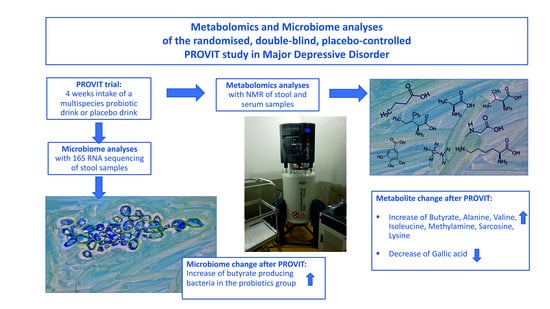
The PROVIT Study—Effects of Multispecies Probiotic Add-on Treatment on Metabolomics in Major Depressive Disorder—A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Details of the Probiotic Supplementation
2.3. Metabolomics
2.3.1. Reagents
2.3.2. Metabolomic Quantification Using NMR
2.4. Microbiome Analysis
2.5. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive Statistics of the PROVIT Metabolomics Cohort
3.2. Untargeted Metabolomic Assessment of Serum Reveals No Significant Differences
3.3. NMR-Based Metabolomics Analysis of Stool Reveals Changes Induced by Probiotics
3.4. Strong Correlations between Metabolites and Microbial Species Exist
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Malhi, G.S.; Mann, J.J. Course and prognosis. Lancet 2018, 392, 2299–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- COVID-19 Mental Disorders Collaborators. Global Prevalence and Burden of Depressive and Anxiety Disorders in 204 Countries and Territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 Pandemic. Lancet 2021, 398, 1700–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, M.; Klesse, C.; Bermejo, I.; Schneider, F.; Berger, M. Unipolar Depression: Diagnostic and Therapeutic Recommendations from the Current S3/National Clinical Practice Guideline. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2010, 107, 700–708. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DGPPN. S3-Leitlinie/Nationale VersorgungsLeitlinie Unipolare Depression Langfassung. 2015. Available online: https://www.dgppn.de/_Resources/Persistent/d689bf8322a5bf507bcc546eb9d61ca566527f2f/S3-NVL_depression-2aufl-vers5-lang.pdf (accessed on 15 July 2022).
- Howard, D.M.; Adams, M.J.; Clarke, T.K.; Hafferty, J.D.; Gibson, J.; Shirali, M.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Hagenaars, S.P.; Ward, J.; Wigmore, E.M.; et al. Genome-Wide Meta-Analysis of Depression Identifies 102 Independent Variants and Highlights the Importance of the Prefrontal Brain Regions. Nat. Neurosci. 2019, 22, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.R.I.; Peyrot, W.J.; Purves, K.L.; Davis, K.A.S.; Rayner, C.; Choi, S.W.; Hubel, C.; Gaspar, H.A.; Kan, C.; Van der Auwera, S.; et al. Genome-Wide Gene-Environment Analyses of Major Depressive Disorder and Reported Lifetime Traumatic Experiences in UK Biobank. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 1430–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schotte, C.K.; Van Den Bossche, B.; De Doncker, D.; Claes, S.; Cosyns, P. A Biopsychosocial Model as a Guide for Psychoeducation and Treatment of Depression. Depress. Anxiety 2006, 23, 312–324. [Google Scholar]
- Pantazatos, S.P.; Huang, Y.Y.; Rosoklija, G.B.; Dwork, A.J.; Arango, V.; Mann, J.J. Whole-Transcriptome Brain Expression and Exon-Usage Profiling in Major Depression and Suicide: Evidence for Altered Glial, Endothelial and ATPase Activity. Mol. Psychiatry 2017, 22, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uchida, S.; Yamagata, H.; Seki, T.; Watanabe, Y. Epigenetic Mechanisms of Major Depression: Targeting Neuronal Plasticity. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 72, 212–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins-de-Souza, D. Proteomics, Metabolomics, and Protein Interactomics in the Characterization of the Molecular Features of Major Depressive Disorder. Dialogues Clin. Neurosci. 2014, 16, 63–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Wade, P.A. Crosstalk between the Microbiome and Epigenome: Messages from Bugs. J. Biochem. 2018, 163, 105–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, T.G.; McMahon, F.J. (Eds.) Psychiatric Genetics: A Primer for Clinical and Basic Scientists, 1st ed.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Coulter, L.; Ibrahimi, M.; Patel, R.; Agius, M. Linking the Psychosocial Aetiology and Neurobiology of Unipolar Depression. Psychiatr. Danub. 2017, 29, 441–446. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Hao, Y.; Fan, F.; Zhang, B. The Role of Microbiome in Insomnia, Circadian Disturbance and Depression. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valles-Colomer, M.; Falony, G.; Darzi, Y.; Tigchelaar, E.F.; Wang, J.; Tito, R.Y.; Schiweck, C.; Kurilshikov, A.; Joossens, M.; Wijmenga, C.; et al. The Neuroactive Potential of the Human Gut Microbiota in Quality of Life and Depression. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 623–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanada, K.; Nakajima, S.; Kurokawa, S.; Barcelo-Soler, A.; Ikuse, D.; Hirata, A.; Yoshizawa, A.; Tomizawa, Y.; Salas-Valero, M.; Noda, Y.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Major Depressive Disorder: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 266, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krautkramer, K.A.; Fan, J.; Backhed, F. Gut Microbial Metabolites as Multi-Kingdom Intermediates. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2021, 19, 77–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of Short Chain Fatty Acids by the Gut Microbiota and their Impact on Human Metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, Y.P.; Bernardi, A.; Frozza, R.L. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids from Gut Microbiota in Gut-Brain Communication. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bot, M.; Milaneschi, Y.; Al-Shehri, T.; Amin, N.; Garmaeva, S.; Onderwater, G.L.J.; Pool, R.; Thesing, C.S.; Vijfhuizen, L.S.; Vogelzangs, N.; et al. Metabolomics Profile in Depression: A Pooled Analysis of 230 Metabolic Markers in 5283 Cases with Depression and 10,145 Controls. Biol. Psychiatry 2020, 87, 409–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konjevod, M.; Nikolac Perkovic, M.; Saiz, J.; Svob Strac, D.; Barbas, C.; Rojo, D. Metabolomics Analysis of Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis in Neurodegenerative and Psychiatric Diseases. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 194, 113681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reininghaus, E.Z.; Wetzlmair, L.C.; Fellendorf, F.T.; Platzer, M.; Queissner, R.; Birner, A.; Pilz, R.; Hamm, C.; Maget, A.; Rieger, A.; et al. Probiotic Treatment in Individuals with Euthymic Bipolar Disorder: A Pilot-Study on Clinical Changes and Compliance. Neuropsychobiology 2020, 79, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiter, A.; Bengesser, S.A.; Hauschild, A.C.; Birkl-Toglhofer, A.M.; Fellendorf, F.T.; Platzer, M.; Farber, T.; Seidl, M.; Mendel, L.M.; Unterweger, R.; et al. Interleukin-6 Gene Expression Changes After a 4-Week Intake of a Multispecies Probiotic in Major Depressive Disorder-Preliminary Results of the PROVIT Study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Trujillo, M.; Athersuch, T.J. Special Issue: NMR-Based Metabolomics. Molecules 2021, 26, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reininghaus, E.; Platzer, M.; Kohlhammer-Dohr, A.; Hamm, C.; Mörkl, S.; Bengesser, S.; Fellendorf, F.; Lahousen, T.; Leitner-Afschar, B.; Schöggl, H.; et al. PROVIT: Supplementary Probiotic Treatment in Depression—A Randomized Controlled Trial. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, D.V.; Lecrubier, Y.; Sheehan, K.H.; Amorim, P.; Janavs, J.; Weiller, E.; Hergueta, T.; Baker, R.; Dunbar, G.C. The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): The Development and Validation of a Structured Diagnostic Psychiatric Interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J. Clin. Psychiatry 1998, 59 (Suppl. 20), 22–33. [Google Scholar]
- Worboys, M. The Hamilton Rating Scale for Depression: The Making of a “Gold Standard” and the Unmaking of a Chronic Illness, 1960–1980. Chronic Illn. 2013, 9, 202–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.T.; Ward, C.H.; Mendelson, M.; Mock, J.; Erbaugh, J. An Inventory for Measuring Depression. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1961, 4, 561–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Kerbl-Knapp, J.; Akhmetshina, A.; Korbelius, M.; Kuentzel, K.B.; Vujic, N.; Horl, G.; Paar, M.; Kratky, D.; Steyrer, E.; et al. Tissue-Specific Landscape of Metabolic Dysregulation during Ageing. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterle, F.; Ross, A.; Schlotterbeck, G.; Senn, H. Probabilistic Quotient Normalization as Robust Method to Account for Dilution of Complex Biological Mixtures. Application in 1H NMR Metabonomics. Anal. Chem. 2006, 78, 4281–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klymiuk, I.; Bilgilier, C.; Stadlmann, A.; Thannesberger, J.; Kastner, M.T.; Hogenauer, C.; Puspok, A.; Biowski-Frotz, S.; Schrutka-Kolbl, C.; Thallinger, G.G.; et al. The Human Gastric Microbiome is Predicated upon Infection with Helicobacter Pylori. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huber, K.; Hofer, D.C.; Trefely, S.; Pelzmann, H.J.; Madreiter-Sokolowski, C.; Duta-Mare, M.; Schlager, S.; Trausinger, G.; Stryeck, S.; Graier, W.F.; et al. N-Acetylaspartate Pathway is Nutrient Responsive and Coordinates Lipid and Energy Metabolism in Brown Adipocytes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell. Res. 2019, 1866, 337–348. [Google Scholar]
- Maher, A.D.; Crockford, D.; Toft, H.; Malmodin, D.; Faber, J.H.; McCarthy, M.I.; Barrett, A.; Allen, M.; Walker, M.; Holmes, E.; et al. Optimization of Human Plasma 1H NMR Spectroscopic Data Processing for High-Throughput Metabolic Phenotyping Studies and Detection of Insulin Resistance Related to Type 2 Diabetes. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 7354–7362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goh, K.K.; Liu, Y.W.; Kuo, P.H.; Chung, Y.E.; Lu, M.L.; Chen, C.H. Effect of Probiotics on Depressive Symptoms: A Meta-Analysis of Human Studies. Psychiatry Res. 2019, 282, 112568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirani, E.; Milajerdi, A.; Mirzaei, H.; Jamilian, H.; Mansournia, M.A.; Hallajzadeh, J.; Ghaderi, A. The Effects of Probiotic Supplementation on Mental Health, Biomarkers of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Psychiatric Disorders: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 2020, 49, 102361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto-Sanchez, M.I.; Hall, G.B.; Ghajar, K.; Nardelli, A.; Bolino, C.; Lau, J.T.; Martin, F.P.; Cominetti, O.; Welsh, C.; Rieder, A.; et al. Probiotic Bifidobacterium Longum NCC3001 Reduces Depression Scores and Alters Brain Activity: A Pilot Study in Patients with Irritable Bowel Syndrome. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 448–459.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BenSaad, L.A.; Kim, K.H.; Quah, C.C.; Kim, W.R.; Shahimi, M. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Ellagic Acid, Gallic Acid and Punicalagin A&B Isolated from Punica Granatum. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinkhani, F.; Heinken, A.; Thiele, I.; Lindenburg, P.W.; Harms, A.C.; Hankemeier, T. The Contribution of Gut Bacterial Metabolites in the Human Immune Signaling Pathway of Non-Communicable Diseases. Gut Microbes 2021, 13, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin-Gallausiaux, C.; Marinelli, L.; Blottiere, H.M.; Larraufie, P.; Lapaque, N. SCFA: Mechanisms and Functional Importance in the Gut. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2021, 80, 37–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocker, U.; Nebe, T.; Herweck, F.; Holt, L.; Panja, A.; Jobin, C.; Rossol, S.; Sartor, R.B.; Singer, M.V. Butyrate Modulates Intestinal Epithelial Cell-Mediated Neutrophil Migration. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2003, 131, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner-Skacel, J.; Dalkner, N.; Moerkl, S.; Kreuzer, K.; Farzi, A.; Lackner, S.; Painold, A.; Reininghaus, E.Z.; Butler, M.I.; Bengesser, S. Sleep and Microbiome in Psychiatric Diseases. Nutrients 2020, 12, 2198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mowat, A.M.; Agace, W.W. Regional Specialization within the Intestinal Immune System. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2014, 14, 667–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furusawa, Y.; Obata, Y.; Fukuda, S.; Endo, T.A.; Nakato, G.; Takahashi, D.; Nakanishi, Y.; Uetake, C.; Kato, K.; Kato, T.; et al. Commensal Microbe-Derived Butyrate Induces the Differentiation of Colonic Regulatory T Cells. Nature 2013, 504, 446–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solis-Ortiz, S.; Arriaga-Avila, V.; Trejo-Bahena, A.; Guevara-Guzman, R. Deficiency in the Essential Amino Acids l-Isoleucine, l-Leucine and l-Histidine and Clinical Measures as Predictors of Moderate Depression in Elderly Women: A Discriminant Analysis Study. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, L.; Wei, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Brain-Gut-Microbiota Axis in Depression: A Historical Overview and Future Directions. Brain Res. Bull. 2022, 182, 44–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, P.; Wang, G.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Bifidobacterium with the Role of 5-Hydroxytryptophan Synthesis Regulation Alleviates the Symptom of Depression and Related Microbiota Dysbiosis. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2019, 66, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Zheng, P.; Li, Y.; Wu, J.; Tan, X.; Zhou, J.; Sun, Z.; Chen, X.; Zhang, G.; Zhang, H.; et al. Landscapes of Bacterial and Metabolic Signatures and their Interaction in Major Depressive Disorders. Sci. Adv. 2020, 6, eaba8555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliphant, K.; Allen-Vercoe, E. Macronutrient Metabolism by the Human Gut Microbiome: Major Fermentation by-Products and their Impact on Host Health. Microbiome 2019, 7, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischbach, M.A.; Sonnenburg, J.L. Eating for Two: How Metabolism Establishes Interspecies Interactions in the Gut. Cell. Host Microbe 2011, 10, 336–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, K.H.; Gil, K.C.; Kim, S.G.; Park, S.Y.; Hwang, K.W. Delphinidin Chloride and its Hydrolytic Metabolite Gallic Acid Promote Differentiation of Regulatory T Cells and have an Anti-Inflammatory Effect on the Allograft Model. J. Food Sci. 2019, 84, 920–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, W.; Zhu, S.; Niu, Z.; Yin, Y. The Protective Effect of Syringic Acid on Dextran Sulfate Sodium-Induced Experimental Colitis in BALB/c Mice. Drug Dev. Res. 2019, 80, 731–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Daza, M.C.; Pulido-Mateos, E.C.; Lupien-Meilleur, J.; Guyonnet, D.; Desjardins, Y.; Roy, D. Polyphenol-Mediated Gut Microbiota Modulation: Toward Prebiotics and further. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 689456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esteban-Torres, M.; Santamaria, L.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Plaza-Vinuesa, L.; Crispie, F.; de Las Rivas, B.; Cotter, P.; Munoz, R. A Diverse Range of Human Gut Bacteria have the Potential to Metabolize the Dietary Component Gallic Acid. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84, e01558-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osawa, R.; Kuroiso, K.; Goto, S.; Shimizu, A. Isolation of Tannin-Degrading Lactobacilli from Humans and Fermented Foods. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3093–3097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacheco-Ordaz, R.; Wall-Medrano, A.; Goni, M.G.; Ramos-Clamont-Montfort, G.; Ayala-Zavala, J.F.; Gonzalez-Aguilar, G.A. Effect of Phenolic Compounds on the Growth of Selected Probiotic and Pathogenic Bacteria. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 66, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarborough, M.J.; Lawson, C.E.; Hamilton, J.J.; Donohue, T.J.; Noguera, D.R. Metatranscriptomic and Thermodynamic Insights into Medium-Chain Fatty Acid Production using an Anaerobic Microbiome. mSystems 2018, 3, e00221-18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scarborough, M.J.; Myers, K.S.; Donohue, T.J.; Noguera, D.R. Medium-Chain Fatty Acid Synthesis by “Candidatus Weimeria Bifida” Gen. Nov., Sp. Nov., and “Candidatus Pseudoramibacter Fermentans” Sp. Nov. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 86, e02242-19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregor, A.; Auernigg-Haselmaier, S.; Trajanoski, S.; Konig, J.; Duszka, K. Colonic Medium-Chain Fatty Acids Act as a Source of Energy and for Colon Maintenance but are Not Utilized to Acylate Ghrelin. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonaz, B.; Bazin, T.; Pellissier, S. The Vagus Nerve at the Interface of the Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visconti, A.; Le Roy, C.I.; Rosa, F.; Rossi, N.; Martin, T.C.; Mohney, R.P.; Li, W.; de Rinaldis, E.; Bell, J.T.; Venter, J.C.; et al. Interplay between the Human Gut Microbiome and Host Metabolism. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 4505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalile, B.; Van Oudenhove, L.; Vervliet, B.; Verbeke, K. The Role of Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Microbiota-Gut-Brain Communication. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2019, 16, 461–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, S.; Bach, M.; Bartova, L.; Dold, M.; Frey, R.; Geretsegger, C.; Haring, C.; Hausmann, A.; Jelem, H.; Kapfhammer, H.-P.; et al. Therapieresistente Depression. Konsensus-Statement—State of the Art 2017. CliniCum Neuropsy 2017, 12, 1–24. [Google Scholar]
- Sajdel-Sulkowska, E.M. Neuropsychiatric Ramifications of COVID-19: Short-Chain Fatty Acid Deficiency and Disturbance of Microbiota-Gut-Brain Axis Signaling. Biomed. Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 7880448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Description | Intervention Group (N = 28) | Placebo Group (N = 29) | Statistics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | χ2 | Sig (p) | |
| Sex (female) | 21 (75.0%) | 24 (82.8%) | 0.516 | 0.473 |
| Smoking (yes) | 8 (29.6%) | 16 (55.2%) | 3.725 | 0.054 |
| Dairy products before trial (yes) | 13 (52.0%) | 7 (28%) | 3.000 | 0.086 |
| Mean (SD) | Mean (SD) | T | p | |
| Age (years) | 44.63 (15.12) | 40.38 (11.30) | −1.205 | 0.233 |
| Waist-to-hip-ratio | 0.86 (0.07) | 0.83 (0.10) | −0.969 | 0.337 |
| Median (Mean rank) | Median (Mean rank) | U | p | |
| Education (years) | 9.50 (28.02) | 9.00 (28.95) | 379 | 0.815 |
| Illness duration (years) | 6.00 (26.54) | 11.00 (28.33) | 339 | 0.677 |
| BMI [kg/m2] | 24.64 (27.52) | 25.63 (30.43) | 446 | 0.523 |
| HbA1c (mmol/mol) | 33.00 (25.31) | 33.00 (26.61) | 308 | 0.754 |
| Description | Intervention Group (N = 28) | Placebo Group (N = 29) | Statistics | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N (%) | N (%) | χ2 | Sig (p) | |
| Atypical antipsychotics | 9 (32.1%) | 10 (34.5%) | 0.035 | 0.851 |
| Anticonvulsants | 3 (10.7%) | 3 (10.3%) | 0.002 | 0.964 |
| Antihypertensive drugs | 4 (14.3%) | 1 (3.4%) | 2.091 | 0.148 |
| Benzodiazepines and hypnotics | 5 (17.9%) | 6 (20.7%) | 0.073 | 0.786 |
| Glutamatergic antidepressants | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0.983 | 0.322 |
| Melatonin-like antidepressants | 0 (0.0%) | 1 (3.4%) | 0.948 | 0.330 |
| Noradrenalin Dopamine Reuptake inhibitor | 1 (3.6%) | 3 (10.3%) | 1.002 | 0.317 |
| Noradrenergic and specific serotonergic antidepressants | 1(3.6%) | 2 (6.9%) | 0.316 | 0.574 |
| Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) | 11 (39.3 %) | 13 (46.4 %) | 0.292 | 0.589 |
| Serotonin antagonist and reuptake inhibitor | 15 (53.6%) | 13 (44.8%) | 0.436 | 0.509 |
| Serotonin–norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors (SNRIs) | 6 (21.4%) | 11 (37.9%) | 1.854 | 0.173 |
| Proton pumps inhibitors | 2 (7.1%) | 4 (13.8%) | 0.669 | 0.413 |
| Tri- and tetracyclic antidepressants (TZA) | 0 (0.0%) | 2 (6.9%) | 2.001 | 0.157 |
| Thyroid medications | 2 (7.1%) | 5 (17.2%) | 1.349 | 0.246 |
| Intervention Group (N = 28) | Placebo Group (N = 29) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | SD | Mean | SD | |
| BDI-II t1 | 31.11 | 8.43 | 33.39 | 10.14 |
| BDI-II t2 | 16.00 | 8.86 | 19.28 | 11.13 |
| HAMD t1 | 15.14 | 6.25 | 14.45 | 4.44 |
| HAMD t2 | 9.30 | 5.61 | 8.28 | 5.91 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kreuzer, K.; Reiter, A.; Birkl-Töglhofer, A.M.; Dalkner, N.; Mörkl, S.; Mairinger, M.; Fleischmann, E.; Fellendorf, F.; Platzer, M.; Lenger, M.; et al. The PROVIT Study—Effects of Multispecies Probiotic Add-on Treatment on Metabolomics in Major Depressive Disorder—A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Metabolites 2022, 12, 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080770
Kreuzer K, Reiter A, Birkl-Töglhofer AM, Dalkner N, Mörkl S, Mairinger M, Fleischmann E, Fellendorf F, Platzer M, Lenger M, et al. The PROVIT Study—Effects of Multispecies Probiotic Add-on Treatment on Metabolomics in Major Depressive Disorder—A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Metabolites. 2022; 12(8):770. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080770
Chicago/Turabian StyleKreuzer, Kathrin, Alexandra Reiter, Anna Maria Birkl-Töglhofer, Nina Dalkner, Sabrina Mörkl, Marco Mairinger, Eva Fleischmann, Frederike Fellendorf, Martina Platzer, Melanie Lenger, and et al. 2022. "The PROVIT Study—Effects of Multispecies Probiotic Add-on Treatment on Metabolomics in Major Depressive Disorder—A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial" Metabolites 12, no. 8: 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080770
APA StyleKreuzer, K., Reiter, A., Birkl-Töglhofer, A. M., Dalkner, N., Mörkl, S., Mairinger, M., Fleischmann, E., Fellendorf, F., Platzer, M., Lenger, M., Färber, T., Seidl, M., Birner, A., Queissner, R., Mendel, L. -M. S., Maget, A., Kohlhammer-Dohr, A., Häussl, A., Wagner-Skacel, J., ... Bengesser, S. (2022). The PROVIT Study—Effects of Multispecies Probiotic Add-on Treatment on Metabolomics in Major Depressive Disorder—A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Metabolites, 12(8), 770. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo12080770