Oral Administration of Fucoidan Can Exert Anti-Allergic Activity after Allergen Sensitization by Enhancement of Galectin-9 Secretion in Blood
Abstract
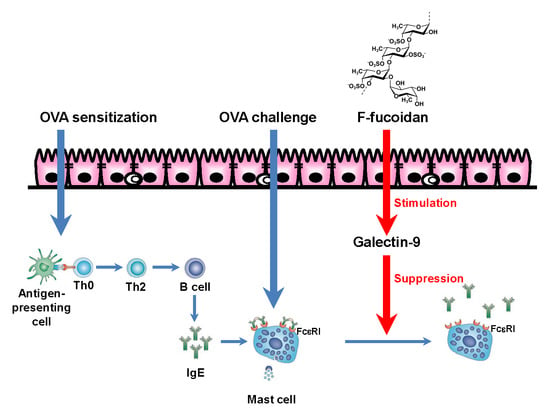
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Mice
2.3. Cell Culture
2.4. Ovalbumin-Induced Allergy Model
2.5. Oral Administration of Fucoidan to Mice
2.6. Measurement of Total IgE, OVA-Specific IgE and OVA Specific IgG1
2.7. Measurement of Galectin-9
2.8. RNA Isolation and Real-Time PCR
2.9. β-Hexosaminidase Assay
2.10. Western Blot of IgE Binding Mast Cells
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Anti-Allergic Effect of Fucoidan in OVA-Induced Allergic Mice
3.2. Anti-Allergic Property of Fucoidan after Sensitization of OVA
3.3. Glectin-9 Contents in Blood and Lgals9 mRNA Expression in Tissues by Administration of Fucoidan after OVA-Sensitization
3.4. Effect of Galectin-9 on Degranulation of Mast Cells
3.5. Affinity of Galaectin-9 to Mast Cells against IgE
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Galli, S.J.; Tsai, M.; Piliponsky, A.M. The development of allergic inflammation. Nature 2008, 454, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Madore, A.M.; Laprise, C. Immunological and genetic aspects of asthma and allergy. J. Asthma Allergy 2010, 3, 107–121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rajan, T.V. The Gell-Coombs classification of hypersensitivity reactions: A re-interpretation. Trends Immunol. 2003, 24, 376–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gould, H.J.; Sutton, B.J. IgE in allergy and asthma today. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 205–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, S.J.; Tsai, M. IgE and mast cells in allergic disease. Nat. Med. 2013, 18, 693–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Geha, R.S.; Jabare, H.H.; Brodeur, S.R. The regulation of immunoglobulin E class-switch recombination. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003, 3, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larche, M.; Akdis, C.A.; Valenta, R. Immunological mechanism of allergen-specific immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, J.; Kanwar, Y.S. Identification and characterization of galectin-9, novel β-galactoside-binding mammalian lectin. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 6078–6086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Seki, M.; Oomizu, S.; Skata, K.M.; Sakata, A.; Arikawa, T.; Watanabe, K.; Ito, K.; Takeshita, K.; Niki, T.; Saita, N.; et al. Galectin-9 suppresses the generation of Th17, promotes the induction of regulatory T cells, and regulates experimental autoimmune arthritis. Clin. Immunol. 2008, 127, 78–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagahara, K.; Arikawa, T.; Oomizu, S.; Kontani, K.; Nobumoto, A.; Tateno, H.; Watanabe, K.; Niki, T.; Katoh, S.; Miyake, M.; et al. Galectin-9 increases Tim-3+ dendritic cells and CD8+ T cells and enhances antitumor immunity via galectin-9-Tim-3 interactions. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 7660–7669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katoh, S.; Ishii, N.; Nobumoto, A.; Takeshita, K.; Dai, S.Y.; Shinonaga, R.; Niki, T.; Nishi, N.; Tominaga, A.; Yamauchi, A.; et al. Galectin-9 inhibits CD44-hyaluronan interaction and suppresses a murine model of allergic asthma. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2007, 176, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niki, T.; Tsutsui, S.; Hirose, S.; Aradono, S.; Sugimoto, Y.; Takeshita, K.; Nishi, N.; Hirashima, M. Galectin-9 is a high affinity IgE-binding lectin with anti-allergic effect by blocking IgE-antigen complex formation. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 32344–32352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Li, B.; Lu, F.; Wei, X.; Zhao, R. Fucoidan: Structure and bioactivity. Molecules 2008, 13, 1671–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhuang, C.; Itoh, H.; Mizuno, T.; Ito, H. Antitumor active fucoidan from the brown seaweed, umitoranoo (Sargassum thunbergii). Biosci. Biothnol. Biochem. 1995, 59, 563–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Sun, J.; Su, X.; Yu, Q.; Yu, Q.; Zhang, P. A review about the development of fucoidan in antitumor activity: Progress and challenges. Carbohydr. Polym. 2016, 154, 96–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ale, M.T.; Maruyama, H.; Tamauchi, H.; Mikkelsen, J.D.; Meyer, A.S. Fucoidan from Sargassum sp. and Fucus vesiculosus reduces cell viability of lung carcinoma and melanoma cells in vitro and activates natural killer cells in mice in vivo. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2011, 49, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, R.; Azuma, Y.; Ojima, T.; Hashimoto, T.; Mizuno, M.; Nishitani, Y.; Yoshida, M.; Azuma, T.; Kanazawa, K. Modulation of platelet aggregation-related eicosanoid production by dietary F-fucoidan from brown alga Laminaria japonica in human subjects. Br. J. Nutr. 2013, 110, 880–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Senthilkumar, K.; Manivasagan, P.; Venkatesan, J.; Kim, S.K. Brown seaweed fucoidan: Biological activity and apoptosis, growth signaling mechanism in cancer. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 60, 366–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Guo, F.; Hu, J.; Zhang, L.; Xue, C.; Zhang, Z.; Li, B. Antithrombotic activity of oral administered low molecular weight fucoidan from Laminaria Japonica. Thromb. Res. 2016, 144, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocha de Souza, M.C.; Marques, C.T.; Guerra Dore, C.M.; Ferreira da Silva, F.R.; Oliveira Rocha, H.A.; Leite, E.L. Antioxidant activities of sulfated polysaccharides from brown and red seaweeds. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 19, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanino, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Ojima, T.; Mizuno, M. F-fucoidan from Saccharina japonica is a novel inducer of galectin-9 and exhibits anti-allergic activity. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2016, 59, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Makabe-Kobayashi, Y.; Hori, Y.; Adachi, T.; Ishigaki-Suzuki, S.; Kikuchi, Y.; Kagaya, Y.; Shirato, K.; Nagy, A.; Ujike, A.; Takai, T.; et al. The control effect of histamine on body temperature and respiratory function in IgE-dependent systemic anaphylaxis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2002, 110, 298–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, E.B.; Strait, R.T.; Hershko, D.; Wang, Q.; Muntel, E.E.; Scribner, T.A.; Zimmermann, N.; Finkelman, F.D.; Rothenberg, M.E. Mast cells are required for experimental oral allergen-induced diarrhea. J. Clin. Investig. 2003, 112, 1666–1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morita, A.; Tanino, Y.; Ojima, T.; Mizuno, M. Influence of temperature on anti-allergic activity of fucoidan extracted from Saccharina japonica. Food Sci. Technol. Res. 2019, 25, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, S.; Yokoyama, Y.; Hashimoto, T.; Mizuno, M. A novel in vitro co-culture model comprised of Coco-2/RBL-2H3 cells to evaluate anti-allergic effects of food factors through the intestine. J. Immunol. Methods 2016, 435, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Than, N.G.; Romero, R.; Balogh, A.; Karpati, E.; Mastrolia, S.A.; Staretz-Chacham, O.; Hahn, S.; Erez, O.; Papp, Z.; Kim, C.J. Galectins: Double-edged swords in the cross-roads of pregnancy complications and female reproductive tract inflammation and neoplasia. J. Pathol. Transl. Med. 2015, 49, 181–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, X.; Song, C.H.; Liu, Z.Q.; Feng, B.S.; Zheng, P.Y.; Li, P.; In, S.H.; Tang, S.G.; Yang, P.C. Intestinal epithelial cells express galectin-9 in patients with food allergy that plays a critical role in sustaining allergic status in mouse intestine. Allergy 2011, 66, 1038–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Li, H.; Margariti, A.; Martin, D.; Zampetaki, A.; Habi, O.; Cockerill, G.; Hu, Y.; Xu, Q.; Zeng, L. Galectin-9 protein expression in endothelial cells is positively regulated by histone deacetylase 3. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 44211–44217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Oomizu, S.; Arikawa, T.; Niki, T.; Kadowaki, T.; Ueno, M.; Nishi, N.; Yamauchi, A.; Hattori, T.; Masaki, T.; Hirashima, M. Cell surface galectin-9 expressing Th cells regulate Th17 and Foxp3+ Treg development by galectin-9 secretion. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e48574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kojima, R.; Ohno, T.; Iikura, M.; Niki, T.; Hirashima, M.; Iwaya, K.; Tsuda, H.; Nonoyama, S.; Matsuda, A.; Saito, H.; et al. Galectin-9 enhances cytokine secretion, but suppresses survival and degranulation, in human mast cell line. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e86106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.W.; Lee, J.H.; Hwang, B.Y.; Mun, S.H.; Ko, N.Y.; Kim, D.K.; Kim, B.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, Y.M.; Choi, W.S. Morin inhibits Fyn kinase in mast cells and IgE-mediated type I hypersensitivity response in vivo. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2009, 77, 1509–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Ma, D.W.; Kang, J.X.; Kulka, M. n-3 Polyunsaturated fatty acids inhibit Fcε receptor I-mediated mast cell activation. J. Nutr. Biochem. 2015, 26, 1580–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramberg, J.E.; Nelson, E.D.; Sinnott, R.A. Immunomodulatory dietary polysaccharides: A systematic review of the literature. Nutr. J. 2010, 9, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vo, T.S.; Ngo, D.H.; Kang, K.H.; Jung, W.K.; Kim, S.K. The beneficial properties of marine polysaccharides in alleviation of allergic responses. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2015, 59, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanase, Y.; Hiragun, T.; Uchida, K.; Ishii, K.; Oomizu, S.; Suzuki, H.; Mihara, S.; Iwamoto, K.; Matsuo, H.; Onishi, N.; et al. Peritoneal injection of fucoidan suppresses the increase of plasma IgE induced by OVA-sensitization. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 387, 435–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- de Kivit, S.; Saeland, E.; Kraneveld, A.D.; van de Kant, H.J.; Schouten, B.; van Esch, B.C.; Knol, J.; Sprikkelman, A.B.; van der Aa, L.B.; Knippels, L.M.; et al. Galectin-9 induced by dietary synbiotics is involved in suppression of allergic symptoms in mice and humans. Allergy 2012, 67, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Control | OVA | OVA + Fucoidan | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Total IgE (μg/mL) | 0.80 ± 0.16 | 10.64 ± 1.28 | 11.52 ± 1.51 |
| OVA specific IgE (ng/mL) | N.D. | 661.26 ± 140.81 | 550.73 ± 70.04 |
| OVA specific IgG1 (μg/mL) | N.D. | 882.45 ± 245.75 | 1203.28 ± 162.13 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mizuno, M.; Sakaguchi, K.; Sakane, I. Oral Administration of Fucoidan Can Exert Anti-Allergic Activity after Allergen Sensitization by Enhancement of Galectin-9 Secretion in Blood. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020258
Mizuno M, Sakaguchi K, Sakane I. Oral Administration of Fucoidan Can Exert Anti-Allergic Activity after Allergen Sensitization by Enhancement of Galectin-9 Secretion in Blood. Biomolecules. 2020; 10(2):258. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020258
Chicago/Turabian StyleMizuno, Masashi, Kana Sakaguchi, and Iwao Sakane. 2020. "Oral Administration of Fucoidan Can Exert Anti-Allergic Activity after Allergen Sensitization by Enhancement of Galectin-9 Secretion in Blood" Biomolecules 10, no. 2: 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020258
APA StyleMizuno, M., Sakaguchi, K., & Sakane, I. (2020). Oral Administration of Fucoidan Can Exert Anti-Allergic Activity after Allergen Sensitization by Enhancement of Galectin-9 Secretion in Blood. Biomolecules, 10(2), 258. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom10020258