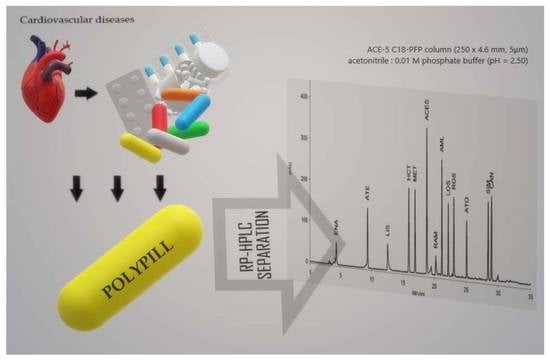
Simple, Accurate and Multianalyte Determination of Thirteen Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients in Polypills by HPLC-DAD
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Standard Solutions and Substances
2.3. Pharmaceutical Preparations
2.4. Sample Preparation
2.5. Instrumentation and HPLC Conditions
2.6. Method Validation
3. Results
3.1. Optimization of Chromatographic Conditions
3.2. Selectivity and System Suitability
3.3. Linearity and LOD and LOQ
3.4. Precision, Accuracy and Robustness
Application to the Analysis of Pharmaceutical Formulations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Kyu, H.H.; Abate, D.; Abate, K.H.; Abay, S.M.; Abbafati, C.; Abbasi, N.; Abbastabar, H.; Abd-Allah, F.; Abdela, J.; Abdelalim, A.; et al. Global, Regional, and National Disability-Adjusted Life-Years (DALYs) for 359 Diseases and Injuries and Healthy Life Expectancy (HALE) for 195 Countries and Territories, 1990-2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet 2018, 392, 1859–1922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roshandel, G.; Khoshnia, M.; Poustchi, H.; Hemming, K.; Kamangar, F.; Gharavi, A.; Ostovaneh, M.R.; Nateghi, A.; Majed, M.; Navabakhsh, B.; et al. Effectiveness of Polypill for Primary and Secondary Prevention of Cardiovascular Diseases (PolyIran): A Pragmatic, Cluster-Randomised Trial. Lancet 2019, 394, 672–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sleight, P.; Pouleur, H.; Zannad, F. Benefits, Challenges, and Registerability of the Polypill. Eur. Heart J. 2006, 27, 1651–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wald, N.J.; Law, M.R. A Strategy to Reduce Cardiovascular Disease by More than 80%. Br. Med. J. 2003, 326, 1419–1423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robles-Martinez, P.; Xu, X.; Trenfield, S.J.; Awad, A.; Goyanes, A.; Telford, R.; Basit, A.W.; Gaisford, S. 3D Printing of a Multi-Layered Polypill Containing Six Drugs Using a Novel Stereolithographic Method. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yusuf, S.; Pais, P.; Sigamani, A.; Xavier, D.; Afzal, R.; Gao, P.; Teo, K.K. Comparison of Risk Factor Reduction and Tolerability of a Full-Dose Polypill (With Potassium) versus Low-Dose Polypill (Polycap) in Individuals at High Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases: The Second Indian Polycap Study (TIPS-2) Investigators. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outcomes 2012, 5, 463–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yusuf, S.; Pais, P.; Afzal, R.; Xavier, D.; Teo, D.; Eikelboom, J.; Sigamani, A.; Mohan, V.; Gupta, R.; Thomas, N. Effects of a Polypill (Polycap) on Risk Factors in Middle-Aged Individuals without Cardiovascular Disease (TIPS): A Phase II, Double-Blind, Randomised Trial. Lancet 2009, 373, 1341–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soliman, E.Z.; Mendis, S.; Dissanayake, W.P.; Somasundaram, N.P.; Gunaratne, P.S.; Jayasingne, I.K.; Furberg, C.D. A Polypill for Primary Prevention of Cardiovascular Disease: A Feasibility Study of the World Health Organization. Trials 2011, 12, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Selak, V.; Elley, C.R.; Crengle, S.; Harwood, M.; Doughty, R.; Arroll, B.; Bryant, L.; Rafter, N.; Vander Hoorn, S.; Wadham, A.; et al. Improving Adherence Using Combination Therapy (IMPACT): Design and Protocol of a Randomised Controlled Trial in Primary Care. Contemp. Clin. Trials 2011, 32, 909–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodgers, A.; Patel, A.; Berwanger, O.; Bots, M.; Grimm, R.; Grobbee, D.E.; Jackson, R.; Neal, B.; Neaton, J.; Poulter, N.; et al. An International Randomised Placebo-Controlled Trial of a Four-Component Combination Pill (“Polypill”) in People with Raised Cardiovascular Risk. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, D.S.; Morris, J.K.; Wald, N.J. Randomized Polypill Crossover Trial in People Aged 50 and Over. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Thom, S.; Field, J.; Poulter, N.; Patel, A.; Prabhakaran, D.; Stanton, A.; Grobbee, D.E.; Bots, M.L.; Reddy, K.S.; Cidambi, R.; et al. Use of a Multidrug Pill in Reducing Cardiovascular Events (UMPIRE): Rationale and Design of a Randomised Controlled Trial of a Cardiovascular Preventive Polypill-Based Strategy in India and Europe. Eur. J. Prev. Cardiol. 2014, 21, 252–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thom, S.; Poulter, N.; Field, J.; Patel, A.; Prabhakaran, D.; Stanton, A.; Grobbee, D.E.; Bots, M.L.; Reddy, K.S.; Cidambi, R.; et al. Effects of a Fixed-Dose Combination Strategy on Adherence and Risk Factors in Patients with or at High Risk of CVD: The UMPIRE Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA-J. Am. Med. Assoc. 2013, 310, 918–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- SECURE—Secondary PrEvention of CardiovascUlar Disease in the Elderly Trial. Available online: https://www.secure-h2020.eu/ (accessed on 30 June 2022).
- Lonn, E.; Bosch, J.; Pogue, J.; Avezum, A.; Chazova, I.; Dans, A.; Diaz, R.; Fodor, G.J.; Held, C.; Jansky, P.; et al. Novel Approaches in Primary Cardiovascular Disease Prevention: The HOPE-3 Trial Rationale, Design, and Participants’ Baseline Characteristics. Can. J. Cardiol. 2016, 32, 311–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janczura, M.; Sip, S.; Cielecka-Piontek, J. The Development of Innovative Dosage Forms of the Fixed-Dose Combination of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Guardia, M.; Armenta, S. Multianalyte Determination versus One-at-a-Time Methodologies; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 57. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, J.V.; Parekh, J.M.; Shah, P.A.; Shah, P.V.; Sanyal, M.; Shrivastav, P.S. Application of an LC–MS/MS Method for the Analysis of Amlodipine, Valsartan and Hydrochlorothiazide in Polypill for a Bioequivalence Study. J. Pharm. Anal. 2017, 7, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lançanova Moreira, A.P.; Gobo, L.A.; Viana, C.; Machado De Carvalho, L. Simultaneous Analysis of Antihypertensive Drugs and Diuretics as Adulterants in Herbal-Based Products by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Anal. Methods 2016, 8, 1881–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslanka, A.; Stolarczyk, M.; Apola, A.; Kwiecien, A.; Hubicka, U.; Opoka, W. Simultaneous Determination of Acetylsalicylic Acid, Hydrochlorothiazide, Enalapril, and Atorvastatin in a Polypill-Based Quaternary Mixture by TLC. J. AOAC Int. 2018, 101, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, A.; Shah, B.; Patel, B. Scholars Research Library Simultaneous Estimation of Atorvastatin Calcium, Ramipril and Aspirin in Capsule Dosage Form Using HPTLC. Der Pharma Chem. 2010, 2, 10–16. [Google Scholar]
- Gawad, D.A.; Elnaggar, M.M.; Belal, T.S. Multi-Analyte HPLC–DAD Method for Concurrent Analysis of Six Antimicrobials and Three Proton Pump Inhibitors Frequently Used in Management of Helicobacter Pylori Infection: Application to Simulated Intestinal Fluid Samples. Chromatographia 2022, 85, 617–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawar, A.K.M.; Rao, A.B.N.N.; Gowri Sankar, D. Simultaneous Estimation of Enalapril Maleate, Hydrochlorothiazide, Aspirin and Atorvastatin in Pure and Its Simulated Dosage Form Using Isocratic RP-HPLC. Der Pharm. Lett. 2011, 3, 58–67. [Google Scholar]
- Pawar, A.K.M.; Sreekanth, K.; Nageswara Rao, A.B.N.; Gowri Sankar, D. An Isocratic Method for the Simultaneous Estimation of Aspirin, Ramipril and Simvastatin by RP-HPLC. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 4, 425–428. [Google Scholar]
- Shetty, S.K.; Surendranath, K.V.; Radhakrishnanand, P.; Borkar, R.M.; Devrukhakar, P.S.; Jogul, J.; Tripathi, U.M. Quantitative Application to a Polypill by the Development of Stability Indicating LC Method for the Simultaneous Estimation of Aspirin, Atorvastatin, Atenolol and Losartan Potassium. Am. J. Anal. Chem. 2010, 1, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talluri, M.V.N.K.; Kalyankar, A.; Ragampeta, S. Synchronized Separation of Atorvastatin—An Antihyperlipidemic Drug with Antihypertensive, Antidiabetic, Antithrombotic Drugs by RP-LC for Determination in Combined Formulations. J. Pharm. Anal. 2012, 2, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sharma, R.; Khanna, S.; Mishra, G.P. Development and Validation of RP-HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Ramipril, Aspirin and Atorvastatin in Pharmaceutical Preparations. E-J. Chem. 2012, 9, 2177–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaalan, R.A.; Belal, T.S.; El Yazbi, F.A.; Elonsy, S.M. Validated Stability-Indicating HPLC-DAD Method of Analysis for the Antihypertensive Triple Mixture of Amlodipine Besylate, Valsartan and Hydrochlorothiazide in Their Tablets. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S1381–S1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ibrahim, M.M.; Hegazy, M.A.; El-Aziz El-Bayoumi, A.; Abd El-Ghani, M.A. Rapid and Sensitive HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Atorvastatin, Hydrochlorothiazide and Losartan and Quantitative Application to Polypill Based Synthetic Ternary Mixture. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 2012, 2012, 4737–4742. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, V.; Shah, R.P.; Singh, S. LC and LC-MS Methods for the Investigation of Polypills for the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Part 1. Separation of Active Components and Classification of Their Interaction/Degradation Products. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2008, 47, 508–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shetty, S.K.; Borkar, R.M.; Devrukhakar, P.S.; Surendranath, K.V.; Radhakrishnanand, P.; Satish, J.; Shastri, N.; Jogul, J.; Tripathi, U.M. RP-HPLC Separation Method for Individual Components of Polycap in Presence of Their Degradation/Interaction Products. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2012, 35, 662–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vishnuvardhan, C.; Radhakrishnanand, P.; Navalgund, S.G.; Atcha, K.R.; Satheeshkumar, N. RP-HPLC Method for the Simultaneous Estimation of Eight Cardiovascular Drugs. Chromatographia 2014, 77, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolarczyk, M.; Apola, A.; Maślanka, A.; Kwiecień, A.; Opoka, W. Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis of Fixed-Dose-Combination Products (FDC, Polypill) Applied in Polytherapy of Hypertensive Disease. Review. Acta Pol. Pharm.-Drug Res. 2018, 75, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ICH Validation of Analytical Procedures: Text and Methodology, Q2 (R1), Geneva. 2005. Available online: https://www.ich.org/page/quality-guidelines (accessed on 20 June 2020).
- Alhazmi, H.A.; Alnami, A.M.; Arishi, M.A.A.; Alameer, R.K.; Al Bratty, M.; Ur Rehman, Z.; Javed, S.A.; Arbab, I.A. A Fast and Validated Reversed-Phase HPLC Method for Simultaneous Determination of Simvastatin, Atorvastatin, Telmisartan and Irbesartan in Bulk Drugs and Tablet Formulations. Sci. Pharm. 2017, 86, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sarisaltik Yaşin, D.; Arslantürk Bingül, A.; Karaküçük, A.; Teksin, Z.Ş. Development and Validation of an HPLC Method Using an Experimental Design for Analysis of Amlodipine Besylate and Enalapril Maleate in a Fixed-Dose Combination. Turk. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 18, 306–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Si-Hung, L.; Bamba, T. A Review of Retention Mechanism Studies for Packed Column Supercritical Fluid Chromatography. Anal. Sci. Adv. 2021, 2, 47–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Polypill | Antiplatelet Drug | Thiazide | β-Blocker | Ca-Channel Blocker | ACE-Inhibitor or Sartan | Statin |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zycad-4 a | ACES 75 mg | No | MET (succ.) 50 mg | No | RAM 5 mg | ATO 10 mg |
| Starpill b | ACES 75 mg | No | ATE 50 mg | No | LOS 50 mg | ATO 10 mg |
| Deplatt-CV c | ACES 75 mg * | No | No | No | No | ATO 20 mg |
| CV-Pill Kit c | ACES 75 mg | No | MET (succ.) 50 mg | No | RAM 5 mg | ATO 10 mg |
| Polycap d | ACES 100 mg | HCT 12.5 mg | ATE 50 mg | No | RAM 5 mg | SIM 20 mg |
| Polytorva e | ACES 75 mg | No | No | No | RAM 5 mg | ATO 10 mg |
| Modlip Cad c | ACES 75 mg | No | No | No | RAM 2.5 mg | ATO 10 mg |
| Exforge HCT f | No | HCT 25 mg | No | AML 10 mg | VAL 160 mg | No |
| Trinomia, Sincronium, Iltria g | ACES 100 mg | No | No | No | RAM 2.5–10 mg | SIM 40 mg |
| Polypill-E h | ACES 81 mg | HCT 12.5 mg | No | No | ENA 5 mg | ATO 20 mg |
| Polypill-V h | ACES 81 mg | HCT 12.5 mg | No | No | VAL 40 mg | ATO 20 mg |
| Time [min] | 0.01 M Phosphate Buffer pH = 2.50 [%] | Acetonitrile [%] |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 95 | 5 |
| 10 | 80 | 20 |
| 30 | 0 | 100 |
| 35 | 95 | 5 |
| Compound | tR (min) | N | As | Rs a |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENA | 4.21 SD = 0.104 RSD = 2.48% | 12,064.0 SD = 344.8 RSD = 2.80% | 1.07 | - |
| ATE | 9.32 SD = 0.06 RSD = 1.05% | 49,535.0 SD = 1415.8 RSD = 2.86% | 0.82 | 31.37 |
| LIS | 12.57 SD = 0.104 RSD = 0.50% | 36,314.2 SD = 1150.9 RSD = 3.17% | 1.37 | 14.89 |
| HCT | 15.93 SD = 0.06 RSD = 0.38% | 121,376.2 SD = 342.60 RSD = 2.82% | 0.99 | 14.37 |
| MET | 16.93 SD = 0.15 RSD = 0.88% | 225,934.4 SD = 2888.4 RSD = 1.28% | 1.22 | 5.83 |
| ACES | 18.81 SD = 0.08 RSD = 0.43% | 239,086.6 SD = 5721.0 RSD = 2.39% | 1.12 | 12.46 |
| RAM | 20.13 SD = 0.09 RSD = 0.46% | 198,583.8 SD = 5743.1 RSD = 2.89% | 1.27 | 5.84 |
| AML | 21.10 SD = 0.09 RSD = 0.42% | 425,173.8 SD = 3890.8 RSD = 0.92% | 1.18 | 5.50 |
| LOS | 22.09 SD = 0.09 RSD = 0.42% | 406,365.8 SD = 7515.6 RSD = 1.84% | 1.08 | 7.38 |
| ROS | 22.96 SD = 0.10 RSD = 0.43% | 450,504.4 SD = 4158.7 RSD = 0.92% | 1.16 | 6.31 |
| ATO | 24.94 SD = 0.12 RSD = 0.46% | 499,586.6 SD = 4304.0 RSD = 0.86% | 1.09 | 14.20 |
| SIM | 28.27 SD = 0.13 RSD = 0.47% | 502,694.6 SD = 11958.5 RSD = 2.38% | 1.08 | 22.30 |
| CAN | 28.77 SD = 0.14 RSD = 0.49% | 516,520.0 SD = 9117.7 RSD = 1.80% | 1.08 | 3.16 |
| API | LOD [mg mL−1] | LOQ [mg mL−1] | Linearity Range [mg mL−1] | Regression Coefficients P = ac + b ± Se a (n = 15) | Sa b Sb | R2 | Normality of Residuals c (SW Test) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| p | W | |||||||
| ENA | 0.0416 | 0.1261 | 0.1250–0.3750 | a = 5642 × 103 b = 11,501 ± 71,163 | 207,879 55,122.2 | 0.9827 | 0.5581 | 0.9521 |
| ATE | 0.0035 | 0.0106 | 0.0250–0.0749 | a = 7215 × 104 b = −117 × 103 ± 76,684 | 1,121,837 59,399 | 0.9969 | 0.9993 | 0.9897 |
| LIS | 0.0358 | 0.1085 | 0.1885–0.5655 | a = 7890 × 103 b = −117 × 103 ± 85,636 | 165,886.9 66,336.1 | 0.9943 | 0.1524 | 0.9134 |
| HCT | 0.0024 | 0.0071 | 0.0125–0.0374 | a = 1815 × 105 b = −194·103 ± 1294 × 102 | 3,786,642 10,0248 | 0.9944 | 0.6269 | 0.9562 |
| MET | 0.0092 | 0.0279 | 0.0500–0.1500 | a = 3612 × 104 b = −154 × 103 ± 1008 × 102 | 735,779.4 78,041.2 | 0.9946 | 0.0189 | 0.8526 |
| ACES | 0.0116 | 0.0350 | 0.0375–0.1125 | a =1020 × 105 b = −72 × 103 ± 3573 × 102 | 3,484,547 276,751 | 0.9850 | 0.8939 | 0.9726 |
| RAM | 0.0923 | 0.2794 | 0.2650–0.7950 | a = 7881 × 103 b = 2458 × 102 ± 2205 × 102 | 303,884.8 170,828.8 | 0.9810 | 0.6950 | 0.9602 |
| AML | 0.0054 | 0.0163 | 0.0250–0.0750 | a = 9058 × 104 b = −184 × 103 ± 1473 × 102 | 2,152,175 114,136 | 0.9927 | 0.9113 | 0.9739 |
| LOS | 0.0009 | 0.0027 | 0.0100–0.0300 | a = 1481 × 105 b = −473 × 102 ± 40,683 | 1,485,532 31,513 | 0.9987 | 0.7750 | 0.9648 |
| ROS | 0.0027 | 0.0081 | 0.0200–0.0600 | a = 8216 × 104 b = −933 × 102 ± 66,954 | 1,222,399 51,862 | 0.9971 | 0.9127 | 0.9740 |
| ATO | 0.0022 | 0.0067 | 0.0150–0.0449 | a = 7903 × 104 b = −755 × 102 ± 5323 × 101 | 1,299,252 41,232 | 0.9965 | 0.8834 | 0.9718 |
| SIM | 0.0030 | 0.0092 | 0.0150–0.0449 | a = 1208 × 105 b = −102 × 103 ± 1108 × 102 | 2,705,490 85,859 | 0.9935 | 0.4461 | 0.9448 |
| CAN | 0.0037 | 0. 0113 | 0.0160–0.0480 | a = 1167 × 105 b = 70,580 ± 1318 × 102 | 3,007,377 102,074 | 0.9914 | 0.9464 | 0.9772 |
| API | Precision, RSD [%] * (n = 3) | Indirect Precision, RSD [%] (n = 3) | Recovery [%] (n = 5) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50% | 100% | 150% | 50% | 100% | 150% | Mean | RSD% | |
| ENA | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.50 | 1.21 | 1.62 | 1.65 | 101.60 | 1.24 |
| ATE | 1.02 | 1.11 | 0.70 | 1.50 | 1.43 | 1.35 | 95.20 | 1.74 |
| LIS | 1.80 | 0.22 | 0.31 | 1.86 | 1.20 | 1.35 | 99.40 | 1.15 |
| HCT | 0.99 | 0.99 | 1.50 | 1.30 | 0.85 | 0.77 | 97.60 | 0.82 |
| MET | 0.24 | 1.05 | 0.24 | 1.30 | 1.24 | 0.78 | 98.08 | 0.37 |
| ACES | 0.8 | 0.36 | 1.40 | 1.29 | 1.64 | 1.91 | 103.07 | 1.12 |
| RAM | 0.93 | 1.29 | 0.53 | 1.12 | 1.55 | 1.07 | 100.40 | 1.67 |
| AML | 0.84 | 0.98 | 0.47 | 1.56 | 1.24 | 0.75 | 97.04 | 0.85 |
| LOS | 0.86 | 0.59 | 0.55 | 1.38 | 0.60 | 0.64 | 96.80 | 1.27 |
| ROS | 0.89 | 0.67 | 0.59 | 0.94 | 0.76 | 1.35 | 104.62 | 1.85 |
| ATO | 0.36 | 0.71 | 0.41 | 1.70 | 1.15 | 0.70 | 103.80 | 0.81 |
| SIM | 1.02 | 1.11 | 0.70 | 1.50 | 1.43 | 1.35 | 97.62 | 1.56 |
| CAN | 0.43 | 0.72 | 0.70 | 1.11 | 0.78 | 1.18 | 95.20 | 1.74 |
| Analysed Mixtures | Nominal Content | Determined Content [mg ± RSD] (n = 5) |
|---|---|---|
| M-1 | ACES (75 mg) ATE (50 mg) LIS (10 mg) SIM (40 mg) | 73.64 ± 0.95 51.96 ± 0.80 10.16 ± 0.88 38.56 ± 0.30 |
| M-2 | ACES (75 mg) ATO (10 mg) RAM (5 mg) MET (50 mg) | 71.88 ± 0.59 10.36 ± 0.53 4.92 ± 0.91 49.10 ± 0.50 |
| M-3 | HCT (12.5 mg) CAN (16 mg) ROS (10 mg) | 12.18 ± 0.69 15.64 ± 0.86 10.26 ± 0.53 |
| M-4 | LOS (25 mg) AML (2.5 mg) ENA (12.5 mg) | 25.70 ± 0.48 2.42 ± 0.79 12.32 ± 0.68 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Żuromska-Witek, B.; Stolarczyk, M.; Szlósarczyk, M.; Kielar, S.; Hubicka, U. Simple, Accurate and Multianalyte Determination of Thirteen Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients in Polypills by HPLC-DAD. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11010025
Żuromska-Witek B, Stolarczyk M, Szlósarczyk M, Kielar S, Hubicka U. Simple, Accurate and Multianalyte Determination of Thirteen Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients in Polypills by HPLC-DAD. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(1):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11010025
Chicago/Turabian StyleŻuromska-Witek, Barbara, Mariusz Stolarczyk, Marek Szlósarczyk, Szymon Kielar, and Urszula Hubicka. 2023. "Simple, Accurate and Multianalyte Determination of Thirteen Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients in Polypills by HPLC-DAD" Chemosensors 11, no. 1: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11010025
APA StyleŻuromska-Witek, B., Stolarczyk, M., Szlósarczyk, M., Kielar, S., & Hubicka, U. (2023). Simple, Accurate and Multianalyte Determination of Thirteen Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients in Polypills by HPLC-DAD. Chemosensors, 11(1), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11010025