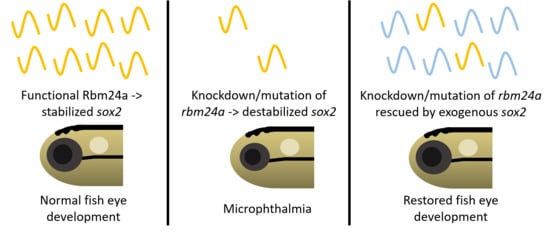
Functional Role of the RNA-Binding Protein Rbm24a and Its Target sox2 in Microphthalmia
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Animal Care
2.2. Microinjection
2.3. Mutagenesis Detection
2.4. Automated Startle Response
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Mutation of rbm24a Leads to Microphthalmia and Cardiomyopathy
3.2. rbm24a RNA Suppression of rbm24a Morpholino Knockdown
3.3. EGFP RNA Does Not Suppress rbm24a Morpholino Knockdown Phenotypes
3.4. sox2 RNA Phenotypically Suppresses rbm24a Morpholino-Induced Microphthalmia
3.5. EGFP RNA Does Not Functionally Suppress rbm24a-Induced Visual Defects
3.6. sox2 RNA Partially Functionally Suppresses rbm24a-Induced Visual Defects
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Johnson, G.J.; Minassian, D.C.; Weale, R.A.; West, S.K. The Epidemiology of Eye Disease; Arnold: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Graw, J. The genetic and molecular basis of congenital eye defects. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2003, 4, 876–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, S.P.; Taylor, A.E.; Sowden, J.C.; Ragge, N.K.; Russell-Eggitt, I.; Rahi, J.S.; Gilbert, C.E. Anophthalmos, microphthalmos, and typical coloboma in the United Kingdom: A prospective study of incidence and risk. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, L.; Fry, M.; Al-Samarraie, M.; Gilbert, C.; Steinkuller, P.G. An update on progress and the changing epidemiology of causes of childhood blindness worldwide. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatric Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2012, 16, 501–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, L.M.; Semina, E.V. Conserved genetic pathways associated with microphthalmia, anophthalmia, and coloboma. Birth Defects Res. Part C Embryo Today Rev. 2015, 105, 96–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Fantes, J.; Ragge, N.K.; Lynch, S.-A.; McGill, N.I.; Collin, J.R.O.; Howard-Peebles, P.N.; Hayward, C.; Vivian, A.J.; Williamson, K.; van Heyningen, V. Mutations in SOX2 cause anophthalmia. Nat. Genet. 2003, 33, 462–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, K.; Yamanaka, S. Induction of pluripotent stem cells from mouse embryonic and adult fibroblast cultures by defined factors. Cell 2006, 126, 663–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, Q.; Chipperfield, H.; Melton, D.A.; Wong, W.H. A gene regulatory network in mouse embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 16438–16443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Kondoh, H.; Lovell-Badge, R. Sox2: Biology and Role in Development and Disease; Academic Press: London, UK, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, J.; Belmonte, J.C.I. The molecular harbingers of early mammalian embryo patterning. Cell 2016, 165, 13–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachke, S.A.; Ho, J.W.; Kryukov, G.V.; O’Connell, D.J.; Aboukhalil, A.; Bulyk, M.L.; Park, P.J.; Maas, R.L. iSyTE: Integrated Systems Tool for Eye gene discovery. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 1617–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Dash, S.; Brastrom, L.K.; Patel, S.D.; Scott, C.A.; Slusarski, D.C.; Lachke, S.A. The master transcription factor SOX2, mutated in anophthalmia/microphthalmia, is post-transcriptionally regulated by the conserved RNA-binding protein RBM24 in vertebrate eye development. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, 591–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brastrom, L.K.; Scott, C.A.; Dawson, D.V.; Slusarski, D.C. A high-throughput assay for congenital and age-related eye diseases in zebrafish. Biomedicines 2019, 7, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.; Hung, L.-H.; Licht, T.; Kostin, S.; Looso, M.; Khrameeva, E.; Bindereif, A.; Schneider, A.; Braun, T. RBM24 is a major regulator of muscle-specific alternative splicing. Dev. Cell 2014, 31, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, E.; Mohibi, S.; de Anda, D.M.; Jiang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. Rbm24, a target of p53, is necessary for proper expression of p53 and heart development. Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 1118–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, J.; Kong, X.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Xu, X. RNA binding protein 24 deletion disrupts global alternative splicing and causes dilated cardiomyopathy. Protein Cell 2019, 10, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Fetka, I.; Radeghieri, A.; Bouwmeester, T. Expression of the RNA recognition motif-containing protein SEB-4 during Xenopus embryonic development. Mech. Dev. 2000, 94, 283–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oberleitner, S. Seb4—An RNA-Binding Protein as a Novel Regulator of Myogenesis during Early Development in Xenopus laevis. Ph.D. Dissertation, Ludwig Maximilian University of Munich, Munich, Germany, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Maragh, S.; Miller, R.A.; Bessling, S.L.; McGaughey, D.M.; Wessels, M.W.; De Graaf, B.; Stone, E.A.; Bertoli-Avella, A.M.; Gearhart, J.D.; Fisher, S. Identification of RNA binding motif proteins essential for cardiovascular development. BMC Dev. Biol. 2011, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maragh, S.; Miller, R.A.; Bessling, S.L.; Wang, G.; Hook, P.W.; McCallion, A.S. Rbm24a and Rbm24b are required for normal somitogenesis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e105460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Grifone, R.; Saquet, A.; Xu, Z.; Shi, D.L. Expression patterns of Rbm24 in lens, nasal epithelium, and inner ear during mouse embryonic development. Dev. Dyn. 2018, 247, 1160–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wagner, D.E.; Weinreb, C.; Collins, Z.M.; Briggs, J.A.; Megason, S.G.; Klein, A.M. Single-cell mapping of gene expression landscapes and lineage in the zebrafish embryo. Science 2018, 360, 981–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, M.; Lu, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, Y.-Z.; Kong, S.-H.; Shi, D.-L. Rbm24 controls poly (A) tail length and translation efficiency of crystallin mRNAs in the lens via cytoplasmic polyadenylation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 7245–7254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vakulskas, C.A.; Dever, D.P.; Rettig, G.R.; Turk, R.; Jacobi, A.M.; Collingwood, M.A.; Bode, N.M.; McNeill, M.S.; Yan, S.; Camarena, J. A high-fidelity Cas9 mutant delivered as a ribonucleoprotein complex enables efficient gene editing in human hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells. Nat. Med. 2018, 24, 1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Roginsky, J. Analyzing CRISPR Editing Results: Synthego Developed a Tool Called ICE to Be More Efficient Than Other Methods. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. News 2018, 38, S24–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, C.A.; Marsden, A.N.; Slusarski, D.C. Automated, high-throughput, in vivo analysis of visual function using the zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 2016, 245, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Team, R.C. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; The R Foundation: Vienna, Austria, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Poon, K.L.; Tan, K.T.; Wei, Y.Y.; Ng, C.P.; Colman, A.; Korzh, V.; Xu, X.Q. RNA-binding protein RBM24 is required for sarcomere assembly and heart contractility. Cardiovasc. Res. 2012, 94, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cohen-Barak, O.; Yi, Z.; Hagiwara, N.; Monzen, K.; Komuro, I.; Brilliant, M.H. Sox6 regulation of cardiac myocyte development. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 5941–5948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Garside, V.C.; Cullum, R.; Alder, O.; Lu, D.Y.; Vander Werff, R.; Bilenky, M.; Zhao, Y.; Jones, S.J.; Marra, M.A.; Underhill, T.M. SOX9 modulates the expression of key transcription factors required for heart valve development. Development 2015, 142, 4340–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Asakura, M.; Inoue, H.; Nakamura, T.; Sano, M.; Niu, Z.; Chen, M.; Schwartz, R.J.; Schneider, M.D. Sox17 is essential for the specification of cardiac mesoderm in embryonic stem cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3859–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]







| Uninjected | rbm24a CRISPR F0 | |
|---|---|---|
| Normal | 83 | 4 |
| Microphthalmia | 0 | |
| Microphthalmia and CVD 1 | 28 | |
| CVD | 1 | |
| Other 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Total | 84 | 34 |
| Uninjected | rbm24a MO | rbm24a MO + rbm24a RNA | rbm24a RNA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 45 | 7 | 10 | 21 |
| Microphthalmia | 14 | 4 | 2 | |
| Microphthalmia and CVD | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| CVD | 1 | |||
| Other | 5 | 5 | 1 | |
| Total | 45 | 32 | 25 | 31 |
| Uninjected | rbm24a MO | rbm24a MO + EGFP RNA | EGFP RNA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 63 | 2 | 1 | 28 |
| Microphthalmia | 2 | 6 | 10 | 2 |
| Microphthalmia and CVD | 13 | 6 | ||
| CVD | ||||
| Other | 4 | 9 | ||
| Total | 63 | 25 | 26 | 30 |
| Uninjected | rbm24a MO | rbm24a MO + sox2 RNA | sox2 RNA | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Normal | 13 | 3 | 12 | 17 |
| Microphthalmia | 2 | |||
| Microphthalmia and CVD | 4 | 3 | ||
| CVD | ||||
| Other | 1 | 5 | 4 | 6 |
| Total | 14 | 12 | 17 | 25 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Brastrom, L.K.; Scott, C.A.; Wang, K.; Slusarski, D.C. Functional Role of the RNA-Binding Protein Rbm24a and Its Target sox2 in Microphthalmia. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020100
Brastrom LK, Scott CA, Wang K, Slusarski DC. Functional Role of the RNA-Binding Protein Rbm24a and Its Target sox2 in Microphthalmia. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(2):100. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020100
Chicago/Turabian StyleBrastrom, Lindy K., C. Anthony Scott, Kai Wang, and Diane C. Slusarski. 2021. "Functional Role of the RNA-Binding Protein Rbm24a and Its Target sox2 in Microphthalmia" Biomedicines 9, no. 2: 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020100
APA StyleBrastrom, L. K., Scott, C. A., Wang, K., & Slusarski, D. C. (2021). Functional Role of the RNA-Binding Protein Rbm24a and Its Target sox2 in Microphthalmia. Biomedicines, 9(2), 100. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9020100