Ruthenium Complexes as Sensitizers in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells
Abstract
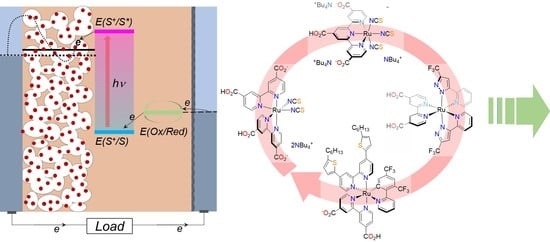
:1. Introduction
2. Sensitizers
3. Ruthenium Complexes
3.1. Ruthenium Complexes with Isothiocyanate Ligands
3.2. Toward Isothiocyanate Free Ruthenium Complexes
3.3. Cyclometalated Ruthenium(II) Complexes
4. Solar Cells with Co and Cu Electrolytes
5. Future Perspectives
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gray, H.B. Powering the planet with solar fuel. Nat. Chem. 2009, 1, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewis, N.S.; Nocera, D.G. Powering the planet: Chemical challenges in solar energy utilization. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 15729–15735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Regan, B.; Grätzel, M. A low-cost, high-efficiency solar cell based on dye-sensitized colloidal TiO2 films. Nature 1991, 353, 737–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grätzel, M. Solar Energy Conversion by Dye-Sensitized Photovoltaic Cells. Inorg. Chem. 2005, 44, 6841–6851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ito, S.; Murakami, T.N.; Comte, P.; Liska, P.; Grätzel, C.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Grätzel, M. Fabrication of thin film dye sensitized solar cells with solar to electric power conversion efficiency over 10%. Thin Solid Films 2008, 516, 4613–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakiage, K.; Aoyama, Y.; Yano, T.; Oya, K.; Fujisawa, J.; Hanaya, M. Highly-efficient dye-sensitized solar cells with collaborative sensitization by silyl-anchor and carboxy-anchor dyes. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 15894–15897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, R.A. On the Theory of Oxidation-Reduction Reactions Involving Electron Transfer. I. J. Chem. Phys. 1956, 24, 966–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, R.A. Electrostatic Free Energy and Other Properties of States Having Nonequilibrium Polarization. I. J. Chem. Phys. 1956, 24, 979–989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marcus, R.A.; Sutin, N. Electron transfers in chemistry and biology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Rev. Bioenergy 1985, 811, 265–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerischer, H. Electrochemical Techniques for the Study of Photosensitization. Photochem. Photobiol. 1972, 16, 243–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerischer, H.; Willig, F. Reaction of excited dye molecules at electrodes. In Physical and Chemical Applications of Dyestuffs; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1976; pp. 31–84. ISBN 978-3-540-38098-6. [Google Scholar]
- Ardo, S.; Meyer, G.J. Photodriven heterogeneous charge transfer with transition-metal compounds anchored to TiO 2 semiconductor surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 115–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shockley, W.; Queisser, H.J. Detailed balance limit of efficiency of p-n junction solar cells. J. Appl. Phys. 1961, 32, 510–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagfeldt, A.; Boschloo, G.; Sun, L.; Kloo, L.; Pettersson, H. Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 6595–6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pashaei, B.; Shahroosvand, H.; Grätzel, M.; Nazeeruddin, M.K. Influence of Ancillary Ligands in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 9485–9564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orgel, L.E. Double bonding in chelated metal complexes. J. Chem. Soc. 1961, 3683–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desilvestro, J.; Grätzel, M.; Kavan, L.; Moser, J.; Augustynski, J. Highly Efficient Sensitization of Titanium Dioxide. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1985, 107, 2988–2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachopoulos, N.; Liska, P.; Augustynski, J.; Graetzel, M. Very efficient visible light energy harvesting and conversion by spectral sensitization of high surface area polycrystalline titanium dioxide films. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 1216–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liska, P.; Vlachopoulos, N.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Comte, P.; Gratzel, M. cis-Diaquabis(2,2/-bipyridyl-4,4’-dicarboxylate)-ruthenium(II) Sensitizes Wide Band Gap Oxide Semiconductors Very Efficiently over a Broad Spectral Range in the Visible. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1988, 110, 3686–3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amadelli, R.; Argazzi, R.; Bignozzi, C.A.; Scandola, F. Design of Antenna–Sensitizer Polynuclear Complexes. Sensitization of Titanium Dioxide with [Ru(bpy)2(CN)2]2Ru(bpy(COO)2)22−. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1990, 112, 7099–7103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Kay, A.; Rodicio, I.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Mueller, E.; Liska, P.; Vlachopoulos, N.; Grätzel, M. Conversion of light to electricity by cis-X2bis(2,2′-bipyridyl-4,4′-dicarboxylate)ruthenium(II) charge-transfer sensitizers (X = Cl−, Br−, I−, CN−, and SCN−) on nanocrystalline titanium dioxide electrodes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 6382–6390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Jirousek, M.; Liska, P.; Vlachopoulos, N.; Shklover, V.; Fischer, C.-H.; Grätzel, M. Acid−Base Equilibria of (2,2′-Bipyridyl-4,4′-dicarboxylic acid)ruthenium(II) Complexes and the Effect of Protonation on Charge-Transfer Sensitization of Nanocrystalline Titania. Inorg. Chem. 1999, 38, 6298–6305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerischer, H. Neglected problems in the pH dependence of the flatband potential of semiconducting oxides and semiconductors covered with oxide layers. Electrochim. Acta 1989, 34, 1005–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, S.G.; Hupp, J.T. Semiconductor-Based Interfacial Electron-Transfer Reactivity: Decoupling Kinetics from pH-Dependent Band Energetics in a Dye-Sensitized Titanium Dioxide/Aqueous Solution System. J. Phys. Chem. 1996, 100, 6867–6870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozik, A.J. Photoelectrochemistry: Applications to Solar Energy Conversion. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem. 1978, 29, 189–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.Y.; Schlichthörl, G.; Nozik, A.J.; Grätzel, M.; Frank, A.J. Charge Recombination in Dye-Sensitized Nanocrystalline TiO2 Solar Cells. J. Phys. Chem. B 1997, 101, 2576–2582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazeeruddin, M.K.; De Angelis, F.; Fantacci, S.; Selloni, A.; Viscardi, G.; Liska, P.; Ito, S.; Takeru, B.; Grätzel, M. Combined experimental and DFT-TDDFT computational study of photoelectrochemical cell ruthenium sensitizers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 16835–16847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Snaith, H.J. Estimating the Maximum Attainable Efficiency in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2010, 20, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koops, S.E.; O’Regan, B.C.; Barnes, P.R.F.; Durrant, J.R. Parameters Influencing the Efficiency of Electron Injection in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4808–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Regan, B.C.; Durrant, J.R. Kinetic and Energetic Paradigms for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: Moving from the Ideal to the Real. Acc. Chem. Res. 2009, 42, 1799–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, D.F.; Meyer, G.J. Electron Injection at Dye-Sensitized Semiconductor Electrodes. Annu. Rev. Phys. Chem 2005, 56, 119–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Péchy, P.; Renouard, T.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Comte, P.; Liska, P.; Cevey, L.; Costa, E.; Shklover, V.; et al. Engineering of Efficient Panchromatic Sensitizers for Nanocrystalline TiO2-Based Solar Cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Black, D.S.C.; Deacon, G.B.; Thomas, N.C. New decarbonylation reactions of carbonylruthenium(II) complexes. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1982, 65, L75–L76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- St. Black, D.C.; Deacon, G.B.; Thomas, N.C. Ruthenium Carbonyl Complexes. I* Synthesis of [Ru(CO)2(bidentate)2]2+ Complexes. Aust. J. Chem. 1982, 35, 2445–2453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strouse, G.F.; Anderson, P.A.; Schoonover, J.R.; Meyer, T.J.; Keene, F.R. Synthesis of polypyridyl complexes of ruthenium(II) containing three different bidentate ligands. Inorg. Chem. 1992, 31, 3004–3006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.A.; Strouse, G.F.; Treadway, J.A.; Keene, F.R.; Meyer, T.J. Black MLCT Absorbers. Inorg. Chem. 1994, 33, 3863–3864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, P.A.; Deacon, G.B.; Haarmann, K.H.; Richard Keene, F.; Meyer, T.J.; Reitsma, D.A.; Skelton, B.W.; Strouse, G.F.; Thomas, N.C.; Treadway, J.A.; et al. Designed Synthesis of Mononuclear Tris(heteroleptic) Ruthenium Complexes Containing Bidentate Polypyridyl Ligands. Inorg. Chem. 1995, 34, 6145–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Péchy, P.; Quagliotto, P.; Barolo, C.; Viscardi, G.; Grätzel, M. Design, synthesis, and application of amphiphilic ruthenium polypyridyl photosensitizers in solar cells based on nanocrystalline TiO2 films. Langmuir 2002, 18, 952–954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freedman, D.A.; Evju, J.K.; Pomije, M.K.; Mann, K.R. Convenient synthesis of tris-heteroleptic ruthenium(II) polypyridyl complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 5711–5715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Grätzel, M.; Shklover, V. Stepwise Assembly of Tris-Heteroleptic Polypyridyl Complexes of Ruthenium(II). Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 5251–5259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Moser, J.E.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Sekiguchi, T.; Grätzel, M. A stable quasi-solid-state dye-sensitized solar cell with an amphiphilic ruthenium sensitizer and polymer gel electrolyte. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 402–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, P.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Moser, J.E.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Comte, P.; Aranyos, V.; Hagfeldt, A.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Grätzel, M. Stable new sensitizer with improved light harvesting for nanocrystalline dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv. Mater. 2004, 16, 1806–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Klein, C.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Gr??tzel, M. A high molar extinction coefficient sensitizer for stable dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 808–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, D.; Ito, S.; Wenger, B.; Klein, C.; Moser, J.E.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Grätzel, M. High molar extinction coefficient heteroleptic ruthenium complexes for thin film dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 4146–4154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, D.; Klein, C.; Ito, S.; Moser, J.E.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Evans, N.; Duriaux, F.; Grätzel, C.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Grätzel, M. High-Efficiency and stable mesoscopic dye-sensitized solar cells based on a high molar extinction coefficient ruthenium sensitizer and nonvolatile electrolyte. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1133–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Wu, S.-J.; Wu, C.-G.; Chen, J.-G.; Ho, K.-C. A Ruthenium Complex with Superhigh Light-Harvesting Capacity for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 5822–5825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Wu, S.-J.; Li, J.-Y.; Wu, C.-G.; Chen, J.-G.; Ho, K.-C. A New Route to Enhance the Light-Harvesting Capability of Ruthenium Complexes for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3888–3891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Shi, D.; Zhang, J.; Wang, M.; Jing, X.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Wang, P.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Grätzel, M. Enhance the optical absorptivity of nanocrystalline TiO2 film with high molar extinction coefficient ruthenium sensitizers for high performance dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 10720–10728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhang, M.; Cai, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, P. An extremely high molar extinction coefficient ruthenium sensitizer in dye-sensitized solar cells: The effects of π-conjugation extension. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 14559–14566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Yu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, S.; Shi, D.; Gao, F.; Wang, P. Dye-sensitized solar cells with a high absorptivity ruthenium sensitizer featuring a 2-(hexylthio)thiophene conjugated bipyridine. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 6290–6297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Wang, M.; Li, J.Y.; Pootrakulchote, N.; Alibabaei, L.; Ngoc-Le, C.H.; Decoppet, J.D.; Tsai, J.H.; Grätzel, C.; Wu, C.G.; et al. Highly efficient light-harvesting ruthenium sensitizer for thin-film dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3103–3109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karthikeyan, C.S.; Wietasch, H.; Thelakkat, M. Highly efficient solid-state dye-sensitized TiO2 solar cells using donor-antenna dyes capable of multistep charge-transfer cascades. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 1091–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shi, D.; Wang, M.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Wang, P.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Grätzel, M. A new heteroleptic ruthenium sensitizer enhances the absorptivity of mesoporous titania film for a high efficiency dye-sensitized solar cell. Chem. Commun. 2008, 107, 2635–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.J.; Lim, K.; Choi, H.; Fan, S.; Kang, M.S.; Gao, G.; Kang, H.S.; Ko, J. New efficient ruthenium sensitizers with unsymmetrical indeno[1,2-b]thiophene or a fused dithiophene ligand for dye-sensitized solar cells. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 8351–8357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-G.; Wu, S.-J.; Li, J.-Y.; Wu, C.-G.; Ho, K.-C. Multifunctionalized ruthenium-based supersensitizers for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2008, 47, 7342–7345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.-Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chen, J.-G.; Tan, C.-J.; Lee, K.-M.; Wu, S.-J.; Tung, Y.-L.; Tsai, H.-H.; Ho, K.-C.; Wu, C.-G. Heteroleptic ruthenium antenna-dye for high-voltage dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 7158–7164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.Y.; Pootrakulchote, N.; Wu, S.J.; Wang, M.; Li, J.Y.; Tsai, J.H.; Wu, C.G.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Grätzel, M. New ruthenium sensitizer with carbazole antennas for efficient and stable Thin-film Dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 20752–20757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Baik, C.; Kim, S.; Kang, M.-S.; Xu, X.; Kang, H.S.; Kang, S.O.; Ko, J.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Grätzel, M. Molecular engineering of hybrid sensitizers incorporating an organic antenna into ruthenium complex and their application in solar cells. New J. Chem. 2008, 32, 2233–2237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, A.V; Ramos, L.D.; Frin, K.P.M.; de Oliveira, K.T.; Polo, A.S. A high efficiency ruthenium(II) tris-heteroleptic dye containing 4,7-dicarbazole-1,10-phenanthroline for nanocrystalline solar cells. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 46487–46494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.C.; Kong, F.T.; Ghadari, R.; Li, Z.Q.; Guo, F.L.; Liu, X.P.; Huang, Y.; Yu, T.; Hayat, T.; Dai, S.Y. Unravelling the structural-electronic impact of arylamine electron-donating antennas on the performances of efficient ruthenium sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Power Sources 2017, 346, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.-S.; Huang, C.-H.; Huang, Y.-Y.; Zhang, B.-W.; Xie, P.-H.; Hou, Y.-J.; Ibrahim, K.; Qian, H.-J.; Liu, F.-Q. Photoelectric behavior of nanocrystalline TiO2 electrode with a novel terpyridyl ruthenium complex. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2002, 71, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funaki, T.; Yanagida, M.; Onozawa-Komatsuzaki, N.; Kawanishi, Y.; Kasuga, K.; Sugihara, H. Ruthenium (II) complexes with π expanded ligand having phenylene-ethynylene moiety as sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2009, 93, 729–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vougioukalakis, G.C.; Stergiopoulos, T.; Kantonis, G.; Kontos, A.G.; Papadopoulos, K.; Stublla, A.; Potvin, P.G.; Falaras, P. Terpyridine- and 2,6-dipyrazinylpyridine-coordinated ruthenium(II) complexes: Synthesis, characterization and application in TiO2-based dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. A Chem. 2010, 214, 22–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onozawa-Komatsuzaki, N.; Yanagida, M.; Funaki, T.; Kasuga, K.; Sayama, K.; Sugihara, H. Near-IR sensitization of nanocrystalline TiO2 with a new ruthenium complex having a 2,6-bis(4-carboxyquinolin-2-yl)pyridine ligand. Inorg. Chem. Commun. 2009, 12, 1212–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onozawa-Komatsuzaki, N.; Yanagida, M.; Funaki, T.; Kasuga, K.; Sayama, K.; Sugihara, H. Near-IR dye-sensitized solar cells using a new type of ruthenium complexes having 2,6-bis(quinolin-2-yl)pyridine derivatives. In Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells; North-Holland: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; Volume 95, pp. 310–314. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.H.; Wu, K.L.; Chi, Y.; Cheng, Y.M.; Chou, P.T. Tris(thiocyanate) ruthenium(II) sensitizers with functionalized dicarboxyterpyridine for dye-sensitized solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8270–8274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, M.; Masuo, J.; Tohata, Y.; Obuchi, K.; Masaki, N.; Murakami, T.N.; Koumura, N.; Hara, K.; Fukui, A.; Yamanaka, R.; et al. Improvement of TiO2/dye/electrolyte interface conditions by positional change of alkyl chains in modified panchromatic Ru complex dyes. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 1028–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Numata, Y.; Singh, S.P.; Islam, A.; Iwamura, M.; Imai, A.; Nozaki, K.; Han, L. Enhanced light-harvesting capability of a panchromatic Ru(II) sensitizer based on π-extended terpyridine with a 4-methylstylryl group for dye-sensitized solar cells. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2013, 23, 1817–1823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Lam, B.X.T.; Andersen, A.R.; Hansen, P.E.; Lund, T. Photovoltaic performance and characteristics of dye-sensitized solar cells prepared with the n719 thermal degradation products [Ru(LH)2(NCS)(4-tert-butylpyridine)][N(Bu)4] and [Ru(LH)2(NCS)(1-methylbenzimidazole)][N(Bu)4]. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 2011, 2533–2539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nguyen, P.T.; Degn, R.; Nguyen, H.T.; Lund, T. Thiocyanate ligand substitution kinetics of the solar cell dye Z-907 by 3-methoxypropionitrile and 4-tert-butylpyridine at elevated temperatures. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2009, 93, 1939–1945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Ta, H.M.; Lund, T. Thermal thiocyanate ligand substitution kinetics of the solar cell dye N719 by acetonitrile, 3-methoxypropionitrile, and 4-tert-butylpyridine. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2007, 91, 1934–1942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbotto, A.; Coluccini, C.; Dell’Orto, E.; Manfredi, N.; Trifiletti, V.; Salamone, M.M.; Ruffo, R.; Acciarri, M.; Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; et al. Thiocyanate-free cyclometalated ruthenium sensitizers for solar cells based on heteroaromatic-substituted 2-arylpyridines. Dalton Trans. 2012, 41, 11731–11738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dragonetti, C.; Valore, A.; Colombo, A.; Roberto, D.; Trifiletti, V.; Manfredi, N.; Salamone, M.M.; Ruffo, R.; Abbotto, A. A new thiocyanate-free cyclometallated ruthenium complex for dye-sensitized solar cells: Beneficial effects of substitution on the cyclometallated ligand. J. Organomet. Chem. 2012, 714, 88–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dragonetti, C.; Colombo, A.; Magni, M.; Mussini, P.; Nisic, F.; Roberto, D.; Ugo, R.; Valore, A.; Valsecchi, A.; Salvatori, P.; et al. Thiocyanate-free ruthenium(II) sensitizer with a pyrid-2-yltetrazolate ligand for dye-sensitized solar cells. Inorg. Chem. 2013, 52, 10723–10725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Valore, A.; Coluccini, C.; Manfredi, N.; Abbotto, A. Thiocyanate-free ruthenium(II) 2,2′-bipyridyl complexes for dye-sensitized solar cells. Polyhedron 2014, 82, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, A.; Dragonetti, C.; Magni, M.; Meroni, D.; Ugo, R.; Marotta, G.; Grazia Lobello, M.; Salvatori, P.; De Angelis, F. New thiocyanate-free ruthenium(II) sensitizers with different pyrid-2-yl tetrazolate ligands for dye-sensitized solar cells. Dalton Trans. 2015, 44, 11788–11796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.-L.; Hsu, H.-C.; Chen, K.; Chi, Y.; Chung, M.-W.; Liu, W.-H.; Chou, P.-T. Development of thiocyanate-free, charge-neutral Ru(II) sensitizers for dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 5124–5126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-W.; Wu, K.-L.; Ghadiri, E.; Lobello, M.G.; Ho, S.-T.; Chi, Y.; Moser, J.-E.; De Angelis, F.; Grätzel, M.; Nazeeruddin, M.K. Engineering of thiocyanate-free Ru(II) sensitizers for high efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 2423–2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, K.-L.; Ku, W.-P.; Clifford, J.N.; Palomares, E.; Ho, S.-T.; Chi, Y.; Liu, S.-H.; Chou, P.-T.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Grätzel, M. Harnessing the open-circuit voltage via a new series of Ru(II) sensitizers bearing (iso-)quinolinyl pyrazolate ancillaries. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moehl, T.; Tsao, H.N.; Wu, K.L.; Hsu, H.C.; Chi, Y.; Ronca, E.; De Angelis, F.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Grätzel, M. High open-circuit voltages: Evidence for a sensitizer-induced TiO2 conduction band shift in Ru(II)-dye sensitized solar cells. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 4497–4502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.-S.; Chen, K.; Hong, Y.-H.; Liu, W.-H.; Li, T.-H.; Lai, C.-H.; Chou, P.-T.; Chi, Y.; Lee, G.-H. Neutral, panchromatic Ru(II) terpyridine sensitizers bearing pyridine pyrazolate chelates with superior DSSC performance. Chem. Commun. 2009, 0, 5844–5846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-W.; Chou, C.-C.; Hu, F.-C.; Wu, K.-L.; Chi, Y.; Clifford, J.N.; Palomares, E.; Liu, S.-H.; Chou, P.-T.; Wei, T.-C.; et al. Panchromatic Ru(II) sensitizers bearing single thiocyanate for high efficiency dye sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 17618–17627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.C.; Wu, K.L.; Chi, Y.; Hu, W.P.; Yu, S.J.; Lee, G.H.; Lin, C.L.; Chou, P.T. Ruthenium(II) sensitizers with heteroleptic tridentate chelates for dye-sensitized solar cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 2054–2058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, K.L.; Li, C.H.; Chi, Y.; Clifford, J.N.; Cabau, L.; Palomares, E.; Cheng, Y.M.; Pan, H.A.; Chou, P.T. Dye molecular structure device open-circuit voltage correlation in Ru(II) sensitizers with heteroleptic tridentate chelates for dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 7488–7496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, C.C.; Hu, F.C.; Yeh, H.H.; Wu, H.P.; Chi, Y.; Clifford, J.N.; Palomares, E.; Liu, S.H.; Chou, P.T.; Lee, G.H. Highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells based on panchromatic ruthenium sensitizers with quinolinylbipyridine anchors. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 178–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, Y.; Wu, K.-L.; Wei, T.-C. Ruthenium and Osmium Complexes That Bear Functional Azolate Chelates for Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Chem. Asian J. 2015, 10, 1098–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reveco, P.; Medley, J.H.; Garber, A.R.; Bhacca, N.S.; Selbin, J. Study of a Cyclometalated Complex of Ruthenium by 400-MHz Two-Dimensional Proton NMR. Inorg. Chem. 1985, 24, 1096–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reveco, P.; Schmehl, R.H.; Cherry, W.R.; Fronczek, F.R.; Selbin, J. Cyclometalated complexes of ruthenium. 2. Spectral and electrochemical properties and X-ray structure of bis(2,2’-bipyridine)(4-nitro-2-(2-pyridyl)phenyl)ruthenium(II). Inorg. Chem. 1985, 24, 4078–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reveco, P.; Cherry, W.R.; Medley, J.; Garber, A.; Gale, R.J.; Selbin, J. Cyclometalated Complexes of Ruthenium. 3. Spectral, Electrochemical, and Two-Dimensional Proton NMR of [Ru(bpy)2(cyclometalating ligand)]+. Inorg. Chem. 1986, 25, 1842–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constable, E.C.; Holmes, J.M. A cyclometallated analogue of tris(2,2′-bipyridine)ruthenium(II). J. Organomet. Chem. 1986, 301, 203–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collin, J.P.; Beley, M.; Sauvage, J.P.; Barigelletti, F. A room temperature luminescent cyclometalated ruthenium(II) complex of 6-phenyl-2,2’-bipyridine. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1991, 186, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barigelletti, F.; Ventura, B.; Collin, J.-P.; Kayhanian, R.; Gavina, P.; Sauvage, J.-P. Electrochemical and spectroscopic properties of cyclometallated and non-cyclometallated ruthenium(II) complexes containing sterically hindering ligands of the phenanthroline and terpyridine families. Eur. J. Inorg. Chem. 2000, 2000, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ott, S.; Borgström, M.; Hammarström, L.; Johansson, O. Rapid energy transfer in bichromophoric tris-bipyridyl/cyclometallated ruthenium(II) complexes. Dalton Trans. 2006, 1434–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadman, S.H.; Lutz, M.; Tooke, D.M.; Spek, A.L.; František Hartl; Havenith, R.W.A.; Van Klink, G.P.M.; Van Koten, G. Consequences of N,C,N′- and C,N,N′-coordination modes on electronic and photophysical properties of cyclometalated aryl ruthenium(II) complexes. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 1887–1900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadman, S.H.; Van Leeuwen, Y.M.; Havenith, R.W.A.; Van Klink, G.P.M.; Van Koten, G. A redox asymmetric, cyclometalated ruthenium dimer: Toward upconversion dyes in dye-sensitized TiO2 solar cells. Organometallics 2010, 29, 5635–5645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgström, M.; Ott, S.; Lomoth, R.; Bergquist, J.; Hammarström, L.; Johansson, O. Photoinduced energy transfer coupled to charge separation in a Ru(II)-Ru(II)-acceptor triad. Inorg. Chem. 2006, 45, 4820–4829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koizumi, T.A.; Tomon, T.; Tanaka, K. Terpyridine-analogous (N,N,C)-Tridentate ligands: Synthesis, structures, and electrochemical properties of ruthenium(II) complexes bearing tridentate pyridinium and pyridinylidene ligands. Organometallics 2003, 22, 970–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadman, S.H.; Kroon, J.M.; Bakker, K.; Lutz, M.; Spek, A.L.; van Klink, G.P.M.; van Koten, G. Cyclometalated ruthenium complexes for sensitizing nanocrystalline TiO2 solar cells. Chem. Commun. 2007, 1907–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wadman, S.H.; Kroon, J.M.; Bakker, K.; Havenith, R.W.A.; Van Klink, G.P.M.; Van Koten, G. Cyclometalated organoruthenium complexes for application in dye-sensitized solar cells. Organometallics 2010, 29, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kreitner, C.; Mengel, A.K.C.; Lee, T.K.; Cho, W.; Char, K.; Kang, Y.S.; Heinze, K. Strongly Coupled Cyclometalated Ruthenium Triarylamine Chromophores as Sensitizers for DSSCs. Chem. Eur. J. 2016, 22, 8915–8928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreitner, C.; Heinze, K. The photochemistry of mono- and dinuclear cyclometalated bis(tridentate)ruthenium(II) complexes: Dual excited state deactivation and dual emission. Dalton Trans. 2016, 45, 5640–5658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, C.J.; Nie, H.J.; Yang, W.W.; Shao, J.Y.; Yao, J.; Zhong, Y.W. Strongly coupled cyclometalated ruthenium-triarylamine hybrids: Tuning electrochemical properties, intervalence charge transfer, and spin distribution by substituent effects. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 17466–17477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katagiri, S.; Sakamoto, R.; Maeda, H.; Nishimori, Y.; Kurita, T.; Nishihara, H. Terminal redox-site effect on the long-range electron conduction of Fe(tpy)2 oligomer wires on a gold electrode. Chem. Eur. J. 2013, 19, 5088–5096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghazada, S.; Zimmermann, I.; Ren, Y.; Wang, P.; Nazeeruddin, M.K. Bis-Tridentate-Cyclometalated Ruthenium Complexes with Extended Anchoring Ligand and Their Performance in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. ChemistrySelect 2018, 3, 1585–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bomben, P.G.; Robson, K.C.D.; Sedach, P.A.; Berlinguette, C.P. On the viability of cyclometalated Ru(II) complexes for light-harvesting applications. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 9631–9643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnefous, C.; Chouai, A.; Thummel, R.P. Cyclometalated complexes of Ru(II) with 2-aryl derivatives of quinoline and 1,10-phenanthroline. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 5851–5859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, K.C.D.; Koivisto, B.D.; Yella, A.; Sporinova, B.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Baumgartner, T.; Grätzel, M.; Berlinguette, C.P. Design and development of functionalized cyclometalated ruthenium chromophores for light-harvesting applications. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 5494–5508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wadman, S.H.; Havenith, R.W.A.; Hartl, F.; Lutz, M.; Spek, A.L.; Van Klink, G.P.M.; Van Koten, G. Redox chemistry and electronic properties of 2,3,5,6-tetrakis(2-pyridyl) pyrazine-bridged diruthenium complexes controlled by N,C,N′-biscyclometalated ligands. Inorg. Chem. 2009, 48, 5685–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetzer, L.; Boff, B.; Ali, M.; Xiangjun, M.; Collin, J.-P.; Sirlin, C.; Gaiddon, C.; Pfeffer, M. Library of second-generation cycloruthenated compounds and evaluation of their biological properties as potential anticancer drugs: Passing the nanomolar barrier. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 8869–8878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, Z.; Wu, Y. Photoinduced electron transfer dynamics of cyclometalated ruthenium (II)-naphthalenediimide dyad at NiO photocathode. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 18315–18324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessho, T.; Yoneda, E.; Yum, J.H.; Guglielmi, M.; Tavernelli, L.; Lmai, H.; Rothlisberger, U.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Grätzel, M. New paradigm in molecular engineering of sensitizers for solar cell applications. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5930–5934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomben, P.G.; Koivisto, B.D.; Berlinguette, C.P. Cyclometalated ru complexes of type [RuII(N^N)2(C^N)]z: Physicochemical response to substituents installed on the anionic ligand. Inorg. Chem. 2010, 49, 4960–4971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polander, L.E.; Yella, A.; Curchod, B.F.E.; Ashari Astani, N.; Teuscher, J.; Scopelliti, R.; Gao, P.; Mathew, S.; Moser, J.-E.; Tavernelli, I.; et al. Towards Compatibility between Ruthenium Sensitizers and Cobalt Electrolytes in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 8731–8735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghazada, S.; Gao, P.; Yella, A.; Marotta, G.; Moehl, T.; Teuscher, J.; Moser, J.-E.; De Angelis, F.; Grätzel, M.; Nazeeruddin, M.K. Ligand Engineering for the Efficient Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells with Ruthenium Sensitizers and Cobalt Electrolytes. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 6653–6659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghazada, S.; Ren, Y.; Wang, P.; Nazeeruddin, M.K. Effect of Donor Groups on the Performance of Cyclometalated Ruthenium Sensitizers in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 13437–13445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomben, P.G.; Gordon, T.J.; Schott, E.; Berlinguette, C.P. A trisheteroleptic cyclometalated RuII sensitizer that enables high power output in a dye-sensitized solar cell. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 10682–10685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bomben, P.G.; Borau-Garcia, J.; Berlinguette, C.P. Three is not a crowd: Efficient sensitization of TiO2 by a bulky trichromic trisheteroleptic cycloruthenated dye. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5599–5601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motley, T.C.; Troian-Gautier, L.; Brennaman, M.K.; Meyer, G.J. Excited-State Decay Pathways of Tris(bidentate) Cyclometalated Ruthenium(II) Compounds. Inorg. Chem. 2017, 56, 13579–13592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, K.C.D.; Koivisto, B.D.; Berlinguette, C.P. Derivatization of bichromic cyclometalated Ru(II) complexes with hydrophobic substituents. Inorg. Chem. 2012, 51, 1501–1507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robson, K.C.D.; Sporinova, B.; Koivisto, B.D.; Schott, E.; Brown, D.G.; Berlinguette, C.P. Systematic modulation of a bichromic cyclometalated ruthenium(II) scaffold bearing a redox-active triphenylamine constituent. Inorg. Chem. 2011, 50, 6019–6028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nusbaumer, H.; Moser, J.-E.; Shaik, M.Z.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Grätzel, M. CoII(dbbip)22+ Complex Rivals Tri-iodide/Iodide Redox Mediator in Dye-Sensitized Photovoltaic Cells. J. Phys. Chem. B 2001, 105, 10461–10464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldt, S.M.; Wang, G.; Boschloo, G.; Hagfeldt, A. Effects of Driving Forces for Recombination and Regeneration on the Photovoltaic Performance of Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells using Cobalt Polypyridine Redox Couples. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 21500–21507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yum, J.-H.; Baranoff, E.; Kessler, F.; Moehl, T.; Ahmad, S.; Bessho, T.; Marchioro, A.; Ghadiri, E.; Moser, J.-E.; Yi, C.; et al. A cobalt complex redox shuttle for dye-sensitized solar cells with high open-circuit potentials. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yella, A.; Lee, H.-W.; Tsao, H.N.; Yi, C.; Chandiran, A.K.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Diau, E.W.-G.; Yeh, C.-Y.; Zakeeruddin, S.M.; Grätzel, M. Porphyrin-Sensitized Solar Cells with Cobalt (II/III)–Based Redox Electrolyte Exceed 12 Percent Efficiency. Science 2011, 334, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew, S.; Yella, A.; Gao, P.; Humphry-Baker, R.; Curchod, B.F.E.; Ashari-Astani, N.; Tavernelli, I.; Rothlisberger, U.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Grätzel, M. Dye-sensitized solar cells with 13% efficiency achieved through the molecular engineering of porphyrin sensitizers. Nat. Chem. 2014, 6, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Feldt, S.M.; Lohse, P.W.; Kessler, F.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Grätzel, M.; Boschloo, G.; Hagfeldt, A. Regeneration and recombination kinetics in cobalt polypyridine based dye-sensitized solar cells, explained using Marcus theory. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 7087–7097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldt, S.M.; Gibson, E.A.; Gabrielsson, E.; Sun, L.; Boschloo, G.; Hagfeldt, A. Design of organic dyes and cobalt polypyridine redox mediators for high-efficiency dye-sensitized solar cells. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 16714–16724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mosconi, E.; Yum, J.-H.; Kessler, F.; Gómez García, C.J.; Zuccaccia, C.; Cinti, A.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Grätzel, M.; De Angelis, F. Cobalt Electrolyte/Dye Interactions in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells: A Combined Computational and Experimental Study. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 19438–19453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aghazada, S.; Zimmermann, I.; Scutelnic, V.; Nazeeruddin, M.K. Synthesis and Photophysical Characterization of Cyclometalated Ruthenium Complexes with N-Heterocyclic Carbene Ligands. Organometallics 2017, 36, 2397–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sousa, S.; Ducasse, L.; Kauffmann, B.; Toupance, T.; Olivier, C. Functionalization of a ruthenium-diacetylide organometallic complex as a next-generation push-pull chromophore. Chem. Eur. J. 2014, 20, 7017–7024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa, S.; Lyu, S.; Ducasse, L.; Toupance, T.; Olivier, C. Tuning visible-light absorption properties of Ru–diacetylide complexes: Simple access to colorful efficient dyes for DSSCs. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 18256–18264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brauchli, S.Y.; Malzner, F.J.; Constable, E.C.; Housecroft, C.E. Copper(I)-based dye-sensitized solar cells with sterically demanding anchoring ligands: Bigger is not always better. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 48516–48525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Housecroft, C.E.; Constable, E.C. The emergence of copper(I)-based dye sensitized solar cells. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 8386–8398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sandroni, M.; Favereau, L.; Planchat, A.; Akdas-Kilig, H.; Szuwarski, N.; Pellegrin, Y.; Blart, E.; Le Bozec, H.; Boujtita, M.; Odobel, F. Heteroleptic copper(I)–polypyridine complexes as efficient sensitizers for dye sensitized solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 2014, 2, 9944–9947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Duchanois, T.; Etienne, T.; Monari, A.; Beley, M.; Assfeld, X.; Haacke, S.; Gros, P.C. A new record excited state 3MLCT lifetime for metalorganic iron(II) complexes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 12550–12556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monat, J.E.; McCusker, J.K. Femtosecond excited-state dynamics of an iron(II) polypyridyl solar cell sensitizer model. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2000, 122, 4092–4097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, W.W.; Cameron, L.A.; Zarkesh, R.A.; Ziller, J.W.; Heyduk, A.F. Donor-acceptor ligand-to-ligand charge-transfer coordination complexes of nickel(II). Inorg. Chem. 2014, 53, 8825–8837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cameron, L.A.; Ziller, J.W.; Heyduk, A.F. Near-IR absorbing donor–acceptor ligand-to-ligand charge-transfer complexes of nickel(II). Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 1807–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



























| Groups a | Dye | JSC, mA·cm−2 | VOC, mV | FF, % | PCE, % | Notes b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTU | CYC-B1 | 23.92 | 650 | 55.0 | 8.54 | 20 μm thick mesoporous film; 80 μm between electrodes [46,47]. |
| CYC-B3 | 15.7 | 669 | 70.5 | 7.39 | ||
| CJW-E1 | 21.6 | 669 | 62.6 | 9.02 | ||
| CIAC & EPFL | C101 | 17.94 | 777.7 | 78.5 | 11.0 | 7 μm of transparent TiO2 + 5 μm scattering TiO2; dipping solution: Dye-Cheno [48]. |
| CIAC | C103 | 18.35 | 760 | 74.8 | 10.4 | 7.5 μm of transparent TiO2 + 5 μm scattering TiO2 [49]. |
| C107 | 19.18 | 739 | 75.1 | 10.7 | ||
| CIAC & EPFL | C104 | 17.87 | 760 | 77.6 | 10.53 | 7 μm of transparent TiO2 + 4 μm scattering TiO2; dipping solution: Dye-Cheno (1–1) [53]. |
| KU | JK-188 | 18.60 | 720 | 71 | 9.54 | 10 μm of transparent TiO2 + 4 μm scattering TiO2 [54]. |
| JK-189 | 18.90 | 630 | 73 | 8.70 | ||
| NCU & EPFL | CYC-B11 | 18.3 | 704 | 73 | 9.4 | 8 μm of transparent TiO2 + 5 μm scattering TiO2; dipping solution: Dye-DINHOP (4–1) [51]. |
| CIAC | C106 | 19.2 | 776 | 76 | 11.29 | 7 μm of transparent TiO2 + 5 μm scattering TiO2; dipping solution: Dye-Cheno (1–6.7) [50]. |
| NCU | CYC-B6L | 18.2 | 776 | 63.6 | 8.98 | 15 μm thick mesoporous film; 80 μm between electrodes [55]. |
| NTU & NCU | CYC-B7 | 17.4 | 788 | 65.4 | 8.96 | 15 μm thick mesoporous film; 80 μm between electrodes [56]. |
| NCU & EPFL | CYC-B13 | 10.26 | 728 | 68 | 5.1 | 8 μm of transparent TiO2 + 5 μm scattering TiO2 [57]. |
| KU & EPFL | JK-55 | 17.55 | 640 | 72 | 8.2 | 10 μm of transparent TiO2 + 4 μm scattering TiO2; dipping solution: Dye-Cheno (1–3.3) [58]. |
| UFABC | Ru-Phen-Cbz2 | 15.6 | 760 | 71.6 | 8.5 | 13 μm thick mesoporous film; 30 μm between electrodes [59]. |
| HIPS | RC-36 | 19.17 | 721 | 74 | 10.23 | 4 μm of transparent TiO2 + 16 μm scattering TiO2; dipping solution: Dye-DPA (2–1) [60]. |
| Groups a | Dye | JSC, mA·cm−2 | VOC, mV | FF, % | PCE, % | Notes b |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTHU & NTU | PRT-12 | 17 | 750 | 71.5 | 9.1 | 15 μm of transparent TiO2 + 5 μm scattering TiO2; dipping solution: Dye-Cheno (1–33); PCE with N749—6.89% [66]. |
| PRT-13 | 19.7 | 760 | 68.6 | 10.3 | ||
| PRT-14 | 17.8 | 720 | 69.0 | 8.86 | ||
| SU & AIST | MJ-6 | 18.1 | 680 | 71 | 8.7 | 14 μm of transparent TiO2 + 7 μm scattering TiO2; dipping solution: Dye-Cheno (1–100); PCE with N749—9.2% [67]. |
| MJ-10 | 18.3 | 690 | 72 | 9.1 | ||
| NIMS & UT | HIS-2 | 23.07 | 680 | 71 | 11.1 | 25 μm thick mesoporous layer; 40 μm between electrodes; dipping solution: Dye-Cheno (1–67); PCE with N749—10.5% was obtained [68]. |
| Groups a | Dye | JSC, mA·cm−2 | VOC, mV | FF, % | PCE, % | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTHU | TFRS-1 | 15.95 | 830 | 69.3 | 9.18 | 12 μm of transparent TiO2 + 4 μm scattering TiO2; PCE with N719—8.56% [77]. |
| TFRS-2 | 17.15 | 820 | 67.8 | 9.54 | ||
| TFRS-3 | 17.38 | 810 | 63.5 | 8.94 | ||
| NTHU & EPFL | TFRS-4 | 18.7 | 750 | 72.9 | 10.2 | 12 μm of transparent TiO2 + 6 μm scattering TiO2; PCE with N719—9.52%, with TFRS-1 and TFRS-2—8.66% and 9.63% [78]. |
| TFRS-21 | 14.1 | 790 | 69.5 | 7.74 | ||
| TFRS-22 | 15.4 | 740 | 72.8 | 8.30 | ||
| TFRS-24 | 15.5 | 720 | 73.9 | 8.25 | ||
| NTHU, EPFL & NTU | TFRS-51 | 15.4 | 760 | 75 | 8.80 | 12 μm of transparent TiO2 + 6 μm scattering TiO2; pce with TFRS-1—7.84% [79]. |
| TFRS-52 b | 16.3/16.8 | 860/832 | 72/78 | 10.1/10.88 | ||
| TFRS-53 | 14.6 | 780 | 73 | 8.36 | ||
| TFRS-54 | 14.7 | 860 | 71 | 8.94 |
| Groups a | Dye | JSC, mA·cm−2 | VOC, mV | FF, % | PCE, % | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NTU & NTHU | PRT1 | 20.3 | 687 | 65.4 | 9.14 | 18 μm of transparent TiO2 + 4 μm scattering TiO2; PCE with N749—9.07% [81]. |
| PRT2 | 21.7 | 668 | 64.4 | 9.33 | ||
| PRT3 | 20.4 | 720 | 65.3 | 9.59 | ||
| PRT4 | 21.6 | 714 | 65.2 | 10.05 | ||
| PRT21 | 19.0 | 760 | 74.9 | 10.81 | 15 μm of transparent TiO2 + 7 μm scattering TiO2; PCE with N749—9.20% [82]. | |
| PRT22 | 20.4 | 740 | 73.9 | 11.16 | ||
| PRT23 | 18.7 | 760 | 73.4 | 10.43 | ||
| PRT24 | 20.1 | 730 | 71.6 | 10.51 | ||
| NTHU, NTU & NCCU | TF1 | 18.22 | 740 | 67.6 | 9.11 | 15 μm of transparent TiO2 + 5 μm scattering TiO2; PCE with N749—9.22% [83]. |
| TF2 | 20.00 | 790 | 66.5 | 10.5 | ||
| TF3 | 21.39 | 760 | 66.0 | 10.7 | ||
| TF4 | 20.27 | 770 | 67.5 | 10.5 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Aghazada, S.; Nazeeruddin, M.K. Ruthenium Complexes as Sensitizers in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Inorganics 2018, 6, 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020052
Aghazada S, Nazeeruddin MK. Ruthenium Complexes as Sensitizers in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Inorganics. 2018; 6(2):52. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020052
Chicago/Turabian StyleAghazada, Sadig, and Mohammad Khaja Nazeeruddin. 2018. "Ruthenium Complexes as Sensitizers in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells" Inorganics 6, no. 2: 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020052
APA StyleAghazada, S., & Nazeeruddin, M. K. (2018). Ruthenium Complexes as Sensitizers in Dye-Sensitized Solar Cells. Inorganics, 6(2), 52. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics6020052