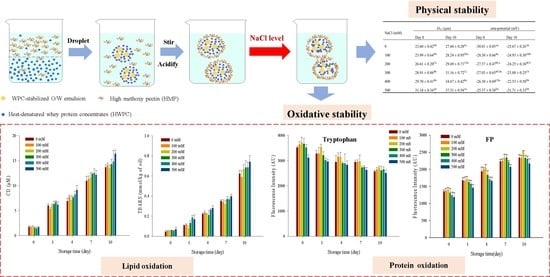
Effects of Sodium Chloride on the Physical and Oxidative Stability of Filled Hydrogel Particles Fabricated with Phase Separation Behavior
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Phase Separation
2.3. O/W Emulsion Formation
2.4. Filled Hydrogel Preparation
2.5. Measurements of Droplet Size, Size Distribution, and Zeta-Potential
2.6. Rheological Behavior
2.6.1. Steady Shear Tests
2.6.2. Frequency Sweep Tests
2.7. Interfacial Layer Thickness
2.8. Color Measurement
2.9. Cryo-Scanning Electron Microscopy (Cryo-SEM)
2.10. Lipid Oxidation Measurements
2.10.1. Conjugated Dienes (CD)
2.10.2. Thiobarbituric Acid-Reactive Substances (TBARS)
2.11. Protein Oxidation Measurements
2.12. Statistical Analyses
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Particle Size and Distribution
3.2. Zeta-Potential
3.3. Apparent Viscosity
3.4. The Viscoelastic Characteristics
3.5. Color Analysis
3.6. Interfacial Layer Thickness
3.7. Microscopic Morphology
3.8. Lipid Oxidation
3.9. Protein Oxidation
3.10. Correlation Analyses
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Berendsen, R.; Güell, C.; Ferrando, M. A procyanidin-rich extract encapsulated in water-in-oil-in-water emulsions produced by premix membrane emulsification. Food Hydrocolloid 2015, 43, 636–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonnet, M.; Cansell, M.; Berkaoui, A.; Ropers, M.H.; Anton, M.; Leal-Calderon, F. Release rate profiles of magnesium from multiple W/O/W emulsions. Food Hydrocolloid 2009, 23, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Emulsion design to improve the delivery of functional lipophilic components. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 1, 1241–1269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matalanis, A.; Lesmes, U.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Fabrication and characterization of filled hydrogel particles based on sequential segregative and aggregative biopolymer phase separation. Food Hydrocolloid 2010, 24, 689–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matalanis, A.; McClements, D.J. Hydrogel microspheres for encapsulation of lipophilic components: Optimization of fabrication and performance. Food Hydrocolloid 2013, 31, 15–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, G.P.; Malone, M.E.; Homan, J.E.; Norton, I.T. A mathematical model of volatile release in mouth from the dispersion of gelled emulsion particles. J. Control. Release 2004, 98, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Z.T.; Ai, M.M.; Zhou, Q.; Guo, S.G.; Zhou, L.D.; Fan, H.; Cao, Y.Y.; Jiang, A.M. Fabrication egg white gel hydrolysates-stabilized oil-in-water emulsion and characterization of its stability and digestibility. Food Hydrocolloid 2020, 102, 105621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, A.; Goh, K.K.T.; Singh, H. Properties of oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by β-lactoglobulin in simulated gastric fluid as influenced by ionic strength and presence of mucin. Food Hydrocolloid 2010, 24, 534–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Sarkar, A. Behaviour of protein-stabilised emulsions under various physiological conditions. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 165, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedi, E.; Majzoobi, M.; Farahnaky, A.; Pourmohammadi, K.; Mahmoudi, M.R. Effect of ionic strength (NaCl and CaCl2) on functional, textural and electrophoretic properties of native and acetylated gluten, gliadin and glutenin. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 2035–2047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hougaard, A.B.; Sijbrandij, A.G.; Varming, C.; Ardö, Y.; Ipsen, R. Emulsifying salt increase stability of cheese emulsions during holding. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 62, 362–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tcholakova, S.; Denkov, N.D.; Ivanov, I.B.; Campbell, B. Coalescence stability of emulsions containing globular milk proteins. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 123, 259–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, F.G.; Zhou, J.Z.; Niu, D.B.; Wang, C.Y.; Liu, Y.T.; Su, Y.J.; Yang, Y.J. Synergistic effects of ovalbumin/gum Arabic complexes on the stability of emulsions exposed to environmental stress. Food Hydrocolloid 2015, 47, 14–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.F.; Luo, L.P.; Liu, C.M.; McClements, D.J. Utilization of anionic polysaccharides to improve the stability of rice glutelin emulsions: Impact of polysaccharide type, pH, salt, and temperature. Food Hydrocolloid 2017, 64, 112–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, Y.; Tang, C.H. Characteristics and oxidative stability of soy protein-stabilized oil-in-water emulsions: Influence of ionic strength and heat pretreatment. Food Hydrocolloid 2014, 37, 149–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.A.; Zhao, S.C.; Chen, J.X.; Wang, H.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B.H. Physical properties and stability of filled hydrogel particles based on biopolymer phase separation: Influence of the ratio of protein to polysaccharide. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 142, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matalanis, A.; McClements, D.J. Influencing the formation and stability of filled hydrogel particles fabricated by protein/polysaccharide phase separation and enzymatic cross-linking. Food Biophys. 2012, 7, 72–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, B.T.; Day, L.; Augustin, M.A. Deamidated wheat protein-dextran Maillard conjugates: Effect of size and location of polysaccharide conjugated on steric stabilization of emulsions at acidic pH. Food Hydrocolloid 2011, 25, 1424–1432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.A.; Feng, Y.Y.; Kong, B.H.; Sun, F.D.; Yang, L.; Liu, Q. Transglutaminase crosslinking promotes physical and oxidative stability of filled hydrogel particles based on biopolymer phase separation. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 172, 429–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Niu, H.L.; Liu, H.T.; Liu, Q.; Kong, B.H. Effect of porcine plasma protein with limited hydrolyzation coupled with Tween 20 on the physical and oxidative stability of oil-in-water emulsions. Food Biophys. 2018, 13, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, K.X.; Shen, Y.L.; Niu, F.G.; Fu, Y.Y. Influence of pure gum on the physicochemical properties of whey protein isolate stabilized oil-in-water emulsions. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2016, 504, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzey, D.; McClements, D.J. Formation, stability and properties of multilayer emulsions for application in the food industry. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 128, 227–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harnsilawat, T.; Pongsawatmanit, R.; McClements, D.J. Stabilization of model beverage cloud emulsions using protein-polysaccharide electrostatic complexes formed at the oil-water interface. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 5540–5547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmyrzaev, A.A.; Schubert, H. Influence of KC1 on the physicochemical properties of whey protein stabilized emulsions. Food Hydrocolloid 2004, 18, 13–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulmyrzaev, A.; Chanamai, R.; McClements, D.J. Influence of pH and CaCl2 on the stability of dilute whey protein stabilized emulsions. Food Res. Int. 2000, 33, 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.C.; McClements, D.J. Functional hydrogel microspheres: Parameters affecting electrostatic assembly of biopolymer particles fabricated from gelatin and pectin. Food Res. Int. 2015, 72, 231–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, X.R.; Du, X.F.; Zhu, G.L.; Cao, C. Induction effect of NaCl on the formation and stability of emulsions stabilized by carboxymethyl starch/xanthan gum combinations. Food Hydrocolloid 2020, 105, 105776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castel, V.; Rubiolo, A.C.; Carrara, C.R. Droplet size distribution, rheological behavior and stability of corn oil emulsions stabilized by a novel hydrocolloid (Brea gum) compared with gum arabic. Food Hydrocolloid 2017, 63, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, M.H.; So, J.H.; Yang, S.M. Rheological evidence for the silica-mediated gelation of xanthan gum. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 216, 320–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shao, P.; Ma, H.L.; Zhu, J.Y.; Qiu, Q. Impact of ionic strength on physicochemical stability of o/w emulsions stabilized by Ulva fasciata polysaccharide. Food Hydrocolloid 2017, 69, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, K.; Khouryieh, H. Influence of electrostatic interactions on the formation and stability of multilayer fish oil-in-water emulsions stabilized by whey protein-xanthan-locust bean complexes. J. Food Eng. 2019, 277, 109893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hu, X.B.; Ye, Y.F.; Wang, M.M.; Wang, J.H. Emulsifying properties of wheat germ: Influence of pH and NaCl. Food Hydrocolloid 2020, 100, 105431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriprablom, J.; Luangpituksa, P.; Wongkongkatep, J.; Pongtharangkul, T.; Suphantharika, M. Influence of pH and ionic strength on the physical and rheological properties and stability of whey protein stabilized o/w emulsions containing xanthan gum. J. Food Eng. 2018, 242, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Z.Q.; Chen, Z.J.; Chang, M.C.; Meng, J.I.; Liu, J.Y.; Feng, C.P. Rheological properties and gel characteristics of polysaccharides from fruit-bodies of Sparassis crispa. Int. J. Food Prop. 2018, 21, 2283–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, J.H.; Xu, L.L.; Su, Y.J.; Chang, C.H.; Yang, Y.J. Flocculation behavior and gel properties of egg yolk/κ-carrageenan composite aqueous and emulsion systems: Effect of NaCl. Food Res. Int. 2002, 132, 108990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, F.F.; Pan, M.K.; Liu, Y.; Guo, N.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.H. Effects of Na+ on the cold gelation between a low-methoxyl pectin extracted from Premna microphylla turcz and soy protein isolate. Food Hydrocolloid 2020, 104, 105762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.; McClements, D.J. Controlling microstructure and physical properties of biopolymer hydrogel particles through modulation of electrostatic interactions. J. Food Eng. 2015, 158, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClements, D.J. Colloidal basis of emulsion color. Curr. Opin. Colloid Interface Sci. 2002, 7, 451–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taha, A.; Ahmed, E.; Hu, T.; Xu, X.Y.; Pan, S.Y.; Hu, H. Effects of different ionic strengths on the physicochemical properties of plant and animal proteins-stabilized emulsions fabricated using ultrasound emulsification. Ultrason. Sonochem. 2019, 58, 104627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.N.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.F. Salting-out and salting-in: Competitive effects of salt on the aggregation behavior of soy protein particles and their emulsifying properties. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 5926–5932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protonotariou, S.; Evageliou, V.; Yanniotis, S.; Mandala, I. The influence of different stabilizers and salt addition on the stability of model emulsions containing olive or sesame oil. J. Food Eng. 2013, 117, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, W.; Meeren, P.V.; Wijaya, C.H.; Patel, A.R. High internal phase emulsions stabilized solely by whey protein isolate and low methoxyl pectin complexes: Effect of pH and polymer concentration. Food Funct. 2016, 8, 584–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.; Degner, B.; Decker, E.A.; McClements, D.J. Oil-filled hydrogel particles for reduced-fat food applications: Fabrication, characterization, and properties. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2013, 20, 324–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osinchak, J.E.; Hultin, H.O.; Zajicek, O.T.; Kelleher, S.D.; Huang, C. Effect of NaCl on catalysis of lipid oxidation by the soluble fraction of fish muscle. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1992, 12, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Zheng, F.; Song, X.Y.; Ren, H.T.; Gong, H. Influence of formulation parameters on lipid oxidative stability of Pickering emulsion stabilized by hydrophobically modified starch particles. Carbohydr. Polym. 2020, 246, 116649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.Z.; Zhou, F.B.; Sun, D.W.; Zhao, M.M. Effect of oxidation on the emulsifying properties of myofibrillar proteins. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2013, 6, 1703–1712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xue, C.Y.; Quan, W.; Qin, F.; Wang, Z.J.; He, Z.Y.; Zeng, M.M.; Chen, J. Assessment the influence of salt and polyphosphate on protein oxidation and Nε-(carboxymethyl)lysine and Nε-(carboxyethyl)lysine formation in roasted beef patties. Meat Sci. 2021, 177, 108489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estéveza, M.; Kyllia, P.; Puolanneb, E.; Kivikaria, R.; Heinonena, M. Fluorescence spectroscopy as a novel approach for the assessment of myofibrillar protein oxidation in oil-in-water emulsions. Meat Sci. 2008, 80, 1290–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kagan, V.E. Lipid Peroxidation in Biomembranes; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Sodium Chloride (NaCl, mM) | The Volume Averaged Diameter (D4,3, μm) | The Surface-Averaged Diameter (D3,2, μm) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Day 0 | Day 10 | Day 0 | Day 10 | |
| 0 | 23.60 ± 0.42 D,b | 26.60 ± 0.28 E,a | 4.82 ± 0.06 D,b | 8.19 ± 0.06 F,a |
| 100 | 23.99 ± 0.64 D,b | 28.24 ± 0.95 D,a | 4.89 ± 0.07 D,b | 8.87 ± 0.11 E,a |
| 200 | 26.61 ± 0.20 C,b | 29.69 ± 0.71 C,D,a | 5.28 ± 0.10 C,b | 9.17 ± 0.14 D,a |
| 300 | 28.91 ± 0.86 B,b | 31.16 ± 0.72 C,a | 5.956 ± 0.06 B,b | 9.84 ± 0.06 C,a |
| 400 | 29.70 ± 0.41 B,b | 34.67 ± 0.42 B,a | 6.17 ± 0.09 A,b | 10.23 ± 0.11 B,a |
| 500 | 31.18 ± 0.34 A,b | 37.51 ± 0.54 A,a | 6.38 ± 0.11 A,b | 11.37 ± 0.10 A,a |
| NaCl (mM) | Zero-Shear Viscosity (η0) | Time Constant (λ) | Dimensionless Exponent (m) | Correlation Coefficient (R2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 0.4939 ± 0.0011 D | 0.0758 ± 0.0012 D | 0.7427 ± 0.0021 B | 0.9888 |
| 100 | 0.5367 ± 0.0037 C | 0.0957 ± 0.0002 B | 0.7069 ± 0.0018 D | 0.9713 |
| 200 | 0.6418 ± 0.0012A | 0.1040 ± 0.0017 A | 0.7056 ± 0.0022 D | 0.9993 |
| 300 | 0.5673 ± 0.0151 B | 0.1010 ± 0.0015 A | 0.6898 ± 0.0041 E | 0.9834 |
| 400 | 0.5290 ± 0.0110 C | 0.0897 ± 0.0021 C | 0.7334 ± 0.0029 C | 0.9786 |
| 500 | 0.4653 ± 0.0102 E | 0.0785 ± 0.0009 D | 0.7673 ± 0.0011 A | 0.9737 |
| NaCl (mM) | log G′ = log a′ + b′ log f | log G″ = log a″ + b″ log f | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model Parameters (a′) | Dimensionless Frequency Indices (b′) | R2 | Model Parameters (a″) | Dimensionless Frequency Indices (b″) | R2 | |
| 0 | 0.0746 ± 0.0039 D | 1.2236 ± 0.0026 A | 0.9937 | 0.3170 ± 0.0211 B | 0.6827 ± 0.0022 A | 0.9764 |
| 100 | 0.0769 ± 0.0011 D | 1.2103 ± 0.0031 B | 0.9925 | 0.3290 ± 0.0165 B | 0.6798 ± 0.0042 A | 0.9792 |
| 200 | 0.1448 ± 0.0058 A | 1.1673 ± 0.0023 D | 0.9979 | 0.4126 ± 0.0219 A | 0.6438 ± 0.0026 C | 0.9777 |
| 300 | 0.1176 ± 0.0037 B | 1.1878 ± 0.0018 C | 0.9975 | 0.3497 ± 0.0179 B | 0.6609 ± 0.0031 B | 0.9789 |
| 400 | 0.0890 ± 0.0033 C | 1.1897 ± 0.0009 C | 0.9971 | 0.3266 ± 0.0204 B | 0.6695 ± 0.0024 B | 0.9798 |
| 500 | 0.0795 ± 0.0038 C,D | 1.1861 ± 0.0012 C | 0.9961 | 0.3364 ± 0.0192 B | 0.6640 ± 0.0039 B | 0.9748 |
| NaCl (mM) | L* Value | a* Value | b* Value | Whiteness |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 59.86 ± 0.48 A | −2.00 ± 0.05 A | −2.75 ± 0.29 A | 59.82 ± 0.12 A |
| 100 | 58.86 ± 0.70 A,B | −2.27 ± 0.60 A | −2.54 ± 0.29 A | 58.72 ± 0.13 B |
| 200 | 57.53 ± 0.61 B,C | −2.18 ± 0.40 A | −2.75 ± 0.20 A | 57.39 ± 0.21 C |
| 300 | 57.31 ± 0.50 C,D | −2.32 ± 0.17 A | −1.89 ± 0.10 B | 57.22 ± 0.14 C |
| 400 | 56.56 ± 0.27 C,D | −1.98 ± 0.12 A | −2.56 ± 0.08 A | 56.44 ± 0.27 D |
| 500 | 56.08 ± 0.27 D | −2.04 ± 0.05 A | −2.89 ± 0.06 A | 55.94 ± 0.32 D |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cao, C.; Li, X.; Yin, Y.; Kong, B.; Sun, F.; Liu, Q. Effects of Sodium Chloride on the Physical and Oxidative Stability of Filled Hydrogel Particles Fabricated with Phase Separation Behavior. Foods 2021, 10, 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051027
Cao C, Li X, Yin Y, Kong B, Sun F, Liu Q. Effects of Sodium Chloride on the Physical and Oxidative Stability of Filled Hydrogel Particles Fabricated with Phase Separation Behavior. Foods. 2021; 10(5):1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051027
Chicago/Turabian StyleCao, Chuanai, Xin Li, Yongchao Yin, Baohua Kong, Fangda Sun, and Qian Liu. 2021. "Effects of Sodium Chloride on the Physical and Oxidative Stability of Filled Hydrogel Particles Fabricated with Phase Separation Behavior" Foods 10, no. 5: 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051027
APA StyleCao, C., Li, X., Yin, Y., Kong, B., Sun, F., & Liu, Q. (2021). Effects of Sodium Chloride on the Physical and Oxidative Stability of Filled Hydrogel Particles Fabricated with Phase Separation Behavior. Foods, 10(5), 1027. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods10051027