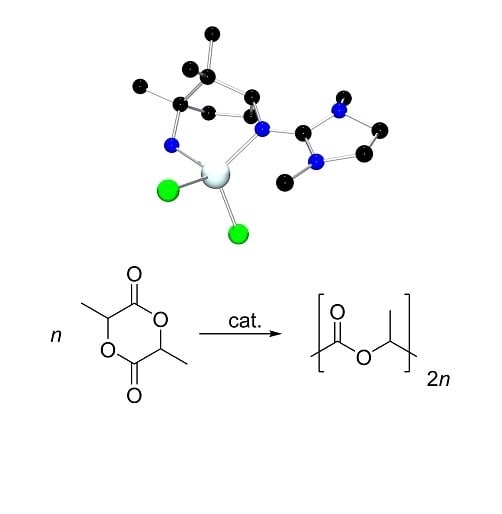
Reactivity of Zinc Halide Complexes Containing Camphor-Derived Guanidine Ligands with Technical rac-Lactide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Zinc Halide Complexes
2.2. Density Functional Theory Calculations
2.3. Polymerization Experiments
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Physical Methods
3.2. X-ray Analyses
3.3. Computational Details
3.4. Polymerization
3.5. General Synthesis of Bisguanidine Ligands with Chloroformamidinium Chlorides
3.6. General Synthesis of Zinc Halide Complexes with Guanidine Ligands
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mekonnen, T.; Mussone, P.; Khalil, H.; Bressler, D. Progress in bio-based plastics and plasticizing modifications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 13379–13398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, T. Biodegradable polymers for biomedical uses. Prog. Polym. Sci. 1994, 19, 663–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Keefe, B.J.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Tolman, W.B. Polymerization of lactide and related cyclic esters by discrete metal complexes. J. Chem. Soc. Dalton Trans. 2001, 2215–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garlotta, D. A Literature Review of Poly(Lactic Acid). J. Polym. Environ. 2001, 9, 63–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platel, R.H.; Hodgson, L.M.; Williams, C.K. Biocompatible Initiators for Lactide Polymerization. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 11–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregory, G.L.; López-Vidal, E.M.; Buchard, A. Polymers from sugars: Cyclic monomer synthesis, ring-opening polymerisation, material properties and applications. Chem. Comm. 2017, 53, 2198–2217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakewell, C.; White, A.J.P.; Long, N.J.; Williams, C.K. Metal-size influence in Iso-selective lactide polymerization. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 9226–9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheaton, C.A.; Hayes, P.G.; Ireland, B.J. Complexes of Mg, Ca and Zn as homogenous catalysts for lactide polymerization. Dalton Trans. 2009, 9226, 4832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dechy-Cabaret, O.; Martin-Vaca, B.; Bourissou, D. Controlled ring-opening polymerization of lactide and glycolide. Chem. Rev. 2004, 104, 6147–6176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Auras, R.; Lim, L.T.; Selke, S.E.M.; Tsuji, H. Poly(Lactic Acid): Synthesis, Structures, Properties, Processing, and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2010; ISBN 9780470649848. [Google Scholar]
- Sudesh, K.; Iwata, T. Sustainability of biobased and biodegradable plastics. CLEAN-Soil Air Water 2008, 36, 433–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auras, R.; Harte, B.; Selke, S. An Overview of Polylactide as Packaging Materials. Macromol. Biosci. 2004, 4, 835–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Inkinen, S.; Hakkarainen, M.; Albertsson, A.C.; Södergård, A. From lactic acid to poly(lactic acid) (PLA): Characterization and analysis of PLA and its precursors. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, C.M. Stereocontrolled ring-opening polymerization of cyclic esters: Synthesis of new polyester microstructures. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, S.A. Sustainable polymers: Opportunities for the next decade. ACS Macro Lett. 2013, 2, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Romain, C.; Williams, C.K. Sustainable polymers from renewable resources. Nature 2016, 540, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, M.H.; Patmore, N.J.; Zhou, Z. Concerning the relative importance of enantiomorphic site vs. chain end control in the stereoselective polymerization of lactides: Reactions of (R,R-salen)-and (S,S-salen)-aluminium alkoxides LAlOCH2R complexes (R = CH3 and S–CHMeCl). Chem. Commun. 2005, 127–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnet, F.; Cowley, A.R.; Mountford, P. Lanthanide Borohydride Complexes Supported by Diaminobis(phenoxide) Ligands for the Polymerization of ε-Caprolactone and l- and rac-Lactide. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 9046–9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, Z.Y.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Feijen, J. [(salen)Al]-Mediated, Controlled and Stereoselective Ring-Opening Polymerization of Lactide in Solution and without Solvent: Synthesis of Highly Isotactic Polylactide Stereocopolymers from Racemic d,l-Lactide. Angew. Chem. 2002, 114, 4692–4695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.Y.; Dijkstra, P.J.; Feijen, J. Controlled and stereoselective polymerization of lactide: Kinetics, selectivity, and microstructures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 11291–11298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spassky, N.; Wisniewski, M.; Pluta, C.; Le Borgne, A. Highly stereoselective polymerization of rac-(d,l)-lactide with a chiral Schiff’s base/aluminium alkoxide initiator. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 1996, 197, 2627–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ovitt, T.M.; Coates, G.W. Stereochemistry of lactide polymerization with chiral catalysts: New opportunities for stereocontrol using polymer exchange mechanisms. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2002, 124, 1316–1326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, M.D.; Davidson, M.G.; Keir, C.G.; Hughes, L.M.; Mahon, M.F.; Apperley, D.C. Zinc(II) Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Species and their Application for the Ring-Opening Polymerisation of rac-Lactide. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 635–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whitelaw, E.L.; Davidson, M.G.; Jones, M.D. Group 4 salalen complexes for the production and degradation of polylactide. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 10004–10006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Stopper, A.; Press, K.; Okuda, J.; Goldberg, I.; Kol, M. Zirconium Complexes of Phenylene-Bridged {ONSO} Ligands: Coordination Chemistry and Stereoselective Polymerization of rac-Lactide. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 9140–9150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sauer, A.; Kapelski, A.; Fliedel, C.; Dagorne, S.; Kol, M.; Okuda, J. Switching the Lactide Polymerization Activity of a Cerium Complex by Redox Reactions. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 9007–9023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermans, C.; Rong, W.; Spaniol, T.P.; Okuda, J. Lanthanum complexes containing a bis(phenolate) ligand with a ferrocene-1,1′-diyldithio backbone: Synthesis, characterization, and ring-opening polymerization of rac-lactide. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 8127–8133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakewell, C.; White, A.J.P.; Long, N.J.; Williams, C.K. Scandium and yttrium phosphasalen complexes as initiators for ring-opening polymerization of cyclic esters. Inorg. Chem. 2015, 54, 2204–2212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanford, M.J.; Dove, A.P. Stereocontrolled ring-opening polymerisation of lactide. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 486–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, M.; Eilerts, N.W.; Huffman, J.C.; Iyer, S.S.; Pacold, M.; Phomphrai, K. Molecular Design of Single-Site Metal Alkoxide Catalyst Precursors for Ring-Opening Polymerization Reactions Leading to Polyoxygenates. 1. Polylactide Formation by Achiral and Chiral Magnesium and Zinc Alkoxides, (η3-L)MOR, Where L = Trispyrazolyl- and Trisindazolylborate Ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 11845–11854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chisholm, M.H.; Gallucci, J.; Phomphrai, K. Lactide polymerization by well-defined calcium coordination complexes: Comparisons with related magnesium and zinc chemistry. Chem. Commun. 2003, 48–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poirier, V.; Roisnel, T.; Carpentier, J.-F.; Sarazin, Y. Zinc and magnesium complexes supported by bulky multidentate amino-ether phenolate ligands: Potent pre-catalysts for the immortal ring-opening polymerisation of cyclic esters. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 523–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamberlain, B.M.; Cheng, M.; Moore, D.R.; Ovitt, T.M.; Lobkovsky, E.B.; Coates, G.W. Polymerization of lactide with zinc and magnesium β-diiminate complexes: Stereocontrol and mechanism. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 3229–3238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.; Attygalle, A.B.; Lobkovsky, E.B.; Coates, G.W. Single-Site Catalysts for Ring-Opening Polymerization: Synthesis of Heterotactic Poly(lactic acid) from rac-Lactide. These homogeneous, molecular compounds have the general formula LnMR, where Ln is a ligand set that remains attached to and thus. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 11583–11584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, A.P.; Gibson, V.C.; Marshall, E.L.; White, A.J.P.; Williams, D.J. Magnesium and zinc complexes of a potentially tridentate β-diketiminate ligand. Dalton Trans. 2004, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisholm, M.H.; Gallucci, J.C.; Phomphrai, K. Comparative study of the coordination chemistry and lactide polymerization of alkoxide and amide complexes of zinc and magnesium with a β-diiminato ligand bearing ether substituents. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 8004–8010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerling, K.A.; Rezayee, N.M.; Rheingold, A.L.; Green, D.B.; Fritsch, J.M. Synthesis and structures of bis-ligated zinc complexes supported by tridentate ketoimines that initiate l-lactide polymerization. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 16498–16508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.-H.; Chen, Y.-J.; Tseng, H.-C.; Lian, C.-J.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Lai, Y.-C.; Hsu, S.C.N.; Chiang, M.Y.; Chen, H.Y. Comparing l-lactide and ε-caprolactone polymerization by using aluminum complexes bearing ketiminate ligands: Steric, electronic, and chelating effects. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 100272–100280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiper, C.; Dittrich, D.; Wölper, C.; Bläser, D.; Roll, J.; Schulz, S. Synthesis, Structure, and Catalytic Activity of Tridentate, Base-Functionalized β-Ketiminate Zinc Complexes in Ring-Opening Polymerization of Lactide. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2014, 2230–2240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiper, C.; Schulz, S.; Wölper, C.; Bläser, D.; Roll, J. Synthesis and single crystal X-ray structures of cationic zinc β-diketiminate complexes. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2013, 639, 1153–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheiper, C.; Wölper, C.; Bläser, D.; Roll, J.; Schulz, S. Syntheses, solid-state structures and catalytic activity of zinc carboxylate complexes in lactide polymerization. Z. Naturforsch. 2014, 69, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, M.D.; Hancock, S.L.; McKeown, P.; Schäfer, P.M.; Buchard, A.; Thomas, L.H.; Mahon, M.F.; Lowe, J.P. Zirconium complexes of bipyrrolidine derived salan ligands for the isoselective polymerisation of rac-lactide. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 15967–15970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jones, M.D.; Brady, L.; McKeown, P.M.; Buchard, A.; Schäfer, P.M.; Thomas, L.H.; Mahon, M.F.M.; Woodman, T.J.; Lowe, J.P. Metal influence on the iso- and hetero-selectivity of complexes of bipyrrolidine derived Salan ligands for the polymerisation of rac-lactide. Chem. Sci. 2015, 5034–5039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kirk, S.M.; Quilter, H.C.; Buchard, A.; Thomas, L.H.; Kociok-Kohn, G.; Jones, M.D. Monomeric and dimeric Al(III) complexes for the production of polylactide. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 13846–13852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Zhao, K.-Q.; Al-Khafaji, Y.; Mo, S.; Prior, T.J.; Elsegood, M.R.; Redshaw, C. Organoaluminium Complexe Derived from Anilines or Schiff Bases for the Ring-Opening Polymerization of ε-Caprolactone, δ-Valerolactone and rac-Lactide. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 1951–1965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Zhao, K.-Q.; Prior, T.J.; Hughes, D.L.; Arbaoui, A.; Elsegood, M.R.J.; Redshaw, C. Structural studies of Schiff-base [2 + 2] macrocycles derived from 2,2′-oxydianiline and the ROP capability of their organoaluminium complexes. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 11990–12005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Khafaji, Y.F.; Elsegood, M.R.J.; Frese, J.W.A.; Redshaw, C. Ring opening polymerization of lactides and lactones by multimetallic alkyl zinc complexes derived from the acids Ph2C(X)CO2H (X = OH, NH2). RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 4510–4517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakewell, C.; Fateh-Iravani, G.; Beh, D.W.; Myers, D.; Tabthong, S.; Hormnirun, P.; White, A.J.P.; Long, N.; Williams, C.K. Comparing a series of 8-quinolinolato complexes of aluminium, titanium and zinc as initiators for the ring-opening polymerization of rac-lactide. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 12326–12337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thevenon, A.; Romain, C.; Bennington, M.S.; White, A.J.P.; Davidson, H.J.; Brooker, S.; Williams, C.K. Dizinc Lactide Polymerization Catalysts: Hyperactivity by Control of Ligand Conformation and Metallic Cooperativity. Angew. Chem. 2016, 128, 8822–8827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nijenhuis, A.J.; Grijpma, D.W.; Pennings, A.J. Lewis acid catalyzed polymerization of l-lactide. Kinetics and mechanism of the bulk polymerization. Macromolecules 1992, 25, 6419–6424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leenslag, J.W.; Pennings, A.J. Synthesis of high-molecular-weight poly(lactide) initiated with tin 2-ethylhexanoate. Makromol. Chem. 1987, 188, 1809–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Degée, P.; Dubois, P.; Jérôme, R.; Jacobsen, S.; Fritz, H.-G. New catalysis for fast bulk ring-opening polymerization of lactide monomers. Macromol. Symp. 1999, 144, 289–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stjerndahl, A.; Finne-Wistrand, A.; Albertsson, A.-C.; Bäckesjö, C.M.; Lindgren, U. Minimization of residual tin in the controlled Sn(II) octoate-catalyzed polymerization of ε-caprolactone. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2008, 87, 1086–1091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, H.; Ritch, J.S.; Hayes, P.G. Toward stereoselective lactide polymerization catalysts: Cationic zinc complexes supported by a chiral phosphinimine scaffold. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 8063–8072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheaton, C.A.; Hayes, P.G. Cationic zinc complexes: A new class of catalyst for living lactide polymerization at ambient temperature. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 8404–8406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheaton, C.A.; Hayes, P.G. Cationic organozinc complexes of a bis(phosphinimine) pincer ligand: Synthesis, structural and polymerization studies. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 3861–3869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ireland, B.J.; Wheaton, C.A.; Hayes, P.G. Cationic Organomagnesium Complexes as Highly Active Initiators for the Ring-Opening Polymerization of ε-Caprolactone. Organometallics 2010, 29, 1079–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheaton, C.A.; Ireland, B.J.; Hayes, P.G. Activated zinc complexes supported by a neutral, phosphinimine-containing ligand: Synthesis and efficacy for the polymerization of lactide. Organometallics 2009, 28, 1282–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.S.; Nayab, S.; Jeong, J.H. Synthesis, characterisation and X-ray structures of zinc(II) complexes bearing camphor-based iminopyridines as pre-catalysts for heterotactic-enriched polylactide from rac-lactide. Polyhedron 2015, 85, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, K.S.; Nayab, S.; Jeong, J.H. Synthesis, characterisation and X-ray structure of Cu(II) and Zn(II) complexes bearing N,N-dimethylethylenamine-camphorylimine ligands: Application in the polymerisation of rac-lactide. Polyhedron 2017, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cushion, M.G.; Mountford, P. Cationic and charge-neutral calcium tetrahydroborate complexes and their use in the controlled ring-opening polymerisation of rac-lactide. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2276–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, T.R.; Breyfogle, L.E.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Tolman, W.B. Stereoelective polymerization of d,l-lactide using N-heterocyclic carbene based compounds. Chem. Commun. 2004, 2504–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, T.R.; Schaller, C.P.; Hillmyer, M.A.; Tolman, W.B. Zinc N-heterocyclic carbene complexes and their polymerization of d,l-lactide. J. Organomet. Chem. 2005, 690, 5881–5891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Ma, H. Aluminum complexes with bidentate amido ligands: Synthesis, structure and performance on ligand-initiated ring-opening polymerization of rac-lactide. Dalton Trans. 2014, 43, 9098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Santos Vieira, I.; Herres-Pawlis, S. Lactide polymerisation with complexes of neutral N-donors-new strategies for robust catalysts. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 765–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuba, A.; Herres-Pawlis, S.; Seewald, O.; Börner, J.; Heuwing, A.J.; Flörke, U.; Henkel, G. A Systematic Study on the Coordination Properties of the Guanidine. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2010, 636, 2641–2649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinmuth, M.; Walter, P.; Enders, M.; Kaifer, E.; Himmel, H.J. Zinc Halide and Alkylzinc Complexes of a Neutral Doubly Base-Stabilized Diborane(4). Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanek, J.; Rösener, T.; Metz, A.; Mannsperger, J.; Hoffmann, A.; Herres-Pawlis, S. Topics in Heterocyclic Chemistry; Springer: Basel, Switzerland, 2015; ISSN 15334880. [Google Scholar]
- Metz, A.; Plothe, R.; Glowacki, B.; Koszalkowski, A.; Scheckenbach, M.; Beringer, A.; Rösener, T.; Michalis de Vasconcellos, J.; Haase, R.; Flörke, U.; et al. Zinc Chloride Complexes with Aliphatic and Aromatic Guanidine Hybrid Ligands and their Activity in the Ring-Opening Polymerisation of d,l-Lactide. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 4974–4987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metz, A.; McKeown, P.; Esser, B.; Gohlke, C.; Kröckert, K.; Laurini, L.; Scheckenbach, M.; McCormick, S.N.; Oswald, M.; Hoffmann, A.; et al. Zn(II) chloride complexes with novel aliphatic, chiral bisguanidine ligands as catalysts in the ring-opening polymerisation of rac-lactide using FT-IR spectroscopy in bulk. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, P.M.; Fuchs, M.; Ohligschläger, A.; Rittinghaus, R.; McKeown, P.; Akin, E.; Schmidt, M.; Hoffmann, A.; Liauw, M.A.; Jones, M.D.; et al. Fast and robust: Novel highly active N,O zinc guanidine catalysts for the ring-opening polymerisation of lactide. ChemSusChem 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Börner, J.; Flörke, U.; Huber, K.; Döring, A.; Kuckling, D.; Herres-Pawlis, S. Lactide polymerisation with air-stable and highly active zinc complexes with guanidine-pyridine hybrid ligands. Chem. Eur. J. 2009, 15, 2362–2376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börner, J.; dos Santos Vieira, I.; Pawlis, A.; Döring, A.; Kuckling, D.; Herres-Pawlis, S. Mechanism of the living lactide polymerization mediated by robust zinc guanidine complexes. Chem. Eur. J. 2011, 17, 4507–4512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Börner, J.; Herres-Pawlis, S.; Flörke, U.; Huber, K. [Bis(guanidine)] Zinc Complexes and their Application in Lactide Polymerisation. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2007, 5645–5651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wern, M.; Ortmeyer, J.; Josephs, P.; Schneider, T.; Neuba, A.; Henkel, G.; Schindler, S. Syntheses, characterization, and reactivity of copper complexes with camphor-like tetramethylguanidine ligands. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herres-Pawlis, S.; Neuba, A.; Seewald, O.; Seshadri, T.; Egold, H.; Flörke, U.; Henkel, G. A library of peralkylated bis-guanidine ligands for use in biomimetic coordination chemistry. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2005, 4879–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantlehner, W.; Haug, E.; Mergen, W.W.; Speh, P.; Maier, T.; Kapassakalidis, J.J.; Bräuner, H.J.; Hagen, H. Orthoamide, XL. Herstellung von 1,1,2,3,3-pentasubstituierten und 1,1,2,2,3,3-hexasubstituierten Guanidiniumsalzen sowie von 1,1,2,3,3-PentaalkyIguanidinen. Liebigs Ann. Chem. Weinheim 1984, 108–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rösener, T.; Bienemann, O.; Sigl, K.; Schopp, N.; Schnitter, F.; Flörke, U.; Hoffmann, A.; Döring, A.; Kuckling, D.; Herres-Pawlis, S. A Comprehensive Study of Copper Guanidine Quinoline Complexes: Predicting the Activity of Catalysts in ATRP with DFT. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 13550–13562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.; Powell, D.R.; Houser, R.P. Structural variation in copper(I) complexes with pyridylmethylamide ligands: Structural analysis with a new four-coordinate geometry index, τ4. Dalton Trans. 2007, 955–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raab, V.; Harms, K.; Sundermeyer, J.; Kovačević, B.; Maksić, Z.B. 1,8-Bis(dimethylethyleneguanidino)-naphthalene: Tailoring the Basicity of Bisguanidine “Proton Sponges” by Experiment and Theory. J. Org. Chem. 2003, 68, 8790–8797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staroverov, V.N.; Scuseria, G.E.; Tao, J.; Perdew, J.P. Comparative assessment of a new nonempirical density functional: Molecules and hydrogen-bonded complexes. J. Chem. Phys. 2009, 12129–12137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigend, F.; Ahlrichs, R. Balanced basis sets of split valence, triple zeta valence and quadruple zeta valence quality for H to Rn: Design and assessment of accuracy. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2005, 7, 3297–3305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, A.; Grunzke, R.; Herres-Pawlis, S. Insights into the influence of dispersion correction in the theoretical treatment of guanidine-quinoline copper(I) complexes. J. Comput. Chem. 2014, 35, 1943–1950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goerigk, L.; Grimme, S. A thorough benchmark of density functional methods for general main group thermochemistry, kinetics, and noncovalent interactions. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2011, 13, 6670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimme, S.; Ehrlich, S.; Goerigk, L. Effect of the damping function in dispersion corrected density functional theory. J. Comput. Chem. 2011, 1456–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinhold, F.; Landis, C. Valency and Bonding—A Natural Bond Orbital Donor-Acceptor Perspective; Cambridge University: New York, NY, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-0521831284. [Google Scholar]
- Glendening, E.D.; Landis, C.R.; Weinhold, F. NBO 6.0: Natural Bond Orbital Analysis Program. J. Comput. Chem. 2013, 34, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glendening, E.D.; Badenhoop, J.K.; Reed, A.E.; Carpenter, J.E.; Bohmann, J.A.; Morales, C.M.; Landis, C.R.; Weinhold, F. NBO 6.0; Theoretical Chemistry Institute, University of Wisconsin: Madison, WI, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Chuck, C.; Davidson, M.G.; Gobius du Sart, G.; Ivanova-Mitseva, P.K.; Kociok-Köhn, G.I.; Manton, L.B. Synthesis and structural characterization of group 4 metal alkoxide complexes of N,N,N′,N′-tetrakis(2-hydroxyethyl)ethylenediamine and their use as initiators in the ring-opening polymerization (ROP) of rac-lactide under industrially relevant conditions. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 10804–10811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonhard, L.; Lygo, B.; Procter, G. Praxis in der Organischen Chemie; VCH Verlagsgesellschaft: Weinheim, Germany, 1996; ISBN 978-3-527-33250-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bruker AXS Inc. SAINT V8.37A; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bruker AXS Inc. SADABS-2008/1; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Bruker AXS Inc. XPREP; Version 5.1/NT; Bruker AXS Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Sheldrick, G.M. Phase annealing in SHELX-90: Direct methods for larger structures. Acta Crystallogr. Sect. A 1990, 46, 467–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hübschle, C.B.; Sheldrick, G.M.; Dittrich, B. ShelXle: A Qt graphical user interface for SHELXL. J. Appl. Cryst. 2011, 44, 1281–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Expanding the Limits of Computational Chemistry; Gaussian 09 Revision E.01; Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Marenich, A.V.; Cramer, C.J.; Truhlar, D.G. Universal solvation model based on solute electron density and on a continuum model of the solvent defined by the bulk dielectric constant and atomic surface tensions. J. Phys. Chem. B 2009, 6378–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krüger, J.; Grunzke, R.; Gesing, S.; Breuers, S.; Brinkmann, A.; de la Garza, L.; Kohlbacher, O.; Kruse, M.; Nagel, W.; Packschies, L.; et al. The MoSGrid Science Gateway: A Complete Solution for Molecular Simulations. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2014, 10, 2232–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herres-Pawlis, S.; Hoffmann, A.; Balasko, A.; Kacsuk, P.; Birkenheuer, G.; Brinkmann, A.; de la Garza, L.; Krüger, J.; Gesing, S.; Grunzke, R.; et al. Quantum chemical meta-workflows in MoSGrid. Concurr. Comput. Pract. Exp. 2015, 27, 344–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gesing, S.; Grunzke, R.; Krüger, J.; Birkenheuer, G.; Wewior, M.; Schäer, P.; Schuller, B.; Schuster, J.; Herres-Pawlis, S.; Breuers, S.; et al. A Single Sign-On Infrastructure for Science Gateways on a Use Case for Structural Bioinformatic. J. Grid Comput. 2012, 10, 769–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]










| C1 | C2 | C3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn–Ngua [Å] | 1.986(3) | 2.013(4) | 2.006(5) |
| Zn–Namine [Å] | 2.053(3) | 2.065(4) | 2.041(5) |
| Zn–X [Å] | 2.246(2), 2.284(2) | 2.261(2), 2.292(2) | 2.395(2), 2.434(2) |
| Namine–Zn–Ngua [°] | 99.8(2) | 100.3(2) | 101.2(2) |
| ∡ (ZnCl2, ZnN2) [°] | 80.3 | 80.6 | 83.4 |
| τ4 [a] | 0.89 | 0.88 | 0.87 |
| ρ [b] | 0.97 | 0.96 | 0.97 |
| Guanidine twist [c] | 35.6 | 13.1 | 7.1 |
| C1 | C2 | C3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn–Ngua | 2.009 | 2.053 | 2.024 |
| Zn–Namine | 2.080 | 2.105 | 2.093 |
| Zn–X | 2.302, 2.314 | 2.303, 2.345 | 2.425, 2.430 |
| NamineZnNgua | 99.3 | 97.9 | 99.1 |
| ∡ (ZnX2, ZnN2) | 83.5 | 75.3 | 88.7 |
| τ4 [a] | 0.86 | 0.81 | 0.89 |
| ρ [b] | 0.97 | 0.95 | 0.96 |
| Guanidine twist [c] | 35.6 | 14.5 | 6.2 |
| C1 | C2 | C3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Zn | 1.56 | 1.56 | 1.49 |
| Namine | −0.95 | −0.95 | −0.95 |
| Ngua | −0.78 | −0.76 | −0.79 |
| Cl/Br | −0.85/−0.85 | −0.85/−0.85 | −0.81/−0.81 |
| Polymerization Method | Ratio (Monomer:Catalyst:Initiator) | Reaction Temperature (°C) | Stirring (rpm) | Quality rac-Lactide | Conversion Determination |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 500:1:0 | 150 | - | technical | 1H NMR |
| b | 1000:1:0 | 140 | 400 | technical | 1H NMR |
| c | 1000:1:10 | 140 | 400 | recrystallized | FT-IR |
| kapp [a] (10−5 s−1) | Conversion (%) [b] | Mn,exp (g/mol) [c] | Mn,calcd. (g/mol) | Đ [c] | Pr [d] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1 | 9.9 | 64 | 20,000 | 46,000 | 1.70 | 0.58 |
| C2 | 7.3 | 55 | 5100 | 39,500 | 1.72 | 0.56 |
| C3 | 12.8 | 62 | 13,000 | 44,500 | 1.74 | 0.54 |
| Polymerization Method | kapp [a] (10−5 s−1) | C (%) [b] | Mn,exp. (g/mol) [c] | Mn,calcd. (g/mol) | Đ [c] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| b | 1.4 | 63 (after 13 h) | 56,000 (after 13 h) | 91,000 | 1.57 (after 13 h) |
| c | 4.8 | 65 (after 7 h) | 8000 (after 7 h) | 9400 | 1.15 (after 7 h) |
| C1 | C2 | C3 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Empirical formula | C13H28Cl2N4Zn | C13H26Cl2N4Zn | C13H26Br2N4Zn |
| Formula mass (g·mol−1) | 376.66 | 374.65 | 463.57 |
| Crystal size (mm) | 0.24 × 0.21 × 0.18 | 0.23 × 0.16 × 0.16 | 0.23 × 0.20 × 0.19 |
| T (K) | 100(2) | 100(2) | 100(2) |
| Crystal system | Orthorhombic | Monoclinic | Monoclinic |
| Space group | P212121 | P21 | P21 |
| a (Å) | 13.478(2) | 9.472(2) | 9.297(2) |
| b (Å) | 15.173(2) | 18.095(3) | 14.257(3) |
| c (Å) | 17.570(2) | 10.133(2) | 13.200(3) |
| α (°) | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| β (°) | 90 | 103.91(1) | 101.84(1) |
| γ (°) | 90 | 90 | 90 |
| V (Å3) | 3593.1(8) | 1685.8(5) | 1712.4(6) |
| Z | 8 | 4 | 4 |
| ρcalcd. (Mg·m−3) | 1.393 | 1.476 | 1.798 |
| μ (mm−1) | 1.661 | 1.770 | 6.098 |
| λ (Å) | 0.71073 | 0.71073 | 0.71073 |
| F(000) | 1584 | 784 | 928 |
| hkl range | −17 ≤ h ≤ 12, ±20, −23 ≤ l ≤ 22 | ±12, ±24, ±13 | ±11, ±17, ±16 |
| Reflections collected | 28,044 | 17,928 | 20,541 |
| Independent reflections | 8953 | 8244 | 7045 |
| Rint. | 0.0776 | 0.0556 | 0.0516 |
| Number of parameters | 391 | 387 | 385 |
| R1 [I ≥ 2σ(I)] | 0.0438 | 0.0434 | 0.0455 |
| wR2 (all data) | 0.0942 | 0.0942 | 0.1164 |
| Goodness-of-fit | 0.946 | 0.985 | 1.027 |
| Largest diff. peak, hole [eÅ−3] | 0.420, −0.413 | 0.449, −0.427 | 1.989, −1.153 |
| Absolute structure parameter | 0.013(10) | 0.000(13) | 0.009(13) |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Metz, A.; Heck, J.; Gohlke, C.M.; Kröckert, K.; Louven, Y.; McKeown, P.; Hoffmann, A.; Jones, M.D.; Herres-Pawlis, S. Reactivity of Zinc Halide Complexes Containing Camphor-Derived Guanidine Ligands with Technical rac-Lactide. Inorganics 2017, 5, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5040085
Metz A, Heck J, Gohlke CM, Kröckert K, Louven Y, McKeown P, Hoffmann A, Jones MD, Herres-Pawlis S. Reactivity of Zinc Halide Complexes Containing Camphor-Derived Guanidine Ligands with Technical rac-Lactide. Inorganics. 2017; 5(4):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5040085
Chicago/Turabian StyleMetz, Angela, Joshua Heck, Clara Marie Gohlke, Konstantin Kröckert, Yannik Louven, Paul McKeown, Alexander Hoffmann, Matthew D. Jones, and Sonja Herres-Pawlis. 2017. "Reactivity of Zinc Halide Complexes Containing Camphor-Derived Guanidine Ligands with Technical rac-Lactide" Inorganics 5, no. 4: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5040085
APA StyleMetz, A., Heck, J., Gohlke, C. M., Kröckert, K., Louven, Y., McKeown, P., Hoffmann, A., Jones, M. D., & Herres-Pawlis, S. (2017). Reactivity of Zinc Halide Complexes Containing Camphor-Derived Guanidine Ligands with Technical rac-Lactide. Inorganics, 5(4), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics5040085