Effects of Introducing Methoxy Groups into the Ancillary Ligands in Bis(diimine) Copper(I) Dyes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis and Compound Characterization
2.2. Solution and Solid-State Absorption Spectra
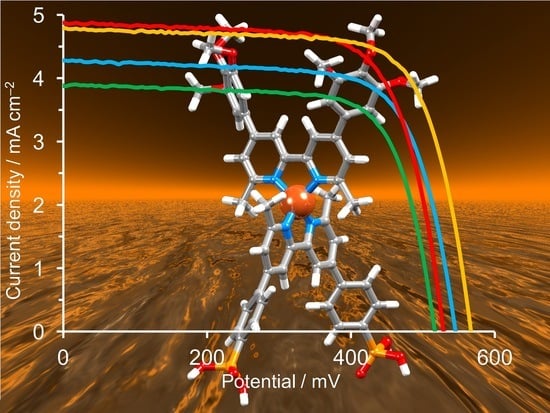
2.3. DSSC Performances
2.4. Characteristics of the HOMO and LUMO Manifolds
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Compound 4a
3.3. Compound 4
3.4. [Cu(1)2][PF6]
3.5. [Cu(3)2][PF6]
3.6. [Cu(4)2][PF6]
3.7. DSSC Fabrication
3.8. Electrodes for Solid-State Absorption Spectroscopy
3.9. DSSC and External Quantum Efficiency (EQE) Measurements
3.10. DFT Calculations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- O’Reagan, B.; Grätzel, M. A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature 1991, 353, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Baranoff, E.; Grätzel, M. Dye-sensitized solar cells. A brief overview. Sol. Energy 2011, 85, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grätzel, M. Recent Advances in Sensitized Mesoscopic Solar Cells. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1788–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grätzel, M. Solar Energy Conversion by Dye-Sensitized Photovoltaic Cells. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 6841–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yella, A.; Lee, H.W.; Tsao, H.N.; Yi, C.; Chandiran, A.K.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Diau, E.W.; Yeh, C.Y.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Grätzel, M. Porphyrin-sensitized solar cells with cobalt (II/III)-based redox electrolyte exceed 12 percent efficiency. Science 2011, 334, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higashino, T.; Imahori, H. Porphyrins as excellent dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells: Recent developments and insights. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 448–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Tang, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Tian, H.; Zhu, W.-H. Porphyrin Cosensitization for a Photovoltaic Efficiency of 11.5%: A Record for Non-Ruthenium Solar Cells Based on Iodine Electrolyte. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 14055–14058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S.; Yella, A.; Gao, P.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Curchod, B.F.; Ashari-Astani, N.; Tavernelli, I.; Rothlisberger, U.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Grätzel, M. Dye-sensitized solar cells with 13% efficiency achieved through the molecular engineering of porphyrin sensitizers. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kakiage, K.; Aoyama, Y.; Yano, T.; Oya, K.; Fujisawa, J.-I.; Hanaya, M. Highly-efficient dye-sensitized solar cells with collaborative sensitization by silyl-anchor and carboxy-anchor dyes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15894–15897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakiage, K.; Aoyama, Y.; Yano, T.; Oya, K.; Kyomen, T.; Hanaya, M. Fabrication of a high-performance dye-sensitized solar cell with 12.8% conversion efficiency using organic silyl-anchor dyes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 6315–6317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Housecroft, C.E.; Constable, C.E. The Emergence of copper(I)-based dye sensitized solar cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8386–8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Magni, M.; Biagini, P.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Roberto, D.; Valore, A. Versatile copper complexes as a convenient springboard for both dyes and redox mediators in dyes sensiatized solar cells. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2016, 322, 69–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroni, M.; Pellegron, Y.; Odobel, F. Heteroleptic bis-diimine copper(I) complexes for applications in solar energy conversion. Compt. Rendus Chim. 2016, 19, 79–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jakubikova, E.; Bowman, D.N. Fe(II)-Polypyridines as Chromophores in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: A Computational Perspective. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Persson, P.; Sundström, V.; Wärnmark, K. Fe N-Heterocyclic Carbene Complexes as Promising Photosensitizers. Acc. Chem. Res. 2016, 49, 1477–1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malzner, F.J.; Brauchli, S.Y.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Neuburger, M. Halos show the path to perfection: peripheral iodo-substituents improve the efficiencies of bis(diimine)copper(I) dyes in dye-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 48712–48723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandroni, M.; Favereau, L.; Planchat, A.; Akdas-Kilig, H.; Szuwarski, N.; Pellegrin, Y.; Blart, E.; Le Bozec, H.; Boujtita, M.; Odobel, F. Heteroleptic copper(I)–polypyridine complexes as efficient sensitizers for dye sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 9944–9947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malzner, F.J.; Willgert, M.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. The way to panchromatic copper(I)-based dye-sensitized solar cells: Co-sensitization with the organic dye SQ2. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 13717–13729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürer, S.O.; Bozic-Weber, B.; Schefer, T.; Wobill, C.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Willgert, M. Understanding why replacing I3−/I− by cobalt(II)/(III) electrolytes in bis(diimine)copper(I)-based dye-sensitized solar cells improves performance. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 12995–13004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ashbrook, L.N.; Elliott, C.M. Dye-Sensitized Solar Cell Studies of a Donor-Appended Bis(2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline) Cu(I) Dye Paired with a Cobalt-Based Mediator. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 3853–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fürer, S.O.; Luu, L.Y.N.; Bozic-Weber, B.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. Improving performance of copper(I)-based dye sensitized solar cells through I3−/I− electrolyte manipulation. Dyes Pigment. 2016, 132, 72–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragonetti, C.; Magni, M.; Colombo, A.; Melchiorre, F.; Biagini, P.; Roberto, D. Coupling of a Copper Dyes with a Copper Electrolyte: A Fascinating Springboard for Sustainable Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. ACS Appl. Energy Mater. 2018, 1, 751–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Büttner, A.; Brauchli, S.Y.; Vogt, R.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. Combining phosphonic acid-functionalized anchoring ligands with asymmetric ancillary ligands in bis(diimine)copper(I) dyes for dye-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 5205–5213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Brauchli, S.Y.; Malzner, F.J.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. Copper(I)-based dye-sensitized solar cells with sterically demanding anchoring ligands: Bigger is not always better. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48516–48525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Cole, J.M. Anchoring Groups for Dye-sensitized Solar Cells. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 3427–3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vioux, A.; Le Bideau, J.; Mutin, P.H.; Leclercq, D. Hybrid Organic–Inorganic Materials Based on organophosphorus Derivatives. Top. Curr. Chem. 2004, 232, 145–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Klein, C.; Moser, J.-E.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Cevey-Ha, N.-L.; Charvet, R.; Comte, P.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Grätzel, M. Amphiphilic Ruthenium Sensitizer with 4,4′-Diphosphonic Acid-2,2′-bipyridine as Anchoring Ligand for Nanocrystalline Dye Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Phys. Chem. B 2004, 108, 17553–17559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic-Weber, B.; Brauchli, S.Y.; Constable, E.C.; Fürer, S.O.; Housecroft, C.E.; Wright, I.A. Hole-transport functionalized copper(I) dye sensitized solar cells. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 4500–4504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malzner, F.J.; Prescimone, A.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Willgert, M. Exploring simple ancillary ligands in copper-based dye-sensitized solar cells: Effects of a heteroatom switch and of co-sensitization. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4671–4685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, E.F. Small Is Beautiful: A Study of Economics as if People Mattered; Blond & Briggs Ltd.: London, UK, 1973. [Google Scholar]
- Eggleston, M.K.; McMillin, D.R.; Koenig, K.S.; Pallenberg, A.J. Steric Effects in the Ground and Excited States of Cu(NN)2+ Systems. Inorg. Chem. 1997, 36, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammett, L.P. The Effect of Structure upon the Reactions of Organic Compounds. Benzene Derivatives. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1937, 59, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, D.H.; Brown, H.C. An Extended Table of Hammett Substituent Constants Based on the Ionization of Substituted Benzoic acids. J. Org. Chem. 1958, 23, 420–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansch, C.; Leo, A.; Taft, R.W. A Survey of Hammett Substituent Constants and Resonance and Field Parameters. Chem. Rev. 1991, 91, 165–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, F.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Song, Q.; Zhu, L. m-Methoxy Substituents in a Tetraphenylethylene-Based Hole-Transport Material for Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 16636–16641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukkala, V.M.; Kankare, J.J. New 2,2′-Bipyridine Derivatives and Their Luminescence Properties with Europium(III) and Terbium(III) Ions. Helv. Chim. Acta 1992, 75, 1578–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Neuburger, M.; Poleschak, I.; Zehnder, M. Functionalised 2,2′-bipyridine ligands for the preparation of metallostars; X-ray structures of free ligands and preparation of copper(I) and silver(I) complexes. Polyhedron 2003, 22, 93–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudebous, A.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Neuburger, M.; Schaffner, S.; Listorti, A.; Sabatini, C.; Barigelletti, F. Preparation and photophysical studies of copper(I) and ruthenium(II) complexes of 4,4′-bis(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)-6,6′-dimethyl-2,2′-bipyridine. Inorg. Chim. Acta 2009, 362, 1825–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic-Weber, B.; Brauchli, S.Y.; Constable, E.C.; Fürer, S.O.; Housecroft, C.E.; Malzner, F.J.; Wright, I.A.; Zampese, J.A. Improving the photoresponse of copper(I) dyes in dye-sensitized solar cells by tuning ancillary and anchoring ligand modules. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 12293–12308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kröhnke, F. The Specific Synthesis of Pyridines and Oligopyridines. Synthesis 1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, B.; Grätzel, M.; Moser, J.-E. Rationale for Kinetic Heterogeneity of Ultrafast Light-Induced Electron Transfer from Ru(II) Complex Sensitizers to Nanocrystalline TiO2. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 12150–12151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorsmølle, V.K.; Wenger, B.; Teuscher, J.; Bauer, C.; Moser, J.-E. Dynamics of Photoinduced Interfacial Electron Transfer and Charge Transport in Dye-Sensitized Mesoscopic Semiconductors. CHIMIA Int. J. Chem. 2007, 61, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozic-Weber, B.; Chaurin, V.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E.; Meuwly, M.; Neuburger, M.; Rudd, J.A.; Schönhofer, E.; Siegfried, L. Exploring copper(I)-based dye-sensitized solar cells: A complementary experimental and TD-DFT investigation. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 14157–14169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kubas, G.J. Tetrakis(Acetonitrile)Copper(I) Hexafluorophosphate. Inorg. Synth. 1979, 19, 90–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauchli, S.Y.; Bozic-Weber, B.; Constable, E.C.; Hostettler, N.; Housecroft, C.E.; Zampese, J.A. Factors controlling the photoresponse of copper(I) diimine dyes containing hole-transporting dendrons in dye-sensitized solar cells. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 34801–34815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spartan′16; Wavefunction Inc.: Irvine, CA, USA, 2017.














| Complex | λmax/nm (εmax/dm3 mol−1 cm−1) | |
|---|---|---|
| π*←π and π*←n | MLCT | |
| [Cu(1)2][PF6] | 255sh (56,600), 275 (68,300), 322 (37,400), 356sh (10,900) | 483 (11,400) |
| [Cu(2)2][PF6]a | 282 (62,500), 316sh (44,300), 329sh (39,000), 357sh (14,100) | 484 (11,400) |
| [Cu(3)2][PF6] | 278 (73,900), 318 (49,000), 354sh (11,400) | 486 (13,600) |
| [Cu(4)2][PF6] | 285 (69,400), 316 (51,600) | 482 (13,100) |
| Dye | On the Day of DSSC Fabrication | ||||
| JSC/mA cm–2 | VOC/mV | ff/% | η/% | Relative η/% | |
| [Cu(5)(1)]+ | 4.27 | 545 | 71 | 1.66 | 28.7 |
| [Cu(5)(1)]+ | 4.20 | 536 | 70 | 1.58 | 27.3 |
| N719 (cell 1) a | 13.29 | 647 | 67 | 5.79 | 100 |
| [Cu(5)(2)]+ | 4.87 | 528 | 71 | 1.82 | 30.1 |
| [Cu(5)(2)]+ | 4.74 | 524 | 72 | 1.80 | 29.8 |
| N719 (cell 2) a | 13.91 | 635 | 68 | 6.04 | 100 |
| [Cu(5)(3)]+ | 3.68 | 528 | 73 | 1.43 | 25.4 |
| [Cu(5)(3)]+ | 3.90 | 516 | 72 | 1.46 | 24.2 |
| N719 (cell 3) a | 13.42 | 631 | 66 | 5.62 | 100 |
| [Cu(5)(4)]+ | 4.79 | 567 | 72 | 1.96 | 33.9 |
| [Cu(5)(4)]+ | 4.68 | 550 | 68 | 1.75 | 30.2 |
| N719 (cell 1) a | 13.29 | 647 | 67 | 5.79 | 100 |
| Dye | 7 Days after DSSC Fabrication | ||||
| JSC/mA cm–2 | VOC/mV | ff/% | η/% | Relative η/% | |
| [Cu(5)(1)]+ | 4.22 | 580 | 70 | 1.72 | 29.7 |
| [Cu(5)(1)]+ | 4.19 | 573 | 70 | 1.68 | 29.0 |
| N719 (cell 1) a | 12.70 | 670 | 68 | 5.80 | 100 |
| [Cu(5)(2)]+ | 4.33 | 569 | 71 | 1.74 | 28.0 |
| [Cu(5)(2)]+ | 5.02 | 565 | 65 | 1.86 | 30.0 |
| N719 (cell 2) a | 13.23 | 690 | 68 | 6.21 | 100 |
| [Cu(5)(3)]+ | 3.23 | 541 | 74 | 1.29 | 21.8 |
| [Cu(5)(3)]+ | 4.30 | 562 | 70 | 1.70 | 28.8 |
| N719 (cell 1) a | 13.05 | 673 | 67 | 5.91 | 100 |
| [Cu(5)(4)]+ | 4.75 | 580 | 67 | 1.86 | 32.1 |
| [Cu(5)(4)]+ | 4.64 | 593 | 65 | 1.80 | 31.0 |
| N719 (cell 3) a | 12.70 | 670 | 68 | 5.80 | 100 |
| Dye | λmax/nm | EQEmax/% |
|---|---|---|
| [Cu(5)(1)]+ | 470 | 42.7 |
| [Cu(5)(1)]+ | 470 | 41.9 |
| [Cu(5)(2)]+ | 480 | 46.5 |
| [Cu(5)(2)]+ | 480 | 45.3 |
| [Cu(5)(3)]+ | 470 | 39.1 |
| [Cu(5)(3)]+ | 470 | 38.0 |
| [Cu(5)(4)]+ | 470 | 45.3 |
| [Cu(5)(4)]+ | 470 | 44.9 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Büttner, A.; Brauchli, S.Y.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. Effects of Introducing Methoxy Groups into the Ancillary Ligands in Bis(diimine) Copper(I) Dyes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Inorganics 2018, 6, 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020040
Büttner A, Brauchli SY, Constable EC, Housecroft CE. Effects of Introducing Methoxy Groups into the Ancillary Ligands in Bis(diimine) Copper(I) Dyes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Inorganics. 2018; 6(2):40. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020040
Chicago/Turabian StyleBüttner, Annika, Sven Y. Brauchli, Edwin C. Constable, and Catherine E. Housecroft. 2018. "Effects of Introducing Methoxy Groups into the Ancillary Ligands in Bis(diimine) Copper(I) Dyes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells" Inorganics 6, no. 2: 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020040
APA StyleBüttner, A., Brauchli, S. Y., Constable, E. C., & Housecroft, C. E. (2018). Effects of Introducing Methoxy Groups into the Ancillary Ligands in Bis(diimine) Copper(I) Dyes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Inorganics, 6(2), 40. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020040