An Electrophilic Deguelin Analogue Inhibits STAT3 Signaling in H-Ras-Transformed Human Mammary Epithelial Cells: The Cysteine 259 Residue as a Potential Target
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Materials
2.2. Cell Culture
2.3. MTT Reduction Assay
2.4. Transient Transfection and the Luciferase Reporter Assay
2.5. siRNA Knockdown of STAT3.
2.6. Western Blot Analysis
2.7. Immunoprecipitation
2.8. Immunocytochemistry
2.9. Measurement of the Autophagy
2.10. Molecular Modeling
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Comparative Effect of Deguelin Analogues on STAT3 Transcriptional Activity
3.2. The α,β-Unsaturated Carbonyl Moiety of SH48 Is Essential for the Inhibition of STAT3 Phosphorylation
3.3. SH48 Forms a Complex with STAT3
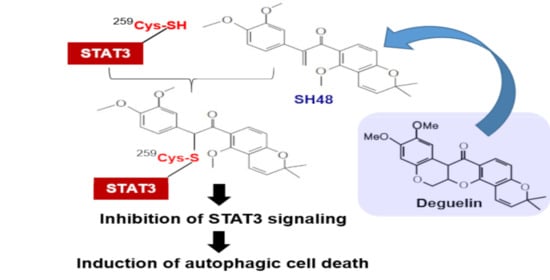
3.4. Cysteine 259 of STAT3 Is a Putative Binding Site of SH48
3.5. SH48 Induces Autophagy
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Surh, Y.-J. Cancer chemoprevention with dietary phytochemicals. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2003, 3, 768–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cragg, G.M.; Pezzuto, J.M. Natural products as a vital source for the discovery of cancer chemotherapeutic and chemopreventive agents. Med. Princ. Pract. 2016, 26, 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clark, E.P. A relation between rotenone, deguelin and tephrosin. Science 1931, 73, 17–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baba, Y.; Fujii, M.; Maeda, T.; Suzuki, A.; Yuzawa, S.; Kato, Y. deguelin induces apoptosis by targeting both EGFR-Akt and IGF1R-Akt pathways in head and neck squamous cell cancer cell lines. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 657179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, Y.-L.; Ji, C.; Bi, Z.-G.; Lu, C.-C.; Wang, R.; Gu, B.; Cheng, L. Deguelin induces both apoptosis and autophagy in cultured head and neck squamous cell carcinoma cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gao, F.; Yu, X.; Li, M.; Zhou, L.; Liu, W.; Li, W.; Liu, H. Deguelin suppresses non-small cell lung cancer by inhibiting EGFR signaling and promoting GSK3β/FBW7-mediated Mcl-1 destabilization. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Liang, Q.; Liu, W.; Zhou, L.; Li, W.; Liu, H. Deguelin, an aurora b kinase inhibitor, exhibits potent anti-tumor effect in human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. EBioMedicine 2017, 26, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kang, W.; Zheng, X.; Wang, P.; Guo, S. Deguelin exerts anticancer activity of human gastric cancer MGC-803 and MKN-45 cells in vitro. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2018, 41, 3157–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Murillo, G.; Salti, G.; Ii, J.K.; Pezzuto, J.; Mehta, R. Deguelin inhibits the growth of colon cancer cells through the induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest. Eur. J. Cancer 2002, 38, 2446–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boreddy, S.R.; Srivastava, S.K. Deguelin suppresses pancreatic tumor growth and metastasis by inhibiting epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in an orthotopic model. Oncogene 2012, 32, 3980–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zheng, W.; Lu, S.; Cai, H.; Kang, M.; Qin, W.; Li, C.; Wu, Y. Deguelin inhibits proliferation and migration of human pancreatic cancer cells in vitro targeting hedgehog pathway. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 12, 2761–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thamilselvan, V.; Menon, M.; Thamilselvan, S. Anticancer efficacy of deguelin in human prostate cancer cells targeting glycogen synthase kinase-3 β/β-catenin pathway. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 129, 2916–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehta, R.; Katta, H.; Alimirah, F.; Patel, R.; Murillo, G.; Peng, X.; Muzzio, M.; Mehta, R.G. Deguelin action involves c-Met and EGFR signaling pathways in triple negative breast cancer cells. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e65113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Robles, A.J.; Cai, S.; Cichewicz, R.H.; Mooberry, S.L. Selective activity of deguelin identifies therapeutic targets for androgen receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 157, 475–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ma, W.; Zheng, W. Deguelin, a novel anti-tumorigenic agent targeting apoptosis, cell cycle arrest and anti-angiogenesis for cancer chemoprevention. Mol. Clin. Oncol. 2013, 1, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, M.A.; Mehraj, U.; Sheikh, B.A. Recent advances in chemotherapeutic implications of deguelin, a plant derived retinoid. Nat. Prod. J. 2020, 10, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varughese, R.S.; Lam, W.S.; Marican, A.A.B.H.; Viganeshwari, S.H.; Bhave, A.S.; Syn, N.L.; Wang, J.; Wong, A.L.; Kumar, A.P.; Lobie, P.E.; et al. Biopharmacological considerations for accelerating drug development of deguelin, a rotenoid with potent chemotherapeutic and chemopreventive potential. Cancer 2019, 125, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrana, J.A.; Boggs, N.; Currie, H.N.; Boyd, J.W. Amelioration of an undesired action of deguelin. Toxicon 2013, 74, 83–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, W.-Y.; Chang, D.J.; Hennessy, B.; Kang, H.J.; Yoo, J.; Han, S.-H.; Kim, Y.-S.; Park, H.-J.; Seo, S.-Y.; Geo, S.-Y.; et al. A novel derivative of the natural agent deguelin for cancer chemoprevention and therapy. Cancer Prev. Res. 2008, 1, 577–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Frank, D.A. STAT signaling in cancer: Insights into pathogenesis and treatment strategies. Cancer Treat. Res. 2003, 115, 267–291. [Google Scholar]
- Loh, C.-Y.; Arya, A.; Naema, A.F.; Wong, W.F.; Sethi, G.; Looi, C.Y. Signal transducer and activator of transcription (STATs) proteins in cancer and inflammation: Functions and therapeutic implication. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Haura, E.B.; Turkson, J.; Jove, R. Mechanisms of Disease: Insights into the emerging role of signal transducers and activators of transcription in cancer. Nat. Clin. Pr. Oncol. 2005, 2, 315–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bromberg, J.F.; Wrzeszczynska, M.H.; Devgan, G.; Zhao, Y.; Pestell, R.G.; Albanese, C.; E Darnell, J. Stat3 as an Oncogene. Cell 1999, 98, 295–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Lee, H.; Herrmann, A.; Buettner, R.; Jove, R. Revisiting STAT3 signalling in cancer: New and unexpected biological functions. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 736–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buettner, R.; Mora, L.B.; Jove, R. Activated STAT signaling in human tumors provides novel molecular targets for therapeutic intervention. Clin. Cancer Res. 2002, 8, 945–954. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, Y.; Mohammad, I.S.; Liu, Z. Overview of the STAT-3 signaling pathway in cancer and the development of specific inhibitors (Review). Oncol. Lett. 2020, 19, 2585–2594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamran, M.Z.; Patil, P.; Gude, R.P. Role of STAT3 in cancer metastasis and translational advances. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 421821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.; Niu, N.; Wei, T.; Tozawa, H.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Wada, Y.; Kapron, C.M.; Liu, J. The roles of signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 3 in tumor angiogenesis. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 69139–69161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jing, N.; Tweardy, D.J. Targeting Stat3 in cancer therapy. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2005, 16, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Crowe, P.J.; Goldstein, D.; Yang, J.-L. STAT3 inhibition, a novel approach to enhancing targeted therapy in human cancers. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1181–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miklóssy, G.; Hilliard, T.S.; Turkson, J. Therapeutic modulators of STAT signalling for human diseases. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2013, 12, 611–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, H.; Jeong, A.J.; Ye, S.-K. Highlighted STAT3 as a potential drug target for cancer therapy. BMB Rep. 2019, 52, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Qin, J.J.; Yan, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, W.-D. STAT3 as a potential therapeutic target in triple negative breast cancer: A systematic review. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 38, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Oyake, T.; Murai, K.; Ishida, Y. Deguelin suppresses cell proliferation via the inhibition of survivin expression and STAT3 phosphorylation in HTLV-1-transformed T cells. Leuk. Res. 2010, 34, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-W.; Klionsky, D.J. The molecular mechanisms of autophage. Mol. Med. 2003, 9, 65–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Levine, B.; Kroemer, G. Autophagy in the pathogenesis of disease. Cell 2008, 132, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, Z.J.; Chee, C.E.; Huang, S.; Sinicrope, F.A. Sinicrope: The role of autophagy in cancer: Therapeutic implications. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2011, 10, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gong, J.; Munoz, A.R.; Chan, D.; Ghosh, R.; Kumar, A.P. STAT3 down regulates LC3 to inhibit autophagy and pancreatic cancer cell growth. Oncotarget 2014, 5, 2529–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Niso-Santano, M.; Adjemian, S.; Takehara, T.; Malik, S.A.; Minoux, H.; Souquere, S.; Mariño, G.; Lachkar, S.; Senovilla, L.; et al. Cytoplasmic STAT3 represses autophagy by inhibiting PKR activity. Mol. Cell 2012, 48, 667–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kim, K.; Kim, S.-J.; Han, Y.T.; Hong, S.-J.; An, H.; Chang, D.-J.; Kim, T.; Lim, B.; Lee, J.; Dong, Z.; et al. Identification of small molecule inhibitors of the STAT3 signaling pathway: Insights into their structural features and mode of action. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 25, 5444–5448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Pireddu, R.; Yang, H.; Urlam, M.K.; Lawrence, H.R.; Guida, W.C.; Lawrence, N.J.; Sebti, S.M. A novel inhibitor of STAT3 homodimerization selectively suppresses STAT3 activity and malignant transformation. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 1922–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.-C.; Hsieh, C.-W.; Wu, C.-C.; Wung, B.-S. Chalcone inhibits the activation of NF-κB and STAT3 in endothelial cells via endogenous electrophile. Life Sci. 2007, 80, 1420–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Shaw, P.E. A STAT3 dimer formed by inter-chain disulphide bridging during oxidative stress. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 322, 1005–1011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, Y.-I.; Kim, S.-J.; Choi, B.-Y.; Cho, K.-C.; Bandu, R.; Kim, K.P.; Kim, D.-H.; Kim, W.; Park, J.S.; Han, B.W.; et al. Curcumin interacts directly with the Cysteine 259 residue of STAT3 and induces apoptosis in H-Ras transformed human mammary epithelial cells. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 6409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debnath, J.; Baehrecke, E.H.; Kroemer, G. Does autophagy contribute to cell death? Autophagy 2005, 1, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, P.; Turkson, J. Targeting STAT3 in cancer: How successful are we? Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2009, 18, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Siveen, K.S.; Sikka, S.; Surana, R.; Dai, X.; Zhang, J.; Kumar, A.; Tan, B.K.; Sethi, G.; Bishayee, A. Targeting the STAT3 signaling pathway in cancer: Role of synthetic and natural inhibitors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Cancer 2014, 1845, 136–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Moscat, J.; Diaz-Meco, M.T. p62 at the crossroads of autophagy, apoptosis, and cancer. Cell 2009, 137, 1001–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Puissant, A.; Fenouille, N.; Auberger, P. When autophagy meets cancer through p62/SQSTM. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2012, 2, 397–413. [Google Scholar]









© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.-J.; Kim, J.-T.; Kim, S.-J.; Cho, N.-C.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.; Suh, Y.-G.; Cho, K.-C.; Kim, K.P.; Surh, Y.-J. An Electrophilic Deguelin Analogue Inhibits STAT3 Signaling in H-Ras-Transformed Human Mammary Epithelial Cells: The Cysteine 259 Residue as a Potential Target. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100407
Hong S-J, Kim J-T, Kim S-J, Cho N-C, Kim K, Lee S, Suh Y-G, Cho K-C, Kim KP, Surh Y-J. An Electrophilic Deguelin Analogue Inhibits STAT3 Signaling in H-Ras-Transformed Human Mammary Epithelial Cells: The Cysteine 259 Residue as a Potential Target. Biomedicines. 2020; 8(10):407. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100407
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Sung-Jun, Jin-Tae Kim, Su-Jung Kim, Nam-Chul Cho, Kyeojin Kim, Seungbeom Lee, Young-Ger Suh, Kyung-Cho Cho, Kwang Pyo Kim, and Young-Joon Surh. 2020. "An Electrophilic Deguelin Analogue Inhibits STAT3 Signaling in H-Ras-Transformed Human Mammary Epithelial Cells: The Cysteine 259 Residue as a Potential Target" Biomedicines 8, no. 10: 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100407
APA StyleHong, S. -J., Kim, J. -T., Kim, S. -J., Cho, N. -C., Kim, K., Lee, S., Suh, Y. -G., Cho, K. -C., Kim, K. P., & Surh, Y. -J. (2020). An Electrophilic Deguelin Analogue Inhibits STAT3 Signaling in H-Ras-Transformed Human Mammary Epithelial Cells: The Cysteine 259 Residue as a Potential Target. Biomedicines, 8(10), 407. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines8100407