Easy-to-Use Chemiluminescent-Based Assay for a Rapid and Low-Cost Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity of Cosmetic Products
Abstract
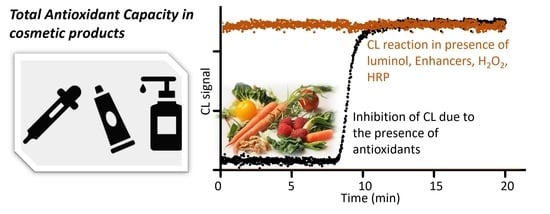
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Reagents
2.2. Analytical Device
2.3. Assay Procedure
2.3.1. Sample Pretreatment
- A total of 0.1 g of sample was dispersed in 1 mL of PBS, vortexed for 1 min and filtrated. The obtained mixture was suitably diluted with PBS at the time of analysis in order to obtain the appearance of the CL signal within the linearity range of the calibration curve.
- A total of 0.1 g of sample was dispersed in 1 mL of Tris buffer solution (0.1 M, pH 8.6) containing 1 mM Triton X-100 (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MO, USA) and 2 mM CaCl2 (TriCaT) and vortexed for 1 min. The obtained mixture was suitably diluted with the TriCaT buffer at the time of analysis in order to obtain the appearance of the CL signal within the linearity range of the calibration curve.
- A total of 0.1 g of sample was dispersed in 1 mL of a solution composed by Isopropyl alchol (60%) and PBS (40%) (IA-PBS) and vortexed for 1 min. The obtained mixture was suitably diluted with PBS at the time of analysis in order to obtain the appearance of the CL signal within the linearity range of the calibration curve.
2.3.2. Analytical Procedure and Data Elaboration
- -
- The instrumental background signal by measuring the signal relative to an empty well;
- -
- The background signal due to the CL substrate in the absence of sample and HRP (4 µL of CL substrate and 16 µL of PBS);
- -
- The blank signal obtained in the absence of antioxidants which serves as a control to verify the correct kinetics of the CL luminol–H2O2–HRP–enhancers system. In this case, 12 µL of PBS, 4 µL of CL substrate, and 4 µL containing the HRP 5 pg/mL enzyme were added to the well.
2.4. Formulations Tested and Samples
3. Results
3.1. Assay Optimization
3.2. Calibration Curve
3.3. Pretreatment of the Sample
3.4. Evaluation of Accuracy and Precision
3.5. Analysis on Real Samples
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- De Lima Cherubim, D.J.; Buzanello Martins, C.V.; Oliveira Fariña, L.; da Silva de Lucca, R.A. Polyphenols as natural antioxidants in cosmetics applications. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 33–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, S.; Ferreira, M.; Oliveira, A.S.; Magalhaes, C.; Sousa, M.E.; Pinto, M.; Sousa Lobo, J.M.; Almeida, I.F. Evolution of the use of anti-oxidants in anti-ageing cosmetics. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2019, 41, 378–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, A.A.; Aiyelaagbe, O.O.; Usman, L.A.; Ameen, O.M.; Lawal, A. Antioxidants: Its medicinal and pharmacological applications. AJPAC 2010, 4, 142–151. [Google Scholar]
- Hoang, H.T.; Moon, J.Y.; Lee, Y.C. Natural Antioxidants from Plant Extracts in Skincare Cosmetics: Recent Applications, Challenges and Perspectives. Cosmetics 2021, 8, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Maris, A.; Melandri, S.; Lesarri, A.; Evangelisti, L. Molecular structure and internal dynamics of the antioxidant 2,6-di-tert-butylphenol. J. Mol. Struc. 2024, 1296, 136910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Maris, A.; Melandri, S.; Lesarri, A.; Evangelisti, L. The Structure of 2,6-Di-tert-butylphenol–Argon by Rotational Spectroscopy. Molecules 2023, 28, 8111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palmieri, M.G.S.; Cruz, L.T.; Bertges, F.S.; Húngaro, H.M.; Batista, L.R.; da Silva, S.S.; do Amaral, M.D.P.H. Enhancement of antioxidant properties from green coffee as promising ingredient for food and cosmetic industries. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Li, A.; Li, S.; Tang, J.; Li, L.; Xiong, L. Natural components in sunscreens: Topical formulations with sun protection factor (SPF). Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 134, 111161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, M.L.; Silva, A.C.; Araújo, C.R.; Esteves, E.A.; Dessimoni-Pinto, N.A. Determinação do potencial antioxidante in vitro de frutos do cerrado brasileiro. Rev. Bras. Frutic. 2013, 35, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Duan, E. Fighting against skin aging: The way from bench to bedside. Cell Transplant. 2018, 27, 729–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farage, M.A.; Miller, K.W.; Elsner, P.; Maibach, H.I. Intrinsic and extrinsic factors in skin ageing: A review. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2008, 30, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rees, J.L. The Genetics of Sun Sensitivity in Humans. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2004, 75, 739–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krutmann, J.; Schikowski, T.; Morita, A.; Berneburg, M. Environmentally-Induced (Extrinsic) Skin Aging: Exposomal Factors and Underlying Mechanisms. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 1096–1103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppé, J.P.; Desprez, P.Y.; Krtolica, A.; Campisi, J. The senescence-associated secretory phenotype: The dark side of tumor suppression. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2010, 5, 99–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flament, F.; Bazin, R.; Qiu, H.; Ye, C.; Laquieze, S.; Rubert, V.; Decroux, A.; Simonpietri, E.; Piot, B. Solar exposure(s) and facial clinical signs of aging in Chinese women: Impacts upon age perception. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 8, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-K.; Zhong, L.; Santiago, J.L. Anti-Inflammatory and Skin Barrier Repair Effects of Topical Application of Some Plant Oils. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 19, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajaram, S.; Jones, J.; Lee, G.J. Plant-based dietary patterns, plant foods, and age-related cognitive decline. Adv. Nutr. 2019, 10 (Suppl. S4), S422–S436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cavinato, M.; Waltenberger, B.; Baraldo, G.; Grade, C.V.; Stuppner, H.; Jansen-Dürr, P. Plant extracts and natural compounds used against UVB-induced photoaging. Biogerontology 2017, 18, 499–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petruk, G.; Del Giudice, R.; Rigano, M.M.; Monti, D.M. Antioxidants from Plants Protect against Skin Photoaging. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 1454936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pisoschi, A.M.; Pop, A. The Role of Antioxidants in the Chemistry of Oxidative Stress: A review. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 97, 55–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kusumawati, I.; Indrayanto, G. Natural antioxidants in cosmetics. In Studies in Natural Products Chemistry; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; Volume 40, pp. 485–505. [Google Scholar]
- Darvin, M.E.; Sterry, W.; Lademann, J.; Vergou, T. The role of carotenoids in human skin. Molecule 2011, 16, 10491–10506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinnell, S.R. Cutaneous photodamage, oxidative stress, and topical antioxidant protection. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2003, 48, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabria, D.; Guardigli, M.; Severi, P.; Trozzi, I.; Pace, A.; Cinti, S.; Mirasoli, M. A smartphone-based chemosensor to evaluate antioxidants in agri-food matrices by in situ AuNP formation. Sensor 2021, 21, 5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ratz-Lyko, A.; Arct, J.; Pytkowska, K. Methods for evaluation of cosmetic antioxidant capacity. Ski. Res. Technol. 2012, 18, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munteanu, I.G.; Apetrei, C. Analytical methods used in determining antioxidant activity: A review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, M.G.; Chiari, B.G.; Correa, M.A.; Chung, M.C.; Isaac, V.L. Validation of an alternative analytical method for the quantification of antioxidant activity in plant extracts. Lat. Am. J. Pharm. 2013, 32, 90–95. [Google Scholar]
- Wahab, N.A.; Rahman, R.A.; Ismail, A.; Mustafa, S.; Hashim, P. Assessment of antioxidant capacity, anti-collagenase and anti-elastase assays of Malaysian unfermented cocoa bean for cosmetic application. Nat. Prod. Chem. Res. 2014, 2, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Pelle, E.; Mammone, T.; Marenus, K.; Dicanio, D.; Maes, D. A test for antioxidant activity in cosmetic formulations. J. Cosm. Sci. 2002, 53, 237–240. [Google Scholar]
- Mapoung, S.; Semmarath, W.; Arjsri, P.; Umsumarng, S.; Srisawad, K.; Thippraphan, P.; Limtrakul, P. Determination of phenolic content, antioxidant activity, and tyrosinase inhibitory effects of functional cosmetic creams available on the Thailand market. Plant 2021, 10, 1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbood, A. Determination of phenolic content and antioxidant activity of some cosmetic creams available in Syrian market. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 11, 280–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beissenhirtz, M.; Scheller, F.; Lisdat, F. Immobilized cytochrome c sensor in organic/aqueous media for the characterization of hydrophilic and hydrophobic antioxidants. Electroanalysis 2003, 15, 1425–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylov, A.V.; Sczech, R.; Lisdat, F. Characterization of antioxidants using a fluidic chip in aqueous/organic media. Analyst 2007, 132, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Othman, A.; Norton, L.; Finny, A.S.; Andreescu, S. Easy-to-use and inexpensive sensors for assessing the quality and traceability of cosmetic antioxidants. Talanta 2020, 208, 120473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharpe, E.; Frasco, T.; Andreescu, D.; Andreescu, S. Portable ceria nanoparticle-based assay for rapid detection of food antioxidants (NanoCerac). Analyst 2013, 138, 249–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ornatska, M.; Sharpe, E.; Andreescu, D.; Andreescu, S. Paper bioassay based on ceria nanoparticles as colorimetric probes. Anal. Chem. 2011, 83, 4273–4280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roda, A.; Arduini, F.; Mirasoli, M.; Zangheri, M.; Fabiani, L.; Colozza, N.; Moscone, D. A challenge in biosensors: Is it better to measure a photon or an electron for ultrasensitive detection? Biosens. Bioelectron. 2020, 155, 112093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabretta, M.M.; Zangheri, M.; Calabria, D.; Lopreside, A.; Montali, L.; Marchegiani, E.; Michelini, E. Based Immunosensors with Bio-Chemiluminescence Detection. Sensor 2021, 21, 4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calabretta, M.M.; Lopreside, A.; Montali, L.; Zangheri, M.; Evangelisti, L.; D’Elia, M.; Michelini, E. Portable light detectors for bioluminescence biosensing applications: A comprehensive review from the analytical chemist’s perspective. Anal. Chim. Acta 2022, 1200, 339583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazzarini, E.; Pace, A.; Trozzi, I.; Zangheri, M.; Guardigli, M.; Calabria, D.; Mirasoli, M. An origami paper-based biosensor for allergen detection by chemiluminescence immunoassay on magnetic microbeads. Biosensor 2022, 12, 825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangheri, M.; Calabretta, M.M.; Calabria, D.; Fiori, J.; Guardigli, M.; Michelini, E.; Evangelisti, L. Immunological analytical techniques for cosmetics quality control and process monitoring. Processes 2021, 9, 1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, T.M.; Kattal, N.; Sharma, R.K.; Sikka, S.C.; Thomas, A.J., Jr.; Mascha, E.; Agarwal, A. Enhanced chemiluminescence assay vs colorimetric assay for measurement of the total antioxidant capacity of human seminal plasma. J. Androl. 2003, 24, 676–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, L.; Plieth, C. Total low-molecular-weight antioxidants as a summary parameter, quantified in biological samples by a chemiluminescence inhibition assay. Nat. Prot. 2010, 5, 1627–1634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Kostov, Y.; Bruck, H.A.; Rasooly, A. Carbon nanotubes with enhanced chemiluminescence immunoassay for CCD-based detection of Staphylococcal enterotoxin B in food. Anal. Chem. 2008, 80, 8532–8537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.Z.; Fu, Y.Z.; Ren, S.W.; Cao, J.T.; Liu, Y.M. A novel chemiluminescence imaging immunosensor for prostate specific antigen detection based on a multiple signal amplification strategy. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2021, 171, 112729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhang, C. A novel paper-based microfluidic enhanced chemiluminescence biosensor for facile, reliable and highly-sensitive gene detection of Listeria monocytogenes. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2015, 209, 399–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabria, D.; Zangheri, M.; Trozzi, I.; Lazzarini, E.; Pace, A.; Mirasoli, M.; Guardigli, M. Smartphone-Based Chemiluminescent Origami µPAD for the Rapid Assessment of Glucose Blood Levels. Biosensors 2021, 11, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Feng, Y.; Liu, F.; Tan, C.; Xu, N.; Jiang, Y.; Tan, Y. Universal smartphone-assisted label-free CRISPR/Cas12a-DNAzyme chemiluminescence biosensing platform for on-site detection of nucleic acid and non-nucleic acid targets. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 274, 115929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Aggarwal, K.; Vinitha, T.U.; Nguyen, T.; Han, J.; Ahn, C.H. A new microchannel capillary flow assay (MCFA) platform with lyophilized chemiluminescence reagents for a smartphone-based POCT detecting malaria. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2020, 6, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabria, D.; Pace, A.; Lazzarini, E.; Trozzi, I.; Zangheri, M.; Guardigli, M.; Mirasoli, M. Smartphone-Based Chemiluminescence Glucose Biosensor Employing a Peroxidase-Mimicking, Guanosine-Based Self-Assembled Hydrogel. Biosensors 2023, 13, 650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zhou, X.; Qi, P. A dual-functional smartphone-based sensor for colorimetric and chemiluminescent detection: A case study for fluoride concentration mapping. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2020, 319, 128254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, D.R.; Soares, R.R.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P. Performance of hydrogenated amorphous silicon thin film photosensors at ultra-low light levels: Towards attomole sensitivities in lab-on-chip biosensing applications. IEEE Sens. J. 2017, 17, 6895–6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, N.M.M.; Dong, T. Measurement of salivary cortisol by a chemiluminescent organic-based immunosensor. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2014, 24, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.W.; Huang, C.C.; Lin, Y.Y.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, K.H.; Su, W.F. Optical properties and photoconductivity of amorphous silicon carbon nitride thin film and its application for UV detection. Diam. Relat. Mater. 2005, 14, 1010–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamei, T.; Paegel, B.M.; Scherer, J.R.; Skelley, A.M.; Street, R.A.; Mathies, R.A. Integrated hydrogenated amorphous Si photodiode detector for microfluidic bioanalytical devices. Anal. Chem. 2003, 75, 5300–5305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Touahir, L.; Moraillon, A.; Allongue, P.; Chazalviel, J.N.; de Villeneuve, C.H.; Ozanam, F.; Gouget-Laemmel, A.C. Highly sensitive and reusable fluorescence microarrays based on hydrogenated amorphous silicon–carbon alloys. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 952–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, P.; Prazeres, D.M.F.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P. Microspot-based ELISA in microfluidics: Chemiluminescence and colorimetry detection using integrated thin-film hydrogenated amorphous silicon photodiodes. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 4063–4071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novo, P.; Moulas, G.; Prazeres, D.M.F.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P. Detection of ochratoxin A in wine and beer by chemiluminescence-based ELISA in microfluidics with integrated photodiodes. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 2013, 176, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conde, J.P.; Pimentel, A.C.; Pereira, A.T.; Gouvêa, A.; Prazeres, D.M.F.; Chu, V. Detection of molecular tags with an integrated amorphous silicon photodetector for biological applications. J. Non Cryst. Solids 2008, 354, 2594–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.T.; Pimentel, A.C.; Chu, V.; Prazeres, D.M.F.; Conde, J.P. Chemiluminescent detection of horseradish peroxidase using an integrated amorphous silicon thin-film photosensor. IEEE Sens. J. 2009, 9, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangheri, M.; Mirasoli, M.; Nascetti, A.; Caputo, D.; Bonvicini, F.; Gallinella, G.; de Cesare, G.; Roda, A. Microfluidic cartridge with integrated array of amorphous silicon photosensors for chemiluminescence detection of viral DNA. Sens. Biosens. Res. 2016, 7, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinto, I.F.; Santos, D.R.; Caneira, C.R.; Soares, R.R.; Azevedo, A.M.; Chu, V.; Conde, J.P. Optical biosensing in microfluidics using nanoporous microbeads and amorphous silicon thin-film photodiodes: Quantitative analysis of molecular recognition and signal transduction. J. Micromech. Microeng. 2018, 28, 094004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Cang, H.; Xie, Y.; Li, H.; Li, H. A miniaturized photodiode-based chemiluminescence sensor for measurement of fractional exhaled nitric oxide. Sens, Actuat. B Chem. 2023, 394, 134402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabria, D.; Trozzi, I.; Lazzarini, E.; Pace, A.; Zangheri, M.; Iannascoli, L.; Mirasoli, M. AstroBio-CubeSat: A lab-in-space for chemiluminescence-based astrobiology experiments. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2023, 226, 115110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Celeiro, M.; Garcia-Jares, C.; Llompart, M.; Lores, M. Recent Advances in Sample Preparation for Cosmetics and Personal Care Products Analysis. Molecules 2021, 26, 4900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girotti, S.; Ferri, E.; Fini, F.; Bolelli, L.; Sabatini, A.G.; Budini, R.; Sichertova, D. Automated and manual luminescent assay of antioxidant capacity: Analytical features by comparison. Talanta 2004, 64, 665–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latimer, G.W., Jr. Appendix F: Guidelines for Standard Method Performance Requirements: Official Methods of Analysis; AOAC International: Rockville, MD, USA, 2016; pp. 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Guideline, I.H. Biooanalytical Method Validation M10; European Medicines Agency: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019.




| Concentration (µM± SD 1) | Recovery (%) 2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PBS | IA-PBS | Triton | PBS | IA-PBS | Triton | |
| Formulation A | ||||||
| A1 | 72 ± 1 | 64 ± 4 | 48 ± 3 | 131 | 116 | 87 |
| A2 | 73 ± 7 | 65 ± 6 | 59 ± 1 | 128 | 113 | 103 |
| Formulation B | ||||||
| B1 | 65 ± 2 | 74 ± 1 | 50 ± 1 | 118 | 135 | 91 |
| B2 | 44 ± 5 | 59 ± 1 | 51 ± 4 | 76 | 104 | 90 |
| Formulation C | ||||||
| C1 | 71 ± 3 | 66 ± 1 | 53 ± 1 | 129 | 120 | 96 |
| C2 | 57 ± 1 | 53 ± 2 | 51 ± 5 | 101 | 92 | 90 |
| Concentration (µM± SD 1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | 30 | 45 | 67.5 | 100 | |
| Formulation 1 | |||||
| Day 1 | 11 ± 1 | 33 ± 4 | 48 ± 3 | 62 ± 5 | 116 ± 9 |
| Day 2 | 12 ± 3 | 25 ± 3 | 50 ± 4 | 61 ± 7 | 98 ± 7 |
| Formulation 2 | |||||
| Day 1 | 9 ± 2 | 32 ± 3 | 41 ± 4 | 73 ± 7 | 110 ± 8 |
| Day 2 | 12 ± 2 | 27 ± 4 | 47 ± 5 | 75 ± 8 | 104 ± 7 |
| Sample | Dilution Factor | Concentration (mM ± SD 1) | Recovery (%) 2 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Micellar water containing natural extracts of green coffee. | 1:10 | 0.4 ± 0.02 | Data about the real concentration not known |
| Micellar water containing antioxidant components from olive leaves | 1:10 | 0.2 ± 0.04 | Data about the real concentration not known |
| Skin toner containing antioxidant molecules extracted from prune Kakadu | 1:150 | 2.2 ± 0.1 | Data about the real concentration not known |
| Facial cream containing a concentration of vitamin C equal to 30%. | 1:30,000 | 1.4 ± 0.4 | 83% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pour, S.R.S.; Calabria, D.; Nascetti, A.; Caputo, D.; De Cesare, G.; Guardigli, M.; Zangheri, M.; Mirasoli, M. Easy-to-Use Chemiluminescent-Based Assay for a Rapid and Low-Cost Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity of Cosmetic Products. Chemosensors 2024, 12, 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12020025
Pour SRS, Calabria D, Nascetti A, Caputo D, De Cesare G, Guardigli M, Zangheri M, Mirasoli M. Easy-to-Use Chemiluminescent-Based Assay for a Rapid and Low-Cost Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity of Cosmetic Products. Chemosensors. 2024; 12(2):25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12020025
Chicago/Turabian StylePour, Seyedeh Rojin Shariati, Donato Calabria, Augusto Nascetti, Domenico Caputo, Giampiero De Cesare, Massimo Guardigli, Martina Zangheri, and Mara Mirasoli. 2024. "Easy-to-Use Chemiluminescent-Based Assay for a Rapid and Low-Cost Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity of Cosmetic Products" Chemosensors 12, no. 2: 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12020025
APA StylePour, S. R. S., Calabria, D., Nascetti, A., Caputo, D., De Cesare, G., Guardigli, M., Zangheri, M., & Mirasoli, M. (2024). Easy-to-Use Chemiluminescent-Based Assay for a Rapid and Low-Cost Evaluation of the Antioxidant Activity of Cosmetic Products. Chemosensors, 12(2), 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/chemosensors12020025