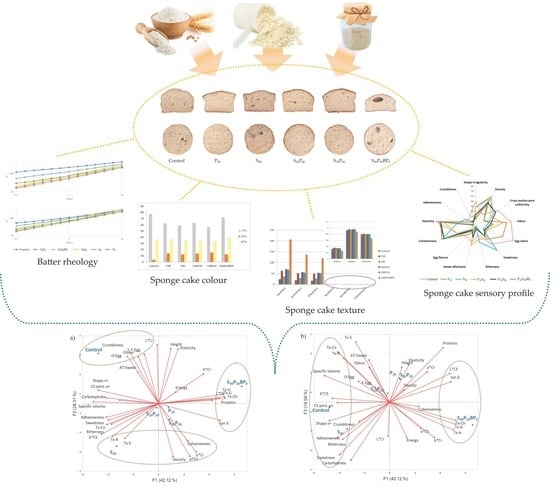
Effect of Sourdough and Whey Protein Addition on the Technological and Nutritive Characteristics of Sponge Cake
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Sponge Cake
2.3. Batter Rheology
2.4. Chemical Composition of Sponge Cake
2.5. Volume Analysis of Sponge Cake
2.6. Colour Measurement of Sponge Cake
2.7. Textural Analysis of Sponge Cake
2.8. Sensory Analysis of Sponge Cake
2.9. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Batter Properties Evaluation
Rheological Behaviour
3.2. Baked Sponge Cake
3.2.1. Chemical Composition
3.2.2. Physical Properties
3.2.3. Colour
3.2.4. Texture
3.2.5. Sensory Evaluation
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pycarelle, S.C.; Winnen, K.L.J.; Bosmans, G.M.; Van Haesendonck, I.; Pareyt, B.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Wheat (Triticum Aestivum L.) Flour Free Lipid Fractions Negatively Impact the Quality of Sponge Cake. Food Chem. 2019, 271, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilderjans, E.; Luyts, A.; Brijs, K.; Delcour, J.A. Ingredient Functionality in Batter Type Cake Making. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 30, 6–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beikzadeh, S.; Peighardoust, S.H.; Beikzadeh, M.; Asghari Javar-Abadi, M.; Homayouni-Rad, A. Effect of Psyllium Husk on Physical, Nutritional, Sensory and Staling Properties of Dietary Prebiotic Sponge Cake. Czech J. Food Sci. 2016, 34, 534–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhou, J.; Yan, B.; Wu, Y.; Zhu, H.; Lian, H.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W.; Fan, D. Effects of Sourdough Addition on the Textural and Physiochemical Attributes of Microwaved Steamed-Cake. LWT 2021, 146, 111396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, Y.; Wang, F.; Huang, W.; Tang, X.; Zou, Q.; Li, Z.; Ogawa, A. Sucrose Substitution by Polyols in Sponge Cake and Their Effects on the Foaming and Thermal Properties of Egg Protein. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 57, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Struck, S.; Gundel, L.; Zahn, S.; Rohm, H. Fiber Enriched Reduced Sugar Muffins Made from Iso-Viscous Batters. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 65, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaboos, H.; Ardabili, S.; Kashaninejad, M. Physico-Chemical, Textural and Sensory Evaluation of Sponge Cake Supplemented with Pumpkin Flour. Int. Food Res. J. 2016, 25, 854–860. [Google Scholar]
- Jyotsna, R.; Sai Manohar, R.; Indrani, D.; Venkateswara Rao, G. Effect of Whey Protein Concentrate on the Rheological and Baking Properties of Eggless Cake. Int. J. Food Prop. 2007, 10, 599–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assad Bustillos, M.; Jonchère, C.; Garnier, C.; Réguerre, A.L.; Della Valle, G. Rheological and Microstructural Characterization of Batters and Sponge Cakes Fortified with Pea Proteins. Food Hydrocoll. 2020, 101, 105553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majzoobi, M.; Ghiasi, F.; Habibi, M.; Hedayati, S.; Farahnaky, A. Influence of Soy Protein Isolate on the Quality of Batter and Sponge Cake. J. Food Processing Preserv. 2014, 38, 1164–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coşkun, Ö.; Pehlivanoğlu, H.; Gülseren, İ. Pilot Scale Assessment for Seed Protein Enrichment of Gluten-free Breads at Varying Water Content Levels and after Protein Modification Treatments. J. Food Processing Preserv. 2020, 44, e14512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Storck, C.R.; da Rosa Zavareze, E.; Gularte, M.A.; Elias, M.C.; Rosell, C.M.; Guerra Dias, A.R. Protein Enrichment and Its Effects on Gluten-Free Bread Characteristics. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 53, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikanlaya, C.; Therdthai, N.; Ritthiruangdej, P.; Zhou, W. Effect of Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose, Whey Protein Concentrate and Soy Protein Isolate Enrichment on Characteristics of Gluten-Free Rice Dough and Bread. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 1760–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Ramírez, M.; Calderón-Domínguez, G.; García-Garibay, M.; Jiménez-Guzmán, J.; Villanueva-Carvajal, A.; de la Paz Salgado-Cruz, M.; Arizmendi-Cotero, D.; Del Moral-Ramírez, E. Effect of Whey Protein Isolate Addition on Physical, Structural and Sensory Properties of Sponge Cake. Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 61, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ammar, I.; Gharsallah, H.; Brahim, A.B.; Attia, H.; Ayadi, M.A.; Hadrich, B.; Felfoul, I. Optimization of Gluten-free Sponge Cake Fortified with Whey Protein Concentrate Using Mixture Design Methodology. Food Chem. 2021, 343, 128457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katina, K.; Arendt, E.; Liukkonen, K.-H.; Autio, K.; Flander, L.; Poutanen, K. Potential of Sourdough for Healthier Cereal Products. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2005, 16, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gänzle, M.G.; Vermeulen, N.; Vogel, R.F. Carbohydrate, Peptide and Lipid Metabolism of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Sourdough. Food Microbiol. 2007, 24, 128–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiele, C.; Gänzle, M.G.; Vogel, R.F. Contribution of Sourdough Lactobacilli, Yeast, and Cereal Enzymes to the Generation of Amino Acids in Dough Relevant for Bread Flavor. Cereal Chem. J. 2002, 79, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadiq, F.A.; Yan, B.; Tian, F.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, W. Lactic Acid Bacteria as Antifungal and Anti-Mycotoxigenic Agents: A Comprehensive Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2019, 18, 1403–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Arora, K.; Ameur, H.; Polo, A.; Di Cagno, R.; Rizzello, C.G.; Gobbetti, M. Thirty Years of Knowledge on Sourdough Fermentation: A Systematic Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 108, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, R.S.; Chavan, S.R. Sourdough Technology-A Traditional Way for Wholesome Foods: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 169–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Peláez, J.; Paesani, C.; Gómez, M. Sourdough Technology as a Tool for the Development of Healthier Grain-Based Products: An Update. Agronomy 2020, 10, 1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cagno, R.; De Angelis, M.; Alfonsi, G.; De Vincenzi, M.; Silano, M.; Vincentini, O.; Gobbetti, M. Pasta Made from Durum Wheat Semolina Fermented with Selected Lactobacilli as a Tool for a Potential Decrease of the Gluten Intolerance. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 4393–4402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahin, A.W.; Rice, T.; Zannini, E.; Axel, C.; Coffey, A.; Lynch, K.M.; Arendt, E.K. Leuconostoc citreum TR116: In-Situ Production of Mannitol in Sourdough and Its Application to Reduce Sugar in Burger Buns. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 302, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castañón, X.; Argaiz, A.; López-Malo, A. Effect of Storage Temperature on the Microbial and Color Stability of Banana Purée with Addition of Vanillin or Potassium Sorbate. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 1999, 5, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, C.I.; Schober, T.J.; Dockery, P.; O’Sullivan, K.; Arendt, E.K. Wheat Sourdough Fermentation: Effects of Time and Acidification on Fundamental Rheological Properties. Cereal Chem. J. 2004, 81, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krstonošić, V.S.; Kalić, M.D.; Dapčević-Hadnađev, T.R.; Lončarević, I.S.; Hadnađev, M.S. Physico-Chemical Characterization of Protein Stabilized Oil-in-Water Emulsions. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2020, 602, 125045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, M.P.; de Oliveira Moreira, R.; Rodrigues, P.H., Jr.; de Freitas Martins, M.C.; Perrone, Í.T.; de Carvalho, A.F. Whey: Technologies for Co-Products Production. Rev. Inst. Laticínios Cândido Tostes 2014, 69, 212–226. [Google Scholar]
- Camargo, L.R.; Silva, L.M.; Komeroski, M.R.; Kist, T.B.L.; Rodrigues, C.E.; de O. Rios, A.; Silva, M.M.; Doneda, D.; de O. Schmidt, H.; Oliveira, V.R. Effect of Whey Protein Addition on the Nutritional, Technological and Sensory Quality of Banana Cake. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018, 53, 2617–2623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alp, H.; Bilgiçli, N. Effect of Transglutaminase on Some Properties of Cake Enriched with Various Protein Sources. J. Food Sci. 2008, 73, S209–S214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Rosa Zavareze, E.; Moraes, K.S.; de Las Mercedes Salas-Mellado, M. Technological and Sensory Quality of Cakes Produced with Milk Whey. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 30, 100–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ramya, H.N.; Anitha, S. Nutritional and Sensory Evaluation of Mango Pulp and Milk Powder Incorporated Sponge Cake. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. Appl. Sci. 2020, 9, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, M.A.; Burrington, K.J.; Hartel, R.W. Whey Protein Phospholipid Concentrate and Delactosed Permeate: Applications in Caramel, Ice Cream, and Cake. J. Dairy Sci. 2016, 99, 6948–6960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sahi, S.S.; Alava, J.M. Functionality of Emulsifiers in Sponge Cake Production. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2003, 83, 1419–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boland, M. Whey Proteins. In Handbook of Food Proteins; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011; pp. 30–55. [Google Scholar]
- Diez-Sánchez, E.; Llorca, E.; Tárrega, A.; Fiszman, S.; Hernando, I. Changing Chemical Leavening to Improve the Structural, Textural and Sensory Properties of Functional Cakes with Blackcurrant Pomace. LWT 2020, 127, 109378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahagún, M.; Bravo-Núñez, Á.; Báscones, G.; Gómez, M. Influence of Protein Source on the Characteristics of Gluten-Free Layer Cakes. LWT 2018, 94, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez, S.; Matta, E.; Osella, C.; de la Torre, M.; Sánchez, H.D. Effect of Soy Flour and Whey Protein Concentrate on Cookie Color. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gänzle, M.G. Enzymatic and Bacterial Conversions during Sourdough Fermentation. Food Microbiol. 2014, 37, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witczak, T.; Juszczak, L.; Ziobro, R.; Korus, J. Rheology of Gluten-Free Dough and Physical Characteristics of Bread with Potato Protein. J. Food Processing Eng. 2017, 40, e12491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germain, J.C.; Aguilera, J.M. Structural Image Analysis of Food Foams and Aerated Food Products. In Bubbles in Food 2; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2008; pp. 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Fiszman, S.M.; Sanz, T.; Salvador, A. Instrumental Assessment of the Sensory Quality of Baked Goods. In Instrumental Assessment of Food Sensory Quality; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2013; pp. 374–402. [Google Scholar]
- Sahin, A.W.; Zannini, E.; Coffey, A.; Arendt, E.K. Sugar Reduction in Bakery Products: Current Strategies and Sourdough Technology as a Potential Novel Approach. Food Res. Int. 2019, 126, 108583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Ingredients (g) | Control | P20 | S30 | S20P20 | S30P20 | S30P20BP0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wheat flour | 100 | 80 | 85 | 70 | 65 | 65 |
| Whey protein (P) | - | 20 | - | 20 | 20 | 20 |
| Sourdough (S) | - | - | 30 | 20 | 30 | 30 |
| Sucrose | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 | 85 |
| Egg albumen | 52.5 | 52.5 | 52.5 | 52.5 | 52.5 | 52.5 |
| Egg yolk | 32.5 | 32.5 | 32.5 | 32.5 | 32.5 | 32.5 |
| Water | 35 | 35 | 20 | 25 | 20 | 20 |
| Baking powder (BP) | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | 3.5 | - |
| Sensory Attribute | Definitions |
|---|---|
| Shape irregularity | Degree to which the shape of the sample deviates from the defined one. (Low–Enormous) |
| Denseness | The number of air holes incorporated in the crumb. (Airy–Densely) |
| Cross-section pore uniformity | Shape and size homogeneity of the holes in the crumb. (Uniform–Uneven) |
| Overall odour intensity | Intensity of overall odour of the sample perceived by direct sniffing of the sample. (Low–Intense) |
| Egg odour | The intensity of odour typical of scrambled egg perceived by direct sniffing of the sample. (Low–Intense) |
| Sweetness | Perception of characteristic taste of sugar. (Low–Intense) |
| Bitterness | Perception of characteristic taste of coffee. (Low–Intense) |
| Sweet aftertaste | Degree of sweet taste intensity perceived after chewing the sample. (Low–Intense) |
| Egg flavour | The intensity of odour typical of scrambled egg perceived during chewing of the sample. (Low–Intense) |
| Cohesiveness in mass | Degree to which the chewed sample holds together. (Loose–Compact) |
| Elasticity | Ability of the product to return to the starting position after tactile compression. (Plastic–Elastic) |
| Adhesiveness | Degree to which the product sticks to the palate after compression between the tongue and the palate. (Low–Intense) |
| Crumbliness | Degree to which sample disintegrates or breaks down after compression. (Low–Intense) |
| Control | P20 | S30 | S20P20 | S30P20 | S30P20BP0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moisture | 23.37 ± 0.06 d | 24.35 ± 0.04 b | 23.63 ± 0.07 c | 23.38 ± 0.01 d | 24.72 ± 0.02 a | 22.11 ± 0.05 e |
| Proteins | 9.14 ± 0.02 e | 14.79 ± 0.06 a | 7.94 ± 0.03 f | 13.45 ± 0.07 d | 13.74 ± 0.11 c | 14.19 ± 0.02 b |
| Fat | 3.86 ± 0.09 b | 2.91 ± 0.04 d | 3.88 ± 0.08 ab | 3.53 ± 0.01 c | 3.95 ± 0.08 ab | 4.05 ± 0.07 a |
| Ash | 1.28 ± 0.01 c | 1.35 ± 0.01 b | 1.28 ± 0.00 c | 1.18 ± 0.00 d | 1.44 ± 0.00 a | 0.70 ± 0.00 e |
| Carbohydrates | 59.84 ± 0.04 b | 54.58 ± 0.13 e | 59.64 ± 0.04 a | 55.49 ± 0.07 d | 53.02 ± 0.21 e | 55.80 ± 0.13 c |
| Total fibre | 2.51 ± 0.07 c | 2.02 ± 0.04 d | 3.63 ± 0.09 a | 2.77 ± 0.05 c | 3.13 ± 0.04 b | 3.15 ± 0.06 b |
| Energy (kcal) | 315.7 | 307.7 | 312.5 | 313.1 | 308.8 | 322.7 |
| Control | P20 | S30 | S20P20 | S30P20 | S30P20BP0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mass (g) | 24.47 ± 0.61 c | 26.58 ± 0.15 a | 25.39 ± 0.31 b | 25.71 ± 0.17 b | 26.61 ± 0.30 a | 25.64 ± 0.09 b |
| Height (mm) | 42.66 ± 1.55 a | 38.11 ± 0.62 c | 39.95 ± 2.51 c | 40.01 ± 2.55 b | 39.53 ± 0.59 bc | 31.52 ± 0.96 d |
| Specific volume (mL/g) | 3.16 ± 0.02 a | 2.68 ± 0.03 c | 2.86 ± 0.08 b | 2.80 ± 0.03 bc | 2.80 ± 0.02 bc | 1.96 ± 0.09 d |
| Colour—crust | ||||||
| L* | 77.59 ± 1.78 a | 62.62 ± 3.52 c | 59.25 ± 6.66 d | 63.22 ± 5.13 c | 56.72 ± 3.04 d | 71.99 ± 2.53 b |
| a* | 3.67 ± 1.57 d | 13.96 ± 1.23 b | 12.49 ± 2.91 c | 13.53 ± 1.60 bc | 15.31 ± 0.90 a | 12.52 ± 2.25 c |
| b* | 36.22 ± 1.19 c | 37.07 ± 0.96 b | 34.98 ± 1.11 d | 34.91 ± 1.98 d | 34.08 ± 1.05 d | 39.87 ± 0.98 a |
| BI | 63.57 | 100.6 | 99.36 | 91.90 | 105.84 | 89.24 |
| Colour—cross-section | ||||||
| L* | 77.42 ± 1.31 d | 83.32 ± 0.68 b | 76.90 ± 0.81 d | 83.23 ± 1.12 b | 81.15 ± 0.80 c | 84.96 ± 0.70 a |
| a* | −1.82 ± 0.18 d | −0.68 ± 0.24 c | 0.34 ± 0.22 a | −0.65 ± 0.14 c | −0.14 ± 0.20 b | −0.01 ± 0.17 b |
| b* | 25.33 ± 1.10 b | 25.23 ± 0.81 b | 28.49 ± 0.80 a | 23.49 ± 0.77 c | 24.92 ± 0.77 b | 19.87 ± 0.37 d |
| Control | P20 | S30 | S20P20 | S30P20 | S30P20BP0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hardness | 23.71 ± 1.14 d | 62.86 ± 6.01 b | 36.67 ± 2.67 c | 69.83 ± 9.52 b | 67.33 ± 5.87 b | 206.18 ± 4.91 a |
| Springiness | 0.92 ± 0.01 b | 0.96 ± 0.01 a | 0.95 ± 0.01 a | 0.96 ± 0.02 a | 0.96 ± 0.01 a | 0.88 ± 0.00 c |
| Cohesiveness | 0.79 ± 0.01 c | 0.81 ± 0.01 a | 0.80 ± 0.00 ab | 0.80 ± 0.01 ab | 0.80 ± 0.00 bc | 0.66 ± 0.00 d |
| Gumminess | 18.68 ± 0.99 d | 50.79 ± 4.54 b | 29.28 ± 2.08 c | 55.96 ± 7.80 b | 53.67 ± 4.46 b | 136.89 ± 2.38 a |
| Chewiness | 17.20 ± 1.11 d | 48.80 ± 4.55 b | 27.78 ± 2.19 c | 53.39 ± 6.17 b | 51.49 ± 3.62 b | 119.76 ± 2.40 a |
| Resilience | 0.32 ± 0.02 b | 0.36 ± 0.01 a | 0.36 ± 0.01 a | 0.34 ± 0.02 ab | 0.34 ± 0.00 ab | 0.26 ± 0.00 c |
| Control | P20 | S30 | S20P20 | S30P20 | S30P20BP0 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Appearance | ||||||
| Shape irregularity | 48.5 ± 0.7 a | 18.5 ± 4.9 c | 38.0 ± 7.1 ab | 38.5 ± 14.8 ab | 23.5 ± 3.5 bc | 14.5 ± 6.3 c |
| Density | 27.0 ± 4.2 d | 59.0 ± 1.4 abc | 63.5 ± 7.8 ab | 68.0 ± 5.7 a | 52.5 ± 6.4 bc | 48.5 ± 0.7 c |
| Cross-section pore uniformity | 54.5 ± 0.7 a | 19.5 ± 13.4 b | 43.0 ± 10.6 a | 36.0 ± 9.9 ab | 48.5 ± 10.6 a | 19.5 ± 4.9 b |
| Odour | ||||||
| Odour intensity | 71.0 ± 9.9 a | 62.5 ± 3.5 a | 23.0 ± 11.3 c | 54.0 ± 11.3 ab | 29.5 ± 0.7 c | 35.5 ± 13.4 bc |
| Egg odour | 80.0 ± 5.7 a | 57.5 ± 3.5 a | 16.0 ± 7.1 b | 23.0 ± 9.9 b | 19.0 ± 2.8 b | 21.0 ± 2.2 b |
| Taste | ||||||
| Sweetness | 47.5 ± 0.7 ab | 34.5 ± 7.8 bc | 64.0 ± 12.7 a | 33.5 ± 2.1 bc | 26.5 ± 9.2 c | 28.5 ± 10.6 bc |
| Bitterness | 17.5 ± 2.1 a | 0.0 ± 0.0 c | 33.0 ± 5.7 a | 26.5 ± 14.8 a | 4.5 ± 0.0 b | 0.0 ± 0.0 c |
| Sweet aftertaste | 33.0 ± 11.3 a | 11.0 ± 1.41 bc | 0.0 ± 0.0 c | 39.0 ± 12.7 a | 22.5 ± 10.6 ab | 6.5 ± 4.9 bc |
| Flavour | ||||||
| Egg flavour | 27.0 ± 5.7 a | 21.5 ± 12.0 ab | 7.0 ± 4.2 b | 6.0 ± 0.7 b | 10.5 ± 3.5 ab | 14.0 ± 4.2 ab |
| Texture | ||||||
| Cohesiveness | 39.5 ± 0.7 b | 72.5 ± 3.5 a | 71.0 ± 1.4 a | 39.5 ± 10.6 b | 67.5 ± 6.7 a | 68.0 ± 0.0 a |
| Elasticity | 80.0 ± 5.7 a | 70.0 ± 5.7 ab | 38.5 ± 0.7 c | 63.5 ± 9.2 b | 70.0 ± 8.5 ab | 73.5 ± 3.5 ab |
| Adhesiveness | 17.5 ± 0.7 b | 13.5 ± 4.9 b | 24.5 ± 4.8 a | 6.0 ± 2.2 c | 6.0 ± 0.0 c | 4.5 ± 0.7 c |
| Crumbliness | 25.0 ± 4.2 a | 9.0 ± 1.4 b | 9.5 ± 6.4 b | 10.0 ± 0.0 b | 10.0 ± 2.8 b | 12.5 ± 10.6 ab |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maravić, N.; Škrobot, D.; Dapčević-Hadnađev, T.; Pajin, B.; Tomić, J.; Hadnađev, M. Effect of Sourdough and Whey Protein Addition on the Technological and Nutritive Characteristics of Sponge Cake. Foods 2022, 11, 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11141992
Maravić N, Škrobot D, Dapčević-Hadnađev T, Pajin B, Tomić J, Hadnađev M. Effect of Sourdough and Whey Protein Addition on the Technological and Nutritive Characteristics of Sponge Cake. Foods. 2022; 11(14):1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11141992
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaravić, Nikola, Dubravka Škrobot, Tamara Dapčević-Hadnađev, Biljana Pajin, Jelena Tomić, and Miroslav Hadnađev. 2022. "Effect of Sourdough and Whey Protein Addition on the Technological and Nutritive Characteristics of Sponge Cake" Foods 11, no. 14: 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11141992
APA StyleMaravić, N., Škrobot, D., Dapčević-Hadnađev, T., Pajin, B., Tomić, J., & Hadnađev, M. (2022). Effect of Sourdough and Whey Protein Addition on the Technological and Nutritive Characteristics of Sponge Cake. Foods, 11(14), 1992. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods11141992