Crude Oil Bioremediation: From Bacteria to Microalgae
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Petroleum Composition
2. Current Bioremediation Techniques
2.1. Bacteria Biodegradation
2.2. Different Bacteria Consortium
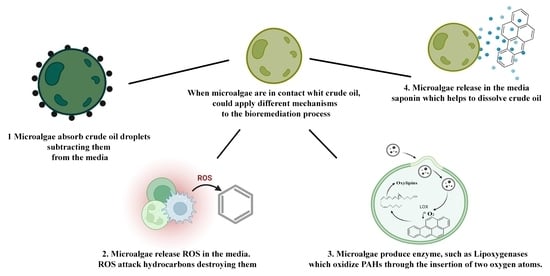
3. Microalgae and Petroleum Bioremediation
4. Mechanism of Action
5. Consortium Microalgae and Bacteria
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ferreira Mota, G.; Germano de Sousa, I.; Luiz Barros de Oliveira, A.; Luthierre Gama Cavalcante, A.; da Silva Moreira, K.; Thálysson Tavares Cavalcante, F.; Erick da Silva Souza, J.; Rafael de Aguiar Falcão, Í.; Guimarães Rocha, T.; Bussons Rodrigues Valério, R.; et al. Biodiesel Production from Microalgae Using Lipase-Based Catalysts: Current Challenges and Prospects. Algal. Res. 2022, 62, 102616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.S.; Robinson, P.R. Springer Handbook of Petroleum Technology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Walters, C. Petroleum. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2020; pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissin, Y. Catagenesis and Composition of Petroleum: Origin of n-Alkanes and Isoalkanes in Petroleum Crudes. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1987, 51, 2445–2457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dooley, S.; Heyne, J.; Won, S.H.; Dievart, P.; Ju, Y.; Dryer, F.L. Importance of a Cycloalkane Functionality in the Oxidation of a Real Fuel. Energy Fuels 2014, 28, 7649–7661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Huang, G.; Zhang, M. Distribution Difference and Significance of Short-Chain Steranes in Humic Coal and Coal-Measure Mudstone of Triassic Xujiahe Formation in Sichuan Basin, SW China. Arab. J. Geosci. 2021, 14, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heibati, B.; Pollitt, K.J.G.; Karimi, A.; Yazdani Charati, J.; Ducatman, A.; Shokrzadeh, M.; Mohammadyan, M. BTEX Exposure Assessment and Quantitative Risk Assessment among Petroleum Product Distributors. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 144, 445–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ossai, I.C.; Ahmed, A.; Hassan, A.; Hamid, F.S. Remediation of Soil and Water Contaminated with Petroleum Hydrocarbon: A Review. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 17, 100526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palacio Lozano, D.C.; Ramírez, C.X.; Sarmiento Chaparro, J.A.; Thomas, M.J.; Gavard, R.; Jones, H.E.; Cabanzo Hernández, R.; Mejia-Ospino, E.; Barrow, M.P. Characterization of Bio-Crude Components Derived from Pyrolysis of Soft Wood and Its Esterified Product by Ultrahigh Resolution Mass Spectrometry and Spectroscopic Techniques. Fuel 2020, 259, 116085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, W.; Zhu, G.; Liu, F.; Li, Z.; Xie, C.; Han, Y. Carboxylic Acids in Petroleum: Separation, Analysis, and Geochemical Significance. Energy Fuels 2021, 35, 12828–12844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gab-Allah, M.A.; Goda, E.S.; Shehata, A.B.; Gamal, H. Critical Review on the Analytical Methods for the Determination of Sulfur and Trace Elements in Crude Oil. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2019, 50, 161–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, C.; Gutierrez, T. Use of Microorganisms in the Recovery of Oil from Recalcitrant Oil Reservoirs: Current State of Knowledge, Technological Advances and Future Perspectives. Front Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tourova, T.P.; Sokolova, D.S.; Semenova, E.M.; Ershov, A.P.; Grouzdev, D.S.; Nazina, T.N. Genomic and Physiological Characterization of Halophilic Bacteria of the Genera Halomonas and Marinobacter from Petroleum Reservoirs. Microbiology 2022, 91, 235–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gutierrez, T.; Berry, D.; Yang, T.; Mishamandani, S.; McKay, L.; Teske, A.; Aitken, M.D. Role of Bacterial Exopolysaccharides (EPS) in the Fate of the Oil Released during the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e67717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nwidee, L.N.; Theophilus, S.; Barifcani, A.; Sarmadivaleh, M.; Iglauer, S.; Nwidee, L.N.; Theophilus, S.; Barifcani, A.; Sarmadivaleh, M.; Iglauer, S. EOR Processes, Opportunities and Technological Advancements. In Chemical Enhanced Oil Recovery (cEOR)—A Practical Overview; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prince, R.C.; Gramain, A.; McGenity, T.J. Prokaryotic Hydrocarbon Degraders. In Handbook of Hydrocarbon and Lipid Microbiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 1669–1692. [Google Scholar]
- Kebede, G.; Tafese, T.; Abda, E.M.; Kamaraj, M.; Assefa, F. Factors Influencing the Bacterial Bioremediation of Hydrocarbon Contaminants in the Soil: Mechanisms and Impacts. J. Chem. 2021, 2021, 9823362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.; Bai, X.; Sheng, H.; Jiao, L.; Zhou, H.; Shao, Z. Distribution of PAHs and the PAH-Degrading Bacteria in the Deep-Sea Sediments of the High-Latitude Arctic Ocean. Biogeosciences Discuss 2014, 11, 13985–14021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcgenity, T.J.; Folwell, B.D.; Mckew, B.A.; Sanni, G.O. Marine Crude-Oil Biodegradation: A Central Role for Interspecies Interactions. Saline Syst. 2012, 8, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Wang, W.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Lai, Q.; Shao, Z. Multiple Alkane Hydroxylase Systems in a Marine Alkane Degrader, Alcanivorax Dieselolei B-5. Env. Microbiol. 2011, 13, 1168–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niepceron, M.; Portet-Koltalo, F.; Merlin, C.; Motelay-Massei, A.; Barray, S.; Bodilis, J. Both Cycloclasticus Spp. and Pseudomonas Spp. as PAH-Degrading Bacteria in the Seine Estuary (France). FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2010, 71, 137–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubinsky, E.A.; Conrad, M.E.; Chakraborty, R.; Bill, M.; Borglin, S.E.; Hollibaugh, J.T.; Mason, O.U.; Piceno, Y.M.; Reid, F.C.; Stringfellow, W.T.; et al. Succession of Hydrocarbon-Degrading Bacteria in the Aftermath of the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill in the Gulf of Mexico. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 10860–10867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentine, D.L.; Kessler, J.D.; Redmond, M.C.; Mendes, S.D.; Heintz, M.B.; Farwell, C.; Hu, L.; Kinnaman, F.S.; Yvon-Lewis, S.; Du, M.; et al. Propane Respiration Jump-Starts Microbial Response to a Deep Oil Spill. Science 2010, 330, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ławniczak, Ł.; Woźniak-Karczewska, M.; Loibner, A.P.; Heipieper, H.J.; Chrzanowski, Ł. Microbial Degradation of Hydrocarbons—Basic Principles for Bioremediation: A Review. Molecules 2020, 25, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ron, E.Z.; Rosenberg, E. Enhanced Bioremediation of Oil Spills in the Sea. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2014, 27, 191–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagarajan, D.; Dong, C.D.; Chen, C.Y.; Lee, D.J.; Chang, J.S. Biohydrogen Production from Microalgae—Major Bottlenecks and Future Research Perspectives. Biotechnol. J. 2021, 16, 2000124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Truskewycz, A.; Gundry, T.D.; Khudur, L.S.; Kolobaric, A.; Taha, M.; Aburto-Medina, A.; Ball, A.S.; Shahsavari, E. Petroleum Hydrocarbon Contamination in Terrestrial Ecosystems—Fate and Microbial Responses. Molecules 2019, 24, 3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, L.; Reynolds, D.; Liu, M.; Stark, M.; Kjelleberg, S.; Webster, N.S.; Thomas, T. Functional Equivalence and Evolutionary Convergence in Complex Communities of Microbial Sponge Symbionts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, E1878–E1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyer, J.; Trannum, H.C.; Bakke, T.; Hodson, P.V.; Collier, T.K. Environmental Effects of the Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill: A Review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2016, 110, 28–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, O.U.; Hazen, T.C.; Borglin, S.; Chain, P.S.G.; Dubinsky, E.A.; Fortney, J.L.; Han, J.; Holman, H.Y.N.; Hultman, J.; Lamendella, R.; et al. Metagenome, Metatranscriptome and Single-Cell Sequencing Reveal Microbial Response to Deepwater Horizon Oil Spill. ISME J. 2012, 6, 1715–1727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, S.K.; Haritash, A.K. Bacterial Degradation of Mixed-PAHs and Expression of PAH-Catabolic Genes. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2022, 39, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.W.; Lee, H.; Lee, A.H.; Kwon, B.O.; Khim, J.S.; Yim, U.H.; Kim, B.S.; Kim, J.J. Microbial Community Composition and PAHs Removal Potential of Indigenous Bacteria in Oil Contaminated Sediment of Taean Coast, Korea. Environ. Pollut. 2018, 234, 503–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Hong, Y.; Odinga, E.S.; Liu, J.; Tsang, D.C.W.; Gao, Y. Bacterial Community and PAH-Degrading Genes in Paddy Soil and Rice Grain from PAH-Contaminated Area. Appl. Soil Ecol. 2021, 158, 103789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugya, Y.A.; Hasan, D.B.; Tahir, S.M.; Imam, T.S.; Ari, H.A.; Hua, X. Microalgae Biofilm Cultured in Nutrient-Rich Water as a Tool for the Phycoremediation of Petroleum-Contaminated Water. Int. J. Phytoremediation 2021, 23, 1175–1183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuttiyathil, M.S.; Mohamed, M.M.; Al-Zuhair, S. Using Microalgae for Remediation of Crude Petroleum Oil-Water Emulsion. Biotechnol. Prog. 2020, 37, e309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Özhan, K.; Miles, S.M.; Gao, H.; Bargu, S. Relative Phytoplankton Growth Responses to Physically and Chemically Dispersed South Louisiana Sweet Crude Oil. Environ. Monit. Assess 2014, 186, 3941–3956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Znad, H.; Al Ketife, A.M.D.; Judd, S.; AlMomani, F.; Vuthaluru, H.B. Bioremediation and Nutrient Removal from Wastewater by Chlorella Vulgaris. Ecol. Eng. 2018, 110, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadass, K.; Megharaj, M.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Naidu, R. Toxicity of Diesel Water Accommodated Fraction toward Microalgae, Pseudokirchneriella Subcapitata and Chlorella Sp. MM3. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2017, 142, 538–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xaaldi Kalhor, A.; Movafeghi, A.; Mohammadi-Nassab, A.D.; Abedi, E.; Bahrami, A. Potential of the Green Alga Chlorella Vulgaris for Biodegradation of Crude Oil Hydrocarbons. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 123, 286–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xaaldi Kalhor, A.; Mohammadi Nassab, A.D.; Abedi, E.; Bahrami, A.; Movafeghi, A. Biodiesel Production in Crude Oil Contaminated Environment Using Chlorella Vulgaris. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamouda, R.A.E.F.; Sorour, N.M.; Yeheia, D.S. Biodegradation of Crude Oil by Anabaena Oryzae, Chlorella Kessleri and Its Consortium under Mixotrophic Conditions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 112, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Sheekh, M.M.; Hamouda, R.A.; Nizam, A.A. Biodegradation of Crude Oil by Scenedesmus Obliquus and Chlorella Vulgaris Growing under Heterotrophic Conditions. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2013, 82, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, P.; AbdulQuadir, M.; Thaher, M.; Khan, S.; Chaudhary, A.K.; Alghasal, G.; Al-Jabri, H.M.S.J. Microalgal Bioremediation of Petroleum-Derived Low Salinity and Low PH Produced Water. J. Appl. Phycol. 2019, 31, 435–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kregiel, D.; Berlowska, J.; Witonska, I.; Antolak, H.; Proestos, C.; Babic, M.; Babic, L.; Zhang, B. Saponin-Based, Biological-Active Surfactants from Plants. In Application and Characterization of Surfactants; InTechOpen: London, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- El-Naggar, N.E.A.; Hussein, M.H.; Shaaban-Dessuuki, S.A.; Dalal, S.R. Production, Extraction and Characterization of Chlorella Vulgaris Soluble Polysaccharides and Their Applications in AgNPs Biosynthesis and Biostimulation of Plant Growth. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haritash, A.K. A Comprehensive Review of Metabolic and Genomic Aspects of PAH-Degradation. Arch. Microbiol. 2020, 202, 2033–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghodrati, M.; Kosari-Nasab, M.; Zarrini, G.; Movafeghi, A. Crude Oil Contamination Enhances the Lipoxygenase Gene Expression in the Green Microalga Scenedesmus Dimorphus. Biointerface Res. Appl. Chem. 2021, 11, 11431–11439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SureshKumar, P.; Thomas, J.; Poornima, V. Structural Insights on Bioremediation of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons Using Microalgae: A Modelling-Based Computational Study. Environ. Monit. Assess 2018, 190, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stebbing, A.R.D. Hormesis—The Stimulation of Growth by Low Levels of Inhibitors. Sci. Total Environ. 1982, 22, 213–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burbano, M.S.J.; Gilson, E. The Power of Stress: The Telo-Hormesis Hypothesis. Cells 2021, 10, 1156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashwaniy, V.R.V.; Perumalsamy, M.; Pandian, S. Enhancing the Synergistic Interaction of Microalgae and Bacteria for the Reduction of Organic Compounds in Petroleum Refinery Effluent. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2020, 19, 100926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernikova, T.N.; Bargiela, R.; Toshchakov, S.V.; Shivaraman, V.; Lunev, E.A.; Yakimov, M.M.; Thomas, D.N.; Golyshin, P.N. Hydrocarbon-Degrading Bacteria Alcanivorax and Marinobacter Associated with Microalgae Pavlova Lutheri and Nannochloropsis Oculata. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 572931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahdavi, H.; Prasad, V.; Liu, Y.; Ulrich, A.C. In Situ Biodegradation of Naphthenic Acids in Oil Sands Tailings Pond Water Using Indigenous Algae-Bacteria Consortium. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 187, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, A.; Fica, Z.; Wanlass, J.; VanDarlin, J.; Sims, R. Nutrient and Suspended Solids Removal from Petrochemical Wastewater via Microalgal Biofilm Cultivation. Chemosphere 2017, 174, 46–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abid, A.; Saidane, F.; Hamdi, M. Feasibility of Carbon Dioxide Sequestration by Spongiochloris Sp Microalgae during Petroleum Wastewater Treatment in Airlift Bioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 234, 297–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; He, L.Y.; Tao, X.Q.; Dang, Z.; Guo, C.L.; Lu, G.N.; Yi, X.Y. Construction of an Artificial Microalgal-Bacterial Consortium That Efficiently Degrades Crude Oil. J. Hazard Mater. 2010, 181, 1158–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.W.; Park, J.S.; Kown, O.Y.; Kang, J.H.; Shim, W.J.; Kim, Y.O. Effects of Crude Oil on Marine Microbial Communities in Short Term Outdoor Microcosms. J. Microbiol. 2010, 48, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Wang, L.; Qiu, S.; Ge, S. Determination of Microalgal Lipid Content and Fatty Acid for Biofuel Production. Biomed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, X.; Mi, Y.; Zhao, C.; Wei, Q. A Comprehensive Review on Carbon Source Effect of Microalgae Lipid Accumulation for Biofuel Production. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 806, 151387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, A.; Agrawal, S.; Nawaz, T.; Pan, S.; Selvaratnam, T. A Review of Algae-Based Produced Water Treatment for Biomass and Biofuel Production. Water 2020, 12, 2351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, C.; Zhang, D. Lipid Production of Chlorella Vulgaris Cultured in Artificial Wastewater Medium. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishshanka, G.K.S.H.; Liyanaarachchi, V.C.; Nimarshana, P.H.V.; Ariyadasa, T.U.; Chang, J.-S. Haematococcus Pluvialis: A Potential Feedstock for Multiple-Product Biorefining. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 344, 131103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Bacteria | Pollutants Degraded | Enzyme |
|---|---|---|
| Alcanivorax spp. | n-alkanes | Hydrolase (AlkB1 and AlkB2) Cytochrome P-450 dependent alkane monooxygenase |
| cycloalkanes | ||
| Gammaproteobacteria | Long C22 and C36 n-alkanes | Monooxygenase binding flavin (AlmA) |
| Cyclocasticus | PAHs | Peptidase Hydrolase |
| Colweillia | ||
| Pseudoalteromonas | ||
| Halomonas | PAHs | Exopolysaccharides |
| Methylomirabilis oxyfera | Methane | Methane monooxygenase |
| Microalgae | Pollutants Degraded | Enzyme |
|---|---|---|
| Chlorophyceae | Total Crude oil | Saponine |
| PAHs | Lypoxygenase | |
| Hydroperoxidase | ||
| THC | ROS production | |
| Chlorella spp. | THC | Extracellular polymeric substances |
| Haematococcus pluvialis | PAHs | Cytochrome P450 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Radice, R.P.; De Fabrizio, V.; Donadoni, A.; Scopa, A.; Martelli, G. Crude Oil Bioremediation: From Bacteria to Microalgae. Processes 2023, 11, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020442
Radice RP, De Fabrizio V, Donadoni A, Scopa A, Martelli G. Crude Oil Bioremediation: From Bacteria to Microalgae. Processes. 2023; 11(2):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020442
Chicago/Turabian StyleRadice, Rosa Paola, Vincenzo De Fabrizio, Antonietta Donadoni, Antonio Scopa, and Giuseppe Martelli. 2023. "Crude Oil Bioremediation: From Bacteria to Microalgae" Processes 11, no. 2: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020442
APA StyleRadice, R. P., De Fabrizio, V., Donadoni, A., Scopa, A., & Martelli, G. (2023). Crude Oil Bioremediation: From Bacteria to Microalgae. Processes, 11(2), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr11020442