Impact of Maternal Obesity on the Gestational Metabolome and Infant Metabolome, Brain, and Behavioral Development in Rhesus Macaques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Feeding and Rearing of Animals
2.3. Sample Collection and Processing
2.4. Metabolite Extraction and Insulin, Cytokine, and Cortisol Measurement
2.5. 1H NMR Spectroscopy Data Acquisition
2.6. Protein Analysis
2.7. Visual Paired-Comparison (VPC) Test
2.8. Human Intruder (HI) Test
2.9. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Obese Mothers Exhibited Increased Insulin Resistance and Higher Inflammation over the Course of Pregnancy
3.2. Maternal Obesity Impacted Energy and One-Carbon Metabolism as Reflected in the Serum and Urine Metabolomes
3.3. Maternal Obesity Altered One-Carbon Metabolism in the Placenta, and Placental Size Was Correlated with HOMA-IR
3.4. Maternal Obesity Led to Larger Infants at Birth with Altered Metabolomic Profiles
3.5. mTOR Pathway of the Prefrontal Cortex in Infants Born to Obese Mothers May Be Elevated
3.6. High Maternal Adiposity Led to Differences in Brain Function of Offspring
4. Discussion
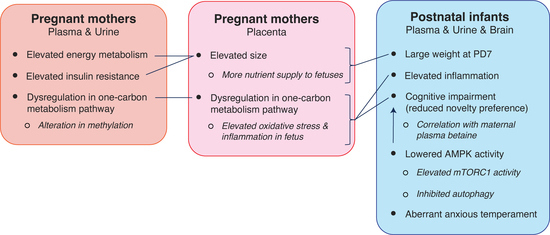
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix A.1. Feeding and Rearing of Animals
Appendix A.2. Metabolite Extraction and Insulin, Cytokine, and Cortisol Measurement
Appendix A.3. Protein Analysis
Appendix A.4. Statistics
References
- Hales, C.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Fryar, C.D.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Obesity and Severe Obesity Among Adults: United States, 2017–2018. NCHS Data Brief 2020, 360, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Flegal, K.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Kit, B.K.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of Obesity and Trends in the Distribution of Body Mass Index among US Adults, 1999–2010. JAMA 2012, 307, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krakowiak, P.; Walker, C.K.; Bremer, A.A.; Baker, A.S.; Ozonoff, S.; Hansen, R.L.; Hertz-Picciotto, I. Maternal Metabolic Conditions and Risk for Autism and Other Neurodevelopmental Disorders. Pediatrics 2012, 129, e1121–e1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deregnier, R.-A.; Nelson, C.A.; Thomas, K.M.; Wewerka, S.; Georgieff, M.K. Neurophysiologic evaluation of auditory recognition memory in healthy newborn infants and infants of diabetic mothers. J. Pediatr. 2000, 137, 777–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgieff, M.K.; Ramel, S.E.; Cusick, S.E. Nutritional influences on brain development. Acta Paediatr. 2018, 107, 1310–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth Control and Disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.Y. Roles of mTOR Signaling in Brain Development. Exp. Neurobiol. 2015, 24, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeffer, C.A.; Klann, E. mTOR signaling: At the crossroads of plasticity, memory and disease. Trends Neurosci. 2010, 33, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Kundu, M.; Viollet, B.; Guan, K.-L. AMPK and mTOR regulate autophagy through direct phosphorylation of Ulk1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2011, 13, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kampmann, U.; Knorr, S.; Fuglsang, J.; Ovesen, P. Determinants of Maternal Insulin Resistance during Pregnancy: An Updated Overview. J. Diabetes Res. 2019, 2019, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oken, E.; Gillman, M.W. Fetal Origins of Obesity. Obes. Res. 2003, 11, 496–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Gudsnuk, K.; Kuo, S.-H.; Cotrina, M.L.; Rosoklija, G.; Sosunov, A.; Sonders, M.S.; Kanter, E.; Castagna, C.; Yamamoto, A.; et al. Loss of mTOR-Dependent Macroautophagy Causes Autistic-like Synaptic Pruning Deficits. Neuron 2014, 83, 1131–1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karling, P.; Wikgren, M.; Adolfsson, R.; Norrback, K.-F. Hypothalamus-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis Hypersuppression Is Associated with Gastrointestinal Symptoms in Major Depression. J. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2016, 22, 292–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Summers, L.; Clingerman, K.J.; Yang, X. Validation of a body condition scoring system in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta): Assessment of body composition by using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry. J. Am. Assoc. Lab. Anim. Sci. 2012, 51, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Silk, J.; Short, J.; Roberts, J.; Kusnitz, J. Gestation length in rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Int. J. Primatol. 1993, 14, 95–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasegawa, Y.; Otoki, Y.; McClorry, S.; Coates, L.C.; Lombardi, R.L.; Taha, A.Y.; Slupsky, C.M. Optimization of a method for the simultaneous extraction of polar and non-polar oxylipin metabolites, DNA, RNA, small RNA, and protein from a single small tissue sample. Methods Protoc. 2020, 3, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, C.K.; VandeVoort, C.A.; Li, C.-S.; Chaffin, C.L.; Capitanio, J.P. Adiposity and weight gain during pregnancy associate independently with behavior of infant rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Dev. Psychobiol. 2018, 60, 629–638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandeleest, J.; Capitanio, J.; Hamel, A.; Meyer, J.; Novak, M.; Mendoza, S.; McCowan, B. Social stability influences the association between adrenal responsiveness and hair cortisol concentrations in rhesus macaques. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2018, 100, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, A.; Willoughby, R.E.; Mishchuk, D.; Alcarraz, B.; Cabezas, C.; Condori, R.E.; David, D.; Encarnacion, R.; Fatteh, N.; Fernandez, J.; et al. Metabolomics of cerebrospinal fluid from humans treated for rabies. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 12, 481–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, M.S.; Hogrefe, C.E.; Vandevoort, C.A. Binge drinking prior to pregnancy detection in a nonhuman primate: Behavioral evaluation of offspring. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2013, 38, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golub, M.S.; Hogrefe, C.E.; Germann, S.L.; Capitanio, J.P.; Lozoff, B. Behavioral consequences of developmental iron deficiency in infant rhesus monkeys. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2006, 28, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burbacher, T.M.; Grant, K.S. Measuring infant memory: Utility of the visual paired-comparison test paradigm for studies in developmental neurotoxicology. Neurotoxicol. Teratol. 2012, 34, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Troisi, A. Displacement activities as a behavioral measure of stress in nonhuman primates and human subjects. Stress 2002, 5, 47–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonek, J.; Krantz, D.; Carmichael, J.; Downing, C.; Jessup, K.; Haidar, Z.; Ho, S.; Hallahan, T.; Kliman, H.J.; McKenna, D. First-trimester screening for early and late preeclampsia using maternal characteristics, biomarkers, and estimated placental volume. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2018, 218, 126.e1–126.e13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sullivan, G.M.; Feinn, R. Using Effect Size—Or Why the p Value Is Not Enough. J. Grad. Med Educ. 2012, 4, 279–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howell, K.; Powell, T.L. Effects of maternal obesity on placental function and fetal development. Reproduction 2017, 153, R97–R108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, S.L.; on behalf of the UPBEAT Consortium; Pasupathy, D.; Sattar, N.; Nelson, S.M.; Lawlor, D.A.; Briley, A.L.; Seed, P.T.; Welsh, P.; Poston, L. Metabolic profiling of gestational diabetes in obese women during pregnancy. Diabetologia 2017, 60, 1903–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagao, H.; Nishizawa, H.; Bamba, T.; Nakayama, Y.; Isozumi, N.; Nagamori, S.; Kanai, Y.; Tanaka, Y.; Kita, S.; Fukuda, S.; et al. Increased Dynamics of Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle and Glutamate Synthesis in Obese Adipose Tissue. J. Biol. Chem. 2017, 292, 4469–4483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, S.; Iyer, C.; Meydani, S.N. Obesity during pregnancy alters maternal oxidant balance and micronutrient status. J. Perinatol. 2013, 34, 105–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ehrenberg, H.M.; Mercer, B.M.; Catalano, P.M. The influence of obesity and diabetes on the prevalence of macrosomia. Am. J. Obstet. Gynecol. 2004, 191, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfensohn, S.; Honess, P. Handbook of Primate Husbandry and Welfare; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-1-4051-5615-8. [Google Scholar]
- Hopper, K.J.; Capozzi, D.K.; Newsome, J.T. Effects of maternal and infant characteristics on birth weight and gestation length in a colony of rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta). Comp. Med. 2008, 58, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Connolly, M.A.; Trentalange, M.; Zeiss, C.J. Long-Term Clinical Outcomes in Diabetic Rhesus Macaques (Macaca mulatta) Treated with Medroxyprogesterone Acetate for Endometriosis. Comp. Med. 2016, 66, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bodkin, N.L.; Metzger, B.L.; Hansen, B.C. Hepatic glucose production and insulin sensitivity preceding diabetes in monkeys. Am. J. Physiol. Metab. 1989, 256, E676–E681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, R.; Raab, S.; Zheng, W.; Wang, J.; Liu, N.; Zhu, T.; Xue, L.; Song, Z.; Mao, J.; et al. Rhesus macaques develop metabolic syndrome with reversible vascular dysfunction responsive to pioglitazone. Circulation 2011, 124, 77–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, H.N.; Woollett, L.A.; Barbour, N.; Prasad, P.D.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. High-fat diet before and during pregnancy causes marked up-regulation of placental nutrient transport and fetal overgrowth in C57/BL6 mice. FASEB J. 2008, 23, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosario, F.J.; Powell, T.L.; Jansson, T. Activation of placental insulin and mTOR signaling in a mouse model of maternal obesity associated with fetal overgrowth. Am. J. Physiol. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 2016, 310, R87–R93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCurdy, C.; Bishop, J.M.; Williams, S.M.; Grayson, B.E.; Smith, M.S.; Friedman, J.E.; Grove, K.L. Maternal high-fat diet triggers lipotoxicity in the fetal livers of nonhuman primates. J. Clin. Investig. 2009, 119, 323–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plucińska, K.; Barger, S.W. Maternal obesity reprograms offspring’s executive brain centers in a sex-specific manner? J. Neurochem. 2018, 145, 358–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, S.E.; Zhang, S.; Chen, L.; Rabinowitz, J.D.; Reyes, T.M. Perinatal high fat diet and early life methyl donor supplementation alter one carbon metabolism and DNA methylation in the brain. J. Neurochem. 2018, 145, 362–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Werling, D.M.; Geschwind, D.H. Sex differences in autism spectrum disorders. Curr. Opin. Neurol. 2013, 26, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deardorff, J.; Smith, L.H.; Petito, L.; Kim, H.; Abrams, B.F. Maternal prepregnancy weight and children’s behavioral and emotional outcomes. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2017, 53, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keim, S.A.; Pruitt, N.T. Gestational weight gain and child cognitive development. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comstock, S.S. Time to change weight gain recommendations for pregnant women with obesity. J. Clin. Investig. 2019, 129, 4567–4569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.; Yamada, K.; Matsushima, M.; Izawa, T.; Furukawa, S.; Kobayashi, Y.; Iwashita, M. Increased maternal insulin resistance promotes placental growth and decreases placental efficiency in pregnancies with obesity and gestational diabetes mellitus. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. Res. 2017, 44, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malti, N.; Merzouk, H.; Merzouk, S.; Loukidi, B.; Karaouzene, N.; Malti, A.; Narce, M. Oxidative stress and maternal obesity: Feto-placental unit interaction. Placenta 2014, 35, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svingen, G.F.; Schartum-Hansen, H.; Pedersen, E.R.; Ueland, P.M.; Tell, G.S.; Mellgren, G.; Njølstad, P.R.; Seifert, R.; Strand, E.; Karlsson, T.; et al. Prospective associations of systemic and urinary choline metabolites with incident type 2 diabetes. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 755–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nathanielsz, P.W.; Yan, J.; Green, R.; Nijland, M.; Miller, J.W.; Wu, G.; McDonald, T.J.; Caudill, M.A. Maternal obesity disrupts the methionine cycle in baboon pregnancy. Physiol. Rep. 2015, 3, e12564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dahlhoff, C.; Desmarchelier, C.; Sailer, M.; Fürst, R.W.; Haag, A.; Ulbrich, S.E.; Hummel, B.; Obeid, R.; Geisel, J.; Bader, B.L.; et al. Hepatic Methionine Homeostasis Is Conserved in C57BL/6N Mice on High-Fat Diet Despite Major Changes in Hepatic One-Carbon Metabolism. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e57387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollset, S.E.; Refsum, H.; Irgens, L.M.; Emblem, B.M.; Tverdal, A.; Gjessing, H.K.; Monsen, A.L.B.; Ueland, P.M. Plasma total homocysteine, pregnancy complications, and adverse pregnancy outcomes: The Hordaland Homocysteine Study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2000, 71, 962–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mailloux, R.J.; McBride, S.L.; Harper, M.-E. Unearthing the secrets of mitochondrial ROS and glutathione in bioenergetics. Trends Biochem. Sci. 2013, 38, 592–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, A.G.; Tulina, N.M.; Barila, G.O.; Hester, M.S.; Elovitz, M. Exposure to intrauterine inflammation alters metabolomic profiles in the amniotic fluid, fetal and neonatal brain in the mouse. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0186656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butte, N.F.; Liu, Y.; Zakeri, I.F.; Mohney, R.P.; Mehta, N.R.; Voruganti, V.S.; Goring, H.H.H.; Cole, S.A.; Comuzzie, A.G. Global metabolomic profiling targeting childhood obesity in the Hispanic population. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2015, 102, 256–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickiewicz, B.; Vogel, H.J.; Wong, H.R.; Winston, B.W. Metabolomics as a novel approach for early diagnosis of pediatric septic shock and its mortality. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 967–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capitanio, J.P.; Mendoza, S.P.; Lerche, N.W.; Mason, W.A. Social stress results in altered glucocorticoid regulation and shorter survival in simian acquired immune deficiency syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1998, 95, 4714–4719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yehuda, R.; Southwick, S.M.; Krystal, J.H.; Bremner, D.; Charney, D.S.; Mason, J.W. Enhanced suppression of cortisol following dexamethasone administration in posttraumatic stress disorder. Am. J. Psychiatry 1993, 150, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grissom, N.M.; Herdt, C.T.; Desilets, J.; Lidsky-Everson, J.; Reyes, T.M. Dissociable deficits of executive function caused by gestational adversity are linked to specific transcriptional changes in the prefrontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 2014, 40, 1353–1363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKee, S.E.; Grissom, N.M.; Herdt, C.T.; Reyes, T.M. Methyl donor supplementation alters cognitive performance and motivation in female offspring from high-fat diet-fed dams. FASEB J. 2017, 31, 2352–2363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surén, P.; Roth, C.; Bresnahan, M.; Haugen, M.; Hornig, M.; Hirtz, D.; Lie, K.K.; Lipkin, W.I.; Magnus, P.; Reichborn-Kjennerud, T.; et al. Association between maternal use of folic acid supplements and risk of autism spectrum disorders in children. JAMA 2013, 309, 570–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oler, J.A.; Fox, A.S.; Shelton, S.E.; Rogers, J.; Dyer, T.D.; Davidson, R.; Shelledy, W.; Oakes, T.R.; Blangero, J.; Kalin, N.H. Amygdalar and hippocampal substrates of anxious temperament differ in their heritability. Nature 2010, 466, 864–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hasegawa, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Taha, A.Y.; Capitanio, J.P.; Bauman, M.D.; Golub, M.S.; Van de Water, J.; VandeVoort, C.A.; Walker, C.K.; Slupsky, C.M. Impact of Maternal Obesity on the Gestational Metabolome and Infant Metabolome, Brain, and Behavioral Development in Rhesus Macaques. Metabolites 2022, 12, 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080764
Hasegawa Y, Zhang Z, Taha AY, Capitanio JP, Bauman MD, Golub MS, Van de Water J, VandeVoort CA, Walker CK, Slupsky CM. Impact of Maternal Obesity on the Gestational Metabolome and Infant Metabolome, Brain, and Behavioral Development in Rhesus Macaques. Metabolites. 2022; 12(8):764. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080764
Chicago/Turabian StyleHasegawa, Yu, Zhichao Zhang, Ameer Y. Taha, John P. Capitanio, Melissa D. Bauman, Mari S. Golub, Judy Van de Water, Catherine A. VandeVoort, Cheryl K. Walker, and Carolyn M. Slupsky. 2022. "Impact of Maternal Obesity on the Gestational Metabolome and Infant Metabolome, Brain, and Behavioral Development in Rhesus Macaques" Metabolites 12, no. 8: 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080764
APA StyleHasegawa, Y., Zhang, Z., Taha, A. Y., Capitanio, J. P., Bauman, M. D., Golub, M. S., Van de Water, J., VandeVoort, C. A., Walker, C. K., & Slupsky, C. M. (2022). Impact of Maternal Obesity on the Gestational Metabolome and Infant Metabolome, Brain, and Behavioral Development in Rhesus Macaques. Metabolites, 12(8), 764. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080764