Characterization of Two Variants at Met 1 of the Human LDLR Gene Encoding the Same Amino Acid but Causing Different Functional Phenotypes
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Clinical Study
2.2. Plasmid Constructs
2.3. Cell Culture and Transfection
2.4. Western Blot Analysis
2.5. LDL Isolation and Labeling
2.6. LDLR Expression and Activity (Lipoprotein Binding and Internalization) by FACS
2.7. Luminometry Assay
2.8. American College of Medical Genetics (ACMG) Classification and In Silico Analysis
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. In Silico and ACMG Classification
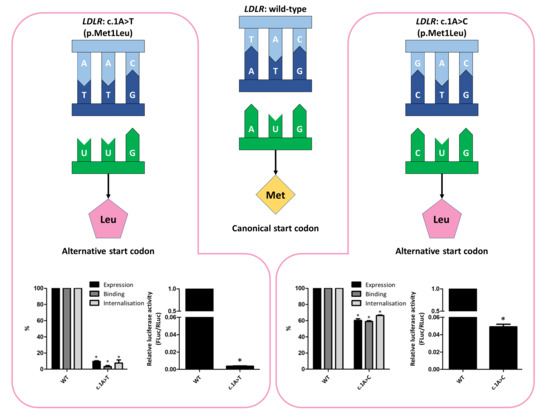
3.2. Functional Profiling of Variants c.1A>T and c.1A>C
3.3. Phenotype of Patients with Variant c.1A>C, p(Met1Leu)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. A receptor-mediated pathway for cholesterol homeostasis. Science (80-) 1986, 232, 34–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Akioyamen, L.E.; Genest, J.; Shan, S.D.; Reel, R.L.; Albaum, J.M.; Chu, A.; Tu, J.V. Estimating the prevalence of heterozygous familial hypercholesterolaemia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berberich, A.J.; Hegele, R.A. The complex molecular genetics of familial hypercholesterolaemia. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2019, 16, 9–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bourbon, M.; Alves, A.C.; Sijbrands, E.J. Low-density lipoprotein receptor mutational analysis in diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2017, 28, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mariano, C.; Alves, A.C.; Medeiros, A.M.; Chora, J.R.; Antunes, M.; Futema, M.; Humphries, S.E.; Bourbon, M. The familial hypercholesterolaemia phenotype: Monogenic familial hypercholesterolaemia, polygenic hypercholesterolaemia and other causes. Clin. Genet. Clin. Genet. 2019, 97, 457–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talmud, P.J.; Shah, S.; Whittall, R.; Futema, M.; Howard, P.; Cooper, J.A.; Harrison, S.C.; Li, K.; Drenos, F.; Karpe, F.; et al. Use of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol gene score to distinguish patients with polygenic and monogenic familial hypercholesterolaemia: A case-control study. Lancet 2013, 381, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Iacocca, M.A.; Chora, J.R.; Carrié, A.; Freiberger, T.; Leigh, S.E.; Defesche, J.C.; Kurtz, C.L.; DiStefano, M.T.; Santos, R.D.; Humphries, S.E.; et al. ClinVar database of global familial hypercholesterolemia-associated DNA variants. Hum. Mutat. 2018, 39, 1631–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Taranto, M.D.; Giacobbe, C.; Fortunato, G. Familial hypercholesterolemia: A complex genetic disease with variable phenotypes. Eur. J. Med. Genet. 2020, 63, 103831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abul-Husn, N.S.; Manickam, K.; Jones, L.K.; Wright, E.A.; Hartzel, D.N.; Gonzaga-Jauregui, C.; O’Dushlaine, C.; Leader, J.B.; Kirchner, H.L.; Lindbuchler, D.M.; et al. Genetic identification of familial hypercholesterolemia within a single U.S. Health care system. Science (80-) 2016, 354, aaf7000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourbon, M.; Alves, A.C.; Alonso, R.; Mata, N.; Aguiar, P.; Padró, T.; Mata, P. Mutational analysis and genotype-phenotype relation in familial hypercholesterolemia: The SAFEHEART registry. Atherosclerosis 2017, 262, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khera, A.V.; Won, H.; Peloso, G.M.; Lawson, K.S.; Bartz, T.M.; Deng, X.; van Leeuwen, E.M.; Natarajan, P.; Emdin, C.A.; Bick, A.G.; et al. Diagnostic Yield of Sequencing Familial Hypercholesterolemia Genes in Severe Hypercholesterolemia. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 2578–2589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez De Isla, L.; Alonso, R.; Watts, G.F.; Mata, N.; Saltijeral Cerezo, A.; Muñiz, O.; Fuentes, F.; Diaz-Diaz, J.L.; de Andrés, R.; Zambón, D.; et al. Attainment of LDL-cholesterol treatment goals in patients with familial hypercholesterolemia: 5-year SAFEHEART registry follow-up. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 1278–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, P.C.J.L.; Morgan, A.C.; Jannes, C.E.; Turolla, L.; Krieger, J.; Santos, R.D.; Pereira, A.C. Presence and type of low density lipoprotein receptor (LDLR) mutation influences the lipid profile and response to lipid-lowering therapy in Brazilian patients with heterozygous familial hypercholesterolemia. Atherosclerosis 2014, 233, 206–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, H.H.; Brown, M.S.; Goldstein, J.L. Molecular genetics of the LDL receptor gene in familial hypercholesterolemia. Hum. Mutat. 1992, 1, 445–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medeiros, A.M.; Alves, A.C.; Francisco, V.; Bourbon, M. Update of the Portuguese Familial Hypercholesterolaemia Study. Atherosclerosis 2010, 212, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medeiros, A.M.; Alves, A.C.; Bourbon, M. Mutational analysis of a cohort with clinical diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia: Considerations for genetic diagnosis improvement. Genet. Med. 2015, 18, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bourbon, M.; Rato, Q. Estudo Português de hipercolesterolemia familiar: Apresentação do estudo e resultados preliminares. Rev. Port. Cardiol. 2006, 25, 999–1013. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chora, J.R.; Iacocca, M.A.; Tichy, L.; Wand, H.; Kurtz, C.L.; Zimmermann, H.; Leon, A.; Williams, M.; Humphries, S.E.; Hooper, A.J.; et al. Title: The Clinical Genome Resource (ClinGen) Familial Hypercholesterolemia Variant Curation Expert Panel consensus guidelines for LDLR variant classification. medRxiv 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, Y.; Sims, G.E.; Murphy, S.; Miller, J.R.; Chan, A.P. Predicting the Functional Effect of Amino Acid Substitutions and Indels. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e46688. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, P.; Henikoff, S.; Ng, P.C. Predicting the effects of coding non-synonymous variants on protein function using the SIFT algorithm. Nat. Protoc. 2009, 4, 1073–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adzhubei, I.A.; Schmidt, S.; Peshkin, L.; Ramensky, V.E.; Bork, P.; Kondrashov, A.S.; Sunyaev, S.R. A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 248–249. Available online: http://www.nature.com/articles/nmeth0410-248 (accessed on 11 March 2021). [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwarz, J.M.; Rödelsperger, C.; Schuelke, M.; Seelow, D. MutationTaster evaluates disease-causing potential of sequence alterations. Nat. Methods 2010, 7, 575–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, N.M.; Rothstein, J.H.; Pejaver, V.; Middha, S.; McDonnell, S.K.; Baheti, S.; Musolf, A.; Li, Q.; Holzinger, E.; Karyadi, D.; et al. REVEL: An Ensemble Method for Predicting the Pathogenicity of Rare Missense Variants. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 877–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ingolia, N.T.; Ghaemmaghami, S.; Newman, J.R.S.; Weissman, J.S. Genome-Wide Analysis in Vivo of Resolution Using Ribosome Profiling. Science (80-) 2009, 324, 218–223. Available online: http://www.pubmedcentral.nih.gov/articlerender.fcgi?artid=2746483&tool=pmcentrez&rendertype=abstract (accessed on 11 March 2021). [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kearse, M.G.; Wilusz, J.E. Non-AUG translation: A new start for protein synthesis in eukaryotes. Genes Dev. 2017, 31, 1717–1731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwab, S.R.; Li, K.C.; Kang, C.; Shastri, N. Constitutive display of cryptic translation products by MHC class I molecules. Science (80-) 2003, 301, 1367–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ingolia, N.T.; Lareau, L.F.; Weissman, J.S. Ribosome Profiling of Mouse Embryonic Stem Cells Reveals the Complexity and Dynamics of Mammalian Proteomes. Cell 2011, 147, 789–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Starck, S.R.; Jiang, V.; Pavon-Eternod, M.; Prasad, S.; McCarthy, B.; Pan, T.; Shastri, N. Leucine-tRNA initiates at CUG start codons for protein synthesis and presentation by MHC class I. Science (80-) 2012, 336, 1719–1723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starck, S.R.; Tsai, J.C.; Chen, K.; Shodiya, M.; Wang, L. Translation from the 5’ untranslated region shapes the integrated stress response. Science (80-) 2016, 351, aad3867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozak, M. Downstream secondary structure facilitates recognition of initiator codons by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1990, 87, 8301–8305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guenther, U.P.; Weinberg, D.E.; Zubradt, M.M.; Tedeschi, F.A.; Stawicki, B.N.; Zagore, L.L.; Brar, G.A.; Licatalosi, D.D.; Bartel, D.P.; Weissman, J.S.; et al. The helicase Ded1p controls use of near-cognate translation initiation codons in 5′ UTRs. Nature 2018, 559, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, A.C.; Alonso, R.; Diaz-Diaz, J.L.; Medeiros, A.M.; Jannes, C.E.; Merchan, A.; Vasques-Cardenas, N.A.; Cuevas, A.; Chacra, A.P.; Krieger, J.E.; et al. Phenotypical, clinical, and molecular aspects of adults and children with homozygous familial hypercholesterolemia in iberoamerica. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2020, 40, 2508–2515. [Google Scholar]
- Langenhoven, E.; Warnich, L.; Thiart, R.; Rubinsztein, D.C.; Van Der Westhuyzen, D.R.; Marais, A.D.; Kotze, M. Two novel point mutations causing receptor-negative familial hypercholesterolemia in a South African Indian homozygote. Atherosclerosis 1996, 125, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, F.J.; Real, J.T.; García-García, A.B.; Civera, M.; Armengod, M.E.; Ascaso, J.F.; Carmena, R. Genetic diagnosis of familial hypercholesterolemia in a South European outbreed population: Influence of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) receptor gene mutations on treatment response to simvastatin in total, LDL, and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 4926–4932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mach, F.; Baigent, C.; Catapano, A.L.; Koskina, K.C.; Casula, M.; Badimon, L.; Chapman, M.J.; De Backer, G.G.; Delgado, V.; Ference, B.A.; et al. 2019 ESC/EAS guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: Lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk. Atherosclerosis 2019, 290, 140–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]


| Variant | PROVEAN | SIFT | Polyphen-2 | Mutation Tester 2 | REVEL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| c.1A>T, p.(Met1Leu) | Neutral | Damaging | Benign | disease causing | 0.638 |
| c.1A>C, p.(Met1Leu) | Neutral | Damaging | Benign | disease causing | 0.638 |
| Variant | ACMG Classification without FS | Points without FS | ACMG Classification after FS * |
|---|---|---|---|
| c.1A>T, p.(Met1Leu) | VUS | PM2, PVS1_Moderate and PP4 | Likely pathogenic |
| c.1A>C, p.(Met1Leu) | Likely pathogenic | PM2, PVS1_Moderate PP1_Moderate, PP4, PS4_Supporting | Pathogenic |
| Family | Age at Referral | Sex | Total-C * [mg/dL] | LDL-C * [mg/dL] | HDL-C * [mg/dL] | TG * [mg/dL] | BMI (Kg/m2) | LLT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1—Index | 22 | F | 439 | 297 | 115 | 135 | NK | No |
| 2—Index | 38 | M | 288 | 222 | 48 | 90 | NK | No |
| 2 | 9 | F | 174 | 108 | 52 | 53 | NK | No |
| 3—Index | 2 | M | 281 | 226 | 47 | 93 | 16.8 | No |
| 3 | 3 | M | 284 | 220 | 51 | 95 | NK | No |
| 3 | 32 | F | 491 | 392 | 77 | 110 | NK | No |
| 4—Index | 12 | M | 257 | 174 | 68 | 32 | 22.6 | Atorvastatin |
| 4 | 41 | F | 227 | 149 | 63 | 50 | NK | Atorvastatin |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Graça, R.; Fernandes, R.; Alves, A.C.; Menezes, J.; Romão, L.; Bourbon, M. Characterization of Two Variants at Met 1 of the Human LDLR Gene Encoding the Same Amino Acid but Causing Different Functional Phenotypes. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091219
Graça R, Fernandes R, Alves AC, Menezes J, Romão L, Bourbon M. Characterization of Two Variants at Met 1 of the Human LDLR Gene Encoding the Same Amino Acid but Causing Different Functional Phenotypes. Biomedicines. 2021; 9(9):1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091219
Chicago/Turabian StyleGraça, Rafael, Rafael Fernandes, Ana Catarina Alves, Juliane Menezes, Luísa Romão, and Mafalda Bourbon. 2021. "Characterization of Two Variants at Met 1 of the Human LDLR Gene Encoding the Same Amino Acid but Causing Different Functional Phenotypes" Biomedicines 9, no. 9: 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091219
APA StyleGraça, R., Fernandes, R., Alves, A. C., Menezes, J., Romão, L., & Bourbon, M. (2021). Characterization of Two Variants at Met 1 of the Human LDLR Gene Encoding the Same Amino Acid but Causing Different Functional Phenotypes. Biomedicines, 9(9), 1219. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9091219