Electronic Effects of the Substituents on Relaxometric and CEST Behaviour of Ln(III)-DOTA-Tetraanilides
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Synthesis
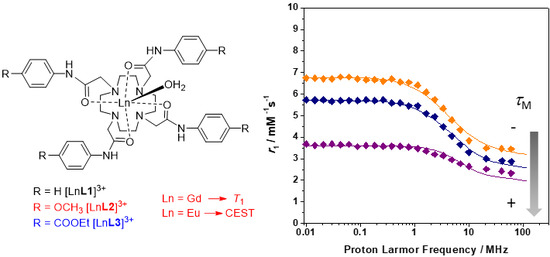
2.2. Relaxometry
2.3. CEST Experiments
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General
3.2. Synthesis of 2-Bromo-N-phenyl-acetamide
3.3. Synthesis of 2-Bromo-N-(4-methoxyphenyl)-acetamide
3.4. Synthesis of 2-Bromo-N-(ethylbenzoate)-acetamide
3.5. Synthesis of 1,4,7,10-Tetrakis((phenyl)carbamoylmethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane (DOTAMPh (L1))
3.6. Synthesis of 1,4,7,10-Tetrakis-((4-methoxyfenil)-carbamoylmethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane (DOTAMMeOPh (L2))
3.7. Synthesis of 1,4,7,10-Tetrakis((4-ethylbenzoate)-carbamoylmethyl)-1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane (DOTAMEtBenz (L3))
3.8. General Procedure for Preparation of Ln(III) Complexes
3.9. 1H Relaxometric Measurements and 1H NMRD Profiles
3.10. VT 17O Relaxation Measurements
3.11. Luminescence Measurements
3.12. Chemical Exchange Saturation Transfer (CEST)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stasiuk, G.J.; Long, N.J. The ubiquitous DOTA and its derivatives: The impact of 1,4,7,10-tetraazacyclododecane-1,4,7,10-tetraacetic acid on biomedical imaging. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 2732–2746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lattuada, L.; Barge, A.; Cravotto, G.; Giovenzana, G.B.; Tei, L. The synthesis and application of polyamino polycarboxylic bifunctional chelating agents. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 3019–3049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brücher, E.; Tircsó, G.; Baranyai, Z.; Kovács, Z.; Sherry, A. Chapter 4: Of the Chemistry of Contrast Agents in Medical Magnetic Resonance Imaging. In Stability and Toxicity of Contrast Agents, 2nd ed.; Helm, L., Tóth, É., Merbach, A.E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Caravan, P.; Ellison, J.J.; McMurry, T.J.; Lauffer, R.B. Gadolinium(III) Chelates as MRI contrast agents: Structure, dynamics, and applications. Chem. Rev. 1999, 99, 2293–2352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wahsner, J.; Gale, E.M.; Rodríguez-Rodríguez, A.; Caravan, P. Chemistry of MRI Contrast Agents: Current Challenges and New Frontiers. Chem. Rev. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heffern, M.C.; Matosziuk, L.M.; Meade, T.J. Lanthanide Probes for Bioresponsive Imaging. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 4496–4539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aime, S.; Barge, A.; Bruce, J.I.; Botta, M.; Howard, J.A.K.; Moloney, J.M.; Parker, D.; de Sousa, A.S.; Woods, M. NMR, Relaxometric, and Structural Studies of the Hydration and Exchange Dynamics of Cationic Lanthanide Complexes of Macrocyclic Tetraamide Ligands. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 5762–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aime, S.; Barge, A.; Batsanov, A.S.; Botta, M.; Delli Castelli, D.; Fedeli, F.; Mortillaro, A.; Parker, D.; Puschmannd, H. Controlling the variation of axial water exchange rates in macrocyclic lanthanide(III) complexes. Chem. Commun. 2002, 10, 1120–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.L.; Parker, D.; Fulton, D.A.; Howard, J.A.K.; Pandya, S.U.; Puschmann, H.; Senanayake, K.; Stenson, P.A.; Badari, A.; Botta, M.; et al. On the role of the counter-ion in defining water structure and dynamics: Order, structure and dynamics in hydrophilic and hydrophobic gadolinium salt complexes. Dalton Trans. 2006, 47, 5605–5616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aime, S.; Barge, A.; Botta, M.; De Sousa, A.S.; Parker, D. Direct NMR Spectroscopic Observation of a Lanthanide-Coordinated Water Molecule whose Exchange Rate Is Dependent on the Conformation of the Complexes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 1998, 37, 2673–2675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aime, S.; Barge, A.; Botta, M.; Parker, D.; De Sousa, A.S. Prototropic vs Whole Water Exchange Contributions to the Solvent Relaxation Enhancement in the Aqueous Solution of a Cationic Gd3+ Macrocyclic Complex. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 4767–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woods, M.; Pasha, A.; Zhao, P.; Tircso, G.; Chowdhury, S.; Kiefer, G.; Woessner, D.E.; Sherry, A.D. Investigations into whole water, prototropic and amide proton exchange in lanthanide(III) DOTA-tetraamide chelates. Dalton Trans. 2011, 40, 6759–6764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Winter, P.; Wu, K.; Sherry, A.D. A Novel Europium(III)-Based MRI Contrast Agent. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 1517–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, K.; Biewer, M.C.; Sherry, A.D. 1H and 17O NMR detection of a lanthanide-bound water molecule at ambient temperatures in pure water as solvent. Inorg. Chem. 2001, 40, 4284–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McVicar, N.; Li, A.X.; Suchy, M.; Hudson, R.H.E.; Menon, R.S.; Bartha, R. Simultaneous in vivo pH and temperature mapping using a PARACEST-MRI contrast agent. Magn. Reson. Med. 2013, 70, 1016–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wojciechowski, F.; Suchy, M.; Jones, C.K.; Hudson, R.H.E.; Merton, R.S.; Bartha, R. A sensitive PARACEST contrast agent for temperature MRI: Eu3+DOTAM-Glycine (Gly)-Phenylalanine (Phe). Magn. Reson. Med. 2008, 59, 374–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milne, M.; Lewis, M.; McVicar, N.; Suchy, M.; Bartha, R.; Hudson, R.H.E. MRI ParaCEST agents that improve amide based pH measurements by limiting inner sphere water T2 exchange. RSC Adv. 2014, 4, 1666–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ratnakar, S.J.; Woods, M.; Lubag, A.J.M.; Kov´acs, Z.; Sherry, A.D. Modulation of Water Exchange in Europium(III) DOTA-Tetraamide Complexes via Electronic Substituent Effects. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 6–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remya, G.S.; Suresh, C.H. Quantification and classification of substituent effects in organic chemistry: A theoretical molecular electrostatic potential study. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2016, 18, 20615–20626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinelli, J.; Balali-Mood, B.; Panizzo, R.; Lythgoe, M.F.; White, A.J.P.; Ferretti, P.; Steinke, J.H.G.; Vilar, R. Coordination chemistry of amide-functionalised tetraazamacrocycles: Structural, relaxometric and cytotoxicity studies. Dalton Trans. 2010, 39, 10056–10067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helm, L.; Morrow, J.R.; Bond, C.J.; Carniato, F.; Botta, M.; Braun, M.; Baranyai, Z.; Pujales-Paradela, R.; Regueiro-Figueroa, M.; Esteban-Gómez, D.; et al. Contrast Agents for MRI: Experimental Methods; Pierre, V.C., Allen, M.J., Eds.; The Royal Society of Chemistry: London, UK, 2017; pp. 121–242. [Google Scholar]
- Solomon, I.; Bloembergen, N. Nuclear Magnetic Interactions in the HF Molecule. J. Chem. Phys. 1956, 25, 261–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloembergen, N.; Morgan, L.O. Proton relaxation times in paramagnetic solutions. Effects of electron spin relaxation. J. Chem. Phys. 1961, 34, 842–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freed, J.H. Dynamic effect of pair correlation functions on spin relaxation by translational diffusion in liquids. II. Finite jumps and independent t1 processes. J. Chem. Phys. 1978, 69, 4034–4037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swift, T.J.; Connick, R.E.J. NMR-relaxation mechanisms of 17O in aqueous solutions of paramagnetic cations and the lifetime of water molecules in the first coordination sphere. J. Chem. Phys. 1962, 37, 307–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terreno, E.; Delli Castelli, D.; Cravotto, G.; Milone, L.; Aime, S. Ln(III)-DOTAMGly complexes: A versatile series to assess the determinants of the efficacy of paramagnetic chemical exchange saturation transfer agents for magnetic resonance imaging applications. Investig. Radiol. 2004, 39, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woessner, D.E.; Zhang, S.; Merritt, M.E.; Sherry, A.D. Numerical solution of the Bloch equations provides insights into the optimum design of PARACEST agents for MRI. Magn. Reson. Med. 2005, 53, 790–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]







| Parameters | [GdL1]3+ | [GdL2]3+ | [GdL3]3+ | [GdDOTAM](CF3SO3)3 b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| r1 (mM−1 s−1) | 3.0 | 3.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| Δ2 (1019 s−2) | 2.0 | 1.0 | 3.9 | 1.7 |
| (ps) | 7.6 | 10.0 | 18.0 | 6.0 |
| (ps) | 120 | 120 | 120 | 80 |
| (µs) | 16.0 | 9.1 | 40.0 | 17.0 |
| ΔHM (kJ mol−1) | 50.7 | 37.4 | 62.0 | 49.0 |
| r (Å) a | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 3.1 |
| A/ħ (106 rad s−1) | −3.6 | −3.4 | −3.6 | - |
| qa | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| a (Å) a | 4.2 | 4.2 | 4.4 | 4.3 |
| D (10−5 cm2 s−1) a | 2.24 | 2.24 | 2.24 | 2.24 |
| ED (kJ mol−1) | −28 | −29 | −28 | −23 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lagostina, V.; Leone, L.; Carniato, F.; Digilio, G.; Tei, L.; Botta, M. Electronic Effects of the Substituents on Relaxometric and CEST Behaviour of Ln(III)-DOTA-Tetraanilides. Inorganics 2019, 7, 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics7040043
Lagostina V, Leone L, Carniato F, Digilio G, Tei L, Botta M. Electronic Effects of the Substituents on Relaxometric and CEST Behaviour of Ln(III)-DOTA-Tetraanilides. Inorganics. 2019; 7(4):43. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics7040043
Chicago/Turabian StyleLagostina, Valeria, Loredana Leone, Fabio Carniato, Giuseppe Digilio, Lorenzo Tei, and Mauro Botta. 2019. "Electronic Effects of the Substituents on Relaxometric and CEST Behaviour of Ln(III)-DOTA-Tetraanilides" Inorganics 7, no. 4: 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics7040043
APA StyleLagostina, V., Leone, L., Carniato, F., Digilio, G., Tei, L., & Botta, M. (2019). Electronic Effects of the Substituents on Relaxometric and CEST Behaviour of Ln(III)-DOTA-Tetraanilides. Inorganics, 7(4), 43. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics7040043