The Effect of Guisangyou Tea on Abnormal Lipid Metabolism in Mice Induced by High-Fat Diet
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Guisangyou Tea
2.3. Experimental and Animals
2.4. Preparation of Water Extract (WE) of GSY Tea
2.5. Animal Grouping and Intervention with GSY Tea Water Extract (WE)
2.6. Sample Collection
2.7. Determination of Serum and Liver Tissue Biochemical Indicators
2.8. Slice Analysis of Liver and Adipose Tissue
2.9. Determination of Expression Levels of Key Genes Related to Lipid and Bile Acid Regulation in the Liver
2.10. Western Blot Analysis for Determination of Protein Levels in Liver Tissue
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Effect of GSY Tea on Body Weight, Fat, and Visceral Index in Mice
3.2. Effect of GSY Tea on Serum and Liver Biochemical Indicators in HFD Mice
3.3. Effect of GSY Tea on Morphology of Hepatocyte and Epididymal Adipose Tissue
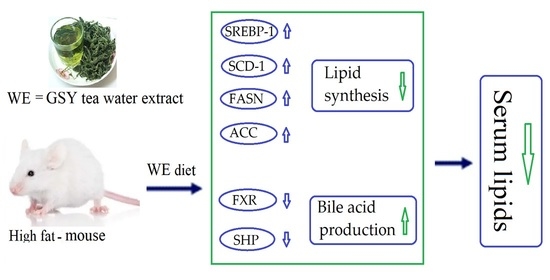
3.4. Effect of GSY Tea on mRNA and Protein Related to Lipid and Bile Acid
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.; Zhao, L.; Gao, L.; Pan, A.; Xue, H. Health policy and public health implications of obesity in China. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 446–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayoral, L.P.; Andrade, G.M.; Mayoral, E.P.; Huerta, T.H.; Canseco, S.P.; Rodal Canales, F.J.; Cabrera-Fuentes, H.A.; Cruz, M.M.; Pérez Santiago, A.D.; Alpuche, J.J.; et al. Obesity subtypes, related biomarkers heterogeneity. Indian J. Med. Res. 2020, 151, 11–21. [Google Scholar]
- Luca, A.C.; Curpan, A.S.; Braha, E.E.; Ţarcă, E.; Iordache, A.C.; Luca, F.A.; Adumitrachioaiei, H. Increasing trends in obesity-related cardiovascular risk factors in Romanian children and adolescents-retrospective study. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Endalifer, M.L.; Diress, G. Epidemiology, predisposing factors, biomarkers, and prevention mechanism of obesity: A systematic review. J. Obesity 2020, 2020, 6134362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malesza, I.J.; Malesza, M.; Walkowiak, J.; Mussin, N.; Walkowiak, D.; Aringazina, R.; Bartkowiak-Wieczorek, J.; Mądry, E. High-fat, western-style diet, systemic inflammation, and gut microbiota: A narrative review. Cells 2021, 10, 3164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nani, A.; Murtaza, B.; Sayed Khan, A.; Khan, N.A.; Hichami, A. Antioxidant and anti-Inflammatory potential of polyphenols contained in Mediterranean diet in obesity: Molecular mechanisms. Molecules 2021, 26, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heck, A.M.; Yanovski, J.A.; Calis, K.A. Orlistat, a new lipase inhibitor for the management of obesity. Pharmacotherapy 2000, 20, 270–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, J.G.; Park, C.Y. Anti-Obesity Drugs: A Review about Their Effects and Safety. Diabetes Metab. J. 2012, 36, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Jiang, S.; Huang, R.; Wang, M.; Cao, H.; Li, Z. Accumulation of Cd by three forage mulberry (Morus atropurpurea Roxb.) cultivars in heavy metal-polluted farmland: A field experiment. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. Int. 2021, 28, 3354–3360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Ji, T.; Su, S.L.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, X.L.; Shang, E.X.; Guo, S.; Qian, D.W.; Duan, J.A. Mulberry leaves ameliorate diabetes via regulating metabolic profiling and AGEs/RAGE and p38 MAPK/NF-κB pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 283, 114713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, G.; Chai, X.; Hou, G.; Zhao, F.; Meng, Q. Phytochemistry, bioactivities and future prospects of mulberry leaves: A review. Food Chem. 2022, 372, 131335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.W.; Yang, T.Y.; Teng, C.S.; Lee, Y.J.; Yu, M.H.; Lee, H.J.; Hsu, L.S.; Wang, C.J. Mulberry leaves extract ameliorates alcohol-induced liver damages through reduction of acetaldehyde toxicity and inhibition of apoptosis caused by oxidative stress signals. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 18, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andallu, B.; Vinay Kumar, A.V.; Varadacharyulu, N.C. Lipid abnormalities in streptozotocin-diabetes: Amelioration by Morus indica L. cv Suguna leaves. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. 2009, 29, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhu, Q.; Wang, X.; Wang, H. Mulberry leaf polyphenols alleviated high-fat diet-induced obesity in mice. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 979058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, D.X.; Lu, D.Y.; Zhang, R.; Zhao, Y.L.; Zhong, Q.Q.; Ji, S.; Wang, L.; Tang, D.Q. Lipid metabolism disorders and lipid mediator changes of mice in response to long-term exposure to high-fat and high sucrose diets and ameliorative effects of mulberry leaves. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 4576–4591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Q.M.; Lim, E.J.; Choi, S.K.; Seo, J.S. Antioxidant effect of grapevine leaf extract on the oxidative stress induced by a high-fat diet in rats. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2014, 23, 849–857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ge, X.; Jiao, T.; Yin, J.; Wang, K.; Li, C.; Guo, S.; Xie, X.; et al. Discovery of betulinic acid derivatives as potent intestinal farnesoid X receptor antagonists to ameliorate nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 13452–13472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.S.; Hao, L.J.; Shi, Y.Y.; Lu, Z.J.; Yu, J.L.; Jiang, S.Q.; Liu, Q.L.; Wang, T.; Guo, S.Y.; Li, P.; et al. Network pharmacology-based analysis on the effects and mechanism of the Wang-Bi capsule for rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. ACS Omega 2022, 7, 7825–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Jiang, L.; Lu, X.; Liu, X.; Ling, M. Curcumin protects radiation-induced liver damage in rats through the NF-κB signaling pathway. BMC Compment. Med. Ther. 2021, 21, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Zhong, J.; Sun, C.; Zhang, J. Effects of aerobic exercise on TC, HDL-C, LDL-C and TG in patients with hyperlipidemia: A protocol of systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e25103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Xiong, C.; Kerang, X.K.; Zhang, X.; Su, S. Protective effect of berberine on doxorubicin-induced acute hepatorenal toxicity in rats. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 13, 3953–3960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vincent, H.K.; Innes, K.E.; Vincent, K.R. Oxidative stress and potential interventions to reduce oxidative stress in overweight and obesity. Diabets Obes. Metab. 2007, 9, 813–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unsal, V.; Cicek, M.; Sabancilar, I. Toxicity of carbon tetrachloride, free radicals and role of antioxidants. Rev. Environ. Health 2021, 36, 279–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, D.; Khanna, S.; Khanna, P.; Kahar, P.; Patel, B.M. Obesity: A chronic low-grade inflammation and its markers. Cureus 2022, 14, e22711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, N.; Wang, C.; Dai, X.; Zhou, M.; Gong, L.; Yu, L.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Phillygenin inhibits LPS-induced activation and inflammation of LX2 cells by TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2020, 248, 112361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saraiva, M.; Vieira, P.; O’Garra, A. Biology and therapeutic potential of interleukin-10. J. Exp. Me. 2020, 217, e20190418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, P.T.; Xie, Z.S.; Kuang, Y.J.; Liu, S.Y.; Zeng, C.; Li, P.; Liu, E.H. Discovery of a potent FKBP38 agonist that ameliorates HFD-induced hyperlipidemia via mTOR/P70S6K/SREBPs pathway. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2021, 11, 3542–3552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Q.N.; Xie, H.M.; Zhang, D.; Liu, J.; Lu, Y.F. Hepatic bile acids and bile acid-related gene expression in pregnant and lactating rats. PeerJ 2013, 1, e143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, J.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Van Kerckhoven, M.; Gianfrancesco, M.A.; Renguet, E.; Bertrand, L.; Cani, P.D.; Lanthier, N.; Cnop, M.; Paquot, N.; et al. Physical activity enhances the improvement of body mass index and metabolism by inulin: A multicenter randomized placebo-controlled trial performed in obese individuals. BMC Med. 2022, 20, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdy, J.C.; Shatzel, J.J. The hematologic consequences of obesity. Eur. J. Haematol. 2021, 106, 306–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Battineni, G.; Sagaro, G.G.; Chintalapudi, N.; Amenta, F.; Tomassoni, D.; Tayebati, S.K. Impact of obesity-induced inflammation on cardiovascular diseases (CVD). Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.J.; Choi, D.H.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, H.Y.; Kwon, T.O.; Kang, D.G.; Lee, H.S. Hypotensive, hypolipidemic, and vascular protective effects of Morus alba L. in rats fed an atherogenic diet. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2021, 39, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Gan, T.; Huang, Y.; Bao, L.; Liu, S.; Cui, X.; Wang, H.; Jiao, F.; Zhang, M.; Su, C.; et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of mulberry leaf flavonoids in vitro and in vivo. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.J.; Liu, C.; Wan, Y.; Yang, L.; Jiang, S.; Qian, D.W.; Duan, J.A. Enterohepatic circulation of bile acids and their emerging roles on glucolipid metabolism. Steroids 2021, 165, 108757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minokoshi, Y.; Kim, Y.B.; Peroni, O.D.; Fryer, L.G.; Müller, C.; Carling, D.; Kahn, B.B. Leptin stimulates fatty-acid oxidation by activating AMP-activated protein kinase. Nature 2002, 415, 339–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seok, S.; Sun, H.; Kim, Y.C.; Kemper, B.; Kemper, J.K. Defective FXR-SHP regulation in obesity aberrantly increases miR-802 expression, promoting insulin resistance and fatty liver. Diabetes 2021, 70, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]







| Gene Number | Forward Primer (5′-3′) | Reverse Primer (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| β-Actin | TCATCACTATTGGCAACGAGC | AACAGTCCGCCTAGAAGCAC |
| SREBP-1 | CACCCTGTAGGTCACCGTTT | GCTCGCTCTAGGAGATGTTCA |
| SCD-1 | GCGATACACTCTGGTGCTCA | TGGTAGTTGTGGAAGCCCTC |
| FASN | CTGGCATTCGTGATGGAGTC | GGGCAGAAGGTCTTGGAGAT |
| ACC | TTGGCCCTGTTGAGCATCTTT | GCCCTCTTTGTACCAGTGACG |
| FXR | CGAGATGCCTGTGACAAAGA | GCAGACCACACACAGCTCAT |
| SHP | TGTCCTAGCCAAGACAGTAGCC | ACCTCGAAGGTCACAGCATC |
| Group | Fat Index/% | |
|---|---|---|
| Epididymal Fat | Perirenal Fat | |
| CON | 0.956 ± 0.195 c | 0.148 ± 0.057 c |
| HFD | 3.790 ± 0.306 a | 0.416 ± 0.032 a |
| WE | 2.022 ± 0.464 b | 0.272 ± 0.045 b |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Ling, N.; Yu, Q.; Wang, H.; Du, Q. The Effect of Guisangyou Tea on Abnormal Lipid Metabolism in Mice Induced by High-Fat Diet. Foods 2023, 12, 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112171
Zhu Y, Zhou X, Ling N, Yu Q, Wang H, Du Q. The Effect of Guisangyou Tea on Abnormal Lipid Metabolism in Mice Induced by High-Fat Diet. Foods. 2023; 12(11):2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112171
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yan, Xianghui Zhou, Nan Ling, Qiming Yu, Huijuan Wang, and Qizhen Du. 2023. "The Effect of Guisangyou Tea on Abnormal Lipid Metabolism in Mice Induced by High-Fat Diet" Foods 12, no. 11: 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112171
APA StyleZhu, Y., Zhou, X., Ling, N., Yu, Q., Wang, H., & Du, Q. (2023). The Effect of Guisangyou Tea on Abnormal Lipid Metabolism in Mice Induced by High-Fat Diet. Foods, 12(11), 2171. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods12112171