y.S. Geographical and climatic dependencies of green tea (Camellia sinensis) metabolites: A (1)H NMR-based metabolomics study. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 10582–10589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, H.S.; Kim, K.M.; Van Den Berg, F.; Hwang, G.S.; Park, W.M.; Lee, C.H.; Hong, Y.S. 1H nuclear magnetic resonance-based metabolomic characterization of wines by grape varieties and production areas. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2008, 56, 8007–8016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Son, H.S.; Hwang, G.S.; Kim, K.M.; Ahn, H.J.; Park, W.M.; Van Den Berg, F.; Hong, Y.S.; Lee, C.H. Metabolomic studies on geographical grapes and their wines using 1H NMR analysis coupled with multivariate statistics. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2009, 57, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, E.J.; Kwon, J.; Park, S.H.; Park, C.; Seo, Y.B.; Shin, H.K.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, K.S.; Choi, S.Y.; Ryu, D.H.; et al. Metabolite profiling of Angelica gigas from different geographical origins using 1H NMR and UPLC-MS analyses. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011, 59, 8806–8815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Guo, J.; Xia, Q.; Zhao, G.; Zhou, H.; Xie, F. Metabolic profiling of Chinese tobacco leaf of different geographical origins by GC-MS. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 2597–2605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zhao, C.; Zhou, H.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, L.; Hu, C.; Li, W.; Peng, X.; et al. A metabolomics study delineating geographical location-associated primary metabolic changes in the leaves of growing tobacco plants by GC-MS and CE-MS. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Putri, S.P.; Irifune, T.; Yusianto; Fukusaki, E. GC/MS based metabolite profiling of Indonesian specialty coffee from different species and geographical origin. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, C.H.; Yeo, H.J.; Park, S.-Y.; Kim, J.K.; Park, S.U. Comparative phytochemical analyses and metabolic profiling of different phenotypes of Chinese cabbage (Brassica Rapa ssp. pekinensis). Foods 2019, 8, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Castro-Puyana, M.; Herrero, M. Metabolomics approaches based on mass spectrometry for food safety, quality and traceability. Trac Trends Anal. Chem. 2013, 52, 74–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castro-Puyana, M.; Pérez-Míguez, R.; Montero, L.; Herrero, M. Reprint of: Application of mass spectrometry-based metabolomics approaches for food safety, quality and traceability. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 96, 62–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.J.; Park, S.-Y.; Valan Arasu, M.; Al-Dhabi, N.A.; Ahn, H.-g.; Kim, J.K.; Park, S.U. Accumulation of carotenoids and metabolic profiling in different cultivars of Tagetes flowers. Molecules 2017, 22, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vrhovsek, U.; Masuero, D.; Gasperotti, M.; Franceschi, P.; Caputi, L.; Viola, R.; Mattivi, F. A versatile targeted metabolomics method for the rapid quantification of multiple classes of phenolics in fruits and beverages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2012, 60, 8831–8840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, T.J.; Choi, J.; Kim, K.W.; Ahn, S.K.; Ha, S.H.; Choi, Y.; Park, N.I.; Kim, J.K. Metabolite profiling of peppers of various colors reveals relationships between tocopherol, carotenoid, and phytosterol content. J. Food Sci. 2017, 82, 2885–2893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinayavekhin, N.; Saghatelian, A. Untargeted metabolomics. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2010, 90, 30.1.1–30.1.24. [Google Scholar]
- Steinfath, M.; Strehmel, N.; Peters, R.; Schauer, N.; Groth, D.; Hummel, J.; Steup, M.; Selbig, J.; Kopka, J.; Geigenberger, P. Discovering plant metabolic biomarkers for phenotype prediction using an untargeted approach. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2010, 8, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, X.; Wang, C.; Zhang, H.; Cai, Z. Non-targeted and targeted metabolomics approaches to diagnosing lung cancer and predicting patient prognosis. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 63437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ralston-Hooper, K.J.; Adamec, J.; Jannash, A.; Mollenhauer, R.; Ochoa-Acuña, H.; Sepúlveda, M.S. Use of GC×GC/TOF-MS and LC/TOF-MS for metabolomic analysis of Hyalella azteca chronically exposed to atrazine and its primary metabolite, desethylatrazine. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 399–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsugawa, H.; Bamba, T.; Shinohara, M.; Nishiumi, S.; Yoshida, M.; Fukusaki, E. Practical non-targeted gas chromatography/mass spectrometry-based metabolomics platform for metabolic phenotype analysis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011, 112, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, H.; Ueda, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Tsuyama, N.; Todoroki, K.; Min, J.Z.; Toyo’oka, T. The great importance of normalization of LC–MS data for highly-accurate non-targeted metabolomics. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2017, 31, e3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schauer, N.; Steinhauser, D.; Strelkov, S.; Schomburg, D.; Allison, G.; Moritz, T.; Lundgren, K.; Roessner-Tunali, U.; Forbes, M.G.; Willmitzer, L. GC–MS libraries for the rapid identification of metabolites in complex biological samples. FEBS Lett. 2005, 579, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horai, H.; Arita, M.; Kanaya, S.; Nihei, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Suwa, K.; Ojima, Y.; Tanaka, K.; Tanaka, S.; Aoshima, K. MassBank: A public repository for sharing mass spectral data for life sciences. J. Mass Spectrom. 2010, 45, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Den Berg, R.A.; Hoefsloot, H.C.; Westerhuis, J.A.; Smilde, A.K.; Van Der Werf, M.J. Centering, scaling, and transformations: Improving the biological information content of metabolomics data. BMC Genom. 2006, 7, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eriksson, L.; Byrne, T.; Johansson, E.; Trygg, J.; Vikström, C. Multi-And Megavariate Data Analysis Basic Principles and Applications; Umetrics Academy: Umea, Sweden, 2013; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, I.-M.; Kim, J.-K.; Lee, K.-J.; Park, S.-K.; Lee, J.-H.; Son, N.-Y.; Jin, Y.-I.; Kim, S.-H. Geographic authentication of Asian rice (Oryza sativa L.) using multi-elemental and stable isotopic data combined with multivariate analysis. Food Chem. 2018, 240, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, I.-M.; Kim, J.-K.; Han, J.-G.; Kong, W.-S.; Kim, S.-Y.; Yang, Y.-J.; An, Y.-J.; Kwon, C.; Chi, H.-Y.; Jung, M.Y. Potential geo-discriminative tools to trace the origins of the dried slices of shiitake (Lentinula edodes) using stable isotope ratios and OPLS-DA. Food Chem. 2019, 295, 505–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, L.; Trygg, J.; Wold, S. CV-ANOVA for significance testing of PLS and OPLS® models. J. Chemometr. 2008, 22, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumhawan, U.; Putri, S.P.; Yusianto; Marwani, E.; Bamba, T.; Fukusaki, E. Selection of discriminant markers for authentication of Asian palm civet coffee (Kopi Luwak): A metabolomics approach. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2013, 61, 7994–8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, G.E.; Gaudillere, J.P.; Pieri, P.; Hilbert, G.; Maucourt, M.; Deborde, C.; Moing, A.; Rolin, D. Microclimate influence on mineral and metabolic profiles of grape berries. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 6765–6775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyeon, H.; Min, C.W.; Moon, K.; Cha, J.; Gupta, R.; Park, S.U.; Kim, S.T.; Kim, J.K. Metabolic profiling-based evaluation of the fermentative behavior of Aspergillus oryzae and Bacillus subtilis for soybean residues treated at different temperatures. Foods 2020, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, M.S.; Baek, S.-H.; Park, S.U.; Im, K.-H.; Kim, J.K. Targeted metabolite profiling to evaluate unintended metabolic changes of genetic modification in resveratrol-enriched rice (Oryza sativa L.). Appl. Biol. Chem. 2017, 60, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, J.G.; Lee, W.-K.; So, K.M.; Kim, J.K. Trial data of the anti-obesity potential of a high resistant starch diet for canines using Dodamssal rice and the identification of discriminating markers in feces for metabolic profiling. Metabolomics 2019, 15, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salek, R.M.; Neumann, S.; Schober, D.; Hummel, J.; Billiau, K.; Kopka, J.; Correa, E.; Reijmers, T.; Rosato, A.; Tenori, L. COordination of Standards in MetabOlomicS (COSMOS): Facilitating integrated metabolomics data access. Metabolomics 2015, 11, 1587–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salek, R.M.; Steinbeck, C.; Viant, M.R.; Goodacre, R.; Dunn, W.B. The role of reporting standards for metabolite annotation and identification in metabolomic studies. GigaScience 2013, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







| Platform | Scaling | Model | R2X | R2Y | Q2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Targeted | UV | PCA | 0.421 | 0.182 | |
| UV | OPLS–DA | 0.359 | 0.774 | 0.638 | |
| Pareto | PCA | 0.634 | 0.133 | ||
| Pareto | OPLS–DA | 0.595 | 0.668 | 0.579 | |
| Non-targeted | UV | PCA | 0.328 | 0.130 | |
| UV | OPLS–DA | 0.219 | 0.900 | 0.777 | |
| Pareto | PCA | 0.491 | 0.167 | ||
| Pareto | OPLS–DA | 0.374 | 0.869 | 0.812 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, T.J.; Park, J.G.; Ahn, S.K.; Kim, K.W.; Choi, J.; Kim, H.Y.; Ha, S.-H.; Seo, W.D.; Kim, J.K. Discrimination of Adzuki Bean (Vigna angularis) Geographical Origin by Targeted and Non-Targeted Metabolite Profiling with Gas Chromatography Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites 2020, 10, 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10030112
Kim TJ, Park JG, Ahn SK, Kim KW, Choi J, Kim HY, Ha S-H, Seo WD, Kim JK. Discrimination of Adzuki Bean (Vigna angularis) Geographical Origin by Targeted and Non-Targeted Metabolite Profiling with Gas Chromatography Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites. 2020; 10(3):112. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10030112
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Tae Jin, Jeong Gon Park, Soon Kil Ahn, Kil Won Kim, Jaehyuk Choi, Hyun Young Kim, Sun-Hwa Ha, Woo Duck Seo, and Jae Kwang Kim. 2020. "Discrimination of Adzuki Bean (Vigna angularis) Geographical Origin by Targeted and Non-Targeted Metabolite Profiling with Gas Chromatography Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry" Metabolites 10, no. 3: 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10030112
APA StyleKim, T. J., Park, J. G., Ahn, S. K., Kim, K. W., Choi, J., Kim, H. Y., Ha, S.-H., Seo, W. D., & Kim, J. K. (2020). Discrimination of Adzuki Bean (Vigna angularis) Geographical Origin by Targeted and Non-Targeted Metabolite Profiling with Gas Chromatography Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites, 10(3), 112. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10030112