Comprehensive Identification of Glycosphingolipids in Human Plasma Using Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography—Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
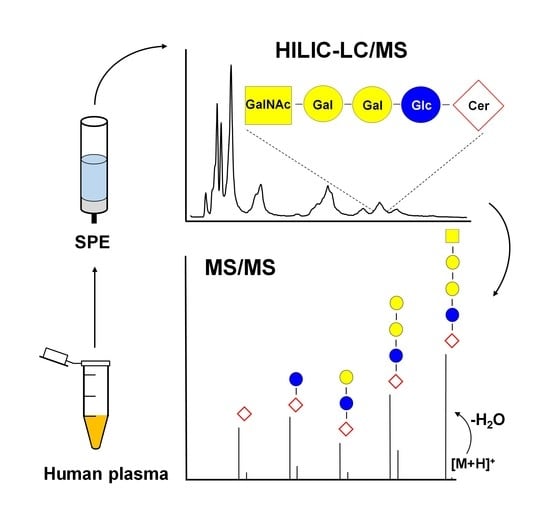
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Nomenclature of Investigated GSL
2.2. Optimization of Sample Preparation
2.2.1. Comparison of SPE Columns
2.2.2. Comparison of Deproteinization Solvents
2.2.3. Effect of MeOH Abundance in Loading Step
2.3. Optimization of Collision Energy
2.4. Separation of Lipid Subclasses in HILIC Mode
2.5. LC-ESI-MS/MS Characterization of Lipids
2.5.1. Neutral GSL
2.5.2. Acidic GSL
2.5.3. Phosphatidylinositols and Lysophosphatidylinositols
2.6. Profile of Lipid Species in Human Plasma
2.7. Extraction Recovery
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals and Standards
3.2. Collection and Processing of Blood Samples
3.3. Sample Preparation
3.4. HPLC Conditions
3.5. MS Conditions
3.6. Data Analysis
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malhotra, R. Membrane Glycolipids: Functional Heterogeneity: A Review. Biochem. Anal. Biochem. 2012, 1, 4172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karlsson, H.; Halim, A.; Teneberg, S. Differentiation of glycosphingolipid-derived glycan structural isomers by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Glycobiology 2010, 20, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gillard, B.K.; Thurmon, L.T.; Marcus, D.M. Variable subcellular localization of glycosphingolipids. Glycobiology 1993, 3, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kiechle, F.L. Review: Glycosphingolipids in Health and Disease. Ann. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2004, 34, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hanada, K. Sphingolipids in infectious diseases. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2005, 58, 131–148. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Levery, S.B. Glycosphingolipid structural analysis and glycosphingolipidomics. Methods Enzymol. 2005, 405, 300–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrecht, S.; Vainauskas, S.; Stöckmann, H.; McManus, C.; Taron, C.H.; Rudd, P.M. Comprehensive Profiling of Glycosphingolipid Glycans Using a Novel Broad Specificity Endoglycoceramidase in a High-Throughput Workflow. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 4795–4802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haynes, C.A.; Allegood, J.C.; Park, H.; Sullards, M.C. Sphingolipidomics: Methods for the comprehensive analysis of sphingolipids. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 2696–2708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merrill, A.H.; Sullards, M.C.; Allegood, J.C.; Kelly, S.; Wang, E. Sphingolipidomics: High-throughput, structure-specific, and quantitative analysis of sphingolipids by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Methods 2005, 36, 207–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweppe, C.H.; Hoffmann, P.; Nofer, J.R.; Pohlentz, G.; Mormann, M.; Karch, H.; Friedrich, A.W.; Müthing, J. Neutral glycosphingolipids in human blood: A precise mass spectrometry analysis with special reference to lipoprotein-associated Shiga toxin receptors. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 2282–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farwanah, H.; Kolter, T. Lipidomics of glycosphingolipids. Metabolites 2012, 2, 134–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kolter, T.; Sandhoff, K. Sphingolipids—Their metabolic pathways and the pathobiochemistry of neurodegenerative diseases. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 1532–1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryland, L.K.; Fox, T.E.; Liu, X.; Loughran, T.P.; Kester, M. Dysregulation of sphingolipid metabolism in cancer. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 11, 138–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farwanah, H.; Kolter, T.; Sandhoff, K. Mass spectrometric analysis of neutral sphingolipids: Methods, applications, and limitations. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2011, 1811, 854–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farwanah, H.; Wirtz, J.; Kolter, T.; Raith, K.; Neubert, R.H.H.; Sandhoff, K. Normal phase liquid chromatography coupled to quadrupole time of flight atmospheric pressure chemical ionization mass spectrometry for separation, detection and mass spectrometric profiling of neutral sphingolipids and cholesterol. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2009, 877, 2976–2982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.H.; Barnes, S.; Sun, Y.; Grabowski, G.A. Multi-system disorders of glycosphingolipid and ganglioside metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 1643–1675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merrill, A.H. Sphingolipid and glycosphingolipid metabolic pathways in the era of sphingolipidomics. Chem. Rev. 2011, 111, 6387–6422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bang, D.Y.; Byeon, S.K.; Moon, M.H. Rapid and simple extraction of lipids from blood plasma and urine for liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2014, 1331, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniotti, J.L.; Vilcaes, A.A.; Demichelis, V.T.; Ruggiero, F.M.; Rodriguez-Walker, M. Glycosylation of glycolipids in cancer: Basis for development of novel therapeutic approaches. Front. Oncol. 2013, 3, 306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Durrant, L.G.; Noble, P.; Spendlove, I. Immunology in the clinic review series; focus on cancer: Glycolipids as targets for tumour immunotherapy. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2012, 167, 206–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anugraham, M.; Everest-Dass, A.V.; Jacob, F.; Packer, N.H. A platform for the structural characterization of glycans enzymatically released from glycosphingolipids extracted from tissue and cells. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 29, 545–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, J.I.; Sakai, S.; Yokota, I.; Okada, K.; Hanamatsu, H.; Kobayashi, T.; Yoshida, Y.; Higashino, K.; Tamura, T.; Igarashi, Y.; et al. Quantitative GSL-glycome analysis of human whole serum based on an EGCase digestion and glycoblotting method. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 2399–2407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Furukawa, K.; Ohmi, Y.; Ohkawa, Y.; Bhuiyan, R.H.; Zhang, P.; Tajima, O.; Hashimoto, N.; Hamamura, K.; Furukawa, K. New era of research on cancer-associated glycosphingolipids. Cancer Sci. 2019, 110, 1544–1551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Matyash, V.; Liebisch, G.; Kurzchalia, T.V.; Shevchenko, A.; Schwudke, D. Lipid extraction by methyl-terf-butyl ether for high-throughput lipidomics. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Satomi, Y.; Hirayama, M.; Kobayashi, H. One-step lipid extraction for plasma lipidomics analysis by liquid chromatography mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Anal. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2017, 1063, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merrill, A.H.; Stokes, T.H.; Momin, A.; Park, H.; Portz, B.J.; Kelly, S.; Wang, E.; Sullards, M.C.; Wang, M.D. Sphingolipidomics: A valuable tool for understanding the roles of sphingolipids in biology and disease. J. Lipid Res. 2009, 50, 97–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skotland, T.; Ekroos, K.; Kavaliauskiene, S.; Bergan, J.; Kauhanen, D.; Lintonen, T.; Sandvig, K. Determining the Turnover of Glycosphingolipid Species by Stable-Isotope Tracer Lipidomics. J. Mol. Biol. 2016, 428, 4856–4866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrientos, R.C.; Zhang, Q. Recent advances in the mass spectrometric analysis of glycosphingolipidome—A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2020, 1132, 134–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaia, J. Mass spectrometry of oligosaccharides. Mass Spectrom. Rev. 2004, 23, 161–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaia, J. Mass Spectrometry and Glycomics. Omics J. Integr. Biol. 2010, 14, 401–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Merrill, A.H.; Sullards, M.C. Opinion article on lipidomics: Inherent challenges of lipidomic analysis of sphingolipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Biol. Lipids 2017, 1862, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Q.; Xie, Y.; Wong, M.; Lebrilla, C.B. Characterization of Cell Glycocalyx with Mass Spectrometry Methods. Cells 2019, 8, 882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Merrill, A.H.; Wang, M.D.; Park, M.; Sullards, M.C. (Glyco)sphingolipidology: An amazing challenge and opportunity for systems biology. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2007, 32, 457–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Sullards, M.C.; Merrill, A.H. An introduction to sphingolipid metabolism and analysis by new technologies. Neuromol. Med. 2010, 12, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wong, M.; Xu, G.; Park, D.; Barboza, M.; Lebrilla, C.B. Intact glycosphingolipidomic analysis of the cell membrane during differentiation yields extensive glycan and lipid changes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Quehenberger, O.; Dennis, E.A. The Human Plasma Lipidome—Mechanisms of Disease, Diversity of Lipids in Human Plasma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 365, 1812–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lydic, T.A.; Busik, J.V.; Reid, G.E. A monophasic extraction strategy for the simultaneous lipidome analysis of polar and nonpolar retina lipids. J. Lipid Res. 2014, 55, 1797–1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, X.; Lankmayr, E. Phospholipid-based matrix effects in LC-MS bioanalysis. Bioanalysis 2011, 3, 349–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yin, A.B.; Hawke, D.; Zhou, D. Mass spectrometric analysis of glycosphingolipid antigens. J. Vis. Exp. 2013, 74, 4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schnaar, R.L. Isolation of Glycosphingolipids. Methods Enzymol. 1994, 230, 348–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodennec, J.; Koul, O.; Aguado, I.; Brichon, G.; Zwingelstein, G.; Portoukalian, J. A procedure for fractionation of sphingolipid classes by solid-phase extraction on aminopropyl cartridges. J. Lipid Res. 2000, 41, 1524–1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaian, M.; Kramer, G.; Poorthuis, B.J.H.M. Quantification of sulfatides and lysosulfatides in tissues and body fluids by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. J. Lipid Res. 2015, 56, 936–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, X.; Cheng, H.; Yang, K.; Gross, R.W.; Han, X. Alkaline methanolysis of lipid extracts extends shotgun lipidomics analyses to the low-abundance regime of cellular sphingolipids. Anal. Biochem. 2007, 371, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, D.D.; Xu, G.; Wong, M.; Phoomak, C.; Liu, M.; Haigh, N.E.; Wongkham, S.; Yang, P.; Maverakis, E.; Lebrilla, C.B. Membrane glycomics reveal heterogeneity and quantitative distribution of cell surface sialylation. Chem. Sci. 2018, 9, 6271–6285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hájek, R.; Jirásko, R.; Lísa, M.; Cífková, E.; Holčapek, M. Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry Characterization of Gangliosides in Biological Samples. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 12425–12432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hájek, R.; Lísa, M.; Khalikova, M.; Jirásko, R.; Cífková, E.; Študent, V.; Vrána, D.; Opálka, L.; Vávrová, K.; Matzenauer, M.; et al. HILIC/ESI-MS determination of gangliosides and other polar lipid classes in renal cell carcinoma and surrounding normal tissues. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2018, 410, 6585–6594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pham, T.H.; Zaeem, M.; Fillier, T.A.; Nadeem, M.; Vidal, N.P.; Manful, C.; Cheema, S.; Cheema, M.; Thomas, R.H. Targeting Modified Lipids during Routine Lipidomics Analysis using HILIC and C30 Reverse Phase Liquid Chromatography coupled to Mass Spectrometry. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 5048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Domon, B.; Costello, C.E. A systematic nomenclature for carbohydrate fragmentations in FAB-MS/MS spectra of glycoconjugates. Glycoconj. J. 1988, 5, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costello, C.E.; Vath, J.E. Tandem mass spectrometry of glycolipids. Methods Enzymol. 1990, 193, 738–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domon, B.; Vath, J.E.; Costello, C.E. Analysis of derivatized ceramides and neutral glycosphingolipids by high-performance tandem mass spectrometry. Anal. Biochem. 1990, 184, 151–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ann, Q.; Adams, J. Structure determination of ceramides and neutral glycosphingolipids by collisional activation of [M + Li]+ ions. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 1992, 3, 260–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- O’Brien, J.P.; Brodbelt, J.S. Structural Characterization of Gangliosides and Glycolipids via Ultraviolet Photodissociation Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 10399–10407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fong, B.Y.; Ma, L.; Khor, G.L.; Van Der Does, Y.; Rowan, A.; McJarrow, P.; MacGibbon, A.K.H. Ganglioside Composition in Beef, Chicken, Pork, and Fish Determined Using Liquid Chromatography-High-Resolution Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2016, 64, 6295–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, K.; Shimizu, T.; Taguchi, R. Targeted analysis of ganglioside and sulfatide molecular species by LC/ESI-MS/MS with theoretically expanded multiple reaction monitoring. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 2678–2689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hsu, F.F.; Bohrer, A.; Turk, J. Electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometric analysis of sulfatide. Determination of fragmentation patterns and characterization of molecular species expressed in brain and in pancreatic islets. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Lipids Lipid Metab. 1998, 1392, 202–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, F.F.; Turk, J. Studies on sulfatides by quadrupole ion-trap mass spectrometry with electrospray ionization: Structural characterization and the fragmentation processes that include an unusual internal galactose residue loss and the classical charge-remote fragmentation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 15, 536–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yuki, D.; Sugiura, Y.; Zaima, N.; Akatsu, H.; Hashizume, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Fujiwara, M.; Sugiyama, K.; Setou, M. Hydroxylated and non-hydroxylated sulfatide are distinctly distributed in the human cerebral cortex. Neuroscience 2011, 193, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovillos, M.J.; Pauling, J.K.; Hannibal-Bach, H.K.; Vionnet, C.; Conzelmann, A.; Ejsing, C.S. Structural characterization of suppressor lipids by high-resolution mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2016, 30, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Quehenberger, O.; Armando, A.M.; Brown, A.H.; Milne, S.B.; Myers, D.S.; Merrill, A.H.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Jones, K.N.; Kelly, S.; Shaner, R.L.; et al. Lipidomics reveals a remarkable diversity of lipids in human plasma1. J. Lipid Res. 2010, 51, 3299–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- U.S. Department of Health and Human Services. Food and Drug Administration. Bioanalytical Method Validation: Guidance for Industry. 2018. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/media/70858/download (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- European Medicines Agency. Guideline on Bioanalytical Method Validation EMEA/CHMP/EWP/192217/2009 Rev. 1 Corr. 2**. 2011. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/documents/scientific-guideline/guideline-bioanalytical-method-validation_en.pdf (accessed on 10 December 2020).
- Wolrab, D.; Chocholoušková, M.; Jirásko, R.; Peterka, O.; Holčapek, M. Validation of lipidomic quantitative methods based on lipid class separation—mass spectrometry: Comparison of supercritical fluid chromatography and hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2020, 412, 2375–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chocholoušková, M.; Jirásko, R.; Vrána, D.; Gatěk, J.; Melichar, B.; Holčapek, M. eversed-phase UHPLC/ESI-MS determination of oxylipins in human plasma: A case study of female breast cancer. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2019, 411, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Sphingosine base | 14:1 | 16:1 | 18:0 | 18:1 | 18:2 | 20:1 | 18:0 OH |
| m/z of NII ion | 208.2 | 236.2 | 266.3 | 264.3 | 262.3 | 292.3 | 282.3 |
| Sphingosine Base | Characteristic Product Ion [m/z] | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Cleavage of Fatty Acid from Carbonyl Group Site | Additional Elimination of CO | Additional Elimination of H2O | |
| 14:1 | 512 | 484 | 466 |
| 16:0 | 542 | 514 | 496 |
| 16:1 | 540 | 512 | 494 |
| 18:0 | 570 | 542 | 524 |
| 18:1 | 568 | 540 | 522 |
| 18:2 | 566 | 538 | 520 |
| 20:0 | 598 | 570 | 552 |
| 20:1 | 596 | 568 | 550 |
| 18:0 OH | 586 | 558 | 540 |
| Lipid Class | Internal Standard (Ceramide Composition) | Concentration in IS Mix (μg/mL) | Concentration in Plasma (μg/mL) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cer | 18:1/12:0 18:1-d7/17:0 | 30:1 35:1-d7 | 0.6 1.5 | 0.06 0.15 |
| GalCer (HexCer) | 18:1/12:0 18:1-d7/13:0 | 30:1 31:1-d7 | 0.2 0.6 | 0.02 0.06 |
| GlcCer (HexCer) | 18:1/12:0 18:1-d5/18:1 | 30:1 36:2-d5 | 3 5 | 0.3 0.5 |
| LacCer (Hex2Cer) | 18:1/12:0 18:1-d7/15:0 | 30:1 33:1-d7 | 14 7 | 1.4 0.7 |
| Gb3 | 18:1/17:0 18:1/18:0-d3 | 35:1 36:1-d3 | 3.5 4.5 | 0.35 0.45 |
| Gb4 | not yet commercially available | |||
| GM3 | 18:1/12:0 18:1/18:0-d5 | 30:1 36:1-d5 | 10 12 | 1 1.2 |
| SHexCer | 18:1/12:0 18:1-d7/13:0 | 30:1 31:1-d7 | 0.45 0.45 | 0.045 0.045 |
| SHex2Cer | not yet commercially available | |||
| FA | 18:1-d9 | --------- | 150 | 15 |
| PI | 18:1-d7/15:0 | 33:1-d7 | 30 | 3 |
| LPI | 15:0-d5 | --------- | 1.5 | 0.15 |
| PE | 14:0/14:0 | 28:0 | 3.75 | 0.375 |
| LPE | 14:0 18:1-d7 | --------- --------- | 3 2.5 | 0.30 0.25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hořejší, K.; Jirásko, R.; Chocholoušková, M.; Wolrab, D.; Kahoun, D.; Holčapek, M. Comprehensive Identification of Glycosphingolipids in Human Plasma Using Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography—Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites 2021, 11, 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030140
Hořejší K, Jirásko R, Chocholoušková M, Wolrab D, Kahoun D, Holčapek M. Comprehensive Identification of Glycosphingolipids in Human Plasma Using Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography—Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites. 2021; 11(3):140. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030140
Chicago/Turabian StyleHořejší, Karel, Robert Jirásko, Michaela Chocholoušková, Denise Wolrab, David Kahoun, and Michal Holčapek. 2021. "Comprehensive Identification of Glycosphingolipids in Human Plasma Using Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography—Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry" Metabolites 11, no. 3: 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030140
APA StyleHořejší, K., Jirásko, R., Chocholoušková, M., Wolrab, D., Kahoun, D., & Holčapek, M. (2021). Comprehensive Identification of Glycosphingolipids in Human Plasma Using Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography—Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. Metabolites, 11(3), 140. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo11030140