Enhanced Anaerobic Performances of Kitchen Wastes in a Semi-Continuous Reactor by EDTA Improving the Water-Soluble Fraction of Fe
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.1.1. KWs and Inoculated Sludge
2.1.2. Chemicals
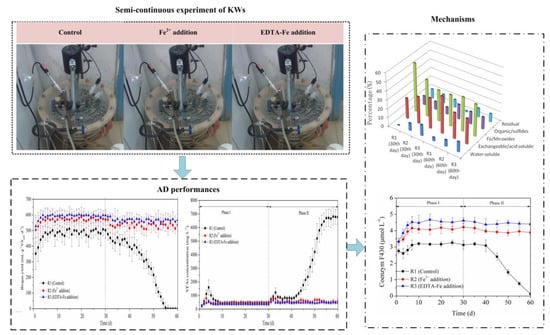
2.2. Experiment Set-Up
2.3. Analytical Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Methane Production
3.2. VFA Concentration and Composition
3.3. Fe Speciation
3.4. Enzyme Activity
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guo, Q.; Dai, X. Analysis on carbon dioxide emission reduction during the anaerobic synergetic digestion technology of sludge and kitchen waste: Taking kitchen waste synergetic digestion project in Zhenjiang as an example. Waste Manag. 2017, 69, 360–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezapour, S.; Samadi, A.; Kalavrouziotis, I.K.; Ghaemian, N. Impact of the uncontrolled leakage of leachate from a municipal solid waste landfill on soil in a cultivated-calcareous environment. Waste Manag. 2018, 82, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taeporamaysamai, O.; Ratanatamskul, C. Co-composting of various organic substrates from municipal solid waste using an on-site prototype vermicomposting reactor. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2016, 113, 357–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Hu, S. Cost recovery of municipal solid waste management in small cities of inland China. Waste Manag. Res. 2014, 32, 340–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braguglia, C.M.; Gallipoli, A.; Gianico, A.; Pagliaccia, P. Anaerobic bioconversion of food waste into energy: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 248, 37–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiran, E.U.; Trzcinski, A.P.; Ng, W.J.; Liu, Y. Bioconversion of food waste to energy: A review. Fuel 2014, 134, 389–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panepinto, D.; Genon, G. Analysis of the extrusion as a pretreatment for the anaerobic digestion process. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2016, 83, 206–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, M.; Liu, J.Y.; Ma, C.N.; Li, Y.Y.; Zou, L.P.; Qian, G.R.; Xu, Z.P. Improving the stability and efficiency of anaerobic digestion of food waste using additives: A critical review. J. Clean Prod. 2018, 192, 316–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Thanh, P.M.; Ketheesan, B.; Stuckey, D.C.; Zhou, Y. Effects of trace metal deficiency and supplementation on a submerged anaerobic membrane bioreactor. Bioresour.Technol. 2017, 241, 161–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Q.G.; Kubota, K.; Qiao, W.; Jing, Z.Q.; Zhang, Y.L.; Yu-You, L. Effect of ammonia inhibition on microbial community dynamic and process functional resilience in mesophilic methane fermentation of chicken manure. J. Chem. Technol. Biot. 2015, 90, 2161–2169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menon, A.; Wang, J.Y.; Giannis, A. Optimization of micronutrient supplement for enhancing biogas production from food waste in two-phase thermophilic anaerobic digestion. Waste Manag. 2017, 59, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.Q.; Wu, S.B.; Guo, J.B.; Zhou, J.; Dong, R.J. Performance and kinetic evaluation of semi-continuously fed anaerobic digesters treating food waste: Role of trace elements. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 178, 297–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choong, Y.Y.; Norli, I.; Abdullah, A.Z.; Yhaya, M.F. Impacts of trace element supplementation on the performance of anaerobic digestion process: A critical review. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 209, 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vintiloiu, A.; Boxriker, M.; Lemmer, A.; Oechsner, H.; Jungbluth, T.; Mathies, E.; Ramhold, D. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) on the bioavailability of trace elements during anaerobic digestion. Chem. Eng. J. 2013, 223, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zitomer, D.H.; Johnson, C.C.; Speece, R.E. Metal stimulation and municipal digester thermophilic/mesophilic activity. J. Environ. Eng.-ASCE 2008, 134, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thanh, P.M.; Ketheesan, B.; Yan, Z.; Stuckey, D.C. Trace metal speciation and bioavailability in anaerobic digestion: A review. Biotechnol. Adv. 2016, 34, 122–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.L.; Zhang, L.; Li, A.M. Enhanced anaerobic digestion of food waste by trace metal elements supplementation and reduced metals dosage by green chelating agent S, S-EDDS via improving metals bioavailability. Water Res. 2015, 84, 266–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Hu, K.; Zheng, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Guo, S.; Zhao, X.; Cui, Z.; Wang, X. Effects of adding EDTA and Fe2+ on the performance of reactor and microbial community structure in two simulated phases of anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 183–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Zhao, H.N.; Chen, S.J.; Long, F.X.; Huang, B.; Yang, B.Q.; Pan, X.J. A magnetically recyclable chitosan composite adsorbent functionalized with EDTA for simultaneous capture of anionic dye and heavy metals in complex wastewater. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 356, 69–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, M.; Lima, M.J.A.; Nascimento, C.F.; Rocha, F.R.P. A green and cost-effective procedure for determination of anionic surfactants in milk with liquid-liquid microextraction and smartphone-based photometric detection. Microchem. J. 2018, 143, 259–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluhar, S.; Jez, E.; Lestan, D. The use of zero-valent Fe for curbing toxic emissions after EDTA-based washing of Pb, Zn and Cd contaminated calcareous and acidic soil. Chemosphere 2019, 215, 482–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Public Health Association (APHA); American Water Works Association (AWWA); Water Environment Federation (WEF). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 20th ed.; APHA: Washington, DC, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Rauret, G.; Lopez-Sanchez, J.F.; Sahuquillo, A.; Rubio, R.; Davidson, C.; Ure, A.; Quevauviller, P. Improvement of the BCR three step sequential extraction procedure prior to the certification of new sediment and soil reference materials. J. Environ. Monit. 1999, 1, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.G.; Jiang, S.; Yuan, H.Y.; Zhou, Q.; Gu, G.W. Hydrolysis and acidification of waste activated sludge at different pHs. Water Res. 2007, 41, 683–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bashiri, G.; Rehan, A.M.; Greenwood, D.R.; Dickson, J.M.J.; Baker, E.N. Metabolic Engineering of Cofactor F-420 Production in Mycobacterium smegmatis. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e15803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kida, K.; Shigematsu, T.; Kijima, J.; Numaguchi, M.; Mochinaga, Y.; Abe, N.; Morimura, S. Influence of Ni2+ and Co2+ on methanogenic activity and the amounts of coenzymes involved in methanogenesis. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2001, 91, 590–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, H.; Yuan, X.; Zhu, W.; Cui, Z.; Wang, X. Optimization of Fe2+ supplement in anaerobic digestion accounting for the Fe-bioavailability. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 250, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.L.; Xu, Z.Y.; Zhao, M.X.; Shi, W.S.; Huang, Z.X.; He, D.; Ruan, W.Q. Construction and evaluation of efficient solid-state anaerobic digestion system via vinegar residue. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2018, 133, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Q.H.; Li, X.F.; Du, G.C.; Chen, J. Effect of nitrilotri acetic acid on bioavailability of nickel during methane fermentation. Chem. Eng. J. 2008, 143, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortner, M.; Rameder, M.; Rachbauer, L.; Bochmann, G.; Fuchs, W. Bioavailability of essential trace elements and their impact on anaerobic digestion of slaughterhouse waste. Biochem. Eng. J. 2015, 99, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferry, J.G. Fundamentals of methanogenic pathways that are key to the biomethanation of complex biomass. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2011, 22, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zandvoort, M.H.; van Hullebusch, E.D.; Fermoso, F.G.; Lens, P.N.L. Trace metals in anaerobic granular sludge reactors: Bioavailability and dosing strategies. Eng. Life Sci. 2006, 6, 293–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Parameters | Unit | KWs | Inoculated Sludge |
|---|---|---|---|
| pH | - | 5.6 ± 0.1 | 7.8 ± 0.1 |
| Total solid (TS) | g·L−1 | 223.8 ± 0.5 | 36.4 ± 0.3 |
| Volatile solid (VS) | g·L−1 | 197.5 ± 1.5 | 20.2 ± 0.3 |
| Ash | % | 11.7 ± 0.2 | - |
| C | % | 49.3 ± 0.5 | - |
| H | % | 7.4 ± 0.1 | - |
| N | % | 2.9 ± 0.1 | - |
| Fe (total) | mg·L−1 | 22.461 ± 0.05 | 53.332 ± 0.05 |
| Fe (soluble) | mg·L−1 | - | 8.785 ± 0.01 |
| Samples | Water-Soluble (%) | Exchangeable/Acid Soluble (%) | Fe/Mn Oxides (%) | Organic/Sulfides (%) | Residual (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| R1 (30th day) | 0.05 ± 0.01 | 23.31 ± 1.10 | 55.51 ± 4.64 | 10.32 ± 0.85 | 10.81 ± 0.92 |
| R2 (30th day) | 8.31 ± 0.72 | 30.54 ± 2.44 | 42.12 ± 3.17 | 9.27 ± 0.48 | 9.76 ± 0.40 |
| R3 (30th day) | 12.43 ± 0.95 | 34.66 ± 1.58 | 35.54 ± 1.65 | 8.20 ± 0.40 | 9.17 ± 0.73 |
| R1 (60th day) | 3.82 ± 0.34 | 42.25 ± 4.05 | 35.83 ± 2.72 | 16.88 ± 0.76 | 1.22 ± 0.06 |
| R2 (60th day) | 7.25 ± 0.30 | 29.52 ± 2.35 | 38.86 ± 3.06 | 14.25 ± 1.65 | 10.12 ± 1.45 |
| R3 (60th day) | 11.37 ± 1.25 | 28.92 ± 1.40 | 36.52 ± 1.82 | 13.84 ± 0.85 | 9.35 ± 0.61 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Kang, X.; Cheng, H. Enhanced Anaerobic Performances of Kitchen Wastes in a Semi-Continuous Reactor by EDTA Improving the Water-Soluble Fraction of Fe. Processes 2019, 7, 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7060351
Liu Y, Kang X, Cheng H. Enhanced Anaerobic Performances of Kitchen Wastes in a Semi-Continuous Reactor by EDTA Improving the Water-Soluble Fraction of Fe. Processes. 2019; 7(6):351. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7060351
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Yali, Xiaorong Kang, and Han Cheng. 2019. "Enhanced Anaerobic Performances of Kitchen Wastes in a Semi-Continuous Reactor by EDTA Improving the Water-Soluble Fraction of Fe" Processes 7, no. 6: 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7060351
APA StyleLiu, Y., Kang, X., & Cheng, H. (2019). Enhanced Anaerobic Performances of Kitchen Wastes in a Semi-Continuous Reactor by EDTA Improving the Water-Soluble Fraction of Fe. Processes, 7(6), 351. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr7060351