Modulation of Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism in HIV-1 Infected Patients with Neurocognitive Impairment: Results from a Clinical Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Study Population
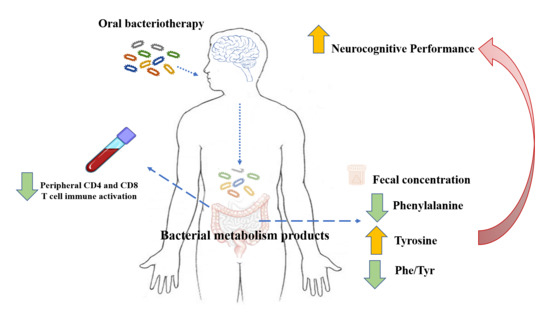
2.2. Effects of Probiotics on Peripheral Immune Activation
2.3. Effects of Probiotics on Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism
2.4. Effects of Probiotics on Neuroinflammation and Cognitive Function
2.5. Measure of Adherence to Probiotics Intake and Safety of the Intervention
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design, Study Population and Ethical Statement
4.2. Eligibility Criteria
4.3. Study Timeline and Investigational Compound
4.4. Peripheral Immune Activation
4.5. Fecal Metabolome
4.6. Bacterial DNA Isolation from Fecal Samples
4.7. ELISA Assay for Evaluation of CSF Neopterin Levels
4.8. Neurocognitive Evaluation
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hsu, D.C.; Sereti, I. Serious Non-AIDS Events: Therapeutic Targets of Immune Activation and Chronic Inflammation in HIV infection. Drugs 2016, 76, 533–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zevin, A.S.; McKinnon, L.; Burgener, A.; Klatt, N.R. Microbial translocation and microbiome dsybiosis in HIV-associated immune activation. Curr. Opin. HIV AIDS 2016, 11, 182–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Klatt, N.R.; Funderburg, N.T.; Brenchley, J.M. Microbial translocation, immune activation, and HIV disease. Trends Microbiol. 2013, 21, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dinan, T.G.; Stilling, R.M.; Stanton, C.; Cryan, J.F. Collective unconscious: How gut microbes shape human behavior. J. Psychiatr Res. 2015, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dinan, T.G.; Cryan, J.F. Gut–brain axis in 2016: Brain-gut-microbiota axis—Mood, metabolism and behaviour. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tillisch, K. The effects of gut microbiota on CNS function in humans. Gut Microbes 2014, 5, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, P.; Zeng, B.; Zhou, C.; Liu, M.; Fang, Z.; Xu, X.; Zeng, L.; Chen, J.; Fan, S.; Du, X.; et al. Gut microbiome remodeling induces depressive-like behaviors through a pathway mediated by the host’s metabolism. Mol. Psychiatry. 2016, 21, 786–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rui, L.; Wentian, L.; Meiyu, P.; Hong, Z. A review of the relationship between the gut microbiota and amino acid metabolism. Amino Acids 2017, 49, 2083–2090. [Google Scholar]
- Gostner, J.M.; Becker, K.; Kurz, K.; Fuchs, D. Disturbed amino acid metabolism in HIV: Association with neuropsychiatric symptoms. Front. Psychiatry 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Keegan, M.R.; Chittiprol, S.; Letendre, S.L.; Winston, A.; Fuchs, D.; Boasso, A.; Iudicello, J.; Ellis, R.J. Tryptophan Metabolism and Its Relationship with Depression and Cognitive Impairment Among HIV-infected Individuals. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2016, 9, 79–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Corano Scheri, G.; Najafi Fard, S.; Schietroma, I.; Mastrangelo, A.; Pinacchio, C.; Giustini, N.; Serafino, S.; De Girolamo, G.; Cavallari, E.N.; Statzu, M.; et al. Modulation of Tryptophan/Serotonin Pathway by Probiotic Supplementation in Human Immunodeficiency Virus–Positive Patients: Preliminary Results of a New Study Approach. Int. J. Tryptophan Res. 2017, 10, 1178646917710668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vujkovic-Cvijin, I.; Dunham, R.M.; Iwai, S.; Maher, M.C.; Albright, R.G.; Broadhurst, M.J.; Hernandez, R.D.; Lederman, M.M.; Huang, Y.; Somsouk, M.; et al. Dysbiosis of the gut microbiota is associated with HIV disease progression and tryptophan catabolism. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 193ra91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jenabian, M.A.; El-Far, M.; Vyboh, K.; Kema, I.; Costiniuk, C.T.; Thomas, R.; Baril, J.-G.; Leblanc, R.; Kanagaratham, C.; Radzioch, D.; et al. Immunosuppressive Tryptophan Catabolism and Gut Mucosal Dysfunction Following Early HIV Infection. JID 2015, 212, 355–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zangerle, R.; Kurz, K.; Neurauter, G.; Kitchen, M.; Sarcletti, M.; Fuchs, D. Increased blood phenylalanine to tyrosine ratio in HIV-1 infection and correction following effective antiretroviral therapy. Brain Behav. Immun. 2010, 24, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shintaku, H. Disorders of tetrahydrobiopterin metabolism and theirtreatment. Curr. Drug Metab. 2002, 3, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ceccarelli, G.; Statzu, M.; Santinelli, L.; Pinacchio, C.; Bitossi, C.; Cavallari, E.N.; Vullo, V.; Scagnolari, C.; d’Ettorre, G. Challenges in the management of HIV infection: Update on the role of probiotic supplementation as a possible complementary therapeutic strategy for cART treated people living with HIV/AIDS. Expert Opin. Biol. Ther. 2019, 19, 949–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carter, G.M.; Esmaeili, A.; Shah, H.; Indyk, D.; Johnson, M.; Andreae, M.; Sacks, H.S. Probiotics in Human Immunodeficiency Virus Infection: A Systematic Review and Evidence Synthesis of Benefits and Risks. Open Forum. Infect. Dis. 2016, 3, ofw164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Angelo, C.; Reale, M.; Costantini, E. Microbiota and Probiotics in Health and HIV Infection. Nutrients 2017, 9, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceccarelli, G.; Brenchley, J.M.; Cavallari, E.N.; Scheri, G.C.; Fratino, M.; Pinacchio, C.; Schietroma, I.; Fard, S.N.; Scagnolari, C.; Mezzaroma, I.; et al. Impact of High-Dose Multi-Strain Probiotic Supplementation on Neurocognitive Performance and Central Nervous System Immune Activation of HIV-1 Infected Individuals. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ceccarelli, G.; Fratino, M.; Selvaggi, C.; Giustini, N.; Serafino, S.; Schietroma, I.; Scheri, G.C.; Pavone, P.; Passavanti, G.; Alunni-Fegatelli, D.; et al. A pilot study on the effects of probiotic supplementation on neuropsychological performance and microRNA-29a-c levels in antiretroviral-treated HIV-1-infected patients. Brain Behav. 2017, 7, e00756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, D.N. Properties and Composition of Normal Cerebrospinal Fluid. Cereb. Fluid Clin. Pract. 2009, 69–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clapp, M.; Aurora, N.; Herrera, L.; Bhatia, M.; Wilen, E.; Wakefield, S. Gut microbiota’s effect on mental health: The gut-brain axis. Clin. Pract 2017, 7, 987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosenblatt, D.; Scriver, C.R. Heterogeneity in Genetic Control of Phenylalanine Metabolism in Man. Nature 1968, 218, 677–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dillon, S.M.; Lee, E.J.; Kotter, C.V.; Austin, G.L.; Dong, Z.; Hecht, D.K.; Gianella, S.; Siewe, B.; Smith, D.M.; Landay, A.L.; et al. An altered intestinal mucosal microbiome in HIV-1 infection is associated with mucosal and systemic immune activation and endotoxemia. Mucosal Immunol. 2014, 7, 983–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ziegler, T.R.; Judd, S.E.; Ruff, J.H.; McComsey, G.A.; Ross Eckard, A. Amino Acid Concentrations in HIV-Infected Youth Compared to Healthy Controls and Associations with CD4 Counts and Inflammation. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 2017, 33, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottiglieri, T.; Laundy, M.; Crellin, R.; Toone, B.K.; Carney, M.W.; Reynolds, E.H. Homocysteine, folate, methylation, and monoamine metabolism in depression. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2000, 269, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoekstra, R.; van den Broek, W.W.; Fekkes, D.; Bruijn, J.A.; Mulder, P.G.; Pepplinkhuizen, L. Effect of electroconvulsive therapy on biopterin and large neutral amino acids in severe, medication-resistant depression. Psychiatry Res. 2001, 103, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, D.J. Depression, anhedonia, and psychomotor symptoms: The role of dopaminergic neurocircuitry. CNS Spectr. 2008, 13, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubé, B.; Benton, T.; Cruess, D.G.; Evans, D.L. Neuropsychiatric manifestations of HIV infection and AIDS. J. Psychiatry Neurosci. 2005, 30, 237–246. [Google Scholar]
- Carrico, A.W.; Antoni, M.H. The Effects of psychological interventions on neuroendocrine hormone regulation and immune status in HIV-positive persons: A review of randomized controlled trials. Psychosom. Med. 2008, 70, 575–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Price, R.W.; Spudich, S. Antiretroviral therapy and central nervous system HIV type 1 infection. J. Infect. Dis. 2008, 197 (Suppl. S3), S294–S306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wirleitner, B.; Reider, D.; Ebner, S.; Boeck, G.; Widner, B.; Jaeger, M.; Schennach, H.; Romani, N.; Fuchs, D. Monocyte-derived dendritic cells release neopterin. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2002, 72, 1148–1153. [Google Scholar]
- Nathan, C.F.; Murray, H.W.; Wiebe, M.E.; Rubin, B.Y. Identification of interferon-gamma as the lymphokine that activates human macrophage oxidative metabolism and antimicrobial activity. J. Exp. Med. 1983, 158, 670–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ribeiro, P.; Pigeon, D.; Kaufman, S. The hydroxylation of phenylalanine and tyrosine by tyrosine hydroxylase from cultured pheochromocytoma cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 1266, 16207–16211. [Google Scholar]
- Vázquez-Castellanos, J.F.; Serrano-Villar, S.; Latorre, A.; Artacho, A.; Ferrús, M.L.; Madrid, N.; Vallejo, A.; Sainz, T.; Martínez-Botas, J.; Ferrando-Martínez, S.; et al. Altered metabolism of gut microbiota contributes to chronic immune activation in HIV-infected individuals. Mucosal Immunol. 2015, 8, 760–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dandekar, S. Pathogenesis of HIV in the Gastrointestinal Tract. Curr. HIV/AIDS Rep. Berl. Ger. 2007, 4, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boasso, A.; Shearer, G.M.; Chougnet, C. Immune dysregulation in human immunodeficiency virus infection: Know it, fix it, prevent it? J. Intern. Med. 2009, 265, 78–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meiboom, S.; Gill, D. Modified spin-echo method for measuring nuclear relaxation times. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 1958, 29, 688–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Foschi, C.; Salvo, M.; Laghi, L.; Zhu, C.; Ambretti, S.; Marangoni, A.; Re, M.C. Impact of Meropenem on Klebsiella Pneumoniae Metabolism. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0207478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dieterle, F.; Ross, A.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Senn, H. Probabilistic Quotient Normalization as Robust Method to Account for Dilution of Complex Biological Mixtures. Application in 1H NMR Metabonomics. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4281–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Ettorre, G.; Baroncelli, S.; Micci, L.; Ceccarelli, G.; Andreotti, M.; Sharma, P.; Fanello, G.; Fiocca, F.; Cavallari, E.N.; Giustini, N.; et al. Reconstitution of Intestinal CD4 and Th17 T Cells in Antiretroviral Therapy Suppressed HIV-Infected Subjects: Implication for Residual Immune Activation from the Results of a Clinical Trial. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e109791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- d’Ettorre, G.; Rossi, G.; Scagnolari, C.; Andreotti, M.; Giustini, N.; Serafino, S.; Schietroma, I.; Scheri, G.C.; Fard, S.N.; Trinchieri, V.; et al. Probiotic supplementation promotes a reduction in T-cell activation, an increase in Th17 frequencies, and a recovery of intestinal epithelium integrity and mitochondrial morphology in ART-treated HIV-1-positive patients. Immun. Inflamm. Dis. 2017, 5, 244–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Characteristics | HIV+ Patients a | Healthy Controls |
|---|---|---|
| N of subjects | 15 | 15 |
| Males | 15 | 15 |
| Age | 42 (24–56) | 41 (25–57) |
| Years from diagnosis | 12.4 (3–28) | NA |
| Years on ARV treatment | 8 (1–17) | NA |
| T CD4 nadir | 247 (25–560) cell/μL | NA |
| T CD4 at enrollment | 736 (493–1315) cell/μL | NA |
| Therapy class (number) | PI (6/15) NRTI (11/15) NNRTI (4/15) NtRTI (5/15) INSTI (4/15) | NA |
| Neurocognitive Tests | T0 a | T6 a | Statistical Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rey–Osterrieth Complex Figure (immediate recall) | 16.4 | 22.1 | 0.002 |
| Rey–Osterrieth Complex Figure (delayed recall) | 16.2 | 23.3 | 0.002 |
| Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (immediate recall) | 43.0 | 52.7 | 0.460 |
| Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (delayed recall) | 8.6 | 11.9 | 0.054 |
| Rey Auditory Verbal Learning Test (recognition) | 94.5 | 98.9 | 0.099 |
| Verbal Fluency | 14.8 | 15.6 | 0.364 |
| Phonological Verbal Fluency | 30.1 | 42.6 | 0.035 |
| Semantic Verbal Fluency | 44.5 | 47.7 | 0.034 |
| Visual Search Test (attentive matrices) | 50.2 | 47.9 | 0.079 |
| Test of Weights and Measures Estimation (time) | 17.5 | 23.0 | 0.400 |
| Test of Weights and Measures Estimation (weight) | 17.5 | 22.0 | 0.034 |
| Test of Weights and Measures Estimation (total) | 37.1 | 44.7 | 0.731 |
| Raven’s Standard Progressive Matrices | 27.0 | 30.6 | 0.202 |
| Verbal Span (forward) | 4.6 | 5.3 | 0.285 |
| Verbal Span (backward) | 4.4 | 4.6 | 1.000 |
| Corsi Block Tapping Test (forward) | 4.6 | 5.2 | 0.117 |
| Corsi Block Tapping Test (backward) | 3.7 | 4.12 | 0.351 |
| Aachener Aphasia Test | 9.0 | 9.0 | 1.000 |
| Trail Making Test A | 54.3 | 46.0 | 0.120 |
| Trail Making Test B | 127.1 | 108.9 | 0.413 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Innocenti, G.P.; Santinelli, L.; Laghi, L.; Borrazzo, C.; Pinacchio, C.; Fratino, M.; Celani, L.; Cavallari, E.N.; Scagnolari, C.; Frasca, F.; et al. Modulation of Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism in HIV-1 Infected Patients with Neurocognitive Impairment: Results from a Clinical Trial. Metabolites 2020, 10, 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070274
Innocenti GP, Santinelli L, Laghi L, Borrazzo C, Pinacchio C, Fratino M, Celani L, Cavallari EN, Scagnolari C, Frasca F, et al. Modulation of Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism in HIV-1 Infected Patients with Neurocognitive Impairment: Results from a Clinical Trial. Metabolites. 2020; 10(7):274. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070274
Chicago/Turabian StyleInnocenti, Giuseppe P., Letizia Santinelli, Luca Laghi, Cristian Borrazzo, Claudia Pinacchio, Mariangela Fratino, Luigi Celani, Eugenio N. Cavallari, Carolina Scagnolari, Federica Frasca, and et al. 2020. "Modulation of Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism in HIV-1 Infected Patients with Neurocognitive Impairment: Results from a Clinical Trial" Metabolites 10, no. 7: 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070274
APA StyleInnocenti, G. P., Santinelli, L., Laghi, L., Borrazzo, C., Pinacchio, C., Fratino, M., Celani, L., Cavallari, E. N., Scagnolari, C., Frasca, F., Antonelli, G., Mastroianni, C. M., d’Ettorre, G., & Ceccarelli, G. (2020). Modulation of Phenylalanine and Tyrosine Metabolism in HIV-1 Infected Patients with Neurocognitive Impairment: Results from a Clinical Trial. Metabolites, 10(7), 274. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo10070274