From Hamamelitannin Synthesis to the Study of Enzymatic Acylations of D-Hamamelose
Abstract
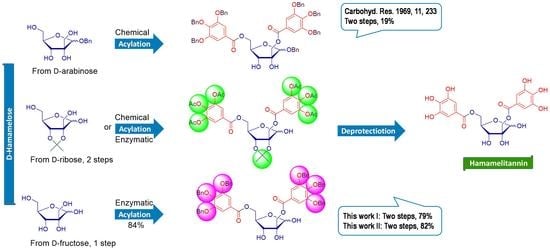
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. General
2.2. Synthesis of Hamamelitannin from D-Ribose
2.2.1. 2,3-O-Isopropylidene-α,β-D-Hamamelofuranose (2)
2.2.2. 3,4,5-Tri-O-Acetylgalloyl Chloride (3)
2.2.3. Acylation Methods for Galloylation of 2 (Table 1)
| Entry | Method 1 | Acyl Donor/Equiv. | Catalyst (Equiv.) | Solvent | Temp. (°C) | Time (h) | 5a 2 (%) | 6a (%) | 7 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | A | 3/2.2 | 2.0/0.5 | CH2Cl2 | 0-rt | 3 | 24 | 22 | 48 |
| 2 | A | 3/3.3 | 3.0/0.75 | CH2Cl2 | 0-rt | 3 | 4 | 9 | 81 |
| 3 | B | 3/2.2 | 1.0 | CH2Cl2 | 0-rt | 2.5 | 19 | 44 | 8 |
| 4 | B | 3/2.2 | 2.2 | CH3CN | 50 | 6 | 35 | 22 | n.d. 3 |
| 5 | B | 3/2.2 | 2.2 | CH2Cl2 | 0-rt | 2 | 5 | 84 | 4 |
| 6 | C | 3/2.2 | 4.9 | CH2Cl2 | rt | 12 | 49 | 21 | |
| 7 | C | 3/2.2 | 4.9 | CH3CN | 40 | 4 | 71 | 22 | 1 |
| 8 | C | 3/3.3 | 11 | CH3CN | 40 | 24 | 9 | 56 | 27 |
| 9 | D | 4a/3.0 | - | t-BuMeO | 37 | 19 | 9 + 34 4 | 6 | n.d. |
2.2.4. Characterization Data of Acylated Products
2.3. Enzymatic Acylation of D-Hamamelose
2.3.1. Preparation of New Derivatives of Vinyl Gallate
2.3.2. Enzymatic Benzoylation of 8
2.3.3. Enzymatic Acylation of 8 by Vinyl Gallates 4d–g
2.3.4. Characterization Data of Acylated Hamameloses
2.4. Removal of Protecting Groups
2.4.1. Simultaneous Deacetylation and Deisopropylidenation of 6a and 7
2.4.2. Debenzylation of 9g
2.4.3. Hamamelitannin (1)
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Hamamelitannin by Acylation of Acceptor 2 Prepared from D-Ribose
3.2. Synthesis of Hamamelitannin by Enzymatic Acylation of D-Hamamelose
3.3. Deprotections for Obtaining Hamamelitannin 1
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khanbabaee, K.; van Ree, T. Tannins: Classification and definition. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2001, 18, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okuda, T.; Ito, H. Tannins of constant structure in medicinal and food plants-hydrolyzable tannins and polyphenols related to tannins. Molecules 2011, 16, 2191–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jourdes, M.; Pouységu, L.; Deffieux, D.; Teissedre, P.-L.; Quideau, S. Hydrolyzable Tannins: Gallotannins and Ellagitannins. In Natural Products; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; Volume 66, pp. 1975–2010. [Google Scholar]
- He, Q.; Shi, B.; Yao, K.; Luo, Y.; Ma, Z. Synthesis of gallotannins. Carbohydr. Res. 2001, 335, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.W.; Dong, H.J.; Cui, C. Bin The synthesis and antitumor activity of twelve galloyl glucosides. Molecules 2015, 20, 2034–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pouységu, L.; Deffieux, D.; Malik, G.; Natangelo, A.; Quideau, S. Synthesis of ellagitannin natural products. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2011, 28, 853–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, W.; Kunz, W.; Loebich, F. Die Struktur des Hamamelitannins. Justus Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1965, 688, 232–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartisch, C.; Kolodziej, H. Galloylhamameloses and proanthocyanidins from Hamamelis virginiana. Phytochemistry 1996, 42, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüttner, F. Beiträge zur Chemie der Rinde von Hamamelis virginica L. Arch. Pharm. 1898, 236, 278–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nonaka, G.; Ishimaru, K.; Tanaka, T.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. XVII. Galloylhamameloses from Castanea crenata L. and Sanguisorba officinalis L. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1984, 32, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozawa, T.; Kobayashi, S.; Seki, R.; Imagawa, H. A New Gallotannin from Bark of Chestnut Tree, Castanea crenata Sieb. et Zucc. Agric. Biol. Chem. 1984, 48, 1411–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonaka, G.; Ageta, M.; Nishioka, I. Tannins and related compounds. XXV. A new class of gallotannins possessing a (-)-shikimic acid core from Castanopsis cuspidata var. sieboldii Nakai. (1). Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1985, 33, 96–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lampire, O.; Mila, I.; Raminosoa, M.; Michon, V.; Herve Du Penhoat, C.; Faucheur, N.; Laprevote, O.; Scalbert, A. Polyphenols isolated from the bark of Castanea sativa Mill. chemical structures and auto-association. Phytochemistry 1998, 49, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, H.; Atsumi, T.; Sakurai, H. Protective activity of hamamelitannin on cell damage of murine skin fibroblasts induced by UVB irradiation. J. Dermatol. Sci. 1995, 10, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korting, H.C.; Schäfer-Korting, M.; Klövekon, W.; Klövekorn, G.; Martin, C.; Laux, P. Comparative efficacy of hamamelis distillate and hydrocortisone cream in atopic eczema. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 1995, 48, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piazza, S.; Martinelli, G.; Magnavacca, A.; Fumagalli, M.; Pozzoli, C.; Terno, M.; Canilli, L.; Angarano, M.; Maranta, N.; Dell’Agli, M.; et al. Unveiling the Ability of Witch Hazel (Hamamelis virginiana L.) Bark Extract to Impair Keratinocyte Inflammatory Cascade Typical of Atopic Eczema. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piazza, S.; Martinelli, G.; Vrhovsek, U.; Masuero, D.; Fumagalli, M.; Magnavacca, A.; Pozzoli, C.; Canilli, L.; Terno, M.; Angarano, M.; et al. Anti-Inflammatory and Anti-Acne Effects of Hamamelis virginiana Bark in Human Keratinocytes. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-González, M.; Rocasalbas, G.; Francesko, A.; Touriño, S.; Torres, J.L.; Tzanov, T. Inhibition of deleterious chronic wound enzymes with plant polyphenols. Biocatal. Biotransform. 2012, 30, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habtemariam, S. Hamamelitannin from Hamamelis virginiana inhibits the tumour necrosis factor-α (TNF)-induced endothelial cell death in vitro. Toxicon 2002, 40, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, E.; Nishimura, N.; Okada, K.; Sekido, C.; Yamamichi, S.; Hasumi, K. Inhibitors of autoactivation of plasma hyaluronan-binding protein (factor VII activating protease). Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2011, 34, 462–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Choi, H.R.; Choi, J.S.; Han, Y.N.; Bae, S.J.; Chung, H.Y. Peroxynitrite scavenging activity of herb extracts. Phyther. Res. 2002, 16, 364–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauer, A.; Hensel, A.; Lhoste, E.; Knasmüller, S.; Mersch-Sundermann, V. Genotoxic and antigenotoxic effects of catechin and tannins from the bark of Hamamelis virginiana L. in metabolically competent, human hepatoma cells (Hep G2) using single cell gel electrophoresis. Phytochemistry 2003, 63, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masaki, H.; Atsumi, T.; Sakurai, H. Hamamelitannin as a new potent active oxygen scavenger. Phytochemistry 1994, 37, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Tena, S.; Fernández-Cachón, M.L.; Carreras, A.; Mateos-Martín, M.L.; Costoya, N.; Moyer, M.P.; Nuñez, M.J.; Torres, J.L.; Cascante, M. Hamamelitannin from witch hazel (Hamamelis virginiana) displays specific cytotoxic activity against colon cancer cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, M.D.; Adikesavan, N.V.; Cirioni, O.; Giacometti, A.; Silvestri, C.; Scalise, G.; Ghiselli, R.; Saba, V.; Orlando, F.; Shoham, M.; et al. Discovery of a quorum-sensing inhibitor of drug-resistant staphylococcal infections by structure-based virtual screening. Mol. Pharmacol. 2008, 73, 1578–1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cobrado, L.; Silva-Dias, A.; Azevedo, M.M.; Pina-Vaz, C.; Rodrigues, A.G. In vivo antibiofilm effect of cerium, chitosan and hamamelitannin against usual agents of catheter-related bloodstream infections. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2013, 68, 126–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brackman, G.; Breyne, K.; De Rycke, R.; Vermote, A.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F.; Meyer, E.; Van Calenbergh, S.; Coenye, T. The Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Hamamelitannin Increases Antibiotic Susceptibility of Staphylococcus aureus Biofilms by Affecting Peptidoglycan Biosynthesis and eDNA Release. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 20321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brackman, G.; Garcia-Fernandez, M.J.; Lenoir, J.; De Meyer, L.; Remon, J.P.; De Beer, T.; Concheiro, A.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Coenye, T. Dressings Loaded with Cyclodextrin–Hamamelitannin Complexes Increase Staphylococcus aureus Susceptibility Toward Antibiotics Both in Single as well as in Mixed Biofilm Communities. Macromol. Biosci. 2016, 16, 859–869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermote, A.; Brackman, G.; Risseeuw, M.D.P.; Coenye, T.; Van Calenbergh, S. Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of novel hamamelitannin analogues as potentiators for vancomycin in the treatment of biofilm related Staphylococcus aureus infections. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. 2016, 24, 4563–4575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermote, A.; Brackman, G.; Risseeuw, M.D.P.; Vanhoutte, B.; Cos, P.; Van Hecke, K.; Breyne, K.; Meyer, E.; Coenye, T.; Van Calenbergh, S. Hamamelitannin analogues that modulate quorum sensing as potentiators of antibiotics against Staphylococcus aureus. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 6551–6555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vermote, A.; Brackman, G.; Risseeuw, M.D.P.; Coenye, T.; Van Calenbergh, S. Novel hamamelitannin analogues for the treatment of biofilm related MRSA infections–A scaffold hopping approach. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 127, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Theisen, L.L.; Erdelmeier, C.A.J.; Spoden, G.A.; Boukhallouk, F.; Sausy, A.; Florin, L.; Muller, C.P. Tannins from Hamamelis virginiana bark extract: Characterization and improvement of the antiviral efficacy against influenza a virus and human papillomavirus. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e88062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Dai, Y.H.; Chen, G.Y.; Tang, C.H.; Huang, W.C.; Yang, J.C.; Wu, Y.C. Drug screening of potential multiple target inhibitors for estrogen receptor-α-positive breast cancer. In Vivo 2021, 35, 761–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Xue, J.; Chen, X.; Elsaid, F.G.; Salem, E.T.; Ghanem, R.A.; El-kott, A.F.; Xu, Z. Bioactivity of hamamelitannin, flavokawain A, and triacetyl resveratrol as natural compounds: Molecular docking study, anticolon cancer, and anti-Alzheimer potentials. Biotechnol. Appl. Biochem. 2022. early view. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, J.; Qiu, G.; Alahmadi, T.A.; Alharbi, S.A.; Wainwright, M.; Duan, W. Biological Activities of Some Natural Compounds and Their Cytotoxicity Studies against Breast and Prostate Cancer Cell Lines and Anti-COVID19 Studies. J. Oleo Sci. 2022, 71, 587–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samdani, M.N.; Morshed, N.; Reza, R.; Asaduzzaman, M.; Islam, A.B.M.M.K. Targeting SARS-CoV-2 non-structural protein 13 via helicase-inhibitor-repurposing and non-structural protein 16 through pharmacophore-based screening. Mol. Divers. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezekiel, A.D.; Overend, W.G.; Williams, N.R. Branched-chain sugars. Carbohydr. Res. 1969, 11, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Overend, W.G.; Williams, N.R. 622. Branched-chain sugars. Part IV. The synthesis of D-hamamelose and D-epihamamelose. J. Chem. Soc. 1965, 3446–3448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, M. Progress on Selective Acylation of Carbohydrate Hydroxyl Groups. Asian J. Org. Chem. 2019, 8, 1813–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadereit, D.; Waldmann, H. Enzymatic protecting group techniques. Chem. Rev. 2001, 101, 3367–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarren, A.M.; Iglesias, L.E. An update of biocatalytic selective acylation and deacylation of monosaccharides. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 16358–16386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, C.A.; Pardo-Tamayo, J.S.; Barbosa, O. Microbial Lipases and Their Potential in the Production of Pharmaceutical Building Blocks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 9933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastihubová, M.; Mastihuba, V.; Bilaničová, D.; Boreková, M. Commercial enzyme preparations catalyse feruloylation of glycosides. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2006, 38, 54–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrea, G.; Riva, S. Medium Engineering of Enzymatic Reactions: E nzyme selectivity in organic solvents can differ from that in water and Properties and Synthetic Applications of Enzymes in Organic Solvents. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2000, 39, 2226–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeuner, B.; Kontogeorgis, G.M.; Riisager, A.; Meyer, A.S. Thermodynamically based solvent design for enzymatic saccharide acylation with hydroxycinnamic acids in non-conventional media. New Biotechnol. 2012, 29, 255–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, W.H.; Kang, J.A.; Lee, H.R.; Park, A.Y.; Chun, P.; Lee, B.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.A.; Jeong, L.S.; Moon, H.R. Efficient and practical synthesis of L-hamamelose. Carbohydr. Res. 2009, 344, 2317–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, P.-T. Branched-chain sugars. I. reaction between furanoses and formaldehyde: A synthesis of D-hamamelose. Tetrahedron Lett. 1978, 19, 1623–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastihubová, M.; Mastihuba, V. Donor specificity and regioselectivity in Lipolase mediated acylations of methyl α-D-glucopyranoside by vinyl esters of phenolic acids and their analogues. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2013, 23, 5389–5392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Zhao, Y. Synthesis of 7-O-galloyl-D-sedoheptulose. Carbohydr. Res. 2007, 342, 1510–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schilling, G.; Keller, A. Zusammensetzug und Konformation von Hamamelose in Lösung. Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1977, 232, 1475–1479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hricovíniová, Z.; Lamba, D.; Hricovíni, M. Structure of 2-C-(hydroxymethyl)-D-ribose (hamamelose) in the solid-state analyzed by CP MAS NMR and X-ray crystallography. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 455–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schilling, G.; Keller, A. Monogalloylhamamelose aus Hamamelis virginiana/Monogalloylhamamelose from Hamamelis virginiana. Z. Naturforsch. C 1986, 41, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, F.; Ralph, J. Facile Synthesis of 4-Hydroxycinnamyl p-Coumarates. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1998, 46, 2911–2913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastihubová, M.; Mastihuba, V.; Kremnicky, L.; Willet, J.L.; Côté, G.L. Chemoenzymatic Preparation of Novel Substrates for Feruloyl Esterases. Synlett 2001, 2001, 1559–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastihubová, M.; Szemesová, J.; Biely, P. Two efficient ways to 2-O- and 5-O-feruloylated 4-nitrophenyl α-L-arabinofuranosides as substrates for differentiation of feruloyl esterases. Tetrahedron Lett. 2003, 44, 1671–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Wong, C.-H. Regioselective benzoylation of sugars mediated by excessive Bu2SnO: Observation of temperature promoted migration. Tetrahedron 2002, 58, 6513–6519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, H.; Pei, Z.; Byström, S.; Ramström, O. Reagent-Dependent Regioselective Control in Multiple Carbohydrate Esterifications. J. Org. Chem. 2007, 72, 1499–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastihubová, M.; Biely, P. Preparation of regioselectively feruloylated p-nitrophenyl α-L-arabinofuranosides and β-D-xylopyranosides-convenient substrates for study of feruloyl esterase specificity. Carbohydr. Res. 2010, 345, 1094–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, B.N.; Kim, H.O.; Moon, H.R.; Seol, S.K.; Jang, S.K.; Lee, K.M.; Jeong, L.S. Synthesis of 2-C-hydroxymethylribofuranosylpurines as potent anti-hepatitis C virus (HCV) agents. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2006, 16, 4190–4194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chyba, A.; Mastihuba, V.; Mastihubová, M. Effective enzymatic caffeoylation of natural glucopyranosides. Bioorgan. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 1567–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chyba, A.; Mastihubová, M.; Mastihuba, V. Regioselective galloylation of methyl β-D-glucopyranoside by a lipase. Mon. Chem. Chem. Mon. 2016, 147, 1137–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehm, S.; Trodler, P.; Pleiss, J. Solvent-induced lid opening in lipases: A molecular dynamics study. Protein Sci. 2010, 19, 2122–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hricovíniová, Z.; Hricovíni, M.; Petruš, L. Stereospecific molybdic acid-catalyzed isomerization of D-fructose to branched-chain aldose. The synthesis of D-hamamelose. Chem. Pap. 1998, 52, 692–698. [Google Scholar]
- Hricovíniová-Bíliková, Z.; Hricovíni, M.; Petrušová, M.; Serianni, A.S.; Petruš, L. Stereospecific molybdic acid-catalyzed isomerization of 2-hexuloses to branched-chain aldoses. Carbohydr. Res. 1999, 319, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Antona, N.; El-Idrissi, M.; Ittobane, N.; Nicolosi, G. Enzymatic procedures in the preparation of regioprotected D-fructose derivatives. Carbohydr. Res. 2005, 340, 319–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatis, H.; Sereti, V.; Kolisis, F.N. Enzymatic synthesis of hydrophilic and hydrophobic derivatives of natural phenolic acids in organic media. J. Mol. Catal. B Enzym. 2001, 11, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, T.W.; Wuts, P.G.M. Protection for the Hydroxyl Group, Including 1,2- and 1,3-Diols. In Greene’s Protective Groups in Organic Synthesis; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2014; Volume 9, pp. 17–471. ISBN 0471160199. [Google Scholar]
- Crepin, V.F.; Faulds, C.B.; Connerton, I.F. Functional classification of the microbial feruloyl esterases. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2004, 63, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Fischer, A.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Schmid, R.D. Lipase-Catalyzed Solid Phase Synthesis of Sugar Fatty Acid Esters. Biocatal. Biotransform. 1996, 14, 269–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]








| Entry | Acyl Donor (3 Equiv.) | Solvent | Time (h) | Diacyls 9d–g 1 (%) | Monoacyls 10d–g 3 (%) | Triacyls 11d–g, 12d–g |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 4d | t-BuOH | 272 | 22 | 67 | n.d. |
| 2 | 4d | t-BuMeO | 212 | 68 | 4 | n.d. |
| 3 | 4e | t-BuOH | 98 | 41 | 51 | n.d. |
| 4 | 4e | t-BuMeO | 46 | 65 | n.d. | 8 4 |
| 5 | 4f | t-BuOH | 102 | n.d. 2 | n.d. | n.d. |
| 6 | 4f | t-BuMeO | 231 | n.d. | n.d. | n.d. |
| 7 | 4g | t-BuOH | 198 | 2 | 15 | n.d. |
| 8 | 4g | CH3CN | 154 | 17 | 16 | n.d. |
| 9 | 4g | t-BuMeO | 96 | 84 | n.d. | n.d. |
| Entry | Compound | Atom | Solvent | 5αF | 2′αF | 5βF | 2′βF | 2′αP | 2′βP |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 1 | Ham 6 | H-1 | DMSO-d6 | 5.14 | 4.89 | 4.48 | 4.85 | ||
| 2 1 | Ham | H-1 | D2O | 5.24 | 5.18 | 5.09 | 4.76 | ||
| 3 1 | Ham | C-1 | DMSO-d6 | 96.6 | 101.4 | 94.5 | 95.0 | ||
| 4 1,2 | Ham | C-1 | D2O | 97.8 | 101.5 | 94.8 | 95.3 | ||
| 5 3 | HG 7 | C-1 | DMSO-d6 | 96.9 | 96.9 | 101.9 | 100.8 | - | 94.3 |
| 6 4 | HG | C-1 | Acetone-d6 | 98.2 | 103.0 | ||||
| 7 5 | HG | C-1 | Acetone-d6 | 96.6 | 101.8 | ||||
| 8 5 | HG | H-1 | Acetone-d6 | 5.43 | 5.31 | ||||
| 9 | 10d | H-1 | CD3OD | 5.31 (0.8) | 5.23 (1) | 5.16 (0.3) | 5.21 (1) | n.d | 4.75 (0.5) |
| 10 | 10d | C-1 | CD3OD | 99.0 | 96.1 | 103.5 | 102.7 | n.d | 96.3 |
| 11 | 10e | H-1 | CD3OD | 5.31 (0.7) | 5.22 (1) | 5.16 (0.1) | 5.20 (0.8) | n.d | 4.74 (0.4) |
| 12 | 10e | C-1 | CD3OD | 99.0 | 96.1 | 102.7 | 102.7 | n.d | 96.2 |
| 13 | 10g | H-1 | CD3OD | 5.30 (0.6) | 5.20 (1) | n.d. | 5.20 (1) | n.d | 4.62 (0.3) |
| 14 | 10g | C-1 | CD3OD | 99.0 | 96.0 | n.d. | 102.7 | n.d | 96.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mastihubová, M.; Mastihuba, V. From Hamamelitannin Synthesis to the Study of Enzymatic Acylations of D-Hamamelose. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030519
Mastihubová M, Mastihuba V. From Hamamelitannin Synthesis to the Study of Enzymatic Acylations of D-Hamamelose. Biomolecules. 2023; 13(3):519. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030519
Chicago/Turabian StyleMastihubová, Mária, and Vladimír Mastihuba. 2023. "From Hamamelitannin Synthesis to the Study of Enzymatic Acylations of D-Hamamelose" Biomolecules 13, no. 3: 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030519
APA StyleMastihubová, M., & Mastihuba, V. (2023). From Hamamelitannin Synthesis to the Study of Enzymatic Acylations of D-Hamamelose. Biomolecules, 13(3), 519. https://doi.org/10.3390/biom13030519