Insights into Comparative Genomics, Codon Usage Bias, and Phylogenetic Relationship of Species from Biebersteiniaceae and Nitrariaceae Based on Complete Chloroplast Genomes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. General Features of the Chloroplast Genomes
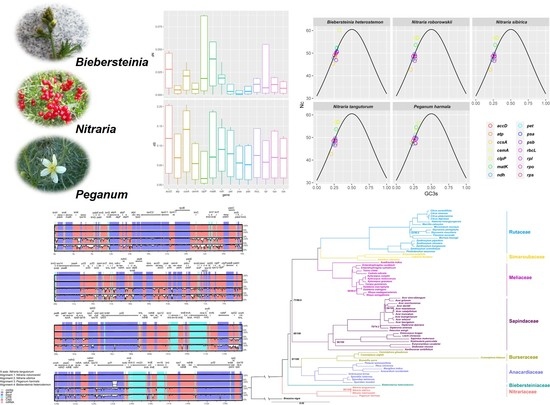
2.2. Genome Comparison
2.3. Variation in Nucleotide Substitution Rates
2.4. Codon Usage Bias
2.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
3. Discussion
3.1. Comparison of the Chloroplast Genomes
3.2. Variation in Nucleotide Substitution Rates
3.3. Codon Usage Bias
3.4. Phylogenetic Analysis within Sapindales
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Plant Materials and DNA Sequencing
4.2. Chloroplast Genome Assembling and Annotation
4.3. Genome Comparison
4.4. Estimation of Nucleotide Substitution Rate
4.5. Codon Usage Bias
4.6. Phylogenetic Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kubitzki, K. The Families and Genera of Vascular Plants: Vol. X Flowering Plants. Eudicots: Sapindales, Cucurbitales, Myrtaceae; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 72–76. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.Y.; Raven, P.H.; Hong, D.Y. Flora of China. Vol.11 Oxalidaceae through Aceraceae; Missouri Botanical Garden: St. Louis, MO, USA, 2008; pp. 31–32. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, B.; Jin, X.; Yin, H.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, H.-K.; Zhang, X.; Tran, L.S.P. Natural Products, Traditional Uses and Pharmacological Activities of the Genus Biebersteinia (Biebersteiniaceae). Plants 2020, 9, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelier, J.B.; Endress, P.K.; De Craene, L.P.R. Comparative floral structure and development of Nitrariaceae (Sapindales) and systematic implications. In Flowers on the Tree of Life; Wanntorp, L., Ronse de Craene, L., Eds.; Cambridge University Press (CUP): Cambridge, UK, 2011; pp. 181–217. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, L.; Chen, X.; Zhu, L.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Yang, X.; Wang, P.; Lu, Y.; Cheng, T.; Shi, J.; et al. NtCIPK9: A Calcineurin B-Like Protein-Interacting Protein Kinase from the Halophyte Nitraria tangutorum, Enhances Arabidopsis Salt Tolerance. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gadek, P.A.; Fernando, E.S.; Quinn, C.J.; Hoot, S.B.; Sheahan, M.C.; Chase, M.W. Sapindales: Molecular Delimitation and Infraordinal Groups. Bot. Soc. Am. 1996, 83, 802–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, F.T.; Vassiliades, D.D.; Morton, C.; Savolainen, V. Phylogenetic relationships of Biebersteinia Stephan (Geraniaceae) inferred from rbcL and atpB sequence comparisons. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1998, 127, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muellner, A.N.; Vassiliades, D.D.; Renner, S.S. Placing Biebersteiniaceae, a herbaceous clade of Sapindales, in a temporal and geographic context. Plant Syst. Evol. 2007, 266, 233–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sheahan, M.C.; Chase, M.W. A phylogenetic analysis of Zygophyllaceae R.Br. based on morphological, anatomical andrbcL DNA sequence data. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1996, 122, 279–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muellner-Riehl, A.N.; Weeks, A.; Clayton, J.W.; Buerki, S.; Nauheimer, L.; Chiang, Y.-C.; Cody, S.; Pell, S.K. Molecular phylogenetics and molecular clock dating of Sapindales based on plastid rbcL, atpB and trnL-trnF DNA sequences. Taxon 2016, 65, 1019–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltis, D.E.; Smith, S.A.; Cellinese, N.; Wurdack, K.J.; Tank, D.C.; Brockington, S.F.; Refulio-Rodriguez, N.F.; Walker, J.B.; Moore, M.J.; Carlsward, B.S.; et al. Angiosperm phylogeny: 17 genes, 640 taxa. Am. J. Bot. 2011, 98, 704–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yamamoto, T.; Vassiliades, D.D.; Tobe, H. Embryology of Biebersteinia (Biebersteiniaceae, Sapindales): Characteristics and comparisons with related families. J. Plant Res. 2014, 127, 599–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.-T.; Yi, T.-S.; Gao, L.-M.; Maria, V.; Zhang, T.; Yang, J.-B.; Gitzendanner, M.A.; Fritsch, P.W.; Cai, J.; Luo, Y.; et al. Origin of angiosperms and the puzzle of the Jurassic gap. Nat. Plants 2019, 5, 461–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-D.; Yang, T.; Lin, L.; Lu, L.-M.; Li, H.-L.; Sun, M.; Liu, B.; Chen, M.; Niu, Y.-T.; Ye, J.-F.; et al. Tree of life for the genera of Chinese vascular plants. J. Syst. Evol. 2016, 54, 277–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Henry, R.J.; Rossetto, M.; Wang, Y.; Chen, S. Plant DNA barcoding: From gene to genome. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 2015, 90, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ravi, V.; Khurana, J.P.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, P. An update on chloroplast genomes. Plant Syst. Evol. 2008, 271, 101–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.J.; Li, D.Z. Advances in Phylogenomics Based on Complete Chloroplast Genomes. Plant Divers. Resour. 2011, 33, 365–375. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.-B.; Campbell, C.S.; Hong, D.-Y.; Wen, J. Phylogenetic relationships and chloroplast capture in the Amelanchier-Malacomeles-Peraphyllum clade (Maleae, Rosaceae): Evidence from chloroplast genome and nuclear ribosomal DNA data using genome skimming. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2020, 147, 106784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.-D.; Jin, J.-J.; Chen, S.-Y.; Chase, M.W.; Soltis, D.E.; Li, H.-T.; Yang, J.-B.; Li, D.-Z.; Yi, T.-S. Diversification of Rosaceae since the Late Cretaceous based on plastid phylogenomics. New Phytol. 2017, 214, 1355–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Green, B.R. Chloroplast genomes of photosynthetic eukaryotes. Plant J. 2011, 66, 34–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, M.; Shinozaki, K.; Zaita, N.; Kusuda, M.; Kumano, M. Clone bank of the tobacco (Nicotiana tabacum) chloroplast genome as a set of overlapping restriction endonuclease fragments: Mapping of eleven ribosomal protein genes. Plant Sci. 1986, 44, 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, M. The chloroplast genome. Plant Mol. Biol. 1992, 19, 149–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peden, J.F. Analysis of codon usage. Bio Syst. 1999, 5, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharp, P.M.; Emery, L.R.; Zeng, K. Forces that influence the evolution of codon bias. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2010, 365, 1203–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharp, P.M.; Stenico, M.; Peden, J.F.; Lloyd, A.T. Codon usage: Mutational bias, translational selection, or both? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1993, 21, 835–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Subramanian, S. Nearly Neutrality and the Evolution of Codon Usage Bias in Eukaryotic Genomes: Figure 1. Genetics 2008, 178, 2429–2432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, H.; Wu, W.B.; Comeron, J.M.; Kreitman, M.; Li, W.-H. Intragenic Spatial Patterns of Codon Usage Bias in Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Genomes. Genetics 2004, 168, 2245–2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xing, Z.B.; Cao, L.; Zhou, M.; Xiu, L.S. Analysis on codon usage of chloroplast genome of Eleutherococcus senticosus. Sci. Agric. Sin. 2013, 38, 661–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolfe, K.H.; Li, W.H.; Sharp, P.M. Rates of nucleotide substitution vary greatly among plant mitochondrial, chloroplast, and nuclear DNAs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1987, 84, 9054–9058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wright, F. The ‘effective number of codons’ used in a gene. Gene 1990, 87, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.; Wang, J.; Gao, Q.-B.; Zhang, F.; Chen, S. The Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Two Lancea Species with Comparative Analysis. Molecules 2018, 23, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhao, X.-L.; Zhu, Z.-M. Comparative Genomics and Phylogenetic Analyses of Christia vespertilionis and Urariopsis brevissima in the Tribe Desmodieae (Fabaceae: Papilionoideae) Based on Complete Chloroplast Genomes. Plants 2020, 9, 1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, C.; Cao, Y. Phylogenetic and Comparative Analyses of Complete Chloroplast Genomes of Chinese Viburnum and Sambucus (Adoxaceae). Plants 2020, 9, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniell, H.; Lin, C.-S.; Yu, M.; Chang, W.-J. Chloroplast genomes: Diversity, evolution, and applications in genetic engineering. Genome Biol. 2016, 17, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Blazier, J.C.; Ruhlman, T.A.; Weng, M.-L.; Rehman, S.K.; Sabir, J.S.M.; Jansen, R.K. Divergence of RNA polymerase α subunits in angiosperm plastid genomes is mediated by genomic rearrangement. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Guisinger Timothy, M.M.; Kuehl, J.V.; Boore, J.L.; Jansen, R.K. Genome-wide analyses of Geraniaceae plastid DNA reveal unprecedented patterns of increased nucleotide substitutions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 18424–18429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Weng, M.-L.; Ruhlman, T.A.; Gibby, M.; Jansen, R.K. Phylogeny, rate variation, and genome size evolution of Pelargonium (Geraniaceae). Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 2012, 64, 654–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, S.; Ruhlman, T.A.; Weng, M.-L.; Hajrah, N.H.; Sabir, J.S.; Jansen, R.K. Contrasting Patterns of Nucleotide Substitution Rates Provide Insight into Dynamic Evolution of Plastid and Mitochondrial Genomes of Geranium. Genome Biol. Evol. 2017, 9, 1766–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bulmer, M. The Selection-Mutation-Drift Theory of Synonymous Codon Usage. Genetics 1991, 129, 897–907. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.-J.; Zhou, J.; Li, Z.-F.; Wang, L.; Gu, X.; Zhong, Y. Comparative Analysis of Codon Usage Patterns Among Mitochondrion, Chloroplast and Nuclear Genes in Triticum aestivum L. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2007, 49, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sloan, D.B.; Taylor, D.R. Testing for Selection on Synonymous Sites in Plant Mitochondrial DNA: The Role of Codon Bias and RNA Editing. J. Mol. Evol. 2010, 70, 479–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Pan, Z.; Gao, S.; He, Y.; Xia, Q.; Jin, Y.; Yao, H. Analysis of synonymous codon usage of chloroplast genome in Porphyra umbilicalis. Genes Genom. 2019, 41, 1173–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, J.J.; Doyle, J.L. A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem. Bull 1987, 19, 11–15. [Google Scholar]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A New Genome Assembly Algorithm and Its Applications to Single-Cell Sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, L.; Chen, H.; Jiang, M.; Wang, L.; Wu, X.; Huang, L.; Liu, C. CPGAVAS2, an integrated plastome sequence annotator and analyzer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W65–W73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laslett, D. ARAGORN, a program to detect tRNA genes and tmRNA genes in nucleotide sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amiryousefi, A.; Hyvönen, J.; Poczai, P. IRscope: An online program to visualize the junction sites of chloroplast genomes. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3030–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazer, K.A.; Pachter, L.; Poliakov, A.; Rubin, E.M.; Dubchak, I. VISTA: Computational tools for comparative genomics. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W273–W279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Librado, P.; Rozas, J. DnaSP v5: A software for comprehensive analysis of DNA polymorphism data. Bioinformatics 2009, 25, 1451–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT multiple sequence alignment software version 7: Improvements in performance and usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z. PAML 4: Phylogenetic Analysis by Maximum Likelihood. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2007, 24, 1586–1591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, D.; Gao, F.; Jakovlić, I.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.X.; Wang, G.-T. PhyloSuite: An integrated and scalable desktop platform for streamlined molecular sequence data management and evolutionary phylogenetics studies. Mol. Ecol. Resour. 2019, 20, 348–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalyaanamoorthy, S.; Minh, B.Q.; Wong, T.K.F.; Von Haeseler, A.; Jermiin, L.S. ModelFinder: Fast model selection for accurate phylogenetic estimates. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 587–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, L.-T.; Schmidt, H.A.; Von Haeseler, A.; Minh, B.Q. IQ-TREE: A Fast and Effective Stochastic Algorithm for Estimating Maximum-Likelihood Phylogenies. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2015, 32, 268–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronquist, F.; Teslenko, M.; Van Der Mark, P.; Ayres, D.L.; Darling, A.; Höhna, S.; Larget, B.; Liu, L.; Suchard, M.A.; Huelsenbeck, J.P. MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian Phylogenetic Inference and Model Choice Across a Large Model Space. Syst. Biol. 2012, 61, 539–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Characteristics | B. heterostemon | N. roborowskii | N. sibirica | N. tangutorum | P. harmala |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total cpDNA size (bp) | 158,795 | 159,397 | 159,364 | 159,383 | 160,068 |
| Length of large single copy (LSC) region | 86,887 | 87,907 | 87,883 | 87,901 | 88,278 |
| Length of inverted repeat (IR) region | 26,779 | 26,589 | 26,586 | 26,586 | 26,469 |
| Length of small single copy (SSC) region | 18,350 | 18,312 | 18,309 | 18,310 | 18,852 |
| Total GC content (%) | 37.90 | 37.32 | 37.27 | 37.15 | 37.50 |
| LSC | 36.21 | 35.20 | 35.20 | 35.19 | 35.60 |
| IR | 42.68 | 42.68 | 42.67 | 42.68 | 42.79 |
| SSC | 32.00 | 31.42 | 31.45 | 31.45 | 31.39 |
| Total number of genes | 135 | 128 | 128 | 128 | 132 |
| Protein-coding genes | 88 | 81 | 81 | 81 | 87 |
| tRNA genes | 39 | 39 | 39 | 39 | 37 |
| rRNA genes | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 | 8 |
| Species | GC | GC1 | GC2 | GC3 | CAI | T3S | C3S | A3S | G3S | GC3S | ENC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| B. heterostemon | 0.391 | 0.477 | 0.397 | 0.300 | 0.170 | 0.464 | 0.172 | 0.420 | 0.173 | 0.269 | 49.74 |
| N. roborowskii | 0.389 | 0.477 | 0.396 | 0.295 | 0.168 | 0.468 | 0.165 | 0.423 | 0.174 | 0.264 | 49.38 |
| N. sibirica | 0.386 | 0.475 | 0.395 | 0.287 | 0.167 | 0.474 | 0.161 | 0.430 | 0.168 | 0.255 | 48.73 |
| N. tangutorum | 0.386 | 0.476 | 0.395 | 0.288 | 0.169 | 0.472 | 0.161 | 0.429 | 0.168 | 0.256 | 48.74 |
| P. harmala | 0.386 | 0.475 | 0.395 | 0.287 | 0.168 | 0.473 | 0.161 | 0.428 | 0.168 | 0.256 | 48.71 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chi, X.; Zhang, F.; Dong, Q.; Chen, S. Insights into Comparative Genomics, Codon Usage Bias, and Phylogenetic Relationship of Species from Biebersteiniaceae and Nitrariaceae Based on Complete Chloroplast Genomes. Plants 2020, 9, 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111605
Chi X, Zhang F, Dong Q, Chen S. Insights into Comparative Genomics, Codon Usage Bias, and Phylogenetic Relationship of Species from Biebersteiniaceae and Nitrariaceae Based on Complete Chloroplast Genomes. Plants. 2020; 9(11):1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111605
Chicago/Turabian StyleChi, Xiaofeng, Faqi Zhang, Qi Dong, and Shilong Chen. 2020. "Insights into Comparative Genomics, Codon Usage Bias, and Phylogenetic Relationship of Species from Biebersteiniaceae and Nitrariaceae Based on Complete Chloroplast Genomes" Plants 9, no. 11: 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111605
APA StyleChi, X., Zhang, F., Dong, Q., & Chen, S. (2020). Insights into Comparative Genomics, Codon Usage Bias, and Phylogenetic Relationship of Species from Biebersteiniaceae and Nitrariaceae Based on Complete Chloroplast Genomes. Plants, 9(11), 1605. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9111605