Application of Infrared Free-Electron Laser Irradiation of Protein Complexes Binding to Salen-Type Schiff Base Zn(II) Complexes Using Secondary Conformational Changes in the Proteins for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease
Abstract
:1. Introduction: The Proteins and Zinc That Cause Alzheimer’s Disease
2. Our Laboratory’s Previous Research on Zn(II) Complexes
2.1. Concept of Molecular Orientation Study in Polymer Films
2.2. Preparations of Zn(II) Complexes
2.3. Examples of Zn(II) Complexes
2.4. Spectra of Zn(II) Complexes
2.5. Polarized Light-Induced Anisotropic Molecular Orientation of Zn(II) Complexes
3. The Structural Changes Caused by Irradiating Proteins Bound to Zinc Complexes with IR-FEL
3.1. Research Using IR-FEL
3.2. X-ray Free-Electron Lasers (X-FEL)
3.3. IR-FEL
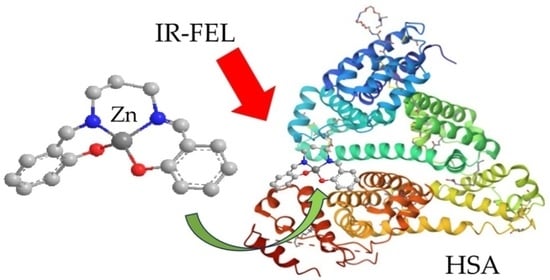
3.4. Irradiating IR-FEL on the Complex of Human Serum Albumin (HSA) and Zinc Complex
3.4.1. IR-FEL Irradiation of Hybrid Material
3.4.2. UV-Vis, CD, and Fluorescence
3.4.3. FT-IR
3.5. Docking Simulation of Lysozyme and Zinc Complexes for IR-FEL Irradiation
3.5.1. Preparation of Metal Complexes
3.5.2. Experimental Procedure
3.5.3. FRET of ZnGlyGlyH and ZnGlyGlyPh
3.5.4. Docking Simulation
3.5.5. Importance of Proper Characterization of Samples Required during Experimental Confirmation of Docking Simulations
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sagai, M. Pathogenesis and prevention of dementia. Jpn. Hum. Care Sci. J. 2010, 3.1, 6–24. [Google Scholar]
- Taisuke Tomita, M.D. γ-secretase for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease Structure-Activity Relationships. Clin. Neurol. 2008, 48, 907–909. [Google Scholar]
- De Benedictis, C.A.; Vilella, A.; Grabrucker, A.M. Alzheimer’s Disease, 6. In The Role of Trace Metals in Alzheimer’s Disease; Codon Publications: Brisbane, Australia, 2019; p. 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, M.; Tanaka, K.-I.; Kato-Negishi, M. Crosstalk of copper and zinc in the pathogenesis of vascular dementia. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2022, 71, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parthasarathy, S.; Long, F.; Miller, Y.; Xiao, Y.; McElheny, D.; Thurber, K.; Ma, B.; Nussinov, R.; Ishii, Y. Molecular-Level Examination of Cu2+ Binding Structure for Amyloid Fibrils of 40-Residue Alzheimer’s β by Solid-State NMR Spectroscopy. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 3390–3400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, B.R.; Ryan, T.M.; Bush, A.I.; Masters, C.L.; Duce, J.A. The role of metallobiology and amyloid-β peptides in Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neurochem. 2012, 120 (Suppl. S1), 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederickson, C.J.; Klitenick, M.A.; Manton, W.I.; Kirkpatrick, J.B. Cytoarchitectonic distribution of zinc in the hippocampus of man and the rat. Brain Res. 1983, 273, 335–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederickson, C.J.; Giblin, L.J.; Rengarajan, B.; Masalha, R.; Frederickson, C.J.; Zeng, Y.; Lopez, E.V.; Koh, J.-Y.; Chorin, U.; Besser, L.; et al. Synaptic release of zinc from brain slices: Factors governing release, imaging, and accurate calculation of concentration. J. Neurosci. Methods 2006, 154, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kay, A.R. Imaging synaptic zinc: Promises and perils. Trends Neurosci. 2006, 29, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, M.; Sadakane, Y.; Mizuno, D. Role of zinc in the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. J. Zinc Nutr. Ther. 2014, 5, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Vogt, K.; Mellor, J.; Tong, G.; Nicoll, R. The actions of synaptically released zinc at hippocampal mossy fiber synapses. Neuron 2000, 26, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mizuno, D.; Kawahara, M. The Molecular Mechanisms of Zinc Neurotoxicity and the Pathogenesis of Vascular Type Senile Dementia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2013, 14, 22067–22081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, K. Neurodegenerative diseases and neurovascular unit disorders. Neurotherapy 2018, 35, 380–384. [Google Scholar]
- National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology Research. Introduction Column, Aducanumab, a New Treatment for Dementia (4). Available online: https://www.ncgg.go.jp/ri/labo/04.html (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology Research. Introduction Column, Aducanumab, a New Treatment for Dementia (5). Available online: https://www.ncgg.go.jp/ri/labo/05.html (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- FDA’s Decision to Approve New Treatment for Alzheimer’s Disease. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/drugs/news-events-human-drugs/fdas-decision-approve-new-treatment-alzheimers-disease (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology Research. Introduction Column, Aducanumab, a New Treatment for Dementia (3). Available online: https://www.ncgg.go.jp/ri/labo/03.html (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Morii, D.; Maeda, Y.; Murakami, M.; Nomura, K.; Hara, Y. Japan-Medical Research Institute Research Report, No. 109 Aducanumab, a New Drug for Alzheimer’s Disease (Aduhelm™) about US FDA Approval, 28 July 2021. Available online: https://www.jmari.med.or.jp/wp-content/uploads/2021/10/RR109.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- National Center for Geriatrics and Gerontology Research. Introduction Column, Aducanumab, a New Treatment for Dementia (1). Available online: https://www.ncgg.go.jp/ri/labo/01.html (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Plowey, E.D.; Bussiere, T.; Rajagovindan, R.; Sebalusky, J.; Hamann, S.; von Hehn, C.; Castrillo-Viguera, C.; Sandrock, A.; Haeberlein, S.B.; van Dyck, C.H.; et al. Alzheimer disease neuropathology in a patient previously treated with aducanumab. Acta Neuropathol. 2022, 144, 143–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- FDA Converts Novel Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment to Traditional Approval Action Follows Confirmatory Trial to Verify Clinical Benefit. Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-converts-novel-alzheimers-disease-treatment-traditional-approval (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- van Dyck, C.H.; Swanson, C.J.; Aisen, P.; Bateman, R.J.; Chen, C.; Gee, M.; Kanekiyo, M.; Li, D.; Reyderman, L.; Cohen, S.; et al. Lecanemab in Early Alzheimer’s Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 9–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biogen and Eisai Launch Multiple Initiatives to Help Patients with Alzheimer’s Disease Access ADUHELM™ 7 June 2021 • NEWS RELEASE. Available online: https://investors.biogen.com/news-releases/news-release-details/biogen-and-eisai-launch-multiple-initiatives-help-patients (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Lin, G.A.; Whittington, M.D.; Synnott, P.G.; McKenna, A.; Campbell, J.; Pearson, S.D.; Rind, D.M. Aducanumab for Alzheimer’s Disease: Effectiveness and Value; Draft Evidence Report. Institute for Clinical and Economic Review, 5 May 2021. Available online: https://icer.org/wp-content/uploads/2020/10/ICER_ALZ_Final_Report_080521-1.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Kawasaki, T. Photo-Dissociation of Amyloid Fibrils by using IR Free Electron Laser. Nippon. Laser Igakkaishi 2015, 36, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Sakai, T.; Zen, H.; Sumitomo, Y.; Nogami, K.; Hayakawa, K.; Yaji, T.; Ohta, T.; Tsukiyama, K.; Hayakawa, Y. Cellulose Degradation by Infrared free-electron laser. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 9064–9068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Yaji, T.; Ohta, T.; Tsukiyama, K. Application of mid-infrared free-electron laser tuned to amide bands for dissociation of aggregate structure of protein. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2016, 23, 152–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawasaki, T.; Tsukiyama, K.; Irizawa, A. Dissolution of a fibrous peptide by terahertz free electron laser. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 10636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Yaji, T.; Ohta, T.; Tsukiyama, K.; Nakamura, K. Dissociation of β-Sheet Stacking of Amyloid β Fibrils by Irradiation of Intense, Short-Pulsed Mid-infrared Laser. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 38, 1039–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, T.; Fujioka, J.; Imai, T.; Tsukiyama, K. Effect of Mid-infrared Free-Electron Laser Irradiation on Refolding of Amyloid-Like Fibrils of Lysozyme into Native Form. Protein J. 2012, 31, 710–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onami, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Aizawa, H.; Haraguchi, T.; Akitsu, T.; Tsukiyama, K.; Palafox, M.A. Degradation of Human Serum Albumin by Infrared free-electron laser Enhanced by Inclusion of a Salen-Type Schiff Base Zn (II) Complex. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onami, Y.; Koya, R.; Kawasaki, T.; Aizawa, H.; Nakagame, R.; Miyagawa, Y.; Haraguchi, T.; Akitsu, T.; Tsukiyama, K.; Palafox, M.A. Investigation by DFT Methods of the Damage of Human Serum Albumin Including Amino Acid Derivative Schiff Base Zn(II) Complexes by IR-FEL Irradiation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takase, M.; Yagi, S.; Haraguchi, T.; Noor, S.; Akitsu, T. Linearly Polarized UV Light-Induced Optical Anisotropy of PVA Films and Flexible Macrocycle Schiff Base Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) Dinuclear Complexes. Symmetry 2018, 10, 760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, T. The Chemical Society of Japan. In Essentials in Chemistry 33 Control of Molecular Orientation; Kyoritsu Shuppan Co., Ltd.: Tokyo, Japan, 2019; pp. 20–23. [Google Scholar]
- Natansohn, A.; Rochon, P. Photoinduced Motions in Azo-Containing Polymers. Chem. Rev. 2002, 102, 4139–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hisaki, I. (MS14) Symmetry, Asymmetry and Chirality in Molecular Aggregation. J. Jpn. Soc. Crystallogr. 2009, 51, 41–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuroda, R.; Harada, T.; Shindo, Y. A solid-state dedicated circular dichroism spectrophotometer: Development and application. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 2001, 72, 3802–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tschierske, C.; Ungar, G. Mirror Symmetry Breaking by Chirality Synchronisation in Liquids and Liquid Crystals of Achiral Molecules. Chemphyschem 2016, 17, 9–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sekine, T.; Niori, T.; Sone, M.; Watanabe, J.; Choi, S.-W.; Takanishi, Y.; Takezoe, H. Origin of Helix in Achiral Banana-Shaped Molecular Systems. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1997, 36, 6455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hough, L.E.; Jung, H.T.; Krüerke, D.; Heberling, M.S.; Nakata, M.; Jones, C.D.; Chen, D.; Link, D.R.; Zasadzinski, J.; Heppke, G.; et al. Helical Nanofilament Phases. Science 2009, 325, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, H.; Takanishi, Y.; Yamamoto, J.; Yoshizawa, A. Photo-Driven Chirality Switching in a Dark Conglomerate Phase of an Achiral Liquid Crystal Trimer. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 3278–3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aritake, Y.; Takanashi, T.; Yamazaki, A.; Akitsu, T. Polarized spectroscopy and hybrid materials of chiral Schiff base Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) complexes with included or separated azo-groups. Polyhedron 2011, 30, 886–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takase, M.; Akitsu, T. Polymer Science Book Series—Volume # 1: “Polymer Science: Research Advances, Practical Applications and Educational Aspects”; Formatex Research Centre: Badajoz, Spain, 2016; pp. 301–308. [Google Scholar]
- Nakatori, H.; Haraguchi, T.; Akitsu, T. Polarized light induced molecular orientation control of rigid Schiff base Ni(II), Cu(II), Zn(II) binuclear complexes as polymer composites. Symmetry 2018, 10, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheldrick, G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 2008, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akitsu, T.; Ito, M.; Palafox, M. Theoretical interpretation of polarized light-induced supramolecular orientation on the basis of normal mode analysis of azobenzene as hybrid materials in PMMA with chiral Schiff base Ni(II), Cu(II), and Zn(II) complexes. J. Appl. Solut. Chem. Model. 2016, 5, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekkat, Z.; Dumont, M. Photoinduced orientation of azo dyes in polymeric films. Characterization of molecular angular mobility. Synth. Met. 1993, 54, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moletti, A.; Coluccini, C.; Pasini, D.; Taglietti, A. A chiral probe for the detection of Cu(II) by UV, CD and emission spectroscopies. Dalton Trans. 2007, 16, 1588–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazaki, A.; Akitsu, T. Polarized spectroscopy and polarized UV light-induced molecular orientation of chiral diphenyl Schiff base Ni(II) and Cu(II) complexes and azobenzene in a PMMA film. RSC Adv. 2012, 2, 2975–2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPring8Notice, Easy Explanation of Research Results X-ray Free Electron Laser Realized by SPring-8 Technology. Available online: http://www.spring8.or.jp/ja/news_publications/research_highlights/no_29/ (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Yokoyama, M.; Oda, F.; Nomaru, K.; Koike, H.; Sobajima, M.; Miura, H.; Hattori, H.; Kawai, M.; Kuroda, H. First lasing of KHI FEL device at the FEL-SUT. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. 2001, 475, 38–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsukiyama, K. Infrared Free-Electron Laser (FEL-TUS) Material Creation and Application to Life Science and Medicine. Available online: https://shingi.jst.go.jp/pdf/2015/tus02.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Miyazaki, D.; Ikeuchi, K. Basic Theory of Polarization and Its Applications.Transactions of Information Processing Society of Japan. Comput. Vis. Image Media 2008, 1, 64–72. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, M.; Toko, H. Beamline Optics Technology Series (9) Controlling the Polarization of Light. J. Jpn. Soc. Synchrotron Radiat. Res. 2006, 19, 444–447. [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda, H. Infrared Free-Electron Laser Facility of the Tokyo University of Science (FEL-TUS). Available online: http://www.jssrr.jp/journal/pdf/14/p175.pdf (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Tokyo University of Science, Tsukiyama Lab., RESEARCH, Laser Spectroscopy and Photochemistry of Small Molecules. Available online: https://www.rs.kagu.tus.ac.jp/tsukilab/research_fel.html (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Rinco, O.; Brenton, J.; Douglas, A.; Maxwell, A.; Henderson, M.; Indrelie, K.; Wessels, J.; Widin, J. The effect of porphyrin structure on binding to human serum albumin by fluorescence spectroscopy. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2009, 208, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirakawa, K.; Ouyang, D.; Ibuki, Y.; Hirohara, S.; Okazaki, S.; Kono, E.; Kanayama, N.; Nakazaki, J.; Segawa, H. Photosensitized Protein-Damaging Activity, Cytotoxicity, and Antitumor Effect of P(V)porphyrins Using Long-Wavelength Visible Light through Electron Transfer. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2018, 31, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Musgrave, I.F.; Day, A.I.; Heimann, K.; Keene, F.R.; Collins, J.G. Eukaryotic Cell Toxicity and HSA Binding of [Ru(Me4phen)(bb7)]2+ and the Effect of Encapsulation in Cucurbit[10]uril. Front. Chem. 2018, 6, 595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, B.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, R.; Xiao, Q.; Liu, Y.; Li, Z. Binding of Cationic Porphyrin to Human Serum Albumin Studied Using Comprehensive Spectroscopic Methods. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavicchioli, M.; Zaballa, A.M.L.; de Paula, Q.A.; Prieto, M.B.; Oliveira, C.C.; Civitareale, P.; Ciriolo, M.R.; Ferreira, A.M.D.C. Oxidative Assets Toward Biomolecules and Cytotoxicity of New Oxindolimine-Copper(II) and Zinc(II) Complexes. Inorganics 2019, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dömötör, O.; Enyedy, A. Binding mechanisms of half-sandwich Rh(III) and Ru(II) arene complexes on human serum albumin: A comparative study. J. Biol. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 24, 703–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akao, K. Development and Application of Secondary Structural Estimation Program of Protein for FTIR (IR-SSE). Jasco Rep. 2002, 44, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Urbanovský, P.; Kotek, J.; Carniato, F.; Botta, M.; Hermann, P. Lanthanide Complexes of DO3A–(Dibenzylamino)methylphosphinate: Effect of Protonation of the Dibenzylamino Group on the Water-Exchange Rate and the Binding of Human Serum Albumin. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 5196–5210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reglinski, J.; Morris, S.; E Stevenson, D. Supporting conformational change at metal centres. Part 2: Four and five coordinate geometry. Polyhedron 2002, 21, 2175–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Li, Y.; Xue, C.; Hu, Z.; Chen, X.; Sheng, F. Effect of Chinese medicine alpinetin on the structure of human serum albumin. Bioorganic Med. Chem. 2005, 13, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, M.-X.; Li, S.; Jiang, M.; Wang, Y.-D. Interactions of human serum albumin with chlorogenic acid and ferulic acid. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2004, 1674, 205–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rainey, K.H.; Patterson, G.H. Photoswitching FRET to monitor protein–protein interactions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 864–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarver, R.W., Jr.; Krueger, W.C. Protein secondary structure from fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: A data base analysis. Anal. Biochem. 1991, 194, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Patel, S. Binding structures of tri-N-acetyl-β-glucosamine in hen egg white lysozyme using molecular dynamics with a polarizable force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2012, 34, 163–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onami, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Haraguchi, T.; Tsukiyama, K.; Moon, D.; Kitahama, Y.; Hosokai, T.; Mastuzaki, H.; Sakiyama, H.; Akitsu, T. Effect of dipeptide derivative Schiff-base Zn(II) complexes on lysozyme molecules damaged by means of IR-FEL irradiation. Trends Photochem. Photobiol. 2022, 21, 15–26. [Google Scholar]
- Rani, C.V.; Kesavan, M.P.; Kumar, G.G.V.; Jeyaraj, M.J.D.; Rajesh, J.; Rajagopal, G. Synthesis, physicochemical characterization and structural studies of new Schiff base ligand and its metal (II) complexes: In silico molecular docking analysis, antimicrobial activity and cytotoxicity. Appl. Organomet. Chem. 2018, 32, e4538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sciortino, G.; Garribba, E.; Maréchal, J.-D. Validation and Applications of Protein–Ligand Docking Approaches Improved for Metalloligands with Multiple Vacant Sites. Inorg. Chem. 2019, 58, 294–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chemical Information Society, Crystal Structure Database/Compound Dictionary Crystal Structure Database CCDC Products, CSD-Discovery, GOLD. Available online: https://www.jaici.or.jp/db/crystal/ccdc/csd-discovery/gold/ (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- CCDC GOLD. Available online: https://www.ccdc.cam.ac.uk/solutions/software/gold/ (accessed on 21 September 2023).
- Inoue, T. Importance of The Basic Technique on Chemical Analysis (6). Chem. Times 2007, 203, 13–14. [Google Scholar]
- Sato, A. New Topics in Organic Elemental Analysis—The Best Determination Techniques for Carbon, Hydrogen, and Nitrogen and Their Applications. Chem. Educ. 2015, 63, 614. [Google Scholar]
- Fujisawa, N.; Onami, Y.; Kawasaki, T.; Haraguchi, T.; Akitsu, T.; Tsukiyama, K. Infrared free-electron laser or Polarized Ultraviolet Photolysis of Hierarchical and Chiral Components of Interleukin-6, AlanylAlanine and Alanine. Trends Pept. Protein Sci. 2020, 5, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


























| t/min | R(π–π∗) | S(π–π∗) | R(CT) | S(CT) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C22H22Cl2N4O2Zn2 + PVA | 0 | 1.007 | 0.0023 | 1.010 | 0.0033 |
| 0.5 | 1.003 | 0.0011 | 1.108 | 0.0346 | |
| 1 | 0.9247 | −0.0258 | 1.018 | 0.0061 | |
| 3 | 0.9135 | −0.0297 | 1.008 | 0.0026 | |
| 5 | 0.9209 | −0.0271 | 0.9935 | −0.0022 | |
| 10 | 0.9826 | −0.0058 | 1.060 | 0.0196 |
| Parameters | B3LYP | MP2 | Parameters | B3LYP | MP2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bond lengths: | O−Zn | 1.909 | 1.894 | Bond angles: | O−Zn−O | 114.7 | 119.7 |
| N−Zn | 2.014 | 2.019 | N−Zn−N | 90.7 | 87.8 | ||
| O⋯O | 3.214 | 3.276 | O25−Zn−N28 | 94.5 | 94.6 | ||
| O⋯O | 2.866 | 2.800 | O25−Zn−N29 | 132.9 | 130.0 |
| Bond | Lengths/Å | Bond | Angles/° |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn1−O1 | 2.012 | O1−Zn1−O2 | 115.24 |
| Zn1−O2 | 2.077 | O1−Zn1−N2 | 160.39 |
| Zn1−N1 | 2.236 | O2−Zn1−N1 | 159.31 |
| Zn1−N2 | 2.026 | N1−Zn1−N2 | 80.14 |
| Bond | Lengths/Å | Bond | Angles/° |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn1−O1 | 1.904 | O1−Zn1−O2 | 120.69 |
| Zn1−O2 | 1.903 | O1−Zn1−N2 | 86.67 |
| Zn1−N1 | 2.009 | O2−Zn1−N1 | 94.45 |
| Zn1−N2 | 2.007 | N1−Zn1−N2 | 90.79 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Takashima, H.; Nakane, D.; Akitsu, T. Application of Infrared Free-Electron Laser Irradiation of Protein Complexes Binding to Salen-Type Schiff Base Zn(II) Complexes Using Secondary Conformational Changes in the Proteins for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Inorganics 2024, 12, 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12020050
Takashima H, Nakane D, Akitsu T. Application of Infrared Free-Electron Laser Irradiation of Protein Complexes Binding to Salen-Type Schiff Base Zn(II) Complexes Using Secondary Conformational Changes in the Proteins for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Inorganics. 2024; 12(2):50. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12020050
Chicago/Turabian StyleTakashima, Hiroshi, Daisuke Nakane, and Takashiro Akitsu. 2024. "Application of Infrared Free-Electron Laser Irradiation of Protein Complexes Binding to Salen-Type Schiff Base Zn(II) Complexes Using Secondary Conformational Changes in the Proteins for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease" Inorganics 12, no. 2: 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12020050
APA StyleTakashima, H., Nakane, D., & Akitsu, T. (2024). Application of Infrared Free-Electron Laser Irradiation of Protein Complexes Binding to Salen-Type Schiff Base Zn(II) Complexes Using Secondary Conformational Changes in the Proteins for the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Inorganics, 12(2), 50. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics12020050