The Value of CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, and CXCL8 as Potential Prognosis Markers in Cervical Cancer: Evidence of E6/E7 from HPV16 and 18 in Chemokines Regulation
Abstract
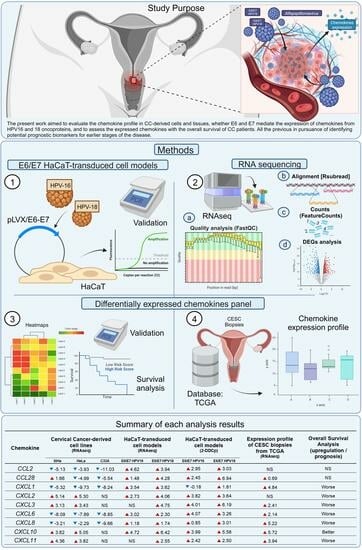
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
2.2. Quantitative PCR
2.3. RNAseq
2.4. Bioinformatics
2.5. Expression Profile
2.6. Survival Analysis
2.7. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Differential Chemokines Expression between Cervical Cancer-Derived Cell Lines and Non-Tumorigenic Keratinocytes
3.2. E6/E7 HPV16 and 18 Modulate the Chemokines Expression
3.3. High Expression of Chemokines in Cervical Cancer Tissues
3.4. Prognostic Outcome Linkage with Chemokines Expression in Cervical Cancer Patients
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Höhn, A.K.; Brambs, C.E.; Hiller, G.G.R.; May, D.; Schmoeckel, E.; Horn, L.C. 2020 WHO Classification of Female Genital Tumors. Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 2021, 81, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, D.; Vignat, J.; Lorenzoni, V.; Eslahi, M.; Ginsburg, O.; Lauby-Secretan, B.; Arbyn, M.; Basu, P.; Bray, F.; Vaccarella, S. Global estimates of incidence and mortality of cervical cancer in 2020: A baseline analysis of the WHO Global Cervical Cancer Elimination Initiative. Lancet Glob. Health 2023, 11, e197–e206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hull, R.; Mbele, M.; Makhafola, T.; Hicks, C.; Wang, S.M.; Reis, R.M.; Mehrotra, R.; Mkhize-Kwitshana, Z.; Kibiki, G.; Bates, D.O.; et al. Cervical cancer in low and middle-income countries (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 2058–2074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruni, L.A.G.; Serrano, B.; Mena, M.; Gómez, D.; Muñoz, J.; Bosch, F.X.; de Sanjosé, S. Human Papillomavirus and Related Diseases in Mexico; Summary Report; Institut Català d’Oncologia/IARC: Barcelona, Spain, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Prendiville, W.S.R. Colposcopy and Treatment of Cervical Precancer; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017; Volume 45, p. 178. [Google Scholar]
- Lim, A.W.; Ramirez, A.J.; Hamilton, W.; Sasieni, P.; Patnick, J.; Forbes, L.J. Delays in diagnosis of young females with symptomatic cervical cancer in England: An interview-based study. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2014, 64, e602–e610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chesson, H.W.; Dunne, E.F.; Hariri, S.; Markowitz, L.E. The estimated lifetime probability of acquiring human papillomavirus in the United States. Sex. Transm. Dis. 2014, 41, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McBride, A.A. Human papillomaviruses: Diversity, infection and host interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2022, 20, 95–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IARC. Human Papillomaviruses; IARC: Lyon, France, 2007; Volume 90, p. 689. [Google Scholar]
- Bruni, L.; Diaz, M.; Castellsagué, X.; Ferrer, E.; Bosch, F.X.; de Sanjosé, S. Cervical human papillomavirus prevalence in 5 continents: Meta-analysis of 1 million women with normal cytological findings. J. Infect. Dis. 2010, 202, 1789–1799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- zur Hausen, H. Papillomaviruses in the causation of human cancers—A brief historical account. Virology 2009, 384, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sanjose, S.; Quint, W.G.; Alemany, L.; Geraets, D.T.; Klaustermeier, J.E.; Lloveras, B.; Bosch, F.X. Human papillomavirus genotype attribution in invasive cervical cancer: A restrospective cross-sectional worldwide study. Lancet Oncol. 2010, 11, 1048–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pal, A.; Kundu, R. Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7: The Cervical Cancer Hallmarks and Targets for Therapy. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 3116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jabbar, S.F.; Abrams, L.; Glick, A.; Lambert, P.F. Persistence of high-grade cervical dysplasia and cervical cancer requires the continuous expression of the human papillomavirus type 16 E7 oncogene. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4407–4414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamato, K.; Yamada, T.; Kizaki, M.; Ui-Tei, K.; Natori, Y.; Fujino, M.; Nishihara, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Nasu, Y.; Saigo, K.; et al. New highly potent and specific E6 and E7 siRNAs for treatment of HPV16 positive cervical cancer. Cancer Gene Ther. 2008, 15, 140–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scheffner, M.; Werness, B.A.; Huibregtse, J.M.; Levine, A.J.; Howley, P.M. The E6 oncoprotein encoded by human papillomavirus types 16 and 18 promotes the degradation of p53. Cell 1990, 63, 1129–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todorovic, B.; Hung, K.; Massimi, P.; Avvakumov, N.; Dick, F.A.; Shaw, G.S.; Banks, L.; Mymryk, J.S. Conserved region 3 of human papillomavirus 16 E7 contributes to deregulation of the retinoblastoma tumor suppressor. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 13313–13323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Roberts, J.; Dakic, A.; Zhang, Y.; Schlegel, R. HPV E7 contributes to the telomerase activity of immortalized and tumorigenic cells and augments E6-induced hTERT promoter function. Virology 2008, 375, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, R.A.; Thomas, M.; Banks, L.; Roberts, S. Activity of the human papillomavirus E6 PDZ-binding motif correlates with an enhanced morphological transformation of immortalized human keratinocytes. J. Cell Sci. 2003, 116, 4925–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghittoni, R.; Accardi, R.; Hasan, U.; Gheit, T.; Sylla, B.; Tommasino, M. The biological properties of E6 and E7 oncoproteins from human papillomaviruses. Virus Genes 2010, 40, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vambutas, A.; Bonagura, V.R.; Steinberg, B.M. Altered expression of TAP-1 and major histocompatibility complex class I in laryngeal papillomatosis: Correlation of TAP-1 with disease. Clin. Diagn. Lab. Immunol. 2000, 7, 79–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.; Liem, A.; Miller, J.A.; Lambert, P.F. Human papillomavirus types 16 E6 and E7 contribute differently to carcinogenesis. Virology 2000, 267, 141–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe-Seyler, K.; Bossler, F.; Braun, J.A.; Herrmann, A.L.; Hoppe-Seyler, F. The HPV E6/E7 Oncogenes: Key Factors for Viral Carcinogenesis and Therapeutic Targets. Trends Microbiol. 2018, 26, 158–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dust, K.; Carpenter, M.; Chen, J.C.; Grant, C.; McCorrister, S.; Westmacott, G.R.; Severini, A. Human Papillomavirus 16 E6 and E7 Oncoproteins Alter the Abundance of Proteins Associated with DNA Damage Response, Immune Signaling and Epidermal Differentiation. Viruses 2022, 14, 1764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomaic, V. Functional Roles of E6 and E7 Oncoproteins in HPV-Induced Malignancies at Diverse Anatomical Sites. Cancers 2016, 8, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iuliano, M.; Mangino, G.; Chiantore, M.V.; Zangrillo, M.S.; Accardi, R.; Tommasino, M.; Fiorucci, G.; Romeo, G. Human Papillomavirus E6 and E7 oncoproteins affect the cell microenvironment by classical secretion and extracellular vesicles delivery of inflammatory mediators. Cytokine 2018, 106, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castro-Amaya, A.M.; Fernandez-Avila, L.; Barron-Gallardo, C.A.; Moreno-Rios, C.E.; Guevara-Hernandez, S.N.; Magana-Torres, M.T.; Pelayo-Aguirre, C.J.; Jave-Suarez, L.F.; Aguilar-Lemarroy, A. E6/E7 from Beta-2-HPVs 122, 38b, and 107 possess transforming properties in a fibroblast model in vitro. Exp. Cell Res. 2022, 414, 113088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Wu, M.; Zhao, X. Role of chemokine systems in cancer and inflammatory diseases. MedComm 2022, 3, e147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCully, M.L.; Kouzeli, A.; Moser, B. Peripheral Tissue Chemokines: Homeostatic Control of Immune Surveillance T Cells. Trends Immunol. 2018, 39, 734–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, C.E.; Nibbs, R.J.B. A guide to chemokines and their receptors. FEBS J. 2018, 285, 2944–2971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balkwill, F. Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 540–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, M.T.; Luster, A.D. Chemokines in cancer. Cancer Immunol. Res. 2014, 2, 1125–1131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yuan, J. Chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 1/chemokine (C-X-C motif) receptor 2 autocrine loop contributes to cellular proliferation, migration and apoptosis in cervical cancer. Bioengineered 2022, 13, 7579–7591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Hendricks, D.T.; Wamunyokoli, F.; Parker, M.I. A growth-related oncogene/CXC chemokine receptor 2 autocrine loop contributes to cellular proliferation in esophageal cancer. Cancer Res. 2006, 66, 3071–3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadomoto, S.; Izumi, K.; Mizokami, A. The CCL20-CCR6 Axis in Cancer Progression. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bose, S.; Saha, P.; Chatterjee, B.; Srivastava, A.K. Chemokines driven ovarian cancer progression, metastasis and chemoresistance: Potential pharmacological targets for cancer therapy. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 86, 568–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liubomirski, Y.; Lerrer, S.; Meshel, T.; Rubinstein-Achiasaf, L.; Morein, D.; Wiemann, S.; Körner, C.; Ben-Baruch, A. Tumor-Stroma-Inflammation Networks Promote Pro-metastatic Chemokines and Aggressiveness Characteristics in Triple-Negative Breast Cancer. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangaj, D.; Bruand, M.; Grimm, A.J.; Ronet, C.; Barras, D.; Duttagupta, P.A.; Lanitis, E.; Duraiswamy, J.; Tanyi, J.L.; Benencia, F.; et al. Cooperation between Constitutive and Inducible Chemokines Enables T Cell Engraftment and Immune Attack in Solid Tumors. Cancer Cell 2019, 35, 885–900.e810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.M.; Zhao, Y.D.; Li, Q.; He, Y.J. Chemokine CCL14 affected the clinical outcome and correlated with immune infiltrates in thyroid carcinoma. Histol. Histopathol. 2023, 38, 695–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parikh, A.; Shin, J.; Faquin, W.; Lin, D.T.; Tirosh, I.; Sunwoo, J.B.; Puram, S.V. Malignant cell-specific CXCL14 promotes tumor lymphocyte infiltration in oral cavity squamous cell carcinoma. J. Immunother. Cancer 2020, 8, e001048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strieter, R.M.; Burdick, M.D.; Mestas, J.; Gomperts, B.; Keane, M.P.; Belperio, J.A. Cancer CXC chemokine networks and tumour angiogenesis. Eur. J. Cancer 2006, 42, 768–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatia, R.; Kavanagh, K.; Stewart, J.; Moncur, S.; Serrano, I.; Cong, D.; Cubie, H.A.; Haas, J.G.; Busby-Earle, C.; Williams, A.R.W.; et al. Host chemokine signature as a biomarker for the detection of pre-cancerous cervical lesions. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 18548–18558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. FastQC A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data. Available online: https://www.bioinformatics.babraham.ac.uk/projects/fastqc/ (accessed on 10 July 2023).
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. The R package Rsubread is easier, faster, cheaper and better for alignment and quantification of RNA sequencing reads. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frankish, A.; Diekhans, M.; Jungreis, I.; Lagarde, J.; Loveland, J.E.; Mudge, J.M.; Sisu, C.; Wright, J.C.; Armstrong, J.; Barnes, I.; et al. GENCODE 2021. Nucleic Acids Res 2021, 49, D916–D923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Y.; Smyth, G.K.; Shi, W. FeatureCounts: An efficient general purpose program for assigning sequence reads to genomic features. Bioinformatics 2013, 30, 923–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Cho, M.; Wang, X. OncoDB: An interactive online database for analysis of gene expression and viral infection in cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D1334–D1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, Á.; Munkácsy, G.; Győrffy, B. Pancancer survival analysis of cancer hallmark genes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morein, D.; Erlichman, N.; Ben-Baruch, A. Beyond Cell Motility: The Expanding Roles of Chemokines and Their Receptors in Malignancy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Kitajima, S.; Kohno, S.; Yoshida, A.; Tange, S.; Sasaki, S.; Okada, N.; Nishimoto, Y.; Muranaka, H.; Nagatani, N.; et al. Retinoblastoma Inactivation Induces a Protumoral Microenvironment via Enhanced CCL2 Secretion. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 3903–3915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.Z.; Zhang, Z.; Zheng, B.H.; Shi, Y.; Duan, M.; Ma, L.J.; Wang, Z.C.; Dong, L.Q.; Dong, P.P.; Shi, J.Y.; et al. CCL15 Recruits Suppressive Monocytes to Facilitate Immune Escape and Disease Progression in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology 2019, 69, 143–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, V.; Tallapragada, S.; Schaar, B.; Kamat, K.; Chanana, A.M.; Zhang, Y.; Patel, S.; Parkash, V.; Rinker-Schaeffer, C.; Folkins, A.K.; et al. Omental macrophages secrete chemokine ligands that promote ovarian cancer colonization of the omentum via CCR1. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrido, F.; Wild, C.M.; Mittelberger, J.; Dobler, F.; Schneider, M.; Ansorge, N.; Köpke, M.; Strieder, A.; Ditsch, N.; Jeschke, U.; et al. The Role of Chemokines in Cervical Cancers. Medicina 2021, 57, 1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artaza-Irigaray, C.; Molina-Pineda, A.; Aguilar-Lemarroy, A.; Ortiz-Lazareno, P.; Limon-Toledo, L.P.; Pereira-Suarez, A.L.; Rojo-Contreras, W.; Jave-Suarez, L.F. E6/E7 and E6(*) From HPV16 and HPV18 Upregulate IL-6 Expression Independently of p53 in Keratinocytes. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Israr, M.; DeVoti, J.A.; Papayannakos, C.J.; Bonagura, V.R. Role of chemokines in HPV-induced cancers. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2022, 87, 170–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, R.; Tao, R.; Li, X.; Shang, T.; Zhao, S.; Ren, Q. Expression profiling of mRNA and functional network analyses of genes regulated by human papilloma virus E6 and E7 proteins in HaCaT cells. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 979087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Zhao, G.; Chen, H.; Wang, W.; Shang, X.; Sun, Q.; Guo, F.; Ma, X. Analysis of therapeutic targets and prognostic biomarkers of CXC chemokines in cervical cancer microenvironment. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishikawa, R.; Suzumori, N.; Nishiyama, T.; Nishikawa, H.; Arakawa, A.; Sugiura-Ogasawara, M. Clinical significance of serum growth-regulated oncogene alpha (GROalpha) in patients with gynecological cancer. Eur. J. Gynaecol. Oncol. 2012, 33, 138–141. [Google Scholar]
- Man, X.; Yang, X.; Wei, Z.; Tan, Y.; Li, W.; Jin, H.; Wang, B. High expression level of CXCL1/GROalpha is linked to advanced stage and worse survival in uterine cervical cancer and facilitates tumor cell malignant processes. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Dong, Y.; Zhao, S.; Bi, F.; Xuan, M.; Zhu, G.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z. CXCL1 promoted the migration and invasion abilities of oral cancer cells and might serve as a promising marker of prognosis in tongue cancer. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2023, 52, 583–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wu, Q.; Wang, C.; Yang, L.; Liu, P.; Ma, C. AKIP1 promotes angiogenesis and tumor growth by upregulating CXC-chemokines in cervical cancer cells. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2018, 448, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhi, W.; Ferris, D.; Sharma, A.; Purohit, S.; Santos, C.; He, M.; Ghamande, S.; She, J.X. Twelve serum proteins progressively increase with disease stage in squamous cell cervical cancer patients. Int. J. Gynecol. Cancer 2014, 24, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Rui, X.; Han, C.; Wang, C.; Xu, L.; Jiang, X. circRNF13, a novel N(6)-methyladenosine-modified circular RNA, enhances radioresistance in cervical cancer by increasing CXCL1 mRNA stability. Cell Death Discov. 2023, 9, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Li, G.; Li, F. A-kinase interacting protein 1, a potential biomarker associated with advanced tumor features and CXCL1/2 in prostate cancer. Int. J. Biol. Markers 2020, 35, 74–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.C.; Baskaran, R.; Lee, N.H.; Hsu, H.H.; Ho, T.J.; Tu, C.C.; Lin, Y.M.; Viswanadha, V.P.; Kuo, W.W.; Huang, C.Y. CXCL2/CXCR2 axis induces cancer stem cell characteristics in CPT-11-resistant LoVo colon cancer cells via Galphai-2 and Galphaq/11. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 11822–11834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Ye, Y.L.; Li, M.X.; Ye, S.B.; Huang, W.R.; Cai, T.T.; He, J.; Peng, J.Y.; Duan, T.H.; Cui, J.; et al. CXCL2/MIF-CXCR2 signaling promotes the recruitment of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and is correlated with prognosis in bladder cancer. Oncogene 2017, 36, 2095–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, S.; Zhou, Y.; Ye, M.; Li, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y. Construction of an immune-related ceRNA network in cervical cancer based on HPV E6 splicing. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 979884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, X.; Hong, Z.; Mao, Y.; Di, W. Correlations of AKIP1, CXCL1 and CXCL2 expressions with clinicopathological features and survival profiles in cervical cancer patients. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 726–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, P.; Ruan, Y.; Yan, Z.; Gao, Y.; Yang, H.; Wang, S. Comprehensive analysis of lymph nodes metastasis associated genes in cervical cancer and its significance in treatment and prognosis. BMC Cancer 2021, 21, 1230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Y.L.; Li, Y.; Man, X.X.; Sui, H.Y.; Zhao, X.L.; Zhang, P.X.; Qu, X.S.; Zhang, H.; Wang, B.X.; Li, J.; et al. CXCL3 overexpression promotes the tumorigenic potential of uterine cervical cancer cells via the MAPK/ERK pathway. J. Cell Physiol. 2020, 235, 4756–4765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Cao, Y.; Shao, M.L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.B.; Wang, J.T.; Liang, L.C.; Shao, W.W.; Qi, Y.L.; Li, Y.; et al. Chemokine CXCL3 mediates prostate cancer cells proliferation, migration and gene expression changes in an autocrine/paracrine fashion. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 861–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, J.; Ren, Q.; Li, Z.; Wang, W.; Guan, J. CXCL3 overexpression affects the malignant behavior of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells via the MAPK signaling pathway. J. Oral Pathol. Med. 2021, 50, 902–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, S.; Fujii, T.; Kukimoto, I.; Yamamoto, N.; Tsukamoto, T.; Ichikawa, R.; Nishio, E.; Iwata, A. Cytokine expression profiles in cervical mucus from patients with cervical cancer and its precursor lesions. Cytokine 2019, 120, 210–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, R.; Shuai, H.; Luo, X.; Wang, X.; Guan, B. The clinical and prognostic value of CXCL8 in cervical carcinoma patients: Immunohistochemical analysis. Biosci. Rep. 2017, 37, BSR20171021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.B.; Xie, F.; Chang, K.K.; Li, M.Q.; Meng, Y.H.; Wang, X.H.; Li, H.; Li, D.J.; Yu, J.J. Hypoxia promotes the proliferation of cervical carcinoma cells through stimulating the secretion of IL-8. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 575–583. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, M.; Ma, Q.; Xu, J.; Fu, S.; Chen, L.; Wang, B.; Wu, J.; Yang, L. Combining CXCL10 gene therapy and radiotherapy improved therapeutic efficacy in cervical cancer HeLa cell xenograft tumor models. Oncol. Lett. 2015, 10, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; He, H.; Xiao, Y.; Hasim, A.; Yuan, J.; Ye, M.; Li, X.; Hao, Y.; Guo, X. CXCL10 Produced by HPV-Positive Cervical Cancer Cells Stimulates Exosomal PDL1 Expression by Fibroblasts via CXCR3 and JAK-STAT Pathways. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 629350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, W.; Xie, X.Y.; Liu, M.R.; Wang, L.L. MicroRNA-101-5p inhibits the growth and metastasis of cervical cancer cell by inhibiting CXCL6. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2019, 23, 1957–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Wu, H.; Bai, X.; Min, S.; Zhang, J.; Li, C. O-Glycosylating Enzyme GALNT2 Predicts Worse Prognosis in Cervical Cancer. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2022, 28, 1610554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, W.-L.; Chen, Q.; Meng, L.-D.; Huang, X.-M.; Shi, G.-d.; Zong, Q.-Q.; Shen, P.; Lu, Y.-C.; Zhang, Y.-H.; Miao, Y.; et al. The YY1/miR-548t-5p/CXCL11 signaling axis regulates cell proliferation and metastasis in human pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, S.; Lv, M.; Yang, X.; Li, M.; Zhang, Z. CXCL11 promotes self-renewal and tumorigenicity of α2δ1+ liver tumor-initiating cells through CXCR3/ERK1/2 signaling. Cancer Lett. 2019, 449, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, H.; Si, L.; Li, Q.; Zhu, X.; Yu, T.; Gang, X. MiR-206 inhibits proliferation and migration of prostate cancer cells by targeting CXCL11. Prostate 2018, 78, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, J.; Jin, D.; Ren, C.; Yang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, C.; Ding, L.; Wu, Z.; Shen, K.; et al. EphA2 Promotes the Development of Cervical Cancer through the CXCL11/PD-L1 Pathway. J. Oncol. 2022, 2022, 4886907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Shen, X.; Li, Z.; Li, W.; Liu, Y. Reduction in immune cell number and loss of 5hmC are associated with lesion grade in cervical carcinogenesis. 3 Biotech 2021, 11, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, M.; Long, J.; Chelariu-Raicu, A.; Mullikin, H.; Vilsmaier, T.; Vattai, A.; Heidegger, H.H.; Batz, F.; Keckstein, S.; Jeschke, U.; et al. Identification of a Novel Tumor Microenvironment Prognostic Signature for Advanced-Stage Serous Ovarian Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 3343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, Q.; Kong, H.; Zeng, Y.; Hao, M.; Yu, T.; Peng, J.; Xu, Z.; Chen, J.; Shi, H. Monocyte chemotactic protein-1 expression as a prognosic biomarker in patients with solid tumor: A meta analysis. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2014, 7, 3876–3886. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Fan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Wang, Z.; Yang, L.; Sun, X.; Wang, Y. Schwann Cell-Derived CCL2 Promotes the Perineural Invasion of Cervical Cancer. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, J.; Yuan, P.; Gui, L.; Wang, Z.; Yin, P.; Gao, W.Q.; Ma, B. CCL28 Downregulation Attenuates Pancreatic Cancer Progression Through Tumor Cell-Intrinsic and -Extrinsic Mechanisms. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211068958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.L.; Liu, K.Y.; Lin, F.J.; Shi, H.M.; Ou, Z.L. CCL28 promotes breast cancer growth and metastasis through MAPK-mediated cellular anti-apoptosis and pro-metastasis. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1393–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fernandez-Avila, L.; Castro-Amaya, A.M.; Molina-Pineda, A.; Hernández-Gutiérrez, R.; Jave-Suarez, L.F.; Aguilar-Lemarroy, A. The Value of CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, and CXCL8 as Potential Prognosis Markers in Cervical Cancer: Evidence of E6/E7 from HPV16 and 18 in Chemokines Regulation. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102655
Fernandez-Avila L, Castro-Amaya AM, Molina-Pineda A, Hernández-Gutiérrez R, Jave-Suarez LF, Aguilar-Lemarroy A. The Value of CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, and CXCL8 as Potential Prognosis Markers in Cervical Cancer: Evidence of E6/E7 from HPV16 and 18 in Chemokines Regulation. Biomedicines. 2023; 11(10):2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102655
Chicago/Turabian StyleFernandez-Avila, Leonardo, Aribert Maryosly Castro-Amaya, Andrea Molina-Pineda, Rodolfo Hernández-Gutiérrez, Luis Felipe Jave-Suarez, and Adriana Aguilar-Lemarroy. 2023. "The Value of CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, and CXCL8 as Potential Prognosis Markers in Cervical Cancer: Evidence of E6/E7 from HPV16 and 18 in Chemokines Regulation" Biomedicines 11, no. 10: 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102655
APA StyleFernandez-Avila, L., Castro-Amaya, A. M., Molina-Pineda, A., Hernández-Gutiérrez, R., Jave-Suarez, L. F., & Aguilar-Lemarroy, A. (2023). The Value of CXCL1, CXCL2, CXCL3, and CXCL8 as Potential Prognosis Markers in Cervical Cancer: Evidence of E6/E7 from HPV16 and 18 in Chemokines Regulation. Biomedicines, 11(10), 2655. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines11102655