Changes in Plasma Lipid Levels Following Cortical Spreading Depolarization in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Familial Hemiplegic Migraine
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
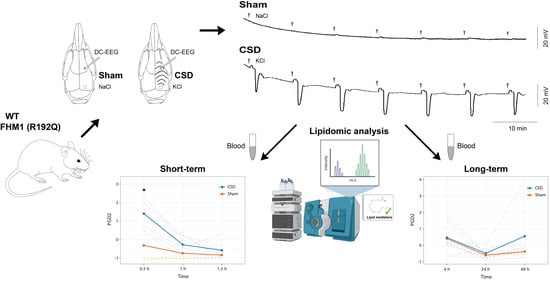
2.1. CSD Characteristics and Physiological Parameters
2.2. Targeted Quantitative Analysis of Lipid Mediators in Peripheral Plasma Following CSD
2.3. PGD2 Shows a Transient Increase Following CSD That Persists Longer in R192Q Mutant Mice
2.4. Long-Term CSD-Related Changes in the Plasma Lipid Metabolome
3. Discussion
Conclusions
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design and Animal Experiments
4.2. CSD Induction and Recording in Anesthetized Mice
4.3. Collection and Preparation of Plasma Samples
4.4. Targeted Analysis of Lipid Mediators
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Goadsby, P.J.; Lipton, R.B.; Ferrari, M.D. Migraine--current understanding and treatment. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 346, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Headache Classification Committee of the International Headache Society (IHS). The international classification of headache disorders, 3rd edition. Cephalalgia 2018, 38, 1–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayata, C.; Lauritzen, M. Spreading Depression, Spreading Depolarizations, and the Cerebral Vasculature. Physiol. Rev. 2015, 95, 953–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Carreira, R.J.; Shyti, R.; Balluff, B.; Abdelmoula, W.M.; van Heiningen, S.H.; van Zeijl, R.J.; Dijkstra, J.; Ferrari, M.D.; Tolner, E.A.; McDonnell, L.A.; et al. Large-scale mass spectrometry imaging investigation of consequences of cortical spreading depression in a transgenic mouse model of migraine. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 26, 853–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Somjen, G.G. Mechanisms of spreading depression and hypoxic spreading depression-like depolarization. Physiol. Rev. 2001, 81, 1065–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gursoy-Ozdemir, Y.; Qiu, J.; Matsuoka, N.; Bolay, H.; Bermphol, D.; Jin, H.; Wang, X.; Rosenberg, G.A.; Lo, E.H.; Moskowitz, M.A. Cortical spreading depression activates and upregulates MMP-9. J. Clin. Investig. 2004, 113, 1447–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shyti, R.; Kohler, I.; Schoenmaker, B.; Derks, R.J.; Ferrari, M.D.; Tolner, E.A.; Mayboroda, O.A.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.J.M. Plasma metabolic profiling after cortical spreading depression in a transgenic mouse model of hemiplegic migraine by capillary electrophoresis--mass spectrometry. Mol. Biosyst. 2015, 11, 1462–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M.D.; Klever, R.R.; Terwindt, G.M.; Ayata, C.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M. Migraine pathophysiology: Lessons from mouse models and human genetics. Lancet Neurol. 2015, 14, 65–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; Pietrobon, D.; Pizzorusso, T.; Kaja, S.; Broos, L.A.; Cesetti, T.; van de Ven, R.C.G.; Tottene, A.; van der Kaa, J.; Plomp, J.J.; et al. A Cacna1a knockin migraine mouse model with increased susceptibility to cortical spreading depression. Neuron 2004, 41, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tottene, A.; Conti, R.; Fabbro, A.; Vecchia, D.; Shapovalova, M.; Santello, M.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.J.M.; Ferrari, M.D.; Pietrobon, D. Enhanced excitatory transmission at cortical synapses as the basis for facilitated spreading depression in Ca(v)2.1 knockin migraine mice. Neuron 2009, 61, 762–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vecchia, D.; Tottene, A.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.; Pietrobon, D. Mechanism underlying unaltered cortical inhibitory synaptic transmission in contrast with enhanced excitatory transmission in CaV2.1 knockin migraine mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2014, 69, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dehghani, A.; Phisonkunkasem, T.; Ozcan, S.Y.; Dalkara, Y.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.J.M.; Tolner, E.A.; Karatas, H. Widespread brain parenchymal HMGB1 and NF-κB neuroinflammatory responses upon cortical spreading depolarization in familial hemiplegic migraine type 1 mice. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 156, 105424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eising, E.; Shyti, R.; ’t Hoen, P.A.C.; Vijfhuizen, L.S.; Huisman, S.M.H.; Broos, L.A.M.; Mahfouz, A.; Reinders, M.J.T.; Ferrari, M.D.; Tolner, E.A.; et al. Cortical Spreading Depression Causes Unique Dysregulation of Inflammatory Pathways in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Migraine. Mol. Neurobiol. 2017, 54, 2986–2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jonasdottir, H.S.; Ioan-Facsinay, A.; Kwekkeboom, J.; Brouwers, H.; Zuurmond, A.; Toes, R.; Deelder, A.M.; Giera, M. An advanced LC MS/MS platform for the analysis of specialized pro-resolving lipid mediators. Chromatographia 2015, 78, 391–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienecke, T.; Olesen, J.; Oturai, P.S.; Ashina, M. Prostacyclin (epoprostenol) induces headache in healthy subjects. Pain 2008, 139, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janoska, M.; Chorążka, K.; Domitrz, I. Migraine frequency and its association with dyslipidemia in women. Neurol. I Neurochir. Pol. 2015, 49, 95–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rist, P.M.; Tzourio, C.; Kurth, T. Associations between lipid levels and migraine: Cross-sectional analysis in the epidemiology of vascular ageing study. Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 1459–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sadeghi, O.; Maghsoudi, Z.; Khorvash, F.; Ghiasvand, R.; Askari, G. The relationship between different fatty acids intake and frequency of migraine attacks. Iran. J. Nurs. Midwifery Res. 2015, 20, 334–339. [Google Scholar]
- Antonova, M.; Wienecke, T.; Olesen, J.; Ashina, M. Prostaglandins in migraine: Update. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferroni, P.; Barbanti, P.; Spila, A.; Fratangeli, F.; Aurilia, C.; Fofi, L.; Egeo, G.; Guadagni, F. Circulating Biomarkers in Migraine: New Opportunities for Precision Medicine. Curr. Med. Chem. 2019, 26, 6191–6206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, E.C.; Lisicki, M.; Fischer, D.; Sándor, P.S.; Schoenen, J. The metabolic face of migraine—From pathophysiology to treatment. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, G.; Anwar, H.; Rasul, A.; Imran, A.; Qasim, M.; Zafar, S.; Imran, M.; Kamran, S.K.S.; Aziz, N.; Razzaq, A.; et al. Lipids as biomarkers of brain disorders. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 60, 351–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onderwater, G.L.J.; Ligthart, L.; Bot, M.; Demirkan, A.; Fu, J.; van der Kallen, C.J.H.; Vijfhuizen, L.S.; Pool, R.; Liu, J.; Vanmolkot, F.H.; et al. Large-scale plasma metabolome analysis reveals alterations in HDL metabolism in migraine. Neurology 2019, 92, e1899–e1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ren, C.; Liu, J.; Zhou, J.; Liang, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Ma, B.; Yin, Y. Lipidomic analysis of serum samples from migraine patients. Lipids Health Dis. 2018, 17, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tuca, J.O.; Planas, J.M.; Parellada, P.P. Increase in PGE2 and TXA2 in the saliva of common migraine patients. Action of calcium channel blockers. Headache 1989, 29, 498–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durham, P.L.; Vause, C.V.; Derosier, F.; McDonald, S.; Cady, R.; Martin, V. Changes in salivary prostaglandin levels during menstrual migraine with associated dysmenorrhea. Headache 2010, 50, 844–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarchielli, P.; Alberti, A.; Codini, M.; Floridi, A.; Gallai, V. Nitric oxide metabolites, prostaglandins and trigeminal vasoactive peptides in internal jugular vein blood during spontaneous migraine attacks. Cephalalgia 2000, 20, 907–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tracey, T.J.; Steyn, F.J.; Wolvetang, E.J.; Ngo, S.T. Neuronal Lipid Metabolism: Multiple Pathways Driving Functional Outcomes in Health and Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, S.P.; Tolner, E.A.; Eikermann-Haerter, K. Animal models of monogenic migraine. Cephalalgia 2016, 36, 704–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Eikermann-Haerter, K.; Lee, J.H.; Yuzawa, I.; Liu, C.H.; Zhou, Z.; Shin, H.K.; Zheng, Y.; Qin, T.; Kurth, T.; Waeber, C.; et al. Migraine mutations increase stroke vulnerability by facilitating ischemic depolarizations. Circulation 2012, 125, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mulder, I.A.; Ogrinc Potočnik, N.; Broos, L.A.M.; Prop, A.; Wermer, M.J.A.; Heeren, R.M.A.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.J.M. Distinguishing core from penumbra by lipid profiles using Mass Spectrometry Imaging in a transgenic mouse model of ischemic stroke. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Golovko, S.A.; Golovko, M.Y. Plasma Unesterified Fatty-Acid Profile Is Dramatically and Acutely Changed under Ischemic Stroke in the Mouse Model. Lipids 2018, 53, 641–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arabadzhieva, D.Y.; Slavov, Z.; Kaprelyan, A. Serum lipid anomalies in adult patients with acute ischemic stroke. Scr. Sci. Med. 2015, 47, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heischmann, S.; Quinn, K.; Cruickshank-Quinn, C.; Liang, L.; Reisdorph, R.; Reisdorph, N.; Patel, M. Exploratory Metabolomics Profiling in the Kainic Acid Rat Model Reveals Depletion of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3 during Epileptogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dreier, J.P.; Major, S.; Pannek, H.W.; Woitzik, J.; Scheel, M.; Wiesenthal, D.; Martus, P.; Winkler, M.K.L.; Hartings, J.A.; Fabricius, M.; et al. Spreading convulsions, spreading depolarization and epileptogenesis in human cerebral cortex. Brain 2012, 135, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlson, L.A.; Ekelund, L.G.; Orö, L. Clinical and metabolic effects of different doses of prostaglandin E1 in man. Prostaglandin and related factors. Acta Med. Scand. 1968, 183, 423–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, R.J.; Murdoch, C.E.; Ali, M.; Purbrick, S.; Ravid, R.; Baxter, G.S.; Tilford, N.; Sheldrick, R.L.G.; Clark, K.L.; Coleman, R.A. EP4 prostanoid receptor-mediated vasodilatation of human middle cerebral arteries. Br. J. Pharm. 2004, 141, 580–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wienecke, T.; Olesen, J.; Ashina, M. Discrepancy between strong cephalic arterial dilatation and mild headache caused by prostaglandin D₂ (PGD₂). Cephalalgia 2011, 31, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.C.; Strassman, A.M.; Burstein, R.; Levy, D. Sensitization and activation of intracranial meningeal nociceptors by mast cell mediators. J. Pharm. Exp. Pharm. Exp. 2007, 322, 806–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mezei, Z.; Kis, B.; Gecse, A.; Tajti, J.; Boda, B.; Telegdy, G.; Vécsei, L. Platelet arachidonate cascade of migraineurs in the interictal phase. Platelets 2000, 11, 222–225. [Google Scholar]
- Viola, S.; Viola, P.; Litterio, P.; Buongarzone, M.P.; Fiorelli, L. Stroke risk and migraine: Near-infrared spectroscopy study. Neurol. Sci. 2012, 33 (Suppl. 1), S173–S175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jenkins, D.W.; Feniuk, W.; Humphrey, P.P. Characterization of the prostanoid receptor types involved in mediating calcitonin gene-related peptide release from cultured rat trigeminal neurons. Br. J. Pharm. 2001, 134, 1296–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Durham, P.L. Calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) and migraine. Headache 2006, 46 (Suppl. 1), S3–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Karatas, H.; Erdener, S.E.; Gursoy-Ozdemir, Y.; Lule, S.; Eren-Koçak, E.; Sen, Z.D.; Dalkara, T. Spreading depression triggers headache by activating neuronal Panx1 channels. Science 2013, 339, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wienecke, T.; Olesen, J.; Oturai, P.S.; Ashina, M. Prostaglandin E2(PGE2) induces headache in healthy subjects. Cephalalgia 2009, 29, 509–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienecke, T.; Olesen, J.; Ashina, M. Prostaglandin I2 (epoprostenol) triggers migraine-like attacks in migraineurs. Cephalalgia 2010, 30, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonova, M.; Wienecke, T.; Olesen, J.; Ashina, M. Prostaglandin E2 induces immediate migraine-like attack in migraine patients without aura. Cephalalgia 2012, 32, 822–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lauritzen, M.; Hansen, A.J.; Kronborg, D.; Wieloch, T. Cortical spreading depression is associated with arachidonic acid accumulation and preservation of energy charge. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 1990, 10, 115–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tassorelli, C.; Greco, R.; Armentero, M.T.; Blandini, F.; Sandrini, G.; Nappi, G. A role for brain cyclooxygenase-2 and prostaglandin-E2 in migraine: Effects of nitroglycerin. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2007, 82, 373–382. [Google Scholar]
- Alsaif, M.; Guest, P.C.; Schwarz, E.; Reif, A.; Kittel-Schneider, S.; Spain, M.; Rahmoune, H.; Bahn, S. Analysis of serum and plasma identifies differences in molecular coverage, measurement variability, and candidate biomarker selection. Proteom. Clin. Appl. 2012, 6, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nattero, G.; Allais, G.; De Lorenzo, C.; Benedetto, C.; Zonca, M.; Melzi, E.; Massobrio, M. Relevance of prostaglandins in true menstrual migraine. Headache 1989, 29, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yazdi, P.G. A review of the biologic and pharmacologic role of docosapentaenoic acid n-3. F1000Res 2013, 2, 256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soveyd, N.; Abdolahi, M.; Bitarafan, S.; Tafakhori, A.; Sarraf, P.; Togha, M.; Okhovat, A.A.; Hatami, M.; Sedighiyan, M.; Djalali, M. Molecular mechanisms of omega-3 fatty acids in the migraine headache. Rev. Iran. J. Neurol. 2017, 16, 210–217. [Google Scholar]
- Franceschini, A.; Vilotti, S.; Ferrari, M.D.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.J.M.; Nistri, A.; Fabbretti, E. TNFα levels and macrophages expression reflect an inflammatory potential of trigeminal ganglia in a mouse model of familial hemiplegic migraine. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e52394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, E.C.; Putananickal, N.; Orsini, A.L.; Vogt, D.R.; Sandor, P.S.; Schoenen, J.; Fischer, D. Mitochondrial function and oxidative stress markers in higher-frequency episodic migraine. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanha, H.M.; Sathyanarayanan, A.; International Headache Genetics Consortium; Nyholt, D.R. Genetic overlap and causality between blood metabolites and migraine. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 108, 2086–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramsden, C.E.; Zamora, D.; Faurot, K.R.; MacIntosh, B.A.; Horowitz, M.; Keyes, G.S.; Yuan, Z.X.; Miller, V.; Lynch, C.; Honvoh, G. Dietary alteration of n-3 and n-6 fatty acids for headache reduction in adults with migraine: Randomized controlled trial. BMJ 2021, 374, n1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramsden, C.E.; Faurot, K.R.; Zamora, D.; Palsson, O.S.; MacIntosh, B.A.; Gaylord, S.; Taha, A.Y.; Rapoport, S.I.; Hibbeln, J.R.; Davis, J.M. Targeted alterations in dietary n-3 and n-6 fatty acids improve life functioning and reduce psychological distress among patients with chronic headache: A secondary analysis of a randomized trial. Pain 2015, 156, 587–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sang, N.; Chen, C. Lipid signaling and synaptic plasticity. Neuroscientist 2006, 12, 425–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardutz, A.; Schoenen, J. NSAIDs in the Acute Treatment of Migraine: A Review of Clinical and Experimental Data. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 1966–1987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitazawa, M.; Kaneko, Y.; Shiratori, R.; Tsukamoto, S.; Oshida, S. Changes of fatty acid composition of brain synaptosomal phospholipids in isoflurane exposure rat. Nihon Arukoru Yakubutsu Igakkai Zasshi 2001, 36, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sano, Y.; Ito, S.; Yoneda, M.; Nagasawa, K.; Matsuura, N.; Yamada, Y.; Uchinaka, A.; Bando, Y.K.; Murohara, T.; Nagata, K. Effects of various types of anesthesia on hemodynamics, cardiac function, and glucose and lipid metabolism in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2016, 311, H1360–H1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söbbeler, F.J.; Carrera, I.; Pasloske, K.; Ranasinghe, M.G.; Kircher, P.; Kästner, S.B.R. Effects of isoflurane, sevoflurane, propofol and alfaxalone on brain metabolism in dogs assessed by proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy (1 H MRS). Randomized Control. Trial. BMC Vet. Res. 2018, 14, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Scher, J.U.; Pillinger, M.H. The anti-inflammatory effects of prostaglandins. J. Investig. Med. 2009, 57, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, P.L.; Kendall, L.V.; Turner, P.V. Clinical Management of Pain in Rodents. Rev. Comp. Med. 2019, 69, 468–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houben, T.; Loonen, I.C.M.; Baca, S.M.; Schenke, M.; Meijer, J.H.; Ferrari, M.D.; Terwindt, G.M.; Voskuyl, R.A.; Charles, A.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.J.M.; et al. Optogenetic induction of cortical spreading depression in anesthetized and freely behaving mice. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2017, 37, 1641–1655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Altamura, C.; Corbelli, I.; de Tommaso, M.; Di Lorenzo, C.; Di Lorenzo, G.; Di Renzo, A. Pathophysiological Bases of Comorbidity in Migraine. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 640574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Experimental Groups | n | Amplitude (mV) | Duration (s) | pH | pCO2 | pO2 | MABP (mm Hg) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short-term WT Sham WT CSD R192Q Sham R192Q CSD | 5 5 5 5 | - 18 ± 5 - 14 ± 6 | - 47 ± 4 - 43 ± 6 | 7.34 ± 0.06 7.35 ± 0.02 7.36 ± 0.04 7.34 ± 0.01 | 32 ± 7 32 ± 5 28 ± 4 33 ± 4 | 115 ± 11 110 ± 12 120 ± 7 115 ± 9 | 77 ± 7 72 ± 4 74 ± 6 79 ± 7 |
| Long-term | |||||||
| WT Sham WT CSD R192Q Sham R192Q CSD | 5 5 5 5 | - 21 ± 3 - 22 ± 1 | - 59 ± 19 - 54 ± 17 | - - - - | - - - - | - - - - | - - - - |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loonen, I.C.M.; Kohler, I.; Ghorasaini, M.; Giera, M.; van den Maagdenberg, A.M.J.M.; Mayboroda, O.A.; Tolner, E.A. Changes in Plasma Lipid Levels Following Cortical Spreading Depolarization in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Familial Hemiplegic Migraine. Metabolites 2022, 12, 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030220
Loonen ICM, Kohler I, Ghorasaini M, Giera M, van den Maagdenberg AMJM, Mayboroda OA, Tolner EA. Changes in Plasma Lipid Levels Following Cortical Spreading Depolarization in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Familial Hemiplegic Migraine. Metabolites. 2022; 12(3):220. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030220
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoonen, Inge C. M., Isabelle Kohler, Mohan Ghorasaini, Martin Giera, Arn M. J. M. van den Maagdenberg, Oleg A. Mayboroda, and Else A. Tolner. 2022. "Changes in Plasma Lipid Levels Following Cortical Spreading Depolarization in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Familial Hemiplegic Migraine" Metabolites 12, no. 3: 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030220
APA StyleLoonen, I. C. M., Kohler, I., Ghorasaini, M., Giera, M., van den Maagdenberg, A. M. J. M., Mayboroda, O. A., & Tolner, E. A. (2022). Changes in Plasma Lipid Levels Following Cortical Spreading Depolarization in a Transgenic Mouse Model of Familial Hemiplegic Migraine. Metabolites, 12(3), 220. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12030220