Influence of Maternal Habitat on Salinity Tolerance of Zygophyllum coccineum with Regard to Seed Germination and Growth Parameters
Abstract
:1. Introduction
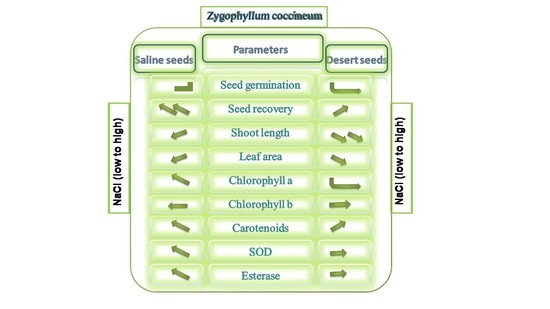
2. Results
2.1. Seed Mass and Length
2.2. Effect of Salinity on Germination
2.3. Growth Parameters
2.4. Photosynthetic Pigments
2.5. Isozyme Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Plant Material
5.2. Effects of Salinity on Germination and Recovery
5.3. Effects of Salinity on Plant Growth
5.3.1. Growth Parameters
5.3.2. Photosynthetic Pigments Measurement
5.3.3. Esterase and SOD Activity
5.4. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Villemereuil, P.; Mouterde, M.; Gaggiotti, O.E.; Till-Bottraud, I. Patterns of phenotypic plasticity and local adaptation in the wide elevation range of the alpine plant Arabis alpina. J. Ecol. 2018, 106, 1952–1971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sork, V.L. Genomic Studies of Local Adaptation in Natural Plant Populations. J. Hered. 2018, 109, 3–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Leimu, R.; Fischer, M. A Meta-Analysis of Local Adaptation in Plants. PLoS ONE 2008, 3, e4010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bradshaw, A.D. Unravelling phenotypic plasticity–why should we bother? New Phytol. 2006, 170, 644–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Mo, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J.; Wu, J.; Wang, J.; Zhao, N.; Gao, Y. Phenotypic plasticity vs. local adaptation in quantitative traits differences of Stipa grandis in semi-arid steppe, China. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkelish, A.A.; Alnusaire, T.S.; Soliman, M.H.; Gowayed, S.; Senousy, H.H.; Fahad, S. Calcium availability regulates antioxidant system, physio-biochemical activities and alleviates salinity stress mediated oxidative damage in soybean seedlings. J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 2019, 92, 258–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhaithloul, H.A.; Soliman, M.H.; Ameta, K.L.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Elkelish, A. Changes in Ecophysiology, Osmolytes, and Secondary Metabolites of the Medicinal Plants of Mentha piperita and Catharanthus roseus Subjected to Drought and Heat Stress. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Esawi, M.A.; Elkelish, A.; Soliman, M.; Elansary, H.O.; Zaid, A.; Wani, S.H. Serratia marcescens BM1 Enhances Cadmium Stress Tolerance and Phytoremediation Potential of Soybean Through Modulation of Osmolytes, Leaf Gas Exchange, Antioxidant Machinery, and Stress-Responsive Genes Expression. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nicotra, A.B.; Atkin, O.K.; Bonser, S.P.; Davidson, A.M.; Finnegan, E.J.; Mathesius, U.; Poot, P.; Purugganan, M.D.; Richards, C.L.; Valladares, F.; et al. Plant phenotypic plasticity in a changing climate. Trends Plant Sci. 2010, 15, 684–692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holeski, L.M.; Jander, G.; Agrawal, A.A. Transgenerational defense induction and epigenetic inheritance in plants. Trends Ecol. Evol. 2012, 27, 618–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, S.Z.; Rasheed, A.; Gul, B.; Khan, M.A.; Nielsen, B.L.; Hameed, A. Maternal salinity improves yield, size and stress tolerance of Suaeda fruticosa seeds. J. Arid Land 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousseau, T.A.; Fox, C.W. The adaptive significance of maternal effects. Trends Ecol. Evol. 1998, 13, 403–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donohue, K.; Schmitt, J. Maternal environmental effects in plants: Adaptive plasticity? In Maternal Effects as Adaptations; Mousseau, T.A., Fox, C.W., Eds.; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 1998; pp. 137–158. [Google Scholar]
- Galloway, L. Maternal effects provide phenotypic adaptation to local environmental conditions. New Phytol. 2005, 166, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Keblawy, A.; Al-Shamsi, N.; Mosa, K. Effect of maternal habitat, temperature and light on germination and salt tolerance of Suaeda vermiculata, a habitat indifferent halophyte of arid Arabian deserts. Seed Sci. Res. 2018, 28, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditommaso, A. Germination behavior of common ragweed (Ambrosia artemisiifolia) populations across a range of salinities. Weed Sci. 2004, 52, 1002–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beaton, L.L.; Dudley, S.A. Maternal effects and drought tolerance determine seedling establishment success in a common roadside plant, Dipsacus fullonum subsp. sylvestris. Botany 2010, 88, 930–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Gul, B. Halophyte seed germination. In Ecophysiology of High Salinity Tolerant Plants; Khan, M.A., Weber, D.J., Eds.; Springer Academic Publishers: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2006; pp. 11–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boestfleisch, C.; Wagenseil, N.B.; Buhmann, A.K.; Seal, C.E.; Wade, E.M.; Muscolo, A.; Papenbrock, J. Manipulating the antioxidant capacity of halophytes to increase their cultural and economic value through saline cultivation. AoB Plants 2014, 6, plu046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, M.; Elkelish, A.; Souad, T.; Alhaithloul, H.; Farooq, M. Brassinosteroid seed priming with nitrogen supplementation improves salt tolerance in soybean. Physiol. Mol. Biol. Plants 2020, 26, 501–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taïbi, K.; Taïbi, F.; Abderrahim, L.A.; Ennajah, A.; Belkhodja, M.; Mulet, J.M. Effect of salt stress on growth, chlorophyll content, lipid peroxidation and antioxidant defence systems in Phaseolus vulgaris L. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2016, 105, 306–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, B. Effect of salt stress on growth and chlorophyll content of some cultivated cotton varieties grown in Syria. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 2012, 43, 1976–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizov, I.; Khanisheva, M.; Ibrahimova, U. Effect of Salinity on Chlorophyll Content and Activity of Photosystems of Wheat Genotypes. In Photosynthesis Research for Food, Fuel and the Future; Advanced Topics in Science and Technology in China; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashrafi, E.; Razmjoo, J.; Zahedi, M.; Pessarakli, M. Selecting alfalfa cultivars for salt tolerance based on some physiochemical traits. Agron. J. 2014, 106, 1758–1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamin, M.; Fahad, S.; Khattak, A.M.; Adnan, M.; Wahid, F.; Raza, A.; Wang, D.; Saud, S.; Noor, M.; Bakhat, H.F.; et al. Developing the first halophytic turfgrasses for the urban landscape from native Arabian desert grass. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2020, 27, 39702–39716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Matsuda, R.; El-khatib, A.A.; Takechi, K.; Takano, H.; Takio, S. Characterization of the superoxide dismutase genes of the halophyte Suaeda maritima in Japan and Egypt. Plant Cell Rep. 2015, 34, 2099–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Matsuda, R.; El-khatib, A.A.; Takechi, K.; Takano, H.; Takio, S. Differential tolerance to high salt with regard to cell growth and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity in calluses of the halophyte Suaeda maritima from Japan and Egypt. Plant Omics 2016, 9, 81–89. [Google Scholar]
- Soliman, M.H.; Abdulmajeed, A.M.; Alhaithloul, H.; Alharbi, B.M.; El-Esawi, M.A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Elkelish, A. Saponin biopriming positively stimulates antioxidants defense, osmolytes metabolism and ionic status to confer salt stress tolerance in soybean. Acta Physiol Plant 2020, 42, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chepyshko, H.; Lai, C.P.; Huang, L.M.; Liu, J.H.; Shaw, J.F. Multifunctionality and diversity of GDSL esterase/lipasegene family in rice (Oryza sativa L. japonica) genome: New insights from bioinformatics analysis. BMC Genom. 2012, 13, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Reyes-Pérez, J.J.; Ruiz-Espinoza, F.H.; Hernández-Montiel, L.G.; de Lucía, B.; Cristiano, G.; Murillo-Amador, B. Evaluation of Glycosyl-Hydrolases, Phosphatases, Esterases and Proteases as Potential Biomarker for NaCl-Stress Tolerance in Solanum lycopersicum L. Varieties. Molecules 2019, 24, 2488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boulos, L. Flora of Egypt; Al Hadara Publishing: Cairo, Egypt, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Jafari, M.; Tavili, A.; Panahi, F.; Zandi Esfahan, E.; Ghorbani, M. Wind Erosion and Regeneration of Vegetation Cover in Arid and Semi-arid Areas. In Reclamation of Arid Lands. Environmental Science and Engineering Series; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 175–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansour, H.A.; Newairy, A.S.A.; Yousef, M.I.; Sheweita, S.A. Biochemical study on the effects of some Egyptian herbs in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Toxicology 2002, 170, 221–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AbouZid, S.; Elshahaat, A.; Ali, S.; Choudhary, M.I. Antioxidant activity of wild plants collected in Beni-Sueif governorate, Upper Egypt. Drug Discov. Ther. 2008, 2, 286–288. [Google Scholar]
- Amin, E.; El-Hawary, S.S.; Fathy, M.M.; Mohammed, R.; Ali, Z.; Tabanca, N.; Wedge, D.E.; Becnel, J.J.; Khan, I.A. Triterpenoidal Saponins: Bioactive Secondary Metabolites from Zygophyllum coccineum. J. Med. Plant Nat. Prod. Res. 2011, 77, 488–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- El-Sherbiny, M.M.; Ismail, A.; EL-Hefnawy, M.E. A preliminary assessment of potential ecological risk and soil contamination by heavy metals around a cement factory, western Saudi Arabia. Open Chem. 2019, 17, 671–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amro, A.N.; Abhary, M.K. Removal of lead and copper ions from water using powdered Zygophyllum coccineum biomass. Int. J. Phytoremediat. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Zandt, P.A.; Mopper, S. The effects of maternal salinity and seed environment on germination and growth in Iris hexagona. Evol. Ecol. Res. 2004, 6, 813–832. [Google Scholar]
- El-Keblawy, A.; Gairola, S.; Bhatt, A.; Mahmoud, T. Effects of maternal salinity on salt tolerance during germination of Suaeda aegyptiaca: A facultative halophyte in the Arab Gulf desert. Plant Spec. Biol. 2017, 32, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Keblawy, A.; Gairola, S.; Bhatt, A. Maternal salinity environment affects salt tolerance during germination in Anabasis setifera: A facultative desert halophyte. J. Arid Land 2016, 8, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begcy, K.; Mariano, E.D.; Lembke, C.G.; Zingaretti, S.M.; Souza, G.M.; Araújo, P.; Menossi, M. Overexpression of an evolutionarily conserved drought-responsive sugarcane gene enhances salinity and drought resilience. Ann. Bot. 2019, 124, 691–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wetson, A.M.; Cassaniti, C.; Flowers, T.J. Do conditions during dormancy influence germination of Suaeda maritima? Ann. Bot. 2008, 101, 1319–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soliman, M.H.; Alnusaire, T.S.; Abdelbaky, N.F.; Alayafi, A.A.; Hasanuzzaman, M.; Rowezak, M.M.; El-Esawi, M.; Elkelish, A. Trichoderma-Induced Improvement in Growth, Photosynthetic Pigments, Proline, and Glutathione Levels in Cucurbita pepo Seedlings under Salt Stress. Phyton 2020, 89, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ungar, I.A. Seed germination and seed-bank ecology in halophytes. In Seed Development and Seed Germination; Kigel, J., Galili, G., Eds.; Marcel Dekker: New York, NY, USA, 1995; pp. 599–628. [Google Scholar]
- Sekmen, A.H.; Turkan, I.; Tanyolac, Z.O.; Ozfidan, C.; Dinc, A. Different antioxidant defense responses to salt stress during germination and vegetative stages of endemic halophyte Gypsophila oblanceolata bark. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2012, 77, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Kasem, A.M.M.; Farghali, K.A. Seed germination of Egyptian Pancratium maritimum under salinity with regard to cytology, antioxidant and reserve mobilization enzymes, and seed anatomy. Flora 2018, 242, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yıldıztugay, E.; Sekmen, A.H.; Turkan, I.; Kucukoduk, M. Elucidation of physiological and biochemical mechanisms of an endemic halophyte Centaurea tuzgoluensis under salt stress. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hassan, M.; Pacurar, A.; López-Gresa, M.P.; Donat-Torres, M.P.; Llinares, J.V.; Boscaiu, M.; Vicente, O. Effects of salt stress on three ecologically distinct Plantago species. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0160236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moghaieb, R.E.A.; Saneoka, H.; Fujita, K. Effect of salinity on osmotic adjustment, glycinebetaine accumulation and the betaine aldehyde dehydrogenase gene expression in two halophyte plants, Salicornia europaea and Suaeda maritima. Plant Sci. 2004, 166, 1345–1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghaleh, M.; Niknam, V.; Ebrahimzadeh, H.; Razavi, K. Salt stress effects on growth, pigments, proteins and lipid peroxidation in Salicornia persica and S. europaea. Biol. Plant. 2009, 53, 243–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naidoo, G.R.; Rughunanan, R. Salt tolerance in the succulent halophyte, Sarcocornia natalensis. J. Exp. Bot. 1990, 41, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, D.C.; Colmer, T.D. Salt tolerance in the halophyte Halosarcia pergranulata subsp. pergranulata. Ann. Bot. 1999, 83, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khan, M.A.; Ungar, I.A.; Showalter, A.M. Salt stimulation and tolerance in an intertidal stem-succulent halophyte. J. Plant. Nutr. 2005, 28, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, J.G.; Santini, B.A.; Martigmpla, F.R.; Jones, G.; Bogaard, A.; Charles, M. Font phytomer–leaf theory: Functional glue linking regenerative with life history strategies and taxonomy with ecology? Ann. Bot. 2017, 120, 633–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akcin, A.; Yalcin, E. Effect of salinity stress on chlorophyll, carotenoid content, and proline in Salicornia prostrata Pall. and Suaeda prostrata Pall. subsp. prostrata (Amaranthaceae). Braz. J. Bot. 2015, 39, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levitt, J. Responses of Plant to Environmental Stress Chilling, Freezing, and High Temperature Stresses, 2nd ed.; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beinsan, C.; Camen, D.; Sumalan, R.; Babau, M. Study concerning salt stress effect on leaf area dynamics and chlorophyll content in four bean local landraces from Banat area. In Proceedings of the 44th Croatian & 4th International Symposium on Agriculture, Opatija, Croatia, 16 February 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Rabhi, M.; Castagna, A.; Remorini, D.; Scattino, C.; Smaoui, A.; Ranieri, A.; Abdelly, C. Photosynthetic responses to salinity in two obligate halophytes: Sesuvium portulacastrum and Tecticornia indica. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2012, 79, 39–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al Hassan, M.; Del Pilar López-Gresa, M.; Boscaiu, M.; Vicente, O. Stress tolerance mechanisms in Juncus: Responses to salinity and drought in three Juncus species adapted to different natural environments. Funct. Plant Biol. 2016, 43, 949–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farghali, K.A. Chlorophyll content and its stability in native species inhabiting the Egyptian Desert. J. Arid Environ. 1998, 40, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramani, B.; Reeck, T.; Debez, A.; Stelzer, R.; Huchzermeyer, B.; Schmidt, A.; Papenbrock, J. Aster tripolium L. and Sesuvium portulacastrum L.: Two halophytes, two strategies to survive in saline habitats. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2006, 44, 395–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micheli, F. Pectin methylesterase: Cell wall enzyme with important roles in plant physiology. Triends Plant Sci. 2001, 6, 414–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiyagarajah, M.; Fry, S.C.; Yeo, A.R. In vitro salt tolerance of cell wall enzymes from halophytes and glycophytes. J. Exp. Bot. 1996, 47, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Radić, S.; Pevalek-Kozlina, B. Differential esterase activity in leaves and roots of Centaurea ragusina L. As a consequence of salinity. Period. Biol. 2012, 112, 253–258. [Google Scholar]
- Gill, S.S.; Tuteja, N. Reactive oxygen species and antioxidant machinery in abiotic stress tolerance in crop plants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2010, 48, 909–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batanouny, K.H.; Ezzat, N.H. Eco-physiological studies on desert plants. I. Autecology of Egyptian Zygophyllum species. Oecologia 1971, 7, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, F.M.; Gadallah, M.A.E.E.; Sayed, S.A.E.M.; Abdel, A.A.E.M. Adaptive mechanisms in Zilla Spinosa and Leptadenia pyrotechnica plants to sever aridity in the Egyptian deserts. Not. Sci. Biol. 2016, 8, 498–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, E.; Kasem, A.M.M.; El-khatib, A. Allelopathic potential of Egyptian halophytes Arthrocnemum macrostachyum and Halocnemum strobilaceum from two coastal areas. Allelopathy J. 2020, 50, 225–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ungar, I.A. The role of hormones in regulating germination of polymorphic seeds and early seedling growth of Atriplex triangularis under saline conditions. Physiol. Plant 1985, 63, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasool, S.G.; Hameed, A.; Ahmed, M.Z.; Khan, M.A.; Gul, B. Comparison of seed germination and recovery responses of a salt marsh halophyte Halopeplis perfoliata to osmotic and ionic treatments. Pak. J. Bot. 2016, 48, 1335–1343. [Google Scholar]
- Abdullahi, M.U.; Jasdanwala, R.T. Enlargement Quotient to Estimate Leaf Area in Two Cultivars of Okra (Abelmoschus esculentus [L.] Moench). J. Agro Crop Sci. 1991, 167, 167–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahneshan, Z.; Nasibi, F.; Moghadam, A.A. Effects of salinity stress on some growth, physiological, biochemical parameters and nutrients in two pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) rootstocks. J. Plant Interact. 2018, 13, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lichtenthaler, H.K. Chlorophylls and Carotenoids: Pigments of Photosynthetic Biomembranes. Methods in Enzymology; Academic Press: Orlando, FL, USA, 1987; Volume 148, pp. 183–350. [Google Scholar]
- Bradford, M.M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principal of protein-dye binding. Anal. Biochem. 1979, 72, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, H.H.; Hamill, D.E.; Weaver, E.A.; Thompson, K.H. Multiple molecular forms of peroxidase and esterases among Nicotina species and amphidiploids. J. Hered. 1970, 61, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, C.A.; Rasband, W.S.; Eliceiri, K.W. NIH image to imageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 671–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| Growth Parameters | Salinity | Habitat | Salinity × Habitat |
|---|---|---|---|
| Degree of Freedom | Degree of Freedom | Degree of Freedom | |
| Mean Squares | Mean Squares | Mean Squares | |
| F-Value | F-Value | F-Value | |
| p-Value | P-Value | p-Value | |
| Seed germination | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| 618.4 | 1.79 | 15.25 | |
| 152.8 | 0.222 | 0.628 | |
| <0.001 | <0.001 | ns | |
| Recovery | 2 | 2 | 4 |
| 6.4 | 81.7 | 0.444 | |
| 24.5 | 313.5 | 1.70 | |
| <0.001 | <0.001 | ns | |
| Shoot length | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| 56.4 | 48.6 | 2.1 | |
| 134.17 | 115.5 | 5.10 | |
| <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Leaf area | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| 0.102 | 0.015 | 0.013 | |
| 106.59 | 16.17 | 14.0 | |
| <0.001 | <0.001 | <0.001 | |
| Chl a | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| 0.001 | 0.023 | 0.001 | |
| 1.61 | 27.73 | 1.06 | |
| ns | <0.001 | ns | |
| Chl b | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| 0 | 0.003 | 0.001 | |
| 0.395 | 3.81 | 0.689 | |
| ns | <0.001 | ns | |
| Carotenoids | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| 0.002 | 0 | 0 | |
| 19.45 | 3.31 | 1.36 | |
| <0.001 | ns | ns | |
| Chl a/b | 3 | 2 | 6 |
| 0.022 | 2.909 | 0.378 | |
| 0.065 | 8.81 | 1.14 | |
| ns | 0.01 | ns | |
| Germination rate index | 3 | 2 | 4 |
| 2337.16 | 2.905 | 13.74 | |
| 385.7 | 0.645 | 2.26 | |
| <0.001 | ns | ns |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mohamed, E.; Kasem, A.M.M.A.; Gobouri, A.A.; Elkelish, A.; Azab, E. Influence of Maternal Habitat on Salinity Tolerance of Zygophyllum coccineum with Regard to Seed Germination and Growth Parameters. Plants 2020, 9, 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111504
Mohamed E, Kasem AMMA, Gobouri AA, Elkelish A, Azab E. Influence of Maternal Habitat on Salinity Tolerance of Zygophyllum coccineum with Regard to Seed Germination and Growth Parameters. Plants. 2020; 9(11):1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111504
Chicago/Turabian StyleMohamed, Elsayed, Ahmed M. M. A. Kasem, Adil A. Gobouri, Amr Elkelish, and Ehab Azab. 2020. "Influence of Maternal Habitat on Salinity Tolerance of Zygophyllum coccineum with Regard to Seed Germination and Growth Parameters" Plants 9, no. 11: 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111504
APA StyleMohamed, E., Kasem, A. M. M. A., Gobouri, A. A., Elkelish, A., & Azab, E. (2020). Influence of Maternal Habitat on Salinity Tolerance of Zygophyllum coccineum with Regard to Seed Germination and Growth Parameters. Plants, 9(11), 1504. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111504