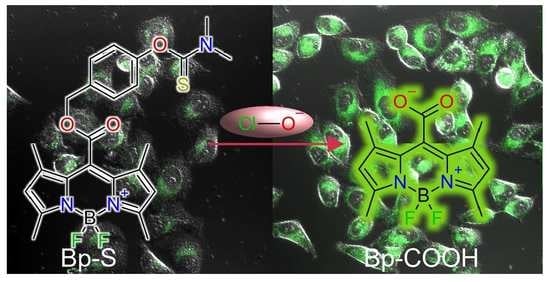
Carboxy Bodipy-Based Fast Trigger Fluorescent Probe for Imaging Endogenous Hypochlorous Acid
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials and Methods
2.2. Equipment
2.3. Synthesis Methods
2.4. DFT Calculations
2.5. Spectroscopic Methods
2.6. Cell Culture and Cytotoxicity
2.7. Confocal Microscopy Imaging
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Rational Design and Synthesis of Bp-S
3.2. Fluorescence Response of Bp-S toward ClO−
3.3. Competition Estimation and pH Influence
3.4. Sensing Response of Bp-S toward ClO−
3.5. Density Functional Theory (DFT) Calculations
3.6. Confocal Fluorescence Imaging Experiments
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, B.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Based Nanomedicine. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 4881–4985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dickinson, B.C.; Chang, C.J. Chemistry and Biology of Reactive Oxygen Species in Signaling or Stress Responses. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Deng, Y.; Feng, S.; Xia, Q.; Gong, S.; Feng, G. A Novel Reaction-Based Fluorescence Probe for Rapid Imaging of HClO in Live Cells, Animals, and Injured Liver Tissues. Talanta 2020, 215, 120901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Wang, F.; Hyun, J.Y.; Wei, T.; Qiang, J.; Ren, X.; Shin, I.; Yoon, J. Recent Progress in the Development of Fluorescent, Luminescent and Colorimetric Probes for Detection of Reactive Oxygen and Nitrogen Species. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 2976–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hampton, M.B.; Kettle, A.J.; Winterbourn, C.C. Inside the Neutrophil Phagosome: Oxidants, Myeloperoxidase, and Bacterial Killing. Blood 1998, 92, 3007–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Cao, Z.; Moore, D.R.; Jackson, P.L.; Barnes, S.; Lambeth, J.D.; Thannickal, V.J.; Cheng, G. Microbicidal Activity of Vascular Peroxidase 1 in Human Plasma via Generation of Hypochlorous Acid. Infect. Immun. 2012, 80, 2528–2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Prokopowicz, Z.M.; Arce, F.; Biedron, R.; Chiang, C.L.-L.; Ciszek, M.; Katz, D.R.; Nowakowska, M.; Zapotoczny, S.; Marcinkiewicz, J.; Chain, B.M. Hypochlorous Acid: A Natural Adjuvant That Facilitates Antigen Processing, Cross-Priming, and the Induction of Adaptive Immunity. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 824–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, L.; Sedgwick, A.C.; Sun, X.; Bull, S.D.; He, X.-P.; James, T.D. Reaction-Based Fluorescent Probes for the Detection and Imaging of Reactive Oxygen, Nitrogen, and Sulfur Species. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2582–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, Q.; Lee, K.-A.; Lee, S.; Lee, K.M.; Lee, W.-J.; Yoon, J. A Highly Specific Fluorescent Probe for Hypochlorous Acid and Its Application in Imaging Microbe-Induced HOCl Production. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 9944–9949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Chen, L.; Xu, Q.; Chen, X.; Yoon, J. Design Principles, Sensing Mechanisms, and Applications of Highly Specific Fluorescent Probes for HOCl/OCl−. Acc. Chem. Res. 2019, 52, 2158–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.-T.; Kwon, N.; Wang, S.; Wang, B.; He, X.; Yoon, J.; Shen, J. Sulfur-Based Fluorescent Probes for HOCl: Mechanisms, Design, and Applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2022, 450, 214232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.-I.; Park, S.; Choi, Y.; Kim, Y. A BODIPY-Based Probe for the Selective Detection of Hypochlorous Acid in Living Cells. Chem. Asian J. 2011, 6, 1358–1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shu, W.; Jia, P.; Chen, X.; Li, X.; Huo, Y.; Liu, F.; Wang, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhu, B.; Yan, L.; et al. A Highly Selective Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for the Sensitive Detection of Hypochlorous Acid and Its Bioimaging Applications. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 64315–64322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yin, X.; Hong, J.; Deng, Y.; Feng, G. A NIR Fluorescence Probe Having Significant Fluorescence Turn-on Signal at 700 Nm and Large Stokes Shift for Rapid Detection of HOCl in vivo. Talanta 2021, 223, 121768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, H.; Li, F.; Chen, Y.; Kwok, R.T.K.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Hou, J.; Tang, B.Z. A Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe Based on AIEgen for Detecting HClO in Living Cells. Chem. Commun. Camb. Engl. 2020, 56, 14613–14616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, X.; Li, Z.; Yang, L.; Han, J.; Han, S. A Self-Referenced Nanodosimeter for Reaction Based Ratiometric Imaging of Hypochlorous Acid in Living Cells. Chem. Sci. 2012, 4, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Q.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Ge, Z.; Huang, H.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. An Endoplasmic Reticulum-Targeted Two-Photon Fluorescent Probe for Bioimaging of HClO Generated during Sleep Deprivation. Spectrochim. Acta. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2020, 229, 117992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenmoku, S.; Urano, Y.; Kojima, H.; Nagano, T. Development of a Highly Specific Rhodamine-Based Fluorescence Probe for Hypochlorous Acid and Its Application to Real-Time Imaging of Phagocytosis. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 7313–7318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cheng, D.; Zhu, L.; Wang, P.; Liu, H.-W.; Chen, M.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.-B. Engineering Dithiobenzoic Acid Lactone-Decorated Si-Rhodamine as a Highly Selective near-Infrared HOCl Fluorescent Probe for Imaging Drug-Induced Acute Nephrotoxicity. Chem. Commun. Camb. Engl. 2019, 55, 10916–10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, S.; Xing, M.; Cao, D.; Lin, W. Fluorescence Response of a Fluorescein Derivative for Hypochlorite Ion and Its Application for Biological Imaging in Wounded Zebrafish and Living Mice. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 327, 128848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, L.; Lin, W.; Xie, Y.; Chen, B.; Song, J. Fluorescent Detection of Hypochlorous Acid from Turn-on to FRET-Based Ratiometry by a HOCl-Mediated Cyclization Reaction. Chem. Weinh. Bergstr. Ger. 2012, 18, 2700–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, B.; Li, P.; Shu, W.; Wang, X.; Liu, C.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Tang, B. Highly Specific and Ultrasensitive Two-Photon Fluorescence Imaging of Native HOCl in Lysosomes and Tissues Based on Thiocarbamate Derivatives. Anal. Chem. 2016, 88, 12532–12538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, D.; Li, G.; Zhang, S.; Zhu, M.; Li, C.; Qiao, R. Mitochondria-Targeted Fluorescence Probe for Endogenous Hypochlorite Imaging in Living Cells and Zebrafishs. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 259, 816–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Yu, H.; Zhu, W.; Yao, X.; Liu, W.; Yang, S.; Zhou, F.; Liu, Y. Near Infrared Fluorescent Probe for in Vivo Bioimaging of Endogenous Hypochlorous Acid. Dyes Pigments 2021, 188, 109218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vedamalai, M.; Kedaria, D.; Vasita, R.; Gupta, I. Oxidation of Phenothiazine Based Fluorescent Probe for Hypochlorite and Its Application to Live Cell Imaging. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2018, 263, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Y.; Zheng, W.; Yao, Y.; Wang, D.; Lv, G.; Li, C. Phenoxazine-based Near-infrared Fluorescent Probes for the Specific Detection of Copper (II) Ions in Living Cells. Chem.—Asian J. 2020, 15, 2864–2867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-R.; Liu, Y.; Feng, X.; Zhao, B.-X. Recent Progress in the Development of Fluorescent Probes for the Detection of Hypochlorous Acid. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 240, 18–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, H.; Fan, J.; Wang, J.; Mu, H.; Peng, X. An “Enhanced PET”-Based Fluorescent Probe with Ultrasensitivity for Imaging Basal and Elesclomol-Induced HClO in Cancer Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 12820–12823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Heo, C.H.; Kim, G.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, H.M.; Yoon, J. Development of Imidazoline-2-Thiones Based Two-Photon Fluorescence Probes for Imaging Hypochlorite Generation in a Co-Culture System. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 4890–4894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, G.-J.; Liang, Z.-Z.; Bi, J.; Zhang, H.; Meng, H.-M.; Su, L.; Gong, Y.-J.; Feng, S.; Zhang, G. A Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probe Based on Photostable Si-Rhodamine for Imaging Hypochlorous Acid during Lysosome-Involved Inflammatory Response. Anal. Chim. Acta 2019, 1048, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Q.; Jia, P.; Zhuang, Z.; Liu, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Sheng, W.; Li, Z.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, B.; et al. Rational Design of a Hepatoma-Specific Fluorescent Probe for HOCl and Its Bioimaging Applications in Living HepG2 Cells. Anal. Chem. 2019, 91, 2163–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, X.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; Li, Y.; Wang, K.; Zhao, Z.; Jiao, X.; Tang, B. A Two-Photon Fluorescent Probe for Ratiometric Visualization of Hypochlorous Acid in Live Cells and Animals Based on a Selenide Oxidation/Elimination Tandem Reaction. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 11965–11968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Chen, L.; Jangili, P.; Sharma, A.; Li, W.; Hou, J.-T.; Qin, C.; Yoon, J.; Kim, J.S. Design and Applications of Fluorescent Detectors for Peroxynitrite. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2018, 374, 36–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, J.-T.; Kim, H.S.; Duan, C.; Ji, M.S.; Wang, S.; Zeng, L.; Ren, W.X.; Kim, J.S. A Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Detecting Hypochlorite in the Endoplasmic Reticulum. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 2533–2536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Yuan, F.; Wang, S.; Duan, R.; Ren, W.X.; Hou, J.-T. Detection of Atherosclerosis-Associated HOCl Using a Mitochondria-Targeted Fluorescent Probe. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2021, 348, 130695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Yang, L.; Wang, Z.; Hua, Y.; Zhang, D.; Bao, B.; Bao, C.; Gong, X.; Zhu, L. Coumarin Photocaging Groups Modified with an Electron-Rich Styryl Moiety at the 3-Position: Long-Wavelength Excitation, Rapid Photolysis, and Photobleaching. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 3722–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platkov, M.; Tirosh, R.; Kaufman, M.; Zurgil, N.; Deutsch, M. Photobleaching of Fluorescein as a Probe for Oxidative Stress in Single Cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2014, 140, 306–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, N.; Szlasa, W.; Saczko, J.; Chwiłkowska, A. Potential of Cyanine Derived Dyes in Photodynamic Therapy. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Kim, H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, Y. A New Strategy for Fluorogenic Esterase Probes Displaying Low Levels of Non-Specific Hydrolysis. Chem.-Eur. J. 2015, 21, 9645–9649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Li, S.; Lv, H.; Shen, J.; He, X.; Peng, B. BODIPY-Based Rapid Response Fluorescence Probe for Sensing and Bioimaging Endogenous Superoxide Anion in Living Cells. Spectrochim. Acta. A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2021, 269, 120766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neese, F.; Wennmohs, F.; Becker, U.; Riplinger, C. The ORCA Quantum Chemistry Program Package. J. Chem. Phys. 2020, 152, 224108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanwell, M.D.; Curtis, D.E.; Lonie, D.C.; Vandermeersch, T.; Zurek, E.; Hutchison, G.R. Avogadro: An Advanced Semantic Chemical Editor, Visualization, and Analysis Platform. J. Cheminformatics 2012, 4, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ulrich, G.; Ziessel, R.; Harriman, A. The Chemistry of Fluorescent Bodipy Dyes: Versatility Unsurpassed. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 1184–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]







Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, H.; Feng, Q.; Hou, J.-T.; Li, Z.; Shen, J. Carboxy Bodipy-Based Fast Trigger Fluorescent Probe for Imaging Endogenous Hypochlorous Acid. Chemosensors 2023, 11, 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11010026
Zhang H, Feng Q, Hou J-T, Li Z, Shen J. Carboxy Bodipy-Based Fast Trigger Fluorescent Probe for Imaging Endogenous Hypochlorous Acid. Chemosensors. 2023; 11(1):26. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11010026
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Hao, Qincong Feng, Ji-Ting Hou, Zhipeng Li, and Jianliang Shen. 2023. "Carboxy Bodipy-Based Fast Trigger Fluorescent Probe for Imaging Endogenous Hypochlorous Acid" Chemosensors 11, no. 1: 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11010026
APA StyleZhang, H., Feng, Q., Hou, J.-T., Li, Z., & Shen, J. (2023). Carboxy Bodipy-Based Fast Trigger Fluorescent Probe for Imaging Endogenous Hypochlorous Acid. Chemosensors, 11(1), 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors11010026