Zoledronate Bound to Ceramics Increases Ectopic Bone Volume Induced by rhBMP6 Delivered in Autologous Blood Coagulum in Rats
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Test Items
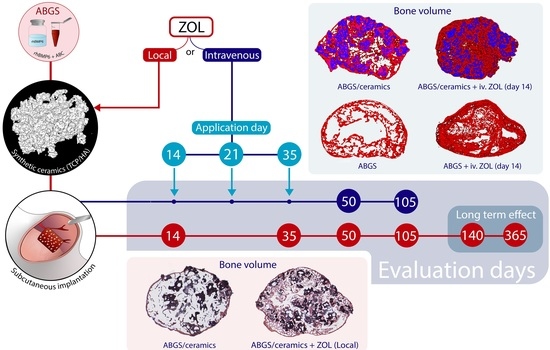
2.2. Experimental Design
2.3. Experimental Animals
2.4. Implant Preparation
2.5. Rat Subcutaneous Implant Assay
2.6. Histology
2.7. Histomorphometry
2.8. MicroCT Analyses
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Zoledronate Local Short-Term Effect on Bone Induction
3.2. Zoledronate Local Mid-Term Effect on Ectopic Bone
3.3. Local Versus Systemic Zoledronate Effect on Ectopic Bone Volume and Structure
3.4. Maintenance of Ectopic Bone over One Year Follow Up
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| BMPs | bone morphogenetic proteins |
| ABC | autologous blood coagulum |
| ABGS | autologous bone graft substitute containing rhBMP6 within autologous blood coagulum |
| BCS | Bone–ceramic structure |
| ZOL | zolendronate |
| TCP/HA | beta-tricalcium phosphate/hydroxyapatite |
References
- Sampath, T.K.; Vukicevic, S. Biology of bone morphogenetic protein in bone repair and regeneration: A role for autologous blood coagulum as carrier. Bone 2020, 141, 115602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vukicevic, S.; Peric, M.; Oppermann, H.; Stokovic, N.; Ivanjko, N.; Erjavec, I.; Kufner, V.; Vnuk, D.; Bubic Spoljar, J.; Pecin, M.; et al. Bone morphogenetic proteins: From discovery to development of a novel autologous bone graft substitute consisting of recombinant human BMP6 delivered in autologous blood coagulum carrier. Rad. CASA Med. Sci. 2020, 544, 26–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripamonti, U.; Klar, R.M.; Renton, L.F.; Ferretti, C. Synergistic induction of bone formation by hOP-1, hTGF-beta3 and inhibition by zoledronate in macroporous coral-derived hydroxyapatites. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 6400–6410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ripamonti, U.; Crooks, J.; Rueger, D.C. Induction of bone formation by recombinant human osteogenic protein-1 and sintered porous hydroxyapatite in adult primates. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2001, 107, 977–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peric, M.; Dumic-Cule, I.; Grcevic, D.; Matijasic, M.; Verbanac, D.; Paul, R.; Grgurevic, L.; Trkulja, V.; Bagi, C.M.; Vukicevic, S. The rational use of animal models in the evaluation of novel bone regenerative therapies. Bone 2015, 70, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gothard, D.; Smith, E.L.; Kanczler, J.M.; Rashidi, H.; Qutachi, O.; Henstock, J.; Rotherham, M.; El Haj, A.; Shakesheff, K.M.; Oreffo, R.O. Tissue engineered bone using select growth factors: A comprehensive review of animal studies and clinical translation studies in man. Eur. Cell Mater. 2014, 28, 166–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burkus, J.K.; Gornet, M.F.; Dickman, C.A.; Zdeblick, T.A. Anterior lumbar interbody fusion using rhBMP-2 with tapered interbody cages. J. Spinal Disord. Tech. 2002, 15, 337–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govender, S.; Csimma, C.; Genant, H.K.; Valentin-Opran, A.; Amit, Y.; Arbel, R.; Aro, H.; Atar, D.; Bishay, M.; Borner, M.G.; et al. Recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2 for treatment of open tibial fractures: A prospective, controlled, randomized study of four hundred and fifty patients. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 2002, 84, 2123–2134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Cai, X.; Huang, J.; Xu, F.; Liu, X.; Wang, Q. Recombinant human BMP-2 for the treatment of open tibial fractures. Orthopedics 2012, 35, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ong, K.L.; Villarraga, M.L.; Lau, E.; Carreon, L.Y.; Kurtz, S.M.; Glassman, S.D. Off-label use of bone morphogenetic proteins in the United States using administrative data. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2010, 35, 1794–1800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferretti, C.; Ripamonti, U. The Conundrum of Human Osteoinduction: Is the Bone Induction Principle Failing Clinical Translation? J. Craniofac. Surg. 2021, 32, 1287–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vukicevic, S.; Oppermann, H.; Verbanac, D.; Jankolija, M.; Popek, I.; Curak, J.; Brkljacic, J.; Pauk, M.; Erjavec, I.; Francetic, I.; et al. The clinical use of bone morphogenetic proteins revisited: A novel biocompatible carrier device OSTEOGROW for bone healing. Int. Orthop. 2014, 38, 635–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grgurevic, L.; Oppermann, H.; Pecin, M.; Erjavec, I.; Capak, H.; Pauk, M.; Karlovic, S.; Kufner, V.; Lipar, M.; Bubic Spoljar, J.; et al. Recombinant Human Bone Morphogenetic Protein 6 Delivered Within Autologous Blood Coagulum Restores Critical Size Segmental Defects of Ulna in Rabbits. JBMR Plus 2019, 3, e10085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vukicevic, S.; Grgurevic, L.; Erjavec, I.; Pecin, M.; Bordukalo-Niksic, T.; Stokovic, N.; Lipar, M.; Capak, H.; Maticic, D.; Windhager, R.; et al. Autologous blood coagulum is a physiological carrier for BMP6 to induce new bone formation and promote posterolateral lumbar spine fusion in rabbits. J. Tissue Eng. Regen. Med. 2020, 14, 147–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grgurevic, L.; Erjavec, I.; Gupta, M.; Pecin, M.; Bordukalo-Niksic, T.; Stokovic, N.; Vnuk, D.; Farkas, V.; Capak, H.; Milosevic, M.; et al. Autologous blood coagulum containing rhBMP6 induces new bone formation to promote anterior lumbar interbody fusion (ALIF) and posterolateral lumbar fusion (PLF) of spine in sheep. Bone 2020, 138, 115448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokovic, N.; Ivanjko, N.; Pecin, M.; Erjavec, I.; Karlovic, S.; Smajlovic, A.; Capak, H.; Milosevic, M.; Bubic Spoljar, J.; Vnuk, D.; et al. Evaluation of synthetic ceramics as compression resistant matrix to promote osteogenesis of autologous blood coagulum containing recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 6 in rabbit posterolateral lumbar fusion model. Bone 2020, 140, 115544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokovic, N.; Ivanjko, N.; Erjavec, I.; Milosevic, M.; Oppermann, H.; Shimp, L.; Sampath, K.T.; Vukicevic, S. Autologous bone graft substitute containing rhBMP6 within autologous blood coagulum and synthetic ceramics of different particle size determines the quantity and structural pattern of bone formed in a rat sucutaneous assay. Bone 2020, 141, 115654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stokovic, N.; Ivanjko, N.; Milesevic, M.; Matic Jelic, I.; Bakic, K.; Rumenovic, V.; Oppermann, H.; Shimp, L.; Sampath, T.K.; Pecina, M.; et al. Synthetic ceramic macroporous blocks as a scaffold in ectopic bone formation induced by recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 6 within autologous blood coagulum in rats. Int. Orthop. 2020, 45, 1097–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pecin, M.; Stokovic, N.; Ivanjko, N.; Smajlovic, A.; Kreszinger, M.; Capak, H.; Vrbanac, Z.; Oppermann, H.; Maticic, D.; Vukicevic, S. A novel autologous bone graft substitute containing rhBMP6 in autologous blood coagulum with synthetic ceramics for reconstruction of a large humerus segmental gunshot defect in a dog: The first veterinary patient to receive a novel osteoinductive therapy. Bone Rep. 2021, 14, 100759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, A.; Bennardo, F.; Brancaccio, Y.; Barone, S.; Femiano, F.; Nucci, L.; Minervini, G.; Fortunato, L.; Attanasio, F.; Giudice, A. Can Bone Compaction Improve Primary Implant Stability? An In Vitro Comparative Study with Osseodensification Technique. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, K.; Krause, C.; Shi, S.; Patterson, M.; Suto, R.; Grgurevic, L.; Vukicevic, S.; van Dinther, M.; Falb, D.; Ten Dijke, P.; et al. Identification of a key residue mediating bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-6 resistance to noggin inhibition allows for engineered BMPs with superior agonist activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 12169–12180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Vukicevic, S.; Grgurevic, L. BMP-6 and mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2009, 20, 441–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vukicevic, S.; Stokovic, N.; Pecina, M. Is ceramics an appropriate bone morphogenetic protein delivery system for clinical use? Int. Orthop. 2019, 43, 1275–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mroz, T.E.; Joyce, M.J.; Lieberman, I.H.; Steinmetz, M.P.; Benzel, E.C.; Wang, J.C. The use of allograft bone in spine surgery: Is it safe? Spine J. 2009, 9, 303–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorozhkin, S.V. Bioceramics of calcium orthophosphates. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 1465–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durdevic, D.; Vlahovic, T.; Pehar, S.; Miklic, D.; Oppermann, H.; Bordukalo-Niksic, T.; Gavrankapetanovic, I.; Jamakosmanovic, M.; Milosevic, M.; Martinovic, S.; et al. A novel autologous bone graft substitute comprised of rhBMP6 blood coagulum as carrier tested in a randomized and controlled Phase I trial in patients with distal radial fractures. Bone 2020, 140, 115551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiari, C.; Grgurevic, L.; Bordukalo-Niksic, T.; Oppermann, H.; Valentinitsch, A.; Nemecek, E.; Staats, K.; Schreiner, M.; Trost, C.; Kolb, A.; et al. Recombinant Human BMP6 Applied Within Autologous Blood Coagulum Accelerates Bone Healing: Randomized Controlled Trial in High Tibial Osteotomy Patients. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2020, 35, 1893–1903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, R.G.; Watts, N.B.; Ebetino, F.H.; Rogers, M.J. Mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates: Similarities and differences and their potential influence on clinical efficacy. Osteoporos. Int. 2008, 19, 733–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murphy, C.M.; Schindeler, A.; Gleeson, J.P.; Yu, N.Y.; Cantrill, L.C.; Mikulec, K.; Peacock, L.; O’Brien, F.J.; Little, D.G. A collagen-hydroxyapatite scaffold allows for binding and co-delivery of recombinant bone morphogenetic proteins and bisphosphonates. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 2250–2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raina, D.B.; Isaksson, H.; Hettwer, W.; Kumar, A.; Lidgren, L.; Tagil, M. A Biphasic Calcium Sulphate/Hydroxyapatite Carrier Containing Bone Morphogenic Protein-2 and Zoledronic Acid Generates Bone. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 26033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Raina, D.B.; Larsson, D.; Mrkonjic, F.; Isaksson, H.; Kumar, A.; Lidgren, L.; Tagil, M. Gelatin- hydroxyapatite- calcium sulphate based biomaterial for long term sustained delivery of bone morphogenic protein-2 and zoledronic acid for increased bone formation: In-vitro and in-vivo carrier properties. J. Control. Release 2018, 272, 83–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, L.; Hoshi, K.; Ejiri, S.; Nakajima, T.; Shingaki, S.; Ozawa, H. Bisphosphonate incadronate inhibits maturation of ectopic bone induced by recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2. J. Bone Miner. Metab. 2003, 21, 5–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ichikawa, K.; Ohta, Y.; Mamoto, K.; Mizokawa, S.; Minoda, Y.; Imai, Y.; Takaoka, K.; Nakamura, H. Local co-application of zoledronate promotes long-term maintenance of newly formed bone induced by recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2016, 480, 314–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Little, D.G.; McDonald, M.; Bransford, R.; Godfrey, C.B.; Amanat, N. Manipulation of the anabolic and catabolic responses with OP-1 and zoledronic acid in a rat critical defect model. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2005, 20, 2044–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, E.J.; Cha, I.H.; Nam, W.; Yook, J.I.; Park, Y.B.; Kim, H.J. Effects of locally administered rhBMP-2 and bisphosphonate on bone regeneration in the rat fibula. Oral Dis. 2018, 24, 1042–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doi, Y.; Miyazaki, M.; Yoshiiwa, T.; Hara, K.; Kataoka, M.; Tsumura, H. Manipulation of the anabolic and catabolic responses with BMP-2 and zoledronic acid in a rat femoral fracture model. Bone 2011, 49, 777–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosemark, P.; Isaksson, H.; Tagil, M. Influence of systemic bisphosphonate treatment on mechanical properties of BMP-induced calluses in a rat fracture model: Comparison of three-point bending and twisting test. J. Orthop. Res. 2014, 32, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitasato, S.; Tanaka, T.; Chazono, M.; Komaki, H.; Kakuta, A.; Inagaki, N.; Akiyama, S.; Marumo, K. Local application of alendronate controls bone formation and beta-tricalcium phosphate resorption induced by recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein-2. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2020, 108, 528–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeppsson, C.; Astrand, J.; Tagil, M.; Aspenberg, P. A combination of bisphosphonate and BMP additives in impacted bone allografts. Acta Orthop. Scand. 2003, 74, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Belfrage, O.; Flivik, G.; Sundberg, M.; Kesteris, U.; Tagil, M. Local treatment of cancellous bone grafts with BMP-7 and zoledronate increases both the bone formation rate and bone density: A bone chamber study in rats. Acta Orthop. 2011, 82, 228–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, I.R.; Green, J.R.; Lyles, K.W.; Reid, D.M.; Trechsel, U.; Hosking, D.J.; Black, D.M.; Cummings, S.R.; Russell, R.G.G.; Eriksen, E.F. Zoledronate. Bone 2020, 137, 115390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stokovic, N.; Ivanjko, N.; Maticic, D.; Luyten, F.P.; Vukicevic, S. Bone Morphogenetic Proteins, Carriers, and Animal Models in the Development of Novel Bone Regenerative Therapies. Materials 2021, 14, 3513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erjavec, I.; Bordukalo-Niksic, T.; Brkljacic, J.; Grcevic, D.; Mokrovic, G.; Kesic, M.; Rogic, D.; Zavadoski, W.; Paralkar, V.M.; Grgurevic, L.; et al. Constitutively Elevated Blood Serotonin Is Associated with Bone Loss and Type 2 Diabetes in Rats. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fortunato, L.; Bennardo, F.; Buffone, C.; Giudice, A. Is the application of platelet concentrates effective in the prevention and treatment of medication-related osteonecrosis of the jaw? A systematic review. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2020, 48, 268–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brancaccio, Y.; Antonelli, A.; Barone, S.; Bennardo, F.; Fortunato, L.; Giudice, A. Evaluation of local hemostatic efficacy after dental extractions in patients taking antiplatelet drugs: A randomized clinical trial. Clin. Oral Investig. 2021, 25, 1159–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Q.; Song, W.X.; Luo, Q.; Tang, N.; Luo, J.; Luo, X.; Chen, J.; Bi, Y.; He, B.C.; Park, J.K.; et al. A comprehensive analysis of the dual roles of BMPs in regulating adipogenic and osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal progenitor cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2009, 18, 545–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Luckman, S.P.; Hughes, D.E.; Coxon, F.P.; Graham, R.; Russell, G.; Rogers, M.J. Nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates inhibit the mevalonate pathway and prevent post-translational prenylation of GTP-binding proteins, including Ras. J. Bone Miner. Res. 1998, 13, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, L.; Tang, T.; Miao, Y.; Zhang, S.; Qu, Z.; Dai, K. Stimulation of osteogenic differentiation and inhibition of adipogenic differentiation in bone marrow stromal cells by alendronate via ERK and JNK activation. Bone 2008, 43, 40–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duque, G.; Rivas, D. Alendronate has an anabolic effect on bone through the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2007, 22, 1603–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marx, R.E. Pamidronate (Aredia) and zoledronate (Zometa) induced avascular necrosis of the jaws: A growing epidemic. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 61, 1115–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Black, D.M.; Delmas, P.D.; Eastell, R.; Reid, I.R.; Boonen, S.; Cauley, J.A.; Cosman, F.; Lakatos, P.; Leung, P.C.; Man, Z.; et al. Once-yearly zoledronic acid for treatment of postmenopausal osteoporosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 356, 1809–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ruggiero, S.L.; Mehrotra, B.; Rosenberg, T.J.; Engroff, S.L. Osteonecrosis of the jaws associated with the use of bisphosphonates: A review of 63 cases. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2004, 62, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drake, M.T.; Clarke, B.L.; Khosla, S. Bisphosphonates: Mechanism of action and role in clinical practice. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2008, 83, 1032–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Stokovic, N.; Ivanjko, N.; Erjavec, I.; Breski, A.; Peric, M.; Vukicevic, S. Zoledronate Bound to Ceramics Increases Ectopic Bone Volume Induced by rhBMP6 Delivered in Autologous Blood Coagulum in Rats. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101487
Stokovic N, Ivanjko N, Erjavec I, Breski A, Peric M, Vukicevic S. Zoledronate Bound to Ceramics Increases Ectopic Bone Volume Induced by rhBMP6 Delivered in Autologous Blood Coagulum in Rats. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(10):1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101487
Chicago/Turabian StyleStokovic, Nikola, Natalia Ivanjko, Igor Erjavec, Anita Breski, Mihaela Peric, and Slobodan Vukicevic. 2021. "Zoledronate Bound to Ceramics Increases Ectopic Bone Volume Induced by rhBMP6 Delivered in Autologous Blood Coagulum in Rats" Biomedicines 9, no. 10: 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101487
APA StyleStokovic, N., Ivanjko, N., Erjavec, I., Breski, A., Peric, M., & Vukicevic, S. (2021). Zoledronate Bound to Ceramics Increases Ectopic Bone Volume Induced by rhBMP6 Delivered in Autologous Blood Coagulum in Rats. Biomedicines, 9(10), 1487. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9101487