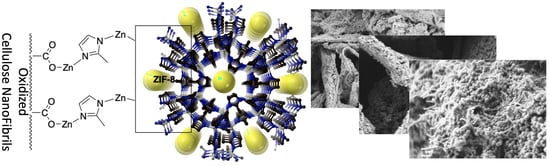
Hybrid Metal-Organic Framework-Cellulose Materials Retaining High Porosity: ZIF-8@Cellulose Nanofibrils
Abstract
:1. Introduction—Cellulose and Metal-Organic Frameworks, MOFs
2. Results and Discussion
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of TEMPO-Oxidized Cellulose Nanofibrils
3.2. Preparation of Free Standing CNF/ZIF-8 Materials
3.3. Characterization
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siró, I.; Plackett, D. Microfibrillated cellulose and new nanocomposite materials: A review. Cellulose 2010, 17, 459–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klemm, D.; Kramer, F.; Moritz, S.; Lindström, T.; Ankerfors, M.; Gray, D.; Dorris, A. Nanocelluloses: A New Family of Nature-Based Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 5438–5466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isogai, A. Wood nanocelluloses: Fundamentals and applications as new bio-based nanomaterials. J. Wood Sci. 2013, 59, 449–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraz, N.; Leschinskaya, A.; Toomadj, F.; Fellström, B.; Strømme, M.; Mihranyan, A. Membrane characterization and solute diffusion in porous composite nanocellulose membranes for hemodialysis. Cellulose 2013, 20, 2959–2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metreveli, G.; Wågberg, L.; Emmoth, E.; Belák, S.; Strømme, M.; Mihranyan, A. A Size—Exclusion Nanocellulose Filter Paper for Virus Removal. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2014, 3, 1546–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mautner, A.; Lee, K.-Y.; Tammelin, T.; Mathew, A.P.; Nedoma, A.J.; Li, K.; Bismarck, A. Cellulose nanopapers as tight aqueous ultra-filtration membranes. React. Funct. Polym. 2015, 86, 209–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, E.A.; Smart, L.E. Solid State Chemistry: An Introduction, 5th ed.; CRC Press, Inc.: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Öhrström, L.; Amombo Noa, F.M. Metal–Organic Frameworks; American Chemical Society: Washington, DC, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Yaghi, O.M.; Kalmutzki, M.J.; Diercks, C.S. Introduction to Reticular Chemistry—Metal-Organic Frameworks and Covalent Organic Frameworks; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Park, J.; Oh, M. Construction of flexible metal–organic framework (MOF) papers through MOF growth on filter paper and their selective dye capture. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 12850–12854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Hankari, S.; Bousmina, M.; El Kadib, A. Biopolymer@Metal-Organic Framework Hybrid Materials: A Critical Survey. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2019, 106, 100579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Sirous, F.; Hussain, C.M. Metal–organic frameworks/biopolymer nanocomposites: From fundamentals toward recent applications in modern technology. New J. Chem. 2021, 45, 8409–8426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccò, R.; Liang, W.; Li, S.; Gassensmith, J.J.; Caruso, F.; Doonan, C.; Falcaro, P. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Cell and Virus Biology: A Perspective. ACS Nano 2018, 12, 13–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, P.-L.; Xie, L.-H.; Joseph, E.A.; Li, J.-R.; Su, X.-O.; Zhou, H.-C. Metal–Organic Frameworks for Food Safety. Chem. Rev. 2019, 119, 10638–10690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kirlikovali, K.O.; Chen, Z.; Islamoglu, T.; Hupp, J.T.; Farha, O.K. Zirconium-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks for the Catalytic Hydrolysis of Organophosphorus Nerve Agents. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 14702–14720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Y.; Apostolopoulou-Kalkavoura, V.; da Costa, M.V.T.; Bergstrom, L.; Stromme, M.; Xu, C. Elastic Aerogels of Cellulose Nanofibers@Metal-Organic Frameworks for Thermal Insulation and Fire Retardancy. Nanomicro Lett. 2020, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zhou, S.Y.; Kong, X.Y.; Zheng, B.; Huo, F.W.; Stromme, M.; Xu, C. Cellulose Nanofiber @ Conductive Metal-Organic Frameworks for High-Performance Flexible Supercapacitors. Acs Nano 2019, 13, 9578–9586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Seo, J.Y.; Kim, H.; Beak, K.-Y. Structural control of cellulose nanofibrous composite membrane with metal organic framework (ZIF-8) for highly selective removal of cationic dye. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 222, 115018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seo, J.Y.; Song, Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Kim, H.; Cho, S.; Baek, K.-Y. Robust Nanocellulose/Metal–Organic Framework Aerogel Composites: Superior Performance for Static and Continuous Disposal of Chemical Warfare Agent Simulants. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 33516–33523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Q.; Chen, J.; Jin, B.; Chu, S.; Peng, R. Modification of ZIF-8 on bacterial cellulose for an efficient selective capture of U(VI). Cellulose 2021, 28, 5241–5256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Küsgens, P.; Siegle, S.; Kaskel, S. Crystal Growth of the Metal—Organic Framework Cu3(BTC)2 on the Surface of Pulp Fibers. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2009, 11, 93–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva Pinto, M.; Sierra-Avila, C.A.; Hinestroza, J.P. In situ synthesis of a Cu-BTC metal–organic framework (MOF 199) onto cellulosic fibrous substrates: Cotton. Cellulose 2012, 19, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, H.S.; Hinestroza, J.P.; Ochoa-Puentes, C.; Sierra, C.A.; Soto, C.Y. Antibacterial Activity Against Escherichia coli of Cu-BTC (MOF-199) Metal-Organic Framework Immobilized onto Cellulosic Fibers. J. Appl. Pol. Sci. 2014, 131, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, R.R.; Hinestroza, J.P. One-step growth of isoreticular luminescent metal–organic frameworks on cotton fibers. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 15198–15204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, J.-L.; Ar, D.; Yu, X.-J.; Liu, J.-X.; Terfort, A. Patterned Deposition of Metal-Organic Frameworks onto Plastic, Paper, and Textile Substrates by Inkjet Printing of a Precursor Solution. Adv. Mat. 2013, 25, 4631–4635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurila, E.; Thunberg, J.; Argent, S.P.; Champness, N.R.; Zacharias, S.; Westman, G.; Öhrström, L. Enhanced Synthesis of Metal-Organic Frameworks on the Surface of Electrospun Cellulose Nanofibers. Adv. Eng. Mat. 2015, 17, 1282–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zeng, G.; Zhao, L.; Lai, Z. Rapid synthesis of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanocrystals in an aqueous system. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 2071–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, S.; Kida, K.; Okita, M.; Ito, Y.; Miyake, Y. Size-controlled Synthesis of Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 (ZIF-8) Crystals in an Aqueous System at Room Temperature. Chem. Lett. 2012, 41, 1337–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kida, K.; Okita, M.; Fujita, K.; Tanaka, S.; Miyake, Y. Formation of high crystalline ZIF-8 in an aqueous solution. CrystEngComm 2013, 15, 1794–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.Y.; Stromme, M.; Xu, C. Highly Transparent, Flexible, and Mechanically Strong Nanopapers of Cellulose Nanofibers @Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Eur. J. 2019, 25, 3515–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, K.; Wang, R.; Boutter, M.; Doherty, C.M.; Mulet, X.; Richardson, J.J. Biomimetic mineralization of metal–organic frameworks around polysaccharides. Chem. Comm. 2017, 53, 1249–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raza, A.; Farrukh, S.; Hussain, A.; Khan, I.U.; Noor, T.; Othman, M.H.D.; Yousaf, M.F. Development of high performance amine functionalized zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8)/cellulose triacetate mixed matrix membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Int. J. Energy Res. 2020, 44, 7989–7999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, M.; Zhang, X.-F.; Feng, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Yao, J. In-situ growing ZIF-8 on cellulose nanofibers to form gas separation membrane for CO2 separation. J. Membr. Sci. 2020, 595, 117579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pimentel, B.R.; Parulkar, A.; Zhou, E.-k.; Brunelli, N.A.; Lively, R.P. Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks: Next-Generation Materials for Energy-Efficient Gas Separations. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 3202–3240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Liu, H.; Zheng, Y.; Wu, Y.; Gao, J. A Novel of PTA/ZIF-8@Cellulose Aerogel Composite Materials for Efficient Photocatalytic Degradation of Organic Dyes in Water. Z. Anorg. Allg. Chem. 2020, 646, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Zhang, M.; Nie, J.; Tan, J.; Song, S.; Luo, Y. Lightweight and porous cellulose-based foams with high loadings of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks-8 for adsorption applications. Carbohydr. Polym. 2019, 208, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bo, S.; Ren, W.; Lei, C.; Xie, Y.; Cai, Y.; Wang, S.; Gao, J.; Ni, Q.; Yao, J. Flexible and porous cellulose aerogels/zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-8) hybrids for adsorption removal of Cr(IV) from water. J. Solid State Chem. 2018, 262, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabipour, H.; Nie, S.; Wang, X.; Song, L.; Hu, Y. Highly flame retardant zeolitic imidazole framework-8@cellulose composite aerogels as absorption materials for organic pollutants. Cellulose 2020, 27, 2237–2251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Z.; Zhang, M.; Lu, Z.; Song, S.; Zhao, Y.; Hao, Y. Functionalization of cellulose fiber by in situ growth of zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (ZIF-8) nanocrystals for preparing a cellulose-based air filter with gas adsorption ability. Cellulose 2018, 25, 1997–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.J.; Tardy, B.L.; Guo, J.; Liang, K.; Rojas, O.J.; Ejima, H. Continuous Metal–Organic Framework Biomineralization on Cellulose Nanocrystals: Extrusion of Functional Composite Filaments. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 6287–6294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- These Results Were Briefly Discussed in a Recent Ph.D. Thesis: Thunberg, J. Chemical Modification of Electrospun Cellulose Nanofibers. Ph.D. Thesis, Chalmers Tekniska Högskola, Göteborg, Sweden, 2015.
- Morris, W.; Stevens, C.J.; Taylor, R.E.; Dybowski, C.; Yaghi, O.M.; Garcia-Garibay, M.A. NMR and X-ray Study Revealing the Rigidity of Zeolitic Imidazolate Frameworks. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 13307–13312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, K.S.; Ni, Z.; Côté, A.P.; Choi, J.Y.; Huang, R.; Uribe-Romo, F.J.; Chae, H.K.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Exceptional chemical and thermal stability of zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 10186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwanninger, M.; Rodrigues, J.C.; Pereira, H.; Hinterstoisser, B. Effects of short-time vibratory ball milling on the shape of FT-IR spectra of wood and cellulose. Vib. Spectrosc. 2004, 36, 23–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Hu, J.; Tang, Y.; Gu, H.; Jiang, M.; Zhang, J. In-situ preparation of hollow cellulose nanocrystals/zeolitic imidazolate framework hybrid microspheres derived from Pickering emulsion. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2020, 572, 160–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okita, Y.; Saito, T.; Isogai, A. Entire Surface Oxidation of Various Cellulose Microfibrils by TEMPO-Mediated Oxidation. Biomacromolecules 2010, 11, 1696–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| Material Sample | CNF a [g] | ZIF-8 Content b [wt%] | BET Surface Area [m2 g−1] |
|---|---|---|---|
| ZIF-CNF-3 | 3 | 79.7 | 1014 |
| ZIF-CNF-5 | 5 | 68.8 | 528 |
| CNF | - | - | 32 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Thunberg, J.; Zacharias, S.C.; Hasani, M.; Oyetunji, O.A.; Noa, F.M.A.; Westman, G.; Öhrström, L. Hybrid Metal-Organic Framework-Cellulose Materials Retaining High Porosity: ZIF-8@Cellulose Nanofibrils. Inorganics 2021, 9, 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9110084
Thunberg J, Zacharias SC, Hasani M, Oyetunji OA, Noa FMA, Westman G, Öhrström L. Hybrid Metal-Organic Framework-Cellulose Materials Retaining High Porosity: ZIF-8@Cellulose Nanofibrils. Inorganics. 2021; 9(11):84. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9110084
Chicago/Turabian StyleThunberg, Johannes, Savannah C. Zacharias, Merima Hasani, Olayinka. A. Oyetunji, Francoise M. Amombo Noa, Gunnar Westman, and Lars Öhrström. 2021. "Hybrid Metal-Organic Framework-Cellulose Materials Retaining High Porosity: ZIF-8@Cellulose Nanofibrils" Inorganics 9, no. 11: 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9110084
APA StyleThunberg, J., Zacharias, S. C., Hasani, M., Oyetunji, O. A., Noa, F. M. A., Westman, G., & Öhrström, L. (2021). Hybrid Metal-Organic Framework-Cellulose Materials Retaining High Porosity: ZIF-8@Cellulose Nanofibrils. Inorganics, 9(11), 84. https://doi.org/10.3390/inorganics9110084