A Review on the Effect from Steel Slag on the Growth of Microalgae
Abstract
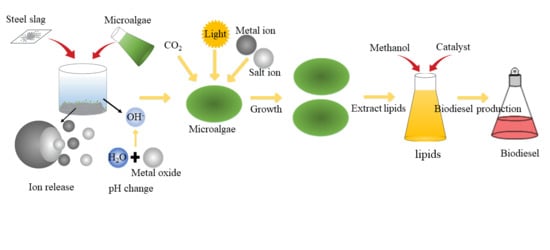
:1. Introduction
2. Steel Slag Characteristics
2.1. Chemical Composition and Physical Properties of Steel Slag
2.2. Dissolution Behavior of Steel Slag in Solution
2.2.1. Dissolution Behavior of Iron, Phosphorus and Calcium in Steel Slag
2.2.2. Dissolution of Silicate in Steel Slag
3. The Effect of Metal Ions on the Growth of Microalgae
4. Study on the Growth Characteristics of Steel Slag on Microalgae
5. Assess the Impact of Microalgae on the Natural Environment and Social Benefits
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shen, H.; Forssberg, E. An Overview of Recovery of Metals from Slags. Waste Manag. 2003, 23, 933–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Bao, Y.; Wang, M. Steel Slag in China: Treatment, Recycling, and Management. Waste Manag. 2018, 78, 318–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, B.; Li, B.; Huang, S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, Y.; Banthia, N. Hydration and Soundness Properties of Phosphoric Acid Modified Steel Slag Powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 254, 119319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drissen, P. Recent Development in Slag Treatment and Dust Recycling. Steel Res. Int. 2009, 80, 737–745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Yu, Q.; Wei, J.; Li, J.; Zhang, P. Preparation of High Performance Blended Cements and Reclamation of Iron Concentrate from Basic Oxygen Furnace Steel Slag. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2011, 56, 48–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Tang, Z.; Li, N.; Cui, L.; Mao, X. Mechanism and Process Study on Steel Slag Enhancement for CO2 Capture by Seawater. Appl. Energy 2020, 276, 115515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Cai, Q.-S. Steel Slag as an Iron Fertilizer for Corn Growth and Soil Improvement in a Pot Experiment. Pedosphere 2006, 16, 519–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Wang, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hu, W.; Ni, W. On the Use of Blast Furnace Slag and Steel Slag in the Preparation of Green Artificial Reef Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 241–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, A.; Cui, J.; He, D.; Tian, N. Theoretical and Experimental on Carbon Dioxide Sequestration Degree of Steel Slag. J. Iron Steel Res. Int. 2012, 19, 29–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omale, S.O.; Choong, T.S.Y.; Abdullah, L.C.; Siajam, S.I.; Yip, M.W. Utilization of Malaysia EAF Slags for Effective Application in Direct Aqueous Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide under Ambient Temperature. Heliyon 2019, 5, e02602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ukwattage, N.L.; Ranjith, P.G.; Li, X. Steel-Making Slag for Mineral Sequestration of Carbon Dioxide by Accelerated Carbonation. Measurement 2017, 97, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Tam, N.F.Y.; Yao, A.; Qiu, R.; Li, W.C.; Ye, Z. Growth and Cd Uptake by Rice (Oryza Sativa) in Acidic and Cd-Contaminated Paddy Soils Amended with Steel Slag. Chemosphere 2017, 189, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasrawi, H. The Use of Steel Slag Aggregate to Enhance the Mechanical Properties of Recycled Aggregate Concrete and Retain the Environment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 54, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Li, R.; Liu, J. Preparation and Properties of Carbonated Steel Slag Used in Cement Cementitious Materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 283, 122667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, F.; Zhao, X.; Peng, K.; Liang, S.; Jia, X.; Qian, L. Catalytic Reforming of Biomass Primary Tar from Pyrolysis over Waste Steel Slag Based Catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2019, 44, 16224–16233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sathasivam, R.; Radhakrishnan, R.; Hashem, A.; Abd-Allah, E.F. Microalgae Metabolites: A Rich Source for Food and Medicine. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2019, 26, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, A.; Sun, C.; Fu, Q.; Liao, Q.; Huang, Y.; Zhu, X.; Li, Q. Biofuel Production from Wet Microalgae Biomass: Comparison of Physicochemical Properties and Extraction Performance. Energy 2020, 212, 118581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, S.; Villanova, V.; Grisafi, F.; Caputo, G.; Brucato, A.; Scargiali, F. Autochthonous Microalgae Grown in Municipal Wastewaters as a Tool for Effectively Removing Nitrogen and Phosphorous. J. Water Process Eng. 2020, 38, 101647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, A.; Thomas-Hall, S.R.; Manzoor, M.; Jabeen, F.; Iqbal, M.; uz Zaman, Q.; Schenk, P.M.; Asif Tahir, M. Mixed Microalgae Consortia Growth under Higher Concentration of CO2 from Unfiltered Coal Fired Flue Gas: Fatty Acid Profiling and Biodiesel Production. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2018, 179, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Suarez Garcia, E.; van Leeuwen, J.; Safi, C.; Sijtsma, L.; Eppink, M.H.M.; Wijffels, R.H.; van den Berg, C. Selective and Energy Efficient Extraction of Functional Proteins from Microalgae for Food Applications. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 268, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Fu, Q.; Liao, Q.; Zhang, H.; Huang, Y.; Xia, A.; Zhu, X. Rheological Properties of Microalgae Slurry for Application in Hydrothermal Pretreatment Systems. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 249, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, H.; Ben, I.; Garrab, M.; Aly, R.; Gagnon, J.; Naghmouchi, K. Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, Cytotoxic and Anticholinesterase Activities of Water-Soluble Polysaccharides Extracted from Microalgae Isochrysis galbana and Nannochloropsis oculata. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 2017, 82, 509–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, L.; Li, H.; Wang, Q. A Novel One-Step Method for Oil-Rich Biomass Production and Harvesting by Co-Cultivating Microalgae with Filamentous Fungi in Molasses Wastewater. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 275, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, H.; Xu, G.; Cheng, H.; Wang, J.; Wan, Y.; Chen, H. An Overview of Utilization of Steel Slag. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2012, 16, 791–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Logeshwari, J.; Sivapullaiah, P.V. Physical, Chemical, Morphological and Strength Characteristics of Steel Slags in View of Its Potential Application in Geotechnical Engineering. Mater. Today Proc. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Qu, Z. Physicochemical Property and Chromium Leaching Behavior in Different Environments of Glass Ceramics Prepared from AOD Stainless Steel Slag. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 805, 1106–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, F.; Yun, S.; Zhang, C.; Xu, H.; Wang, Z. Steel Slag as Accelerant in Anaerobic Digestion for Nonhazardous Treatment and Digestate Fertilizer Utilization. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 282, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mombelli, D.; Mapelli, C.; Barella, S.; Di Cecca, C.; Le Saout, G.; Garcia-Diaz, E. The Effect of Chemical Composition on the Leaching Behaviour of Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) Carbon Steel Slag during a Standard Leaching Test. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2016, 4, 1050–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guo, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhao, J.; Zuo, K. Utilization of Unprocessed Steel Slag as Fine Aggregate in Normal- and High-Strength Concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 204, 41–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cikmit, A.A.; Tsuchida, T.; Hashimoto, R.; Honda, H.; Kang, G.; Sogawa, K. Expansion Characteristic of Steel Slag Mixed with Soft Clay. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 227, 116799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bing, L.; Biao, T.; Zhen, M.; Hanchi, C.; Hongbo, L. Physical and Chemical Properties of Steel Slag and Utilization Technology of Steel Slag at Home and Abroad. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2019, 242, 032012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, L.V.; Barron, A.R. The Recycling and Reuse of Steelmaking Slags—A. Review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2019, 146, 244–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Futatsuka, T.; Shitogiden, K.; Miki, T.; Nagasaka, T.; Hino, M. Dissolution Behavior of Nutrition Elements from Steelmaking Slag into Seawater. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 753–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Gao, X.; Ueda, S.; Kitamura, S. Effect of Fe2+/T.Fe Ratio on the Dissolution Behavior of P from Steelmaking Slag with High P2O5 Content. J. Sustain. Metall. 2018, 4, 443–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Atsumi, H.; Matsuura, H.; Tsukihashi, F. Influence of Gluconic Acid on Dissolution of Si, P and Fe from Steelmaking Slag with Different Composition into Seawater. ISIJ Int. 2014, 54, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miki, T.; Futatsuka, T.; Shitogiden, K.; Nagasaka, T.; Hino, M. Dissolution Behavior of Environmentally Regulated Elements from Steelmaking Slag into Seawater. ISIJ Int. 2004, 44, 762–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, X.; Matsuura, H.; Tsukihashi, F. Dissolution Mechanism of Various Elements into Seawater for Recycling of Steelmaking Slag. ISIJ Int. 2012, 52, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Takahashi, T.; Yokoyama, S. Bioassay of Components Eluted from Electric Arc Furnace Steel Slag Using Microalgae Chlorella. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 1497–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tanaka, M.; Hirata, J.; Nakamoto, D.; Terada, I.; Ryumae, I.; Takahashi, M.; Oikawa, T.; Takahashi, K.; Aimoto, M. Dissolution Behavior of Silicic Acid from Steelmaking Slag to Seawater. Tetsu Hagane J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 2014, 100, 919–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, B.-M.; Lai, W.-L.; Chang, Y.-M.; Liang, Y.-S.; Kao, C.-M. Using Desulfurization Slag as the Aquacultural Amendment for Fish Pond Water Quality Improvement: Mechanisms and Effectiveness Studies. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 143, 1313–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, E.; Yüksel, E.; Altınbaş, M. Effect of Different Iron Sources on Sustainable Microalgae-Based Biodiesel Production Using Auxenochlorella protothecoides. Renew. Energy 2020, 162, 1970–1978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizwan, M.; Mujtaba, G.; Lee, K. Effects of Iron Sources on the Growth and Lipid/Carbohydrate Production of Marine Microalga Dunaliella tertiolecta. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2017, 22, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameri, M.; Baron-Sola, A.; Khavari-Nejad, R.A.; Soltani, N.; Najafi, F.; Bagheri, A.; Martinez, F.; Hernández, L.E. Aluminium Triggers Oxidative Stress and Antioxidant Response in the Microalgae Scenedesmus sp. J. Plant Physiol. 2020, 246–247, 153114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danouche, M.; El Ghachtouli, N.; El Baouchi, A.; El Arroussi, H. Heavy Metals Phycoremediation Using Tolerant Green Microalgae: Enzymatic and Non-Enzymatic Antioxidant Systems for the Management of Oxidative Stress. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Lee, C.-H.; Ko, K.; Lee, Y.-J.; Kim, K.-N.; Kim, M.-K.; Chung, Y.-H.; Kim, D.; Yeo, I.-K.; Oda, T. Use of Phenol-Induced Oxidative Stress Acclimation to Stimulate Cell Growth and Biodiesel Production by the Oceanic Microalga Dunaliella salina. Algal Res. 2016, 17, 61–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, T.; Wang, J.; Zheng, H.; Wu, X.; Wang, Y.; Liu, M.; Xiang, S.; Cao, L.; Ruan, R.; Liu, Y. Characterization of Additional Zinc Ions on the Growth, Biochemical Composition and Photosynthetic Performance from Spirulina platensis. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 269, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Yang, C.; Zeng, G.; Wu, S.; Lin, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Lou, W.; Du, C.; Nie, L.; Zhong, Y. Nutrient Removal from Swine Wastewater with Growing Microalgae at Various Zinc Concentrations. Algal Res. 2020, 46, 101804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Xu, J.; Li, T.; Wang, L.; Deng, T.; Yu, X. Effects of Additional Mg2+ on the Growth, Lipid Production, and Fatty Acid Composition of Monoraphidium sp. FXY-10 under Different Culture Conditions. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 1247–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polat, E.; Yüksel, E.; Altınbaş, M. Mutual Effect of Sodium and Magnesium on the Cultivation of Microalgae Auxenochlorella protothecoides. Biomass Bioenergy 2020, 132, 105441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Cao, J.; Xing, G.; Yuan, H. Lipid Production Combined with Biosorption and Bioaccumulation of Cadmium, Copper, Manganese and Zinc by Oleaginous Microalgae Chlorella minutissima UTEX2341. Bioresour. Technol. 2015, 175, 537–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abinandan, S.; Subashchandrabose, S.R.; Venkateswarlu, K.; Perera, I.A.; Megharaj, M. Acid-Tolerant Microalgae Can Withstand Higher Concentrations of Invasive Cadmium and Produce Sustainable Biomass and Biodiesel at pH 3.5. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 281, 469–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sugie, K.; Taniguchi, A. Bioavailability and Dulability of the Iron Released from a Steelmaking Slag for Tow Thalassiosira Species. Tetsu Hagane J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 2007, 93, 558–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugie, K.; Taniguchi, A. Continuous Supply of Bioavailable Iron for Marine Diatoms from Steelmaking Slag. ISIJ Int. 2011, 51, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Osawa, K.; Asaoka, S.; Madinabeitia, I.; Liao, L.M.; Hirata, S. Enhancement of Marine Phytoplankton Growth by Steel-Making Slag as a Promising Component for the Development of Algal Biofuels. ISIJ Int. 2016, 56, 708–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arita, K.; Umiguchi, Y.; Taniguchi, A. Availability of Steelmaking Slag as a Source of Essential Elements for Phytoplankton. Tetsu Hagane J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 2003, 89, 415–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cañavate, J.P.; Armada, I.; Hachero-Cruzado, I. Aspects of Phosphorus Physiology Associated with Phosphate-Induced Polar Lipid Remodelling in Marine Microalgae. J. Plant Physiol. 2017, 214, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haraguchi, K.; Suzuki, K.; Taniguchi, A. Effects of Steelmaking Slag Addition on Growth of Marine Phytoplankton. ISIJ Int. 2003, 43, 1461–1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Suzuki, M.; Yamamoto, T. Effect of Steel-Making Slag Addition on Growth of the Diatom Skeletonema costatum and the Dinoflagellate Alexandrium tamarense. Tetsu Hagane J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 2005, 91, 783–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishii, M.; Yamamoto, T.; Nakahara, T.; Takeda, K.; Asaoka, S. Effect of Carbonated Steelmaking Slag on the Growth of Benthic Microalgae. Tetsu Hagane J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 2013, 99, 260–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arita, K.; Umiguchi, Y.; Taniguchi, A. Availability of Elements Originated from Steelmaking Slag for Phytoplankton Enriched Simultaneously with Treated Urban Sewage. Tetsu Hagane J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 2003, 89, 422–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Haraguchi, K.; Taniguchi, A. Effect of Simultaneous Enrichment of Dephosphorization Steelmaking Slag and Treated Municipal Sewage on Growth of Coastal Phytoplankton Assemblage. Tetsu Hagane J. Iron Steel Inst. Jpn. 2003, 89, 430–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galès, A.; Triplet, S.; Geoffroy, T.; Roques, C.; Carré, C.; Le Floc’h, E.; Lanfranchi, M.; Simier, M.; Roque d’Orbcastel, E.; Przybyla, C.; et al. Control of the PH for Marine Microalgae Polycultures: A Key Point for CO2 Fixation Improvement in Intensive Cultures. J. CO2 Util. 2020, 38, 187–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogami, R.; Tam, L.T.; Anh, H.T.L.; Quynh, H.T.H.; Thom, L.T.; Nhat, P.V.; Thu, N.T.H.; Hong, D.D.; Wakisaka, M. Growth Promotion Effect of Steelmaking Slag on Spirulina platensis. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2016, 704, 012019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Čabanová, K.; Vlček, J.; Seidlerová, J.; Matějka, V.; Peikertová, P.; Martausová, I.; Kukutschová, J. Chemical and Phase Composition of Metallurgical Slags and Their Effects on Freshwater Green Algae. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, S2–S10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nogami, R.; Ushijima, K.; Nishida, H.; Wakisaka, M. Enhancement of Growth and Lipid Production of Botryococcus braunii by Steel Slags. J. Jpn. Inst. Energy 2017, 96, 372–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakamura, Y.; Taniguchi, A.; Okada, S.; Tokuda, M. Positive Growth of Phytoplankton under Conditions Enriched with Steel-Making Slag Solution. ISIJ Int. 1998, 38, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Rita Sulistya Dewi, E.; Nuravivah, R. Potential Of Microalgae Chlorella vulgaris As Bioremediation Agents of Heavy Metal Pb (Lead) On Culture Media. E3S Web Conf. 2018, 31, 05010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nacorda, J.O.; Martinez-Goss, M.R.; Torreta, N.K.; Merca, F.E. Metal Resistance and Removal by Two Strains of the Green Alga, Chlorella vulgaris Beijerinck, Isolated from Laguna de Bay, Philippines. J. Appl. Phycol. 2007, 19, 701–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, T.-L.; Dao, T.-S.; Bui, H.; Pham, T.; Ngo, T.; Bui, H. Lipid Production Combined with Removaland Bioaccumulation of Pb by Scenedesmus sp.Green Alga. Pol. J. Environ. Stud. 2020, 29, 1785–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanab, S.; Essa, A.; Shalaby, E. Bioremoval Capacity of Three Heavy Metals by Some Microalgae Species (Egyptian Isolates). Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 392–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, J.; Shen, Z.; Li, A.; Ma, T.; Feng, Q.; Sun, Y. Treatment of High-Nitrate Wastewater Mixtures from MnO2 Industry by Chlorella vulgaris. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 291, 121836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Ho, S.-H.; Cheng, C.-L.; Guo, W.-Q.; Nagarajan, D.; Ren, N.-Q.; Lee, D.-J.; Chang, J.-S. Perspectives on the Feasibility of Using Microalgae for Industrial Wastewater Treatment. Bioresour. Technol. 2016, 222, 485–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghizadeh, A.; Farhad dad, F.; Moghaddasi, L.; Rahimi, R. CO2 Capture from Air by Chlorella vulgaris Microalgae in an Airlift Photobioreactor. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 243, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, X.; Xu, M. Stabilized CO2 Capture Performance of Extruded–Spheronized CaO-Based Pellets by Microalgae Templating. Proc. Combust. Inst. 2017, 36, 3977–3984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.-P.; Zhang, Y.; Li, W.-C. Sustainable Microalgae for the Simultaneous Synthesis of Carbon Quantum Dots for Cellular Imaging and Porous Carbon for CO2 Capture. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2017, 493, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branco-Vieira, M.; Mata, T.M.; Martins, A.A.; Freitas, M.A.V.; Caetano, N.S. Economic Analysis of Microalgae Biodiesel Production in a Small-Scale Facility. Energy Rep. 2020, 6, 325–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Wang, N.; Yang, M.; Ding, K.; Wang, Y.-Z.; Huo, D.; Hou, C. Lipid Accumulation and Biodiesel Quality of Chlorella pyrenoidosa under Oxidative Stress Induced by Nutrient Regimes. Renew. Energy 2019, 143, 1782–1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Company Name | Steel (Million Tons) | Steel Slag (Million Tons) | Address |
|---|---|---|---|
| China BaoWu Steel Group | 9547 | 1432.05 | Shanghai |
| HBIS Group | 4656 | 698.4 | Shijiazhuang |
| Jiangsu Shagang Group | 4110 | 616.5 | Zhangjiagang |
| AnSteel Group | 3920 | 588 | Anshan |
| JianLong Group | 3119 | 467.85 | Beijin |
| ShouGang Group | 2934 | 440.1 | Beijin |
| Shandong iron & Steel Group Company Limited | 2758 | 413.7 | Jinan |
| VALIN Group | 2431 | 364.65 | Changsha |
| BenXi Iron & Steel Group | 1618 | 242.7 | Benxi |
| FangDa Group | 1566 | 234.9 | Nanchang |
| BaoGang Group | 1546 | 231.9 | Baotou |
| LiuZhou Steel Group | 1440 | 216 | Liuzhou |
| RiZhao Steel Group | 1420 | 213 | Rizhao |
| CITIC PACIFIC Special Steel Group | 1355 | 203.25 | Jiangyin |
| JingYe Group | 1258 | 188.7 | Shijiazhuang |
| Types of Microalgae | Nutrient Types | Growth Conditions | Growth Effect | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| T. guillardii | A | 33 mg/L | Positive | [57] |
| B | 33 mg/L | Positive | [57] | |
| A | 50 mg/L | Positive | [55] | |
| B and M | 20 mg/L, Sewage 20% | Positive | [61] | |
| A and M | 50 mg/L, Sewage 40% | Positive | [60] | |
| D. subspicatus | D | Not shown | Negative | [64] |
| E | Not shown | Negative | [64] | |
| F | Not shown | Positive | [64] | |
| G | Not shown | Negative | [64] | |
| H | Not shown | Negative | [64] | |
| C. vulgaris | D | Not shown | Negative | [64] |
| E | Not shown | Negative | [64] | |
| F | Not shown | Positive | [64] | |
| G | Not shown | Positive | [64] | |
| H | Not shown | Positive | [64] | |
| Chlorella | I | 100 mg/L | Positive | [38] |
| C | 25 mg/L | Positive | [40] | |
| J | 60–80% Steel slag solution | Positive | [66] | |
| Skeletonema costatum | B | 200 mg/L | Positive | [58] |
| B | 100 mg/L | Positive | [58] | |
| J | 60–80% Steel slag solution | Positive | [66] | |
| Botryococcus braunii | J | 5 g/L | Positive | [65] |
| F | 5 g/L | Positive | [65] | |
| Nitzschia laevis | K | 10 g/L | Positive | [59] |
| L | 5 g/L | Positive | [59] | |
| Alexandrium tamarense | B | 50~100 mg/L | Negative | [58] |
| Spirulina platensis | J | 500 mg/L | Positive | [63] |
| T. oceanica | A | 20 mg/L | Positive | [53] |
| T. nordenskioeldii | A | 20 mg/L | Positive | [53] |
| Thalassiositra angulata | J | 100% Steel slag solution | Positive | [66] |
| Amphidinium carteae | J | 100% Steel slag solution | Positive | [66] |
| Thalassiosira allenii | J | 60–80% Steel slag solution | Positive | [66] |
| Isochrysis galbana | J | 60–80% Steel slag solution | Positive | [66] |
| Chaetoceros gracile | J | 20–60% Steel slag solution | Positive | [66] |
| Rhodomonas lens | J | 20–60% Steel slag solution | Positive | [66] |
| Emiliania huxleyi | J | 20–60% Steel slag solution | Positive | [66] |
| Tetraselmis tetrathela | J | 20–100% Steel slag solution | Positive | [66] |
| Dunaliella tertiolecta | J | 20–100% Steel slag solution | Positive | [66] |
| Synechococcus sp. | J | 20–100% Steel slag solution | Positive | [66] |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yu, Q.; Liu, T.-J.; Cai, S.; Wang, F.-P.; Gao, D.; Wang, X.-M.; Wang, Y.-T.; Zeng, Y.-N. A Review on the Effect from Steel Slag on the Growth of Microalgae. Processes 2021, 9, 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050769
Yu Q, Liu T-J, Cai S, Wang F-P, Gao D, Wang X-M, Wang Y-T, Zeng Y-N. A Review on the Effect from Steel Slag on the Growth of Microalgae. Processes. 2021; 9(5):769. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050769
Chicago/Turabian StyleYu, Qing, Tian-Ji Liu, Shuang Cai, Fu-Ping Wang, Di Gao, Xiao-Man Wang, Yi-Tong Wang, and Ya-Nan Zeng. 2021. "A Review on the Effect from Steel Slag on the Growth of Microalgae" Processes 9, no. 5: 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050769
APA StyleYu, Q., Liu, T. -J., Cai, S., Wang, F. -P., Gao, D., Wang, X. -M., Wang, Y. -T., & Zeng, Y. -N. (2021). A Review on the Effect from Steel Slag on the Growth of Microalgae. Processes, 9(5), 769. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr9050769